Method for treating lignocellulosic biomass with ammonia combined with dilute alkali and normal pressure
A lignocellulose-based, atmospheric-pressure processing technology applied to lignocellulose. It can solve the problems of high loss rate of hemicellulose, difficult sorting and removal of lignin, high energy consumption for ammonia recovery, etc., to achieve the effect of less environmental pollution, simple pretreatment process, and reduction of the addition of nitrogen sources.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
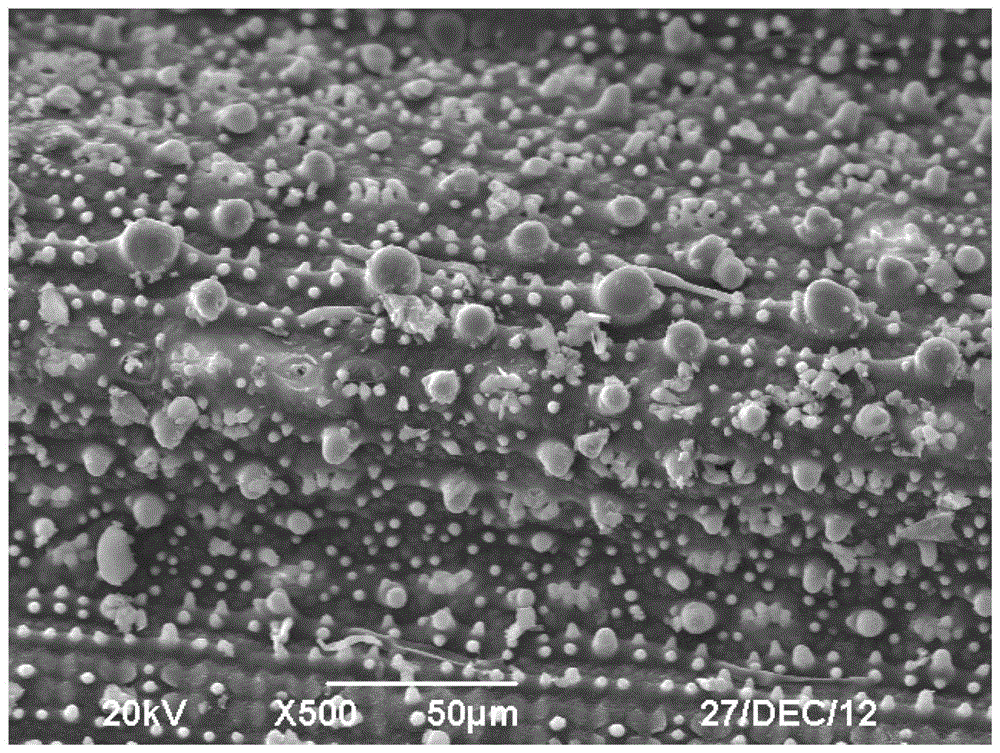
Image
Examples
reference example 1
[0025] Reference Example 1: Chopped rice straw to no more than 2cm, took 10.0g, and washed it with 2% dilute NaOH solution at 95°C for 2 hours to obtain 5.2g (dry weight) of lignocellulose, which contained 3.3g of cellulose , hemicellulose 1.2g, the lignin stripping rate is 82.5%; then use the cellulase produced by Trichoderma viride (Trichoderma viride) ZY-1 solid-state fermentation to carry out saccharification and degradation to produce reducing sugar, select 50FPIU / g substrate for use, solid-liquid The ratio is 1:10, saccharification and degradation at 50°C for 48 hours, the reaction is terminated, and the saccharification solution is extracted to obtain 4.2 g of reducing sugar, and the yield of reducing sugar is 80.2%.
reference example 2
[0026] Reference example 2: Chopped rice straw to no more than 2cm, took 10.0g, passed NH3 at 50°C, treated for 2h, washed with 2% dilute NaOH solution at 95°C for 2h, and obtained lignocellulose 5.1 g (dry weight), containing 3.2g of cellulose, 1.1g of hemicellulose, and a lignin stripping rate of 81.8%; then use the cellulase produced by solid-state fermentation of Trichoderma viride (Trichoderma viride) ZY-1 to carry out saccharification and degradation product For reducing sugar, 50 FPIU / g substrate was selected, the solid-to-liquid ratio was 1:10, saccharified and degraded at 50°C for 48 hours, the reaction was terminated, and the saccharified solution was extracted to obtain 4.1 g of reducing sugar, with a yield of 80.3%.
Embodiment 1
[0027]Implementation Example 1: Shred the rice straw to no more than 2cm, take 10.0g, fumigate with ammonia water at 50°C for 2h, wash with 2% dilute NaOH solution at 95°C for 2h, and obtain 5.6g of lignocellulose ( dry weight), containing 3.9 g of cellulose, 1.4 g of hemicellulose, and a lignin stripping rate of 91.2%; then using the cellulase produced by solid-state fermentation of Trichoderma viride (Trichoderma viride) ZY-1 to carry out saccharification and degradation to produce reducing sugars, Select 50FPIU / g substrate, solid-liquid ratio is 1:10, saccharification and degradation at 50℃ for 48 hours, stop the reaction, extract the saccharification solution, and obtain 5.1g reducing sugar, the yield of reducing sugar is 90.9%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com