Novel OLED (organic light emitting diode) material and application thereof
A new type of luminescent material technology, applied in the field of small molecule OLED materials and organic electroluminescence, can solve the problems affecting the development of organic electroluminescence devices, and achieve the effect of good efficiency and good film stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0056] Preparation and structural characterization of intermediates 3-(3,5-dibromophenyl)pyridine 1 and 3-(3-bromo-5-(3-pyridine)-phenyl)pyridine 2:
[0057] Synthesis of intermediates 1 and 2:
[0058] In a 500mL three-necked flask, add s-tribromobenzene (12.6g, 40mmol), pyridine-3-boronic acid (10.5g, 85mmol), K 2 CO 3 (22g, 160mmol), dioxane (160mL), deionized water (80mL), N 2 protection, adding Pd(PPh 3 ) 4 (800mg), reflux reaction for 18 hours, TLC analysis, the ratio of monosubstituted product 1 to double substituted product 2 is about 2:1, stop the reaction. Separation, collecting the organic phase, anhydrous Na 2 SO 4 Dry, filter, and remove the solvent. The crude product is subjected to silica gel column chromatography and gradient elution. First, petroleum ether is used, and then petroleum ether: ethyl acetate = 1:2 to collect the monosubstituted product 1 and the disubstituted product 2, respectively. 15.0 g of the monosubstituted product was obtained with a...
Embodiment 2
[0064] Preparation and properties of Example 2 OLED material 4PySF:
[0065] 1. Synthesis and structural characterization of OLED material 4PySF:
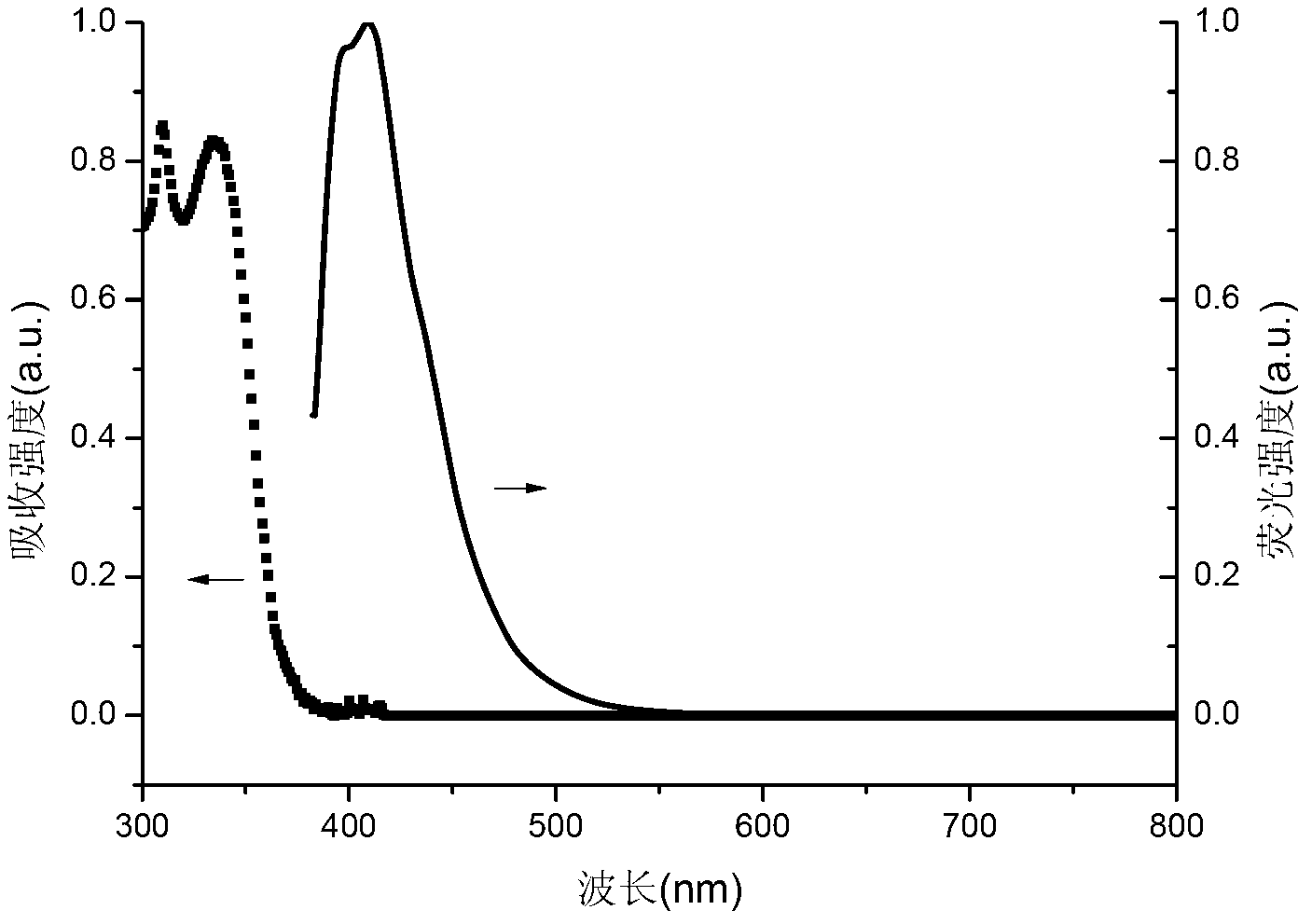
[0066] In a 250mL three-necked flask, add 2,7-spirobifluorene borate (1.7g, 3mmol), intermediate 2 (2.05g, 6.6mmol), K 2 CO 3 (4.1g, 30mmol), N,N-dimethylacetamide (60mL), deionized water (25mL), Pd(PPh 3 ) 4 (500mg), N 2 Protection, reflux reaction for 24 hours, stop reaction. Add 50 mL of water, stir for 10 min, filter with suction, rinse the filter cake with 50 mL of methanol, collect the filter cake, and purify the filter cake by silica gel column chromatography, the eluent is methanol:ethyl acetate=1:10, and 0.82 g of the target product is obtained. The yield was 35.2%. The chemical vapor deposition system was used for further sublimation and purification. The sublimation temperature was 345°C, and 0.38g of the target product was obtained, with a yield of 16.3%.
[0067] 1 H NMR (CDCl 3 ,TMS,500MHz):8.852-8.856(d,4H,J=...
Embodiment 3
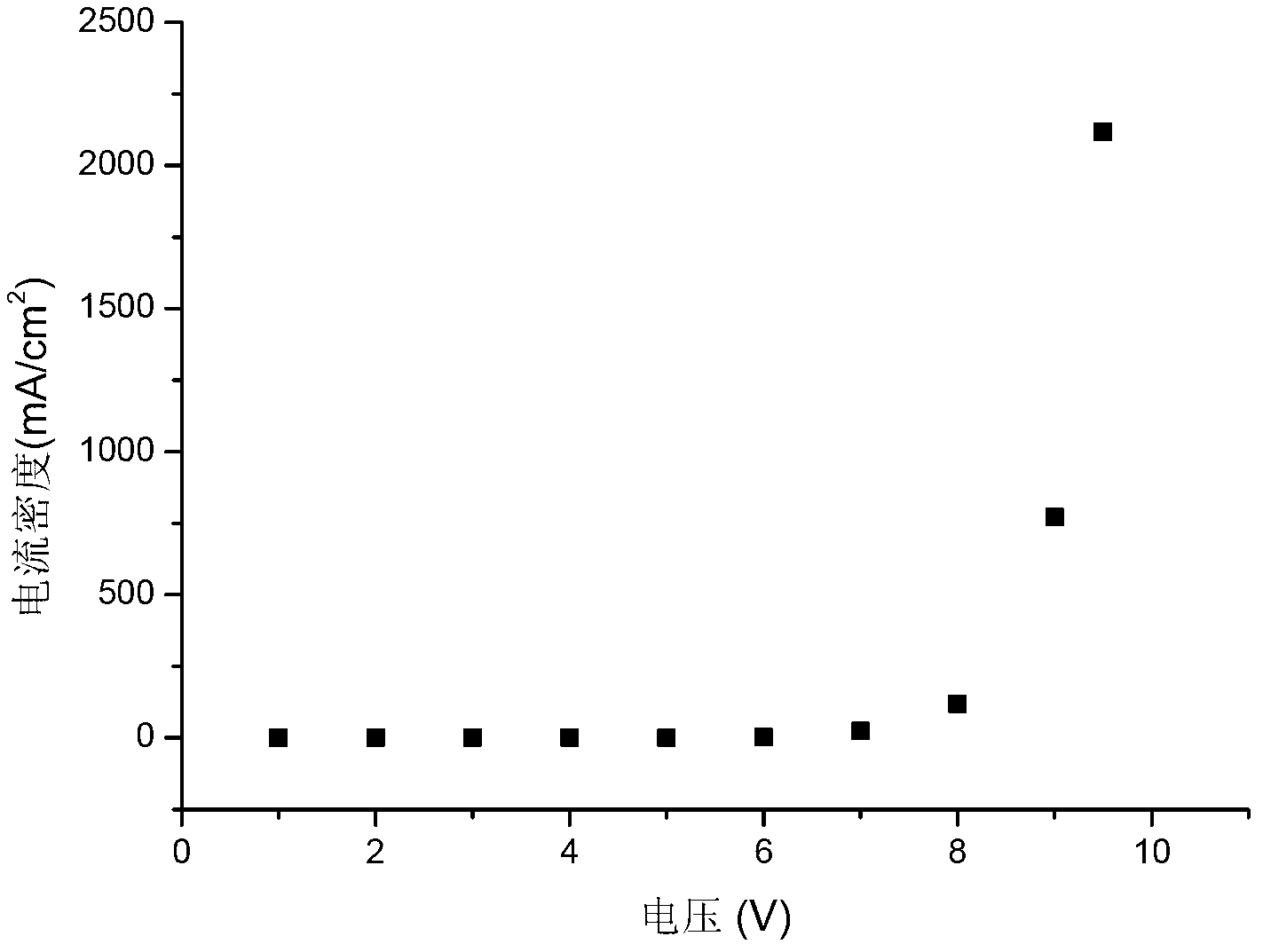
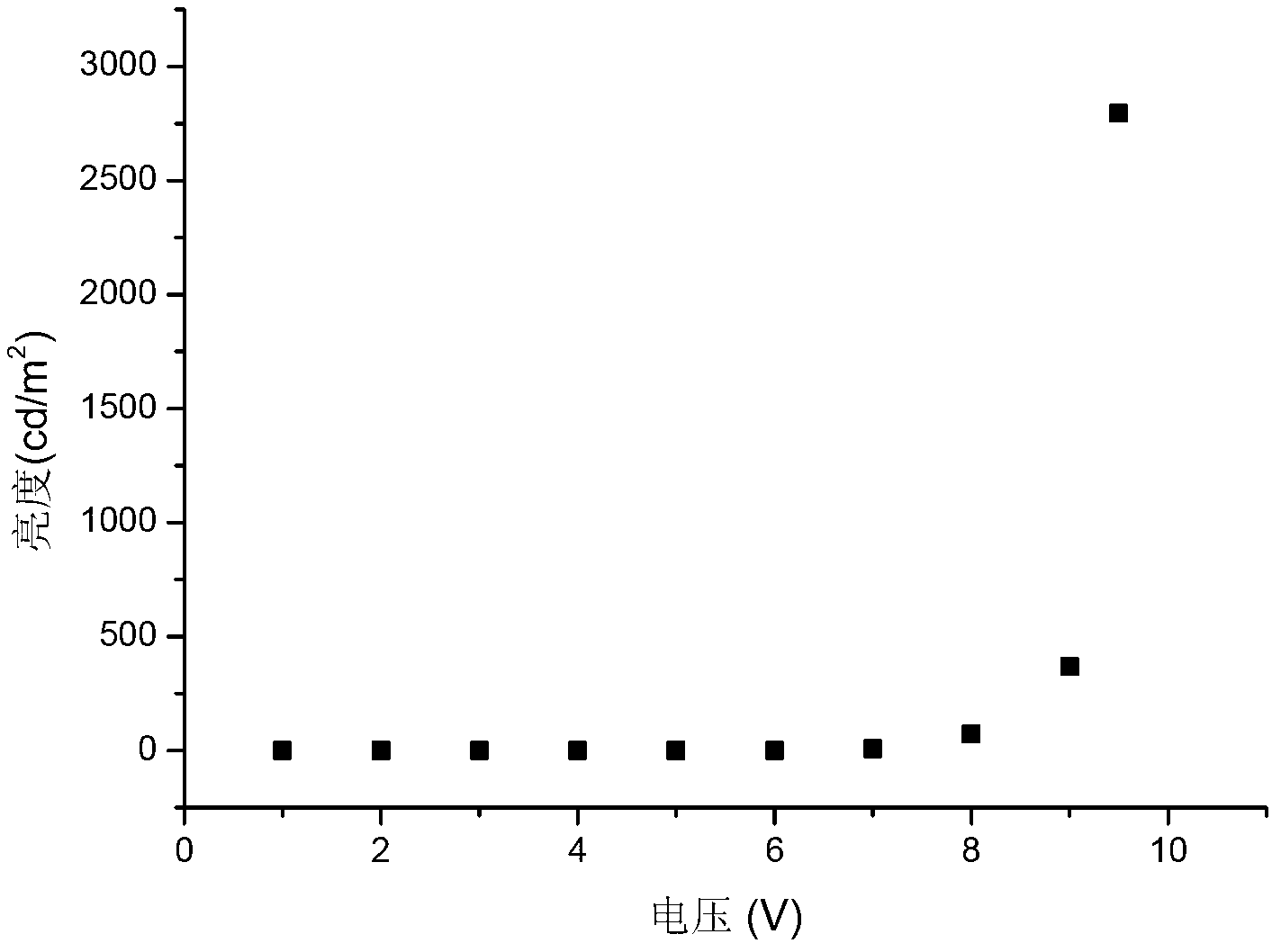
[0071] Example 3 Application of OLED material 4PySF in organic electroluminescent devices
[0072] This embodiment prepares dark blue organic electroluminescent device according to the following method:
[0073] a) Clean ITO (indium tin oxide) glass: ultrasonically clean the ITO glass with deionized water, acetone, and ethanol for 30 minutes each, and then treat it in a plasma cleaner for 5 minutes;
[0074] b) Vacuum-evaporated hole transport layer NPB on the anode ITO glass with a thickness of 50nm;
[0075] c) On top of the hole transport layer NPB, 4PySF, which serves as both the light-emitting layer and the electron transport layer, is vacuum-evaporated with a thickness of 60 nm;
[0076] d) On top of 4PySF, vacuum evaporated electron injection layer LiF with a thickness of 1nm;
[0077] e) On top of the electron injection layer LiF, a cathode Al is vacuum-evaporated with a thickness of 100 nm.
[0078] The structure of the device is ITO / NPB(50nm) / 4PySF(60nm) / LiF(1nm) / ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com