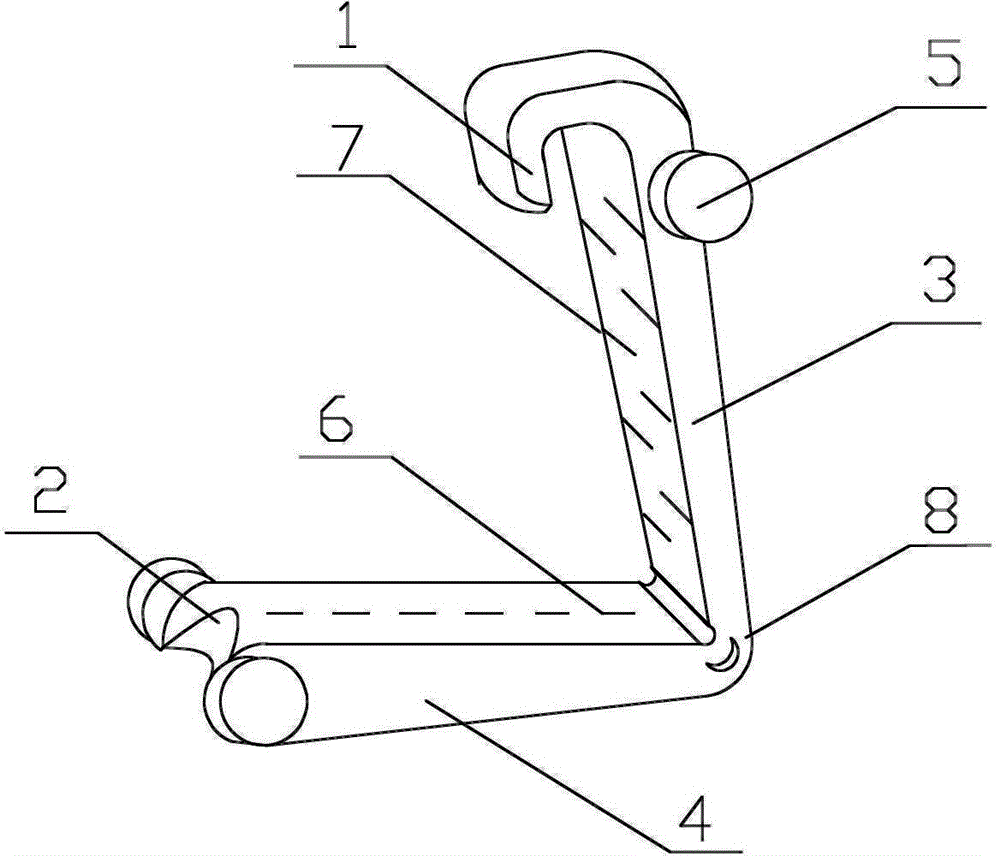
Absorbable vessel ligature clamp and preparation method thereof
A technique for ligating blood vessels and ligating clips, which is applied in the field of preparation of the blood vessel ligating clips, can solve the problems of not developing the biocompatibility of medical materials, the degradation time of the ligation clips is not adjustable, and the degradation time of the blood vessel ligation clips is very short, and the invention achieves Enhanced biocompatibility, controllable degradation performance, and improved biocompatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0041] In addition to the above-mentioned biodegradable aliphatic polyester material, the raw materials for the preparation of the vascular ligation clip of the present invention may contain other conventional auxiliary agents that do not impair its biodegradability, such as medical pigments such as D&C Purple No. 2.
[0042] After the vascular ligation clip is prepared, the present invention further studies its degradation behavior in a buffer solution simulating a body fluid environment, its cytotoxicity by MTT method, its cytocompatibility by in vitro culture method and coagulation by PT. Enzyme time, TT thrombin time and APTT activated partial thromboplastin time were used to detect its coagulation effect.
[0043] In the present invention, the simulated body fluid degradation test is carried out on the vascular ligation clip, and it is found that to make the vascular ligation clip have a longer degradation time, the molecular weight of the polymer should be correspondingly...
Embodiment
[0048] Hereinafter, an embodiment of the present invention will be specifically described by showing examples and comparative examples. However, the present invention is not limited to the following examples.
[0049] (Synthesis of Aliphatic Polyester Materials)
Synthetic example 1
[0050] Synthetic example 1 to the preparation of dioxanone-glutamic acid copolymer 1
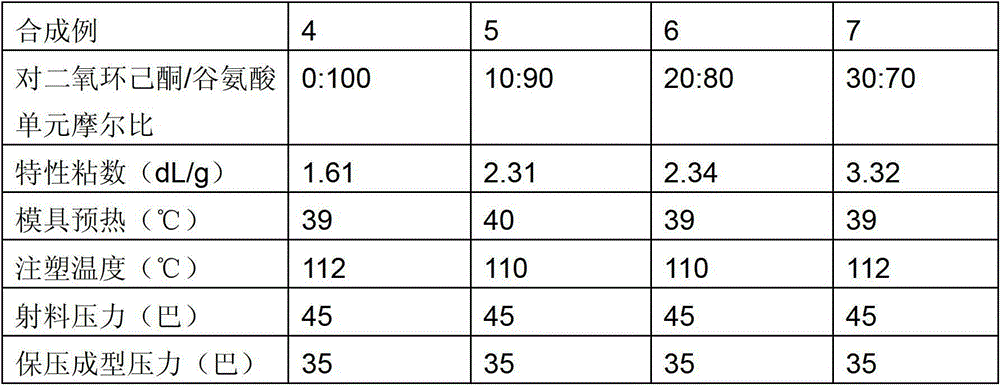
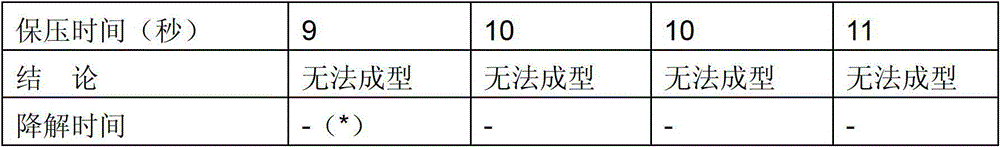
[0051] The two monomers of p-dioxanone and glutamic acid were mixed in a molar ratio of 70:30, weighed 300g and added to the reactor, and 0.02% stannous octoate catalyst was added to the reactor. The reaction system was sealed, and nitrogen gas was introduced to protect the reaction. The temperature of the reaction system was controlled at 120° C., and the reaction was carried out for 10 hours. The reactants were chopped to make pellets with a particle size of 1-8 mm, and 191 g of pellets were obtained by weighing, with a yield of 95.5%. The above pellets were dissolved in a phenol / tetrachloroethane (2:3 / V:V) mixed solution, and the intrinsic viscosity of the copolymer was measured as 3.28dL / g with an Ubbelohde viscometer in a constant temperature water bath at 25°C.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Intrinsic viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Intrinsic viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Intrinsic viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com