In-vitro building method of cell photoaging model
A construction method and photoaging technology, applied in the fields of medicine and cell biology, can solve problems such as changing the state of cell viability, interfering with aging phenotypes, and fluctuation of cell viability, achieving the effects of good viability, good cell viability, and avoiding insufficient viability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064] Isolation and culture of MDFs
[0065] Cells are obtained from C57BL / 6 inbred mice born at 18-24 hours, and mice with ruddy complexion and normal peristalsis should be selected.
[0066] (1) Separate the back skin: After ether anesthesia, immerse the mouse in 75% ethanol for about 10 minutes, wash off the residual ethanol with DMEM, place it in a petri dish, separate the back skin with scissors, and cut off the skin tissue for about 10 minutes. 1cm×1cm, immediately placed in 2% neutral protease, digested at 37°C for 4 hours;
[0067] (2) Digestion of the skin: Take out the skin, separate the epidermis and dermis with tweezers, cut the dermis into pieces, place in 0.1% collagenase, and digest on a constant temperature shaker at 37°C for 2 hours until the tissue blocks basically disappear. Centrifuge at 1500rpm for 5 minutes to collect the precipitate;
[0068] (3) Inoculation: discard the supernatant, and make the cells with DMEM (Gibco, Gland Island, NY, USA) culture ...
Embodiment 2
[0072] UVB irradiation
[0073] (1) Preparation of UVB lamps: Wipe the UVB lamps with 75% ethanol, and pre-sterilize them in an ultra-clean bench for 30 minutes.
[0074] (2) Measurement of UVB radiation dose: Centrifuge tube racks are placed on both sides of the lamp tube to make it 30cm away from the ultra-clean table plane, and the UVB dose is measured with a Lutron UV light meter (Lutron, Taiwan) (the instrument display unit is mJ / cm 2 s), calculate the required irradiation time according to the measured data (irradiation time = 120 / UVB measured dose (calculated value in seconds));
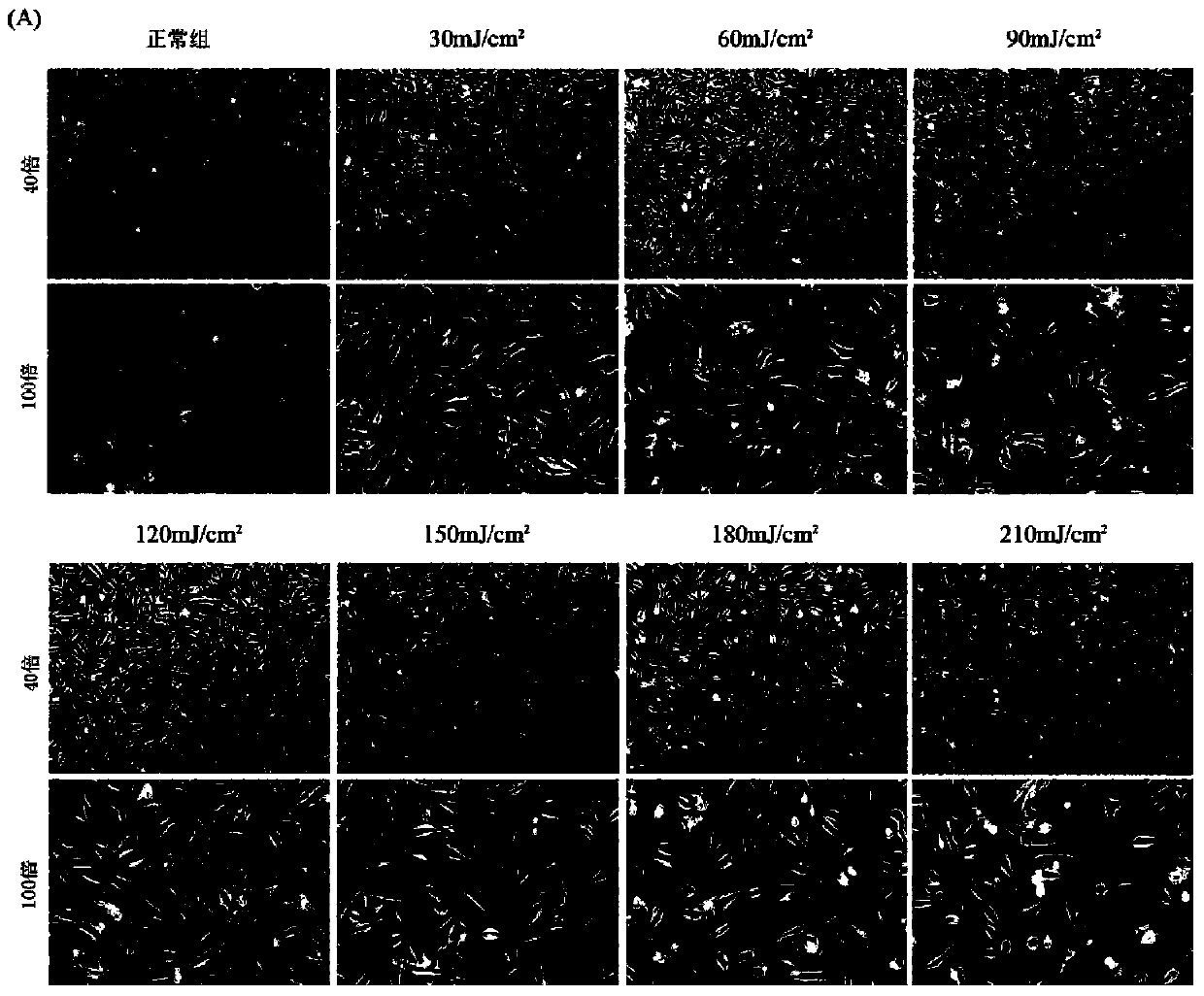
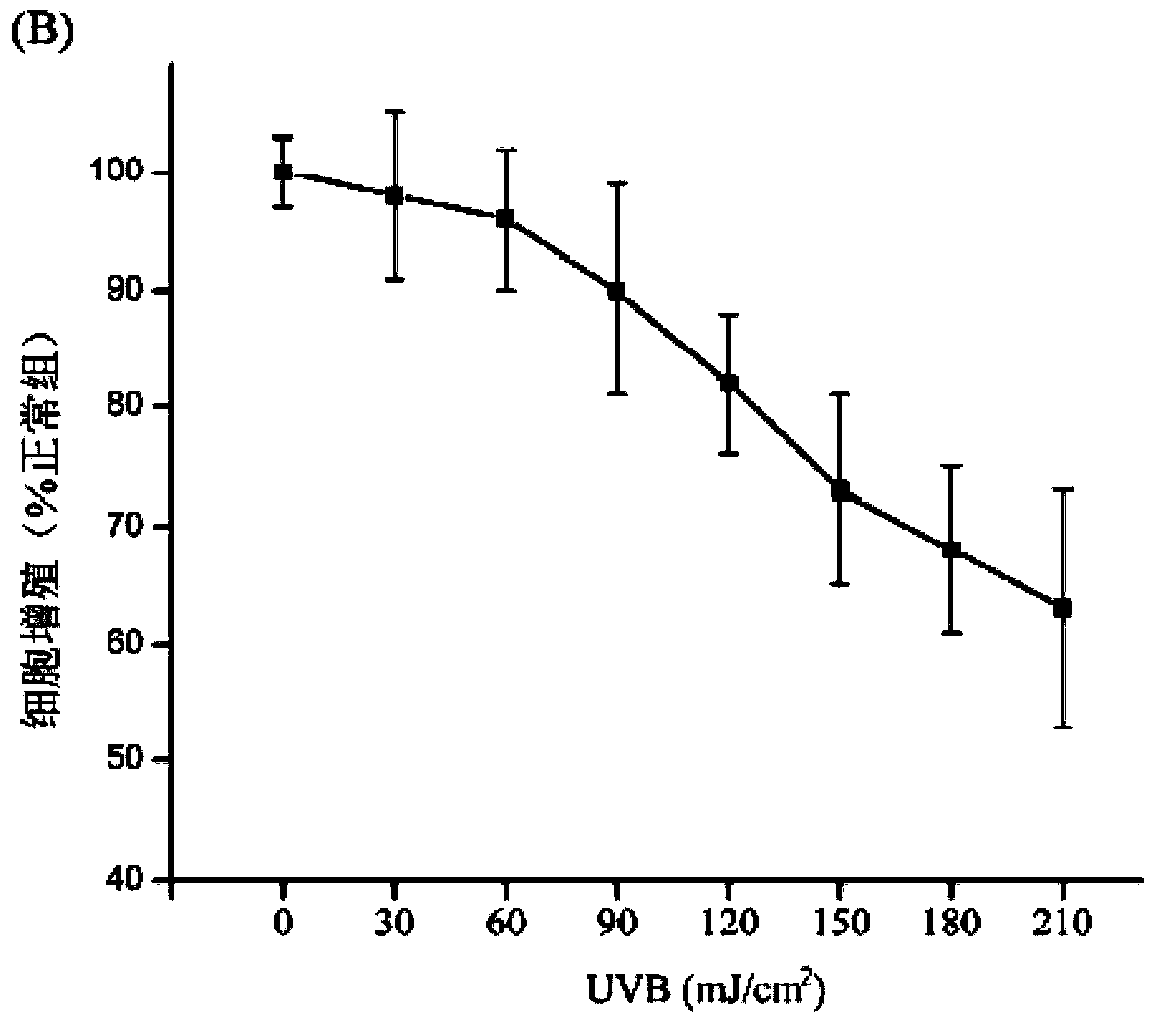
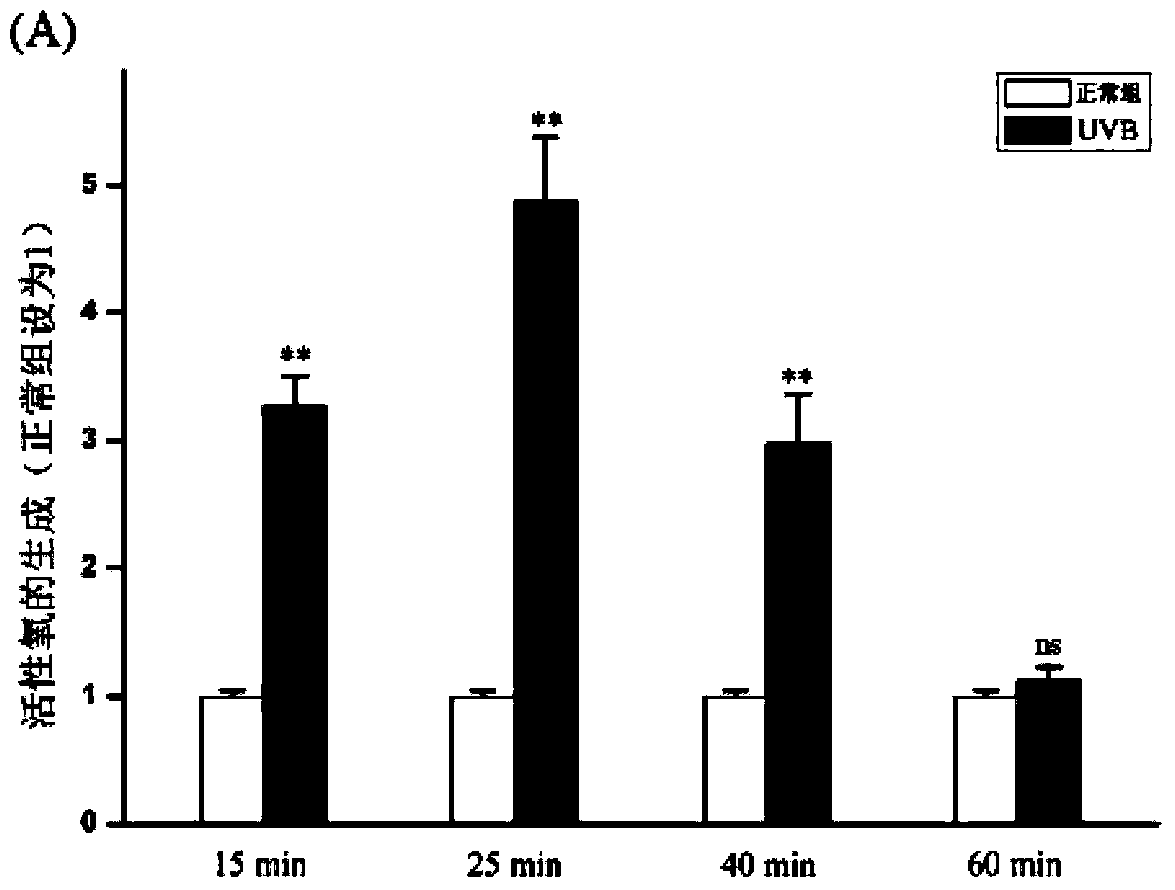
[0075] (3) UVB irradiation: when the degree of confluence of the mouse skin fibroblasts prepared in Example 1 for passage 1-3 (the figure is P2 generation) is 50%, remove the culture medium and cover with a thin layer PBS, open the cover, place it directly under the UVB lamp for the first irradiation, the irradiation dose is 120mJ / cm 2 . After the irradiation, remove the PBS, add 10ml DMEM+...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com