Method for realizing dephosphorization of olitic high-phosphorus iron ore by use of biomass charcoal
A biomass charcoal and high-phosphorus iron ore technology is applied in the fields of iron and steel metallurgy - non-blast furnace ironmaking and metallurgy, which can solve the problems of difficult industrialization and lack of high-quality reducing gas sources, and achieve the effect of short production cycle and high efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
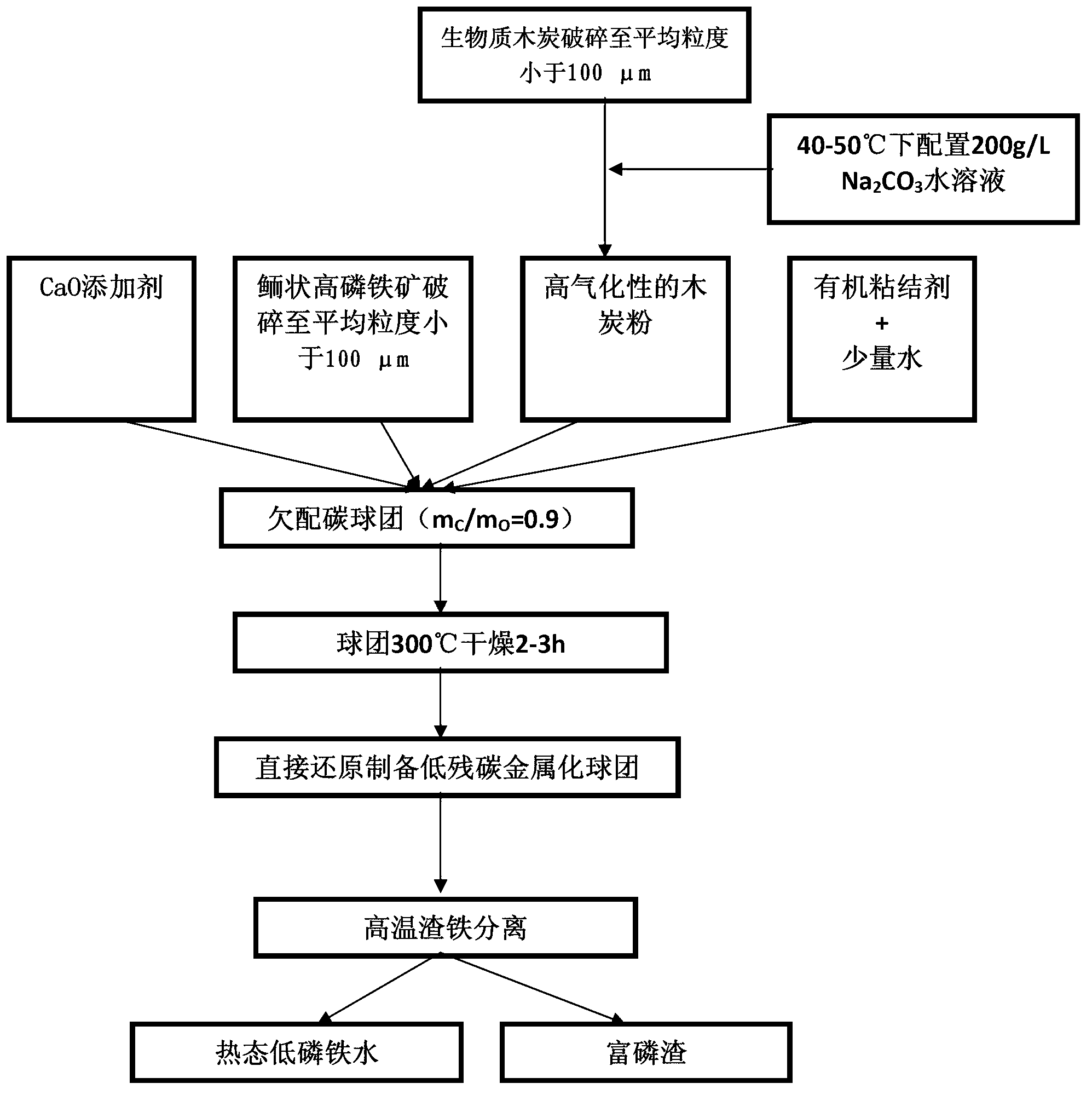
[0061] (1) Charcoal modification: 110g of charcoal is ball-milled, and its average particle size is less than 100μm; at 40°C, the concentration of 200g / L Na 2 CO 3 The aqueous solution is evenly sprayed on the surface of the charcoal powder according to the ratio of 10mL / (100g charcoal), and the charcoal powder is dried in the air atmosphere at 120°C for 1 hour;
[0062] (2) Mineral crushing: take 500g of the above-mentioned oolitic high-phosphorite iron ore for preliminary crushing and after full ball milling, the average particle size will reach less than 100μm;
[0063] (3) Pellet preparation: Mix the above-mentioned iron ore powder, treated charcoal powder and a certain amount of CaO, and the amount of CaO added meets the requirement of CaOwt% / SiO 2 The wt% is 1.0; the mixed material is made into pellets with a diameter of 10.0mm. The ball-making binder adopts 2.0wt% waste paper pulp;
[0064] (4) Dry the pellets at 300°C for 2 hours;
[0065] (5) Direct reduction: Red...
Embodiment 2
[0070] (1) Charcoal modification: 110g of charcoal has been ball milled, and its particle size is less than 100μm; the concentration of 200g / L Na 2 CO 3 Aqueous solution (water temperature 40°C), according to the proportion of 20mL / 100g charcoal evenly sprayed on the surface of charcoal powder, charcoal powder at 120°C, in the air atmosphere, dry for 1h;
[0071] (2) The remaining steps are the same as Example 1.
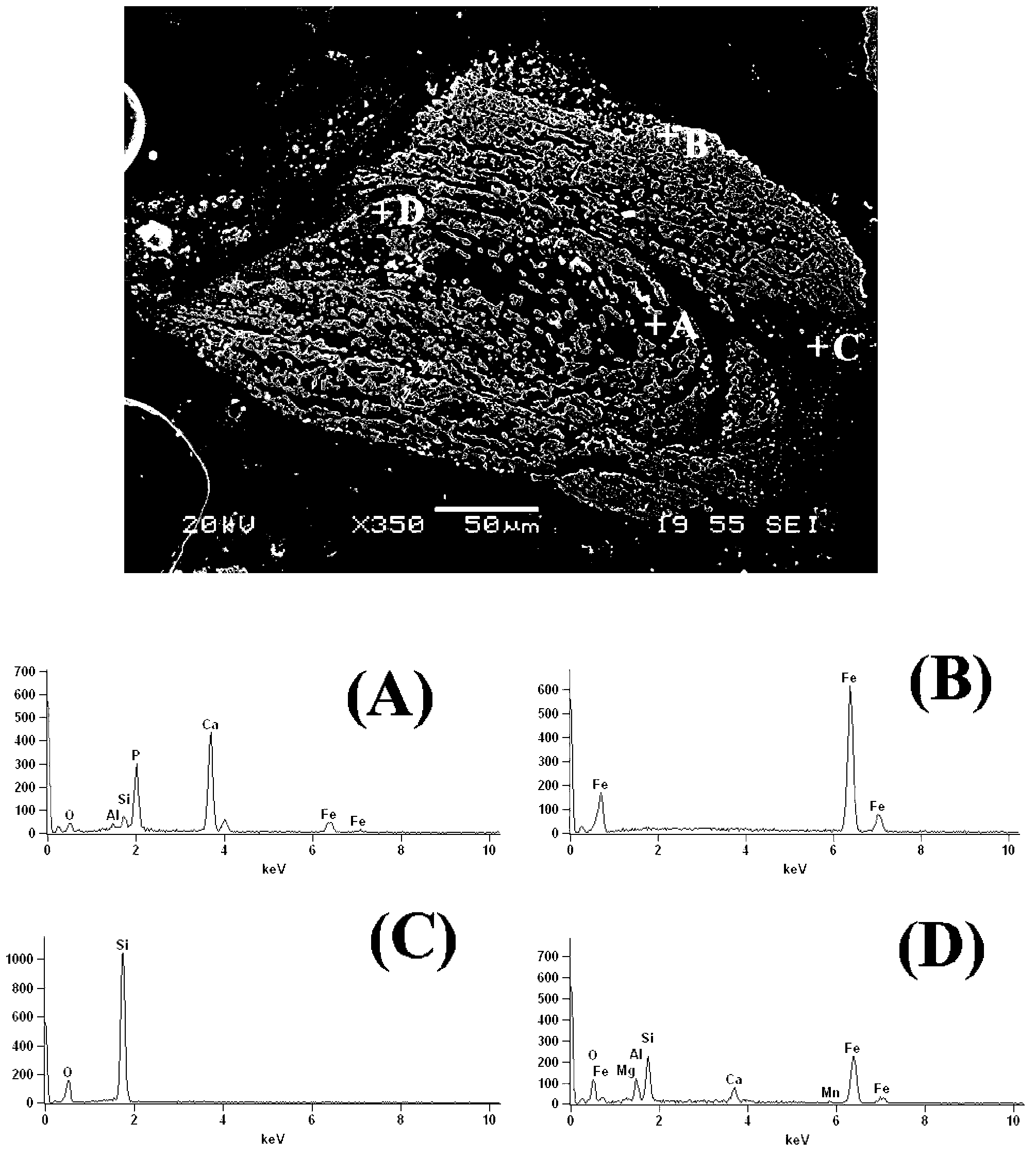
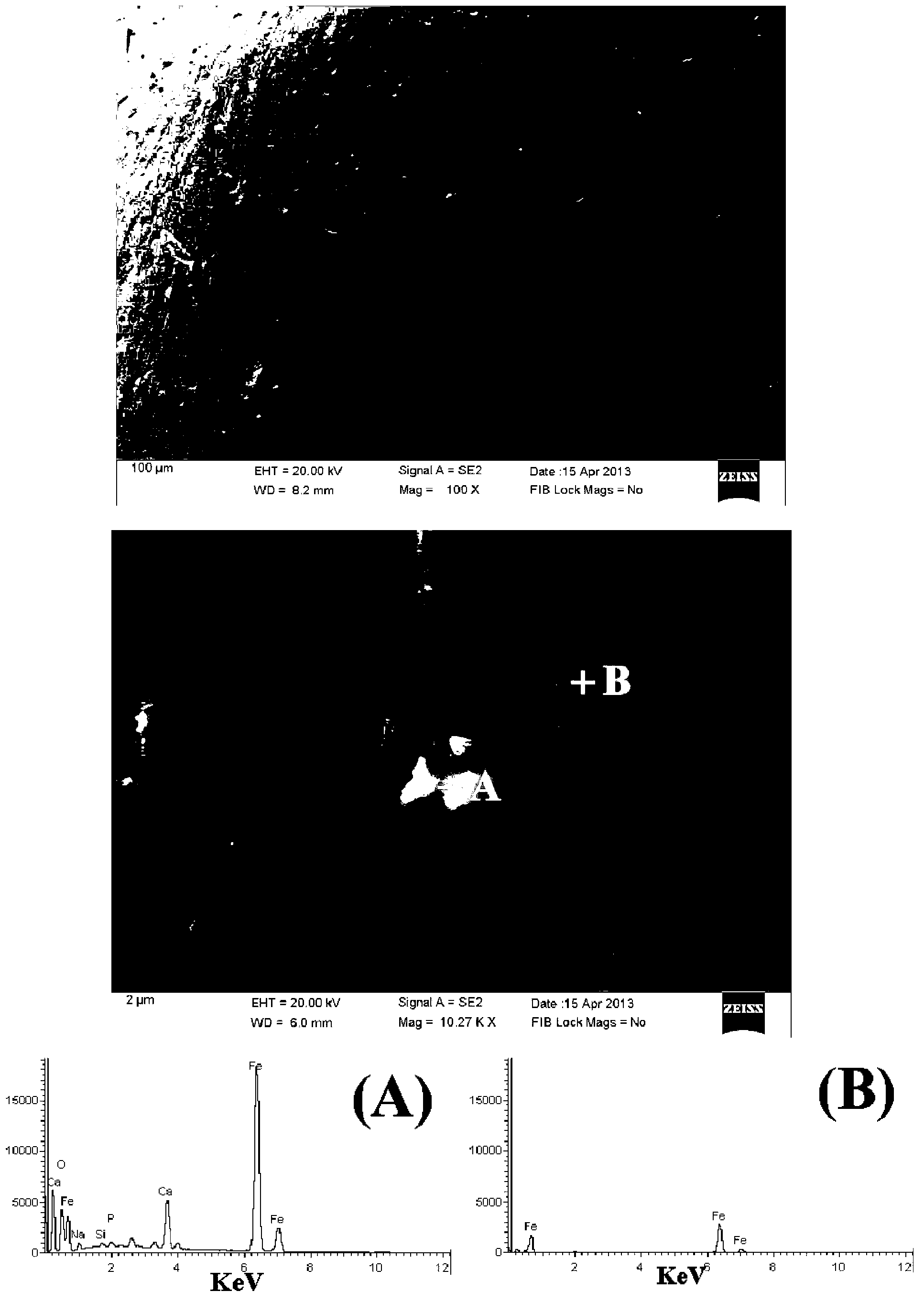
[0072] The metallization rate of metallized pellets obtained by reduction is 86%, and the residual carbon content is 0.52wt%. The phosphorus content of the final molten iron obtained by melting is 0.24wt%, and the metal recovery rate is 82%.
Embodiment 3
[0074] Change the direct reduction conditions (step (3)), and the rest of the steps are the same as in Example 1. The direct reduction conditions in this example are: using a well-type isothermal furnace, the reduction temperature is 1100°C, the reduction time is 25min, and CO / CO 2 Mixed gas 1L / min to keep the furnace atmosphere at P CO2 / P CO =1.0.
[0075] The metallization rate of the metal pellets obtained after reduction is 80%, the residual carbon content of the metallized pellets is 0.37wt%; the phosphorus content of the final molten iron obtained by melting is 0.20wt%, and the metal recovery rate is 75%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com