Artificial liver bioreactor
A bioreactor, artificial liver technology, applied in suction devices and other directions, can solve the problems of low hepatocyte density, uneven artificial liver function, and flow away distribution of hepatocytes, and achieves favorable microenvironment for cell adhesion and good microenvironment. , the effect of increasing the density of hepatocytes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1: Chitosan and galactosylated chitosan materials were used as raw materials for nanofibrous scaffolds to make this novel bioreactor.
[0035]The specific preparation method of the nanofibrous scaffold: dissolving chitosan and galactosylated chitosan in 70% formic acid solution with a concentration of 3-5wt%. Add 10wt% (PEO / galactosylated chitosan) PEO to the above solution under stirring condition, dissolve for 3 hours and centrifuge to remove the bubbles in the solution. The solution was then filled into a 5 ml glass syringe with a 6 gauge needle. Push the solution at a speed of 1ml / h under the impetus of a micro-syringe pump. A voltage of 15 kV was applied across the needle and the collecting plate, and the distance between the collector and the needle was 15 cm. Finally, the electrospun fibers were collected on a built-in plate in a bioreactor, and then dried under vacuum at 40°C for two days to remove residual formic acid.
Embodiment 2
[0036] Embodiment 2: use PLGA as the raw material of nanofiber support to make this novel bioreactor
[0037] The specific preparation method of the nanofiber scaffold: PLGA was dissolved in chloroform to prepare a solution with a concentration of 21.5%, and then the solution was filled into a disposable syringe equipped with a No. 6 needle. A DC voltage of 10-15 kV was applied between the collecting plate and the needle, and the solution was pushed out from the syringe at a speed of 1 ml / h by a micro syringe pump. The distance between the needle and the pedal is 10-15cm. When the spinning was completed, the built-in flat plate covered with PLGA electrospun fibers was removed and placed in a vacuum desiccator for two days to remove residual solvent.
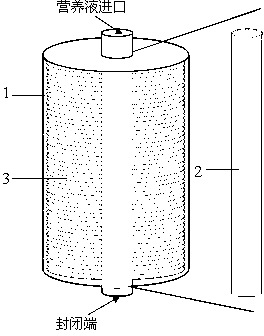
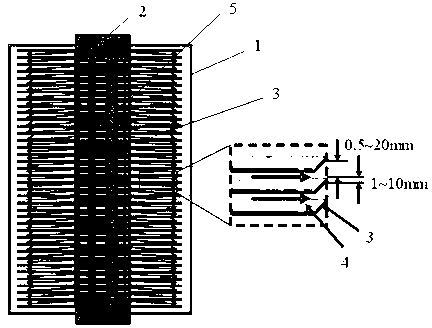
[0038] Encapsulation of the bioreactor: fix the built-in flat plate 3 on the hollow support 2, put the whole into the reactor shell 1, and add a cover to manufacture the artificial liver bioreactor.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Center distance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com