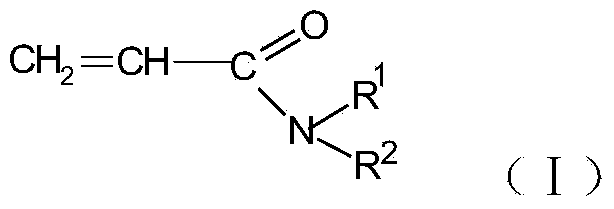
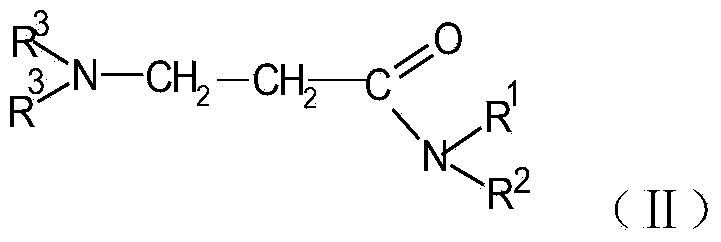
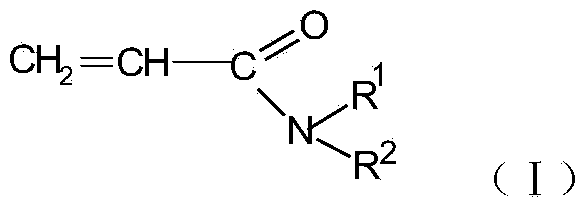
N-substituted acrylic amide synthesized through amine oxide cracking elimination method and method
A technology of acrylamide and amine oxide, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, preparation of carboxylic acid amides, preparation of organic compounds, etc., can solve the problems of high cracking reaction temperature and low utilization rate of equipment.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0079] The preparation of embodiment 1N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAM)
[0080]
[0081] 1) Oxidation reaction of 3-dimethylamino-N-isopropylpropionamide (DMAPPA)
[0082] Add 157g of DMAPPA, 0.38g of sodium tungstate and 0.38g of sodium pyrophosphate into a four-necked flask with a reflux condenser, and add 119g of 30% hydrogen peroxide (excess 5% by mole) dropwise within 30 minutes at 70°C. After reacting at 70-75°C for 3h, cool down to 40°C, add 1.0g MnO 2 , at 50°C for 0.5h to remove excess hydrogen peroxide. Filter to remove MnO 2 , that is, the oxidation product 3-(N-isopropylpropionamide)-N,N-dimethyl-N-amine oxide (DMPPOA) aqueous solution (concentration: 65%). The degree of oxidation of DMAPPA was determined by liquid chromatography to be greater than 99%.
[0083] 2) Cleavage elimination reaction
[0084] Add 100g of the above-prepared amine oxide (DMPPOA) aqueous solution, 80g of solvent MPEG400 and 1g of inhibitor phenothiazine into a three-necked flask equipp...
Embodiment 2
[0085] The preparation of embodiment 2N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAM)
[0086]
[0087] 1) Oxidation reaction of 3-diethylamino-N-isopropylpropionamide (DEAPPA)
[0088] Add 93g of DEAPPA, 0.18g of sodium tungstate and 0.18g of sodium pyrophosphate into a four-necked flask with a reflux condenser, and add 113g of 30% hydrogen peroxide dropwise within 30 minutes at 70°C (molar ratio is 1:2). After reacting at 70-75°C for 5h, add 1.0g MnO after cooling down to 40°C 2 , at 50°C for 0.5h to remove excess hydrogen peroxide. Filter to remove MnO 2 , that is, the oxidation product 3-(N-isopropylpropionamide)-N,N-diethyl-N-amine oxide (DEPPOA) in aqueous solution (concentration: 55%). The degree of oxidation of DEAPPA was determined by liquid chromatography to be greater than 99%.
[0089] 2) Cleavage elimination reaction
[0090] Add 100g of the above-mentioned prepared amine oxide DEPPOA aqueous solution, 60g of xylene and 1g of polymerization inhibitor phenothiazine into a th...
Embodiment 3-13
[0091] Example 3-13 Preparation of N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAM)
[0092] The oxidation product 3-(N-isopropylpropionamide)-N,N-dimethyl-N-amine oxide (DMPPOA) aqueous solution (concentration: 65%) was prepared by the same method as in Example 1.
[0093] Add 100g of the above-prepared amine oxide (DMPPOA) aqueous solution, 1g of inhibitor phenothiazine, and different amounts of solvents into a three-necked flask equipped with a reflux condenser, and perform cracking and elimination reactions at different vacuum degrees and cracking temperatures. Collect fractions in cold traps, and measure the yield of N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAM) in the bottom of the still by liquid chromatography after no liquid distills out or cracks for 1 hour.
[0094] The yields of NIPAM under different types of solvents and their amounts, cracking temperature and vacuum are listed in Table 1.
[0095] The influence of table 1 cleavage condition on NIPAM productive rate
[0096] Experiment n...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com