Use of lotus procyanidin as advanced glycosylation end product formation inhibitor
A kind of advanced glycosylation, lotus flower technology, applied in the field of medicine
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] A pharmaceutical composition with lotus proanthocyanidins as the main active ingredient. Lotus proanthocyanidins account for 70 or 75 or 80%, synergists such as VE, VC, gallocatechin gallate (EGCG) and cysteine and other compounds account for 10 or 15 or 20%, (select the above synergists One of the applications can be) other natural extracts such as lotus leaf extract and ginkgo leaf extract account for 5 or 8 or 10% by weight (the weight ratio of lotus leaf extract and ginkgo leaf extract is 1:1 ). Various capsules, Various health care products or food additives such as tablets or beverages can be made into tablets, capsules, granules, oral liquids, sustained-release preparations, controlled Release preparations, nano preparations, injections any pharmaceutically acceptable dosage form.
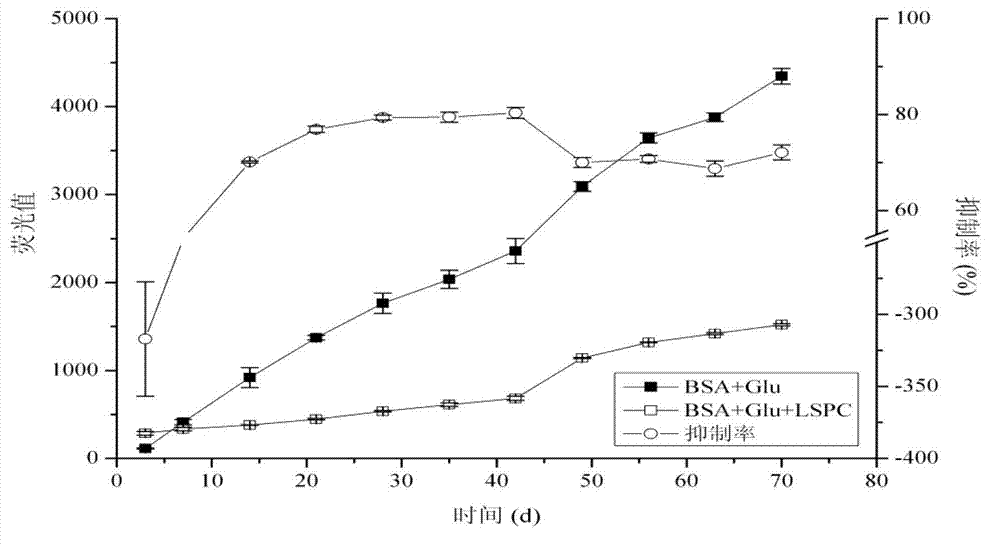
[0054] Inhibitory effect of lotus proanthocyanidins on the formation of advanced glycation end products under simulated physiological environment
[0055] 1 Experimental materia...
Embodiment 2
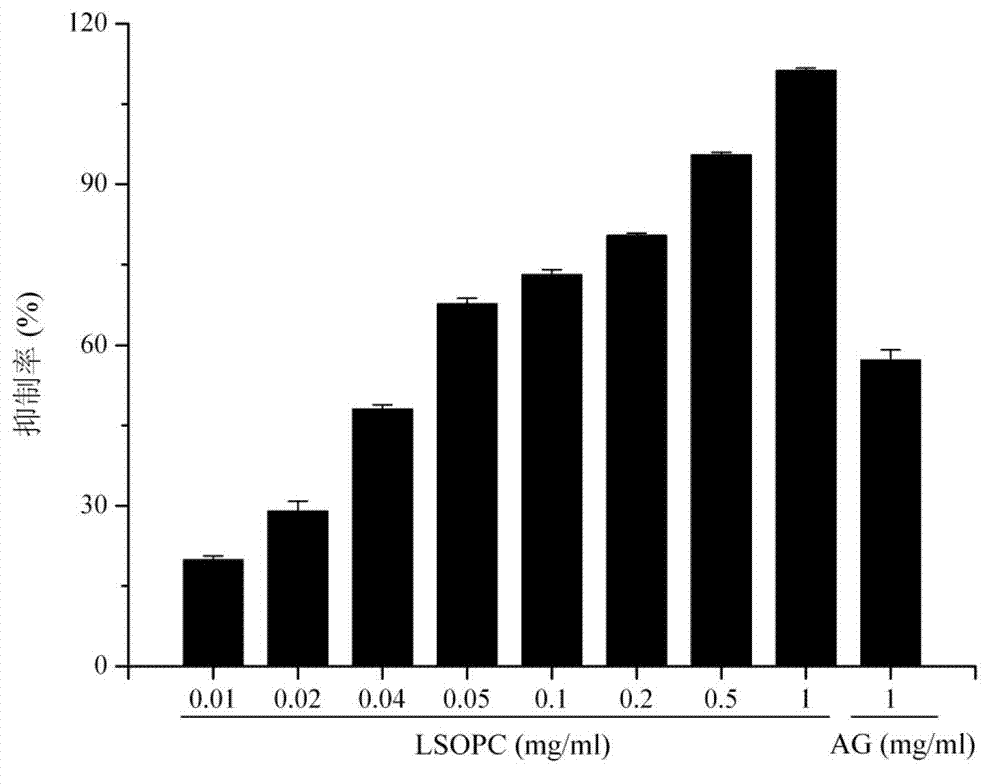
[0081] Example 2: In the simulated food system, the inhibitory effect of lotus proanthocyanidins on the formation of advanced glycation end products
[0082] 1 Experimental materials:
[0083] 1.1 Experimental raw materials: raw material preparation method as in Example 1
[0084] 1.2 Experimental reagents:
[0085] Disodium hydrogen phosphate, sodium dihydrogen phosphate, and α-lactose were all of analytical grade and were purchased from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd.; L-Lysine (L-Lysine) biochemical reagent was purchased from BIOSHARP, Japan.
[0086] 1.3 Main instruments:
[0087] Shimadzu RF5301 fluorescence spectrophotometer, HH-2S constant temperature water bath.
[0088] 2 Experimental method:
[0089] 2.1 The inhibitory effect of LSPC on AGEs under different reaction times, determine the heating reaction time:
[0090] 2.1.1 Experimental method:
[0091] Accurately weigh 1.8016g of α-lactose and 0.731g of L-Lysine (the molar ratio of the substances is 1:1),...
Embodiment 3
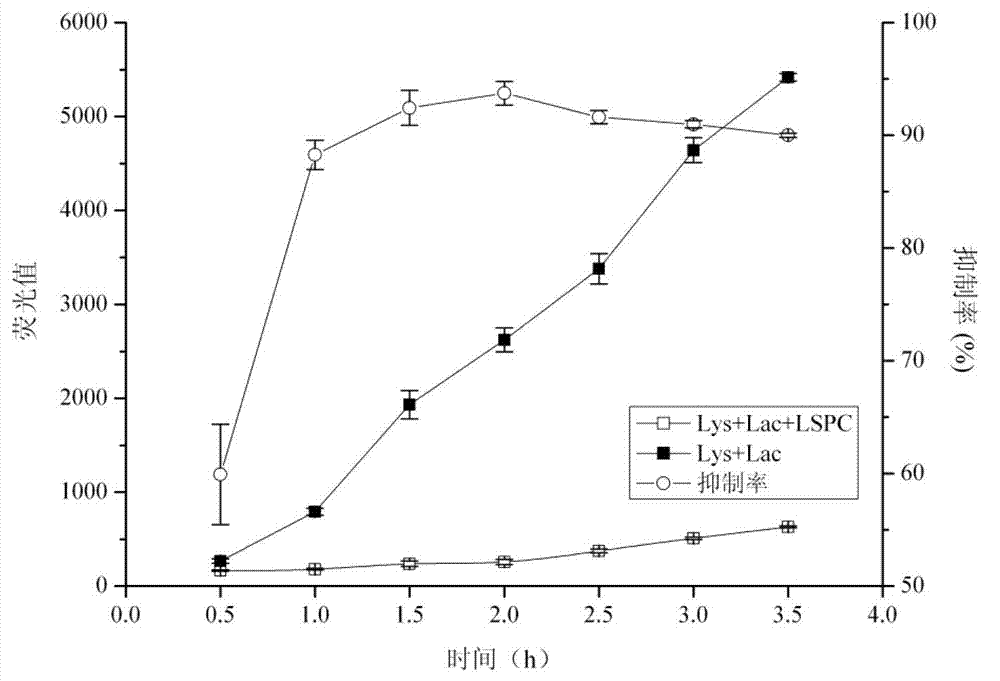
[0105] Example 3: Discussion on the Inhibitory Mechanism of Lotus Proanthocyanidins on the Formation of Advanced Glycation End Products
[0106] 1 Experimental materials:
[0107] 1.1 Experimental raw materials: The raw material preparation method is the same as in Example 1.
[0108] 1.2 Experimental reagents:
[0109] Disodium hydrogen phosphate, sodium dihydrogen phosphate, methylglyoxal, and o-phenylenediamine were all analytically pure, purchased from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd.; aminoguanidine (AG), 2,3-dimethylquinoxaline Catechin and catechin were analytically pure, purchased from sigma; methanol chromatographically pure, purchased from Fisher Scientific, USA.
[0110] 1.3 Main instruments:
[0111] Waters e2695 high performance liquid chromatography, Agilent 1100 high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry.
[0112] 2 Experimental method:
[0113] 2.1 Scavenging effect of LSPC and its monomer Catechin on MGO
[0114] 2.1.1 Experimental meth...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com