Engineering bacteria of inactivated acetolactate synthetase, and applications thereof in producing 1,3-propanediol
A technology of acetolactate and synthase, applied in bacteria, microorganisms, microorganism-based methods, etc., can solve problems such as unknown impact, and achieve the effects of reducing post-extraction pressure, improving conversion rate, and reducing production costs.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] 1. Construction of engineered bacteria with inactivated acetolactate synthase gene inactivated in 2,3-butanediol metabolic pathway
[0026] (l), cloning of acetolactate synthase gene ALS partial sequence
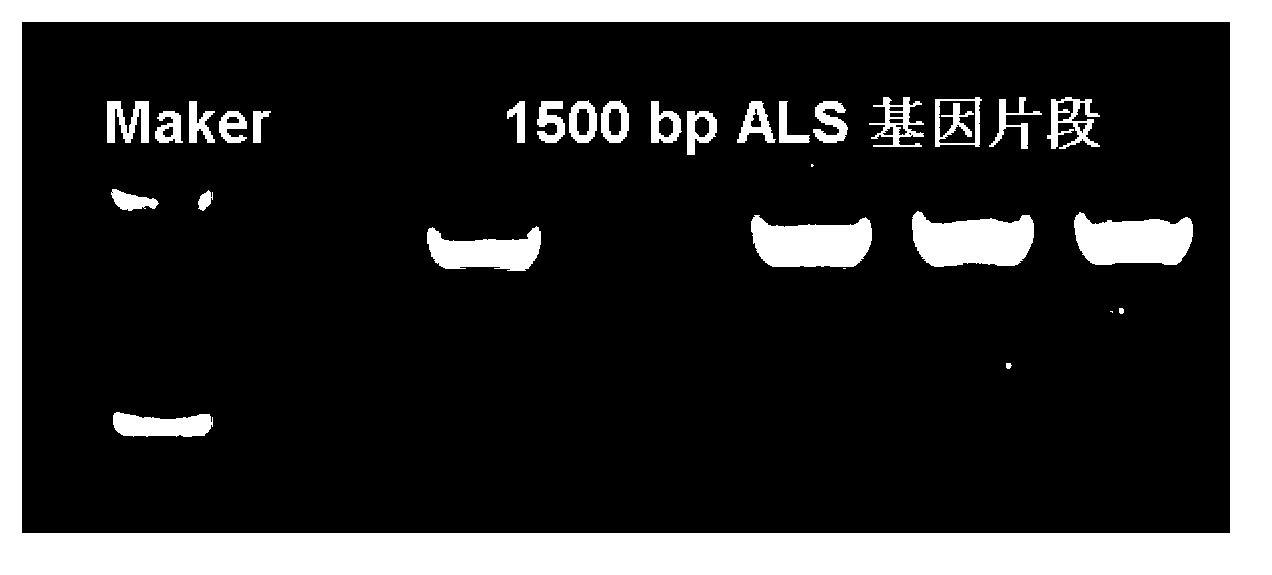
[0027]Primers were designed according to the complete DNA sequence of the acetolactate synthase gene ALS (GenBank number: YP_006633876.1), and its partial homologous sequence was amplified by PCR. . Using the genomic DNA of wild-type Klebsiella pneumoniae (CCTCC M2011075) as a template, under the guidance of primers ALS-F and ALS-R, the partial sequence of the acetolactate synthase gene ALS was amplified by PCR. The PCR amplification conditions were as follows: First 95°C for 3min; then 94°C for 1min, 55°C for 1min, 72°C for 2min, a total of 33 cycles; finally 72°C for 10min. After the reaction, the PCR amplification product was subjected to 1.0% agarose gel electrophoresis, and the target fragment of about 1500bp was recovered and purified ( figure 1 ), clone it i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com