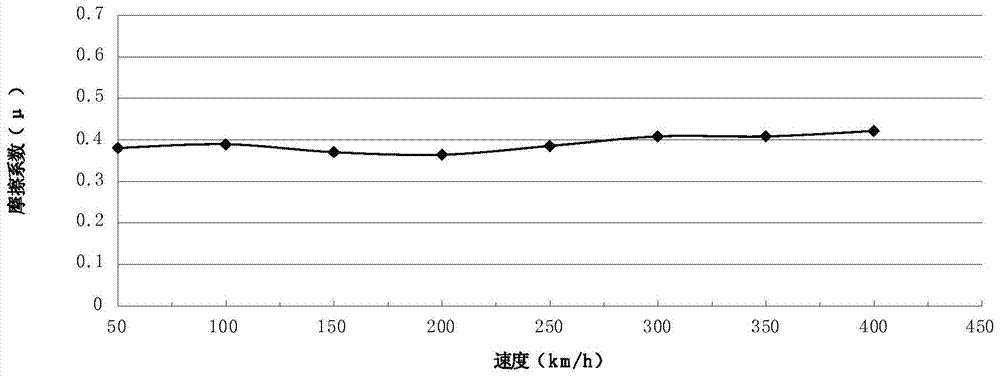
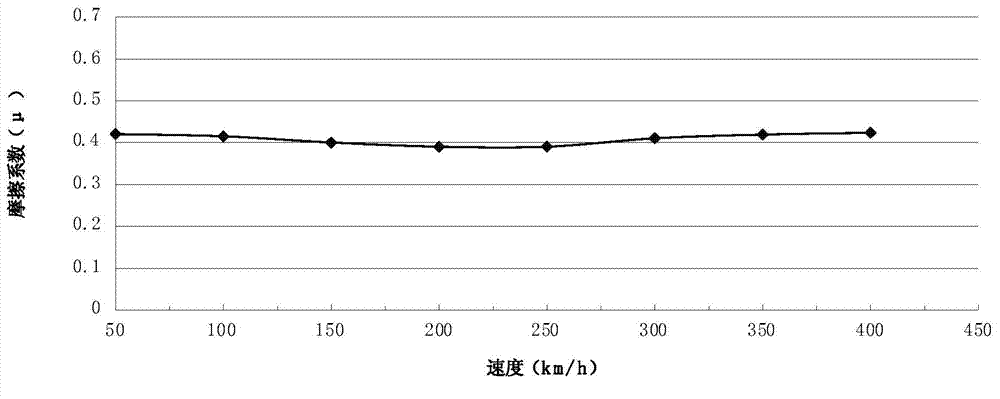
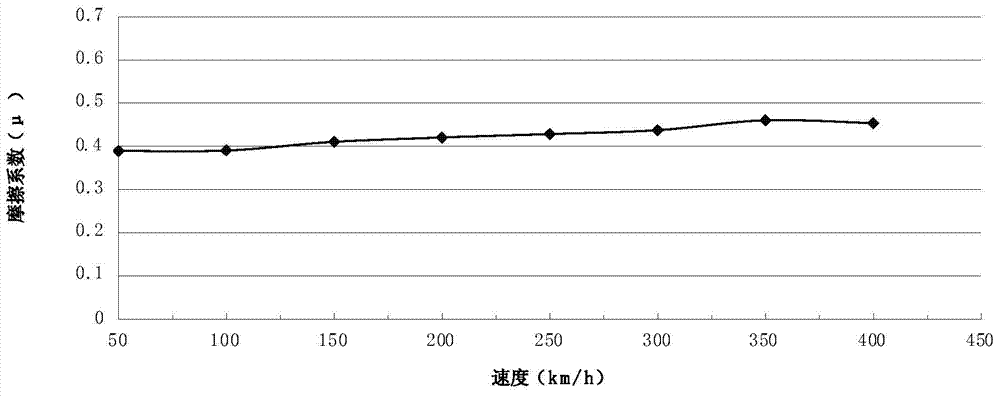
Copper-based powder dispersion ceramic as well as preparation method and application thereof
A copper-based powder and ceramic technology, applied in the field of ceramic materials, can solve the problems of inability to achieve high-speed, high-efficiency, and high-safety performance of high-speed rail transit vehicles, unsatisfactory service life performance of brake pads, and damage to high-speed train attendance efficiency. To achieve the effect of strong kinetic energy absorption and conversion, good heat dissipation and heat recovery, and good effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach
[0088] In the second specific embodiment, the raw materials used to prepare the copper-based powder-dispersed ceramics are composed of the following components by mass percentage:
[0089] Copper powder 50~75, diamond powder 1~5, titanium diboride powder 1~5, silicon carbide powder 1~6, boron carbide 1~6, aluminum powder 2~8, chromium powder 1~4, molybdenum powder 1~ 4. Nickel powder 1~6, tin powder 2~10, graphite powder 5~8, tungsten disulfide powder 1~7;
[0090] In the third specific embodiment, the raw materials used to prepare the copper-based powder-dispersed ceramics are composed of the following components by mass percentage:
[0091] Copper powder 50~75, diamond powder 1~5, titanium diboride powder 1~5, boron nitride powder 1~6, silicon nitride powder 1~6, aluminum powder 2~8, chromium powder 1~4, molybdenum powder 1~4, nickel powder 1~6, tin powder 2~10, graphite powder 5~8, tungsten disulfide powder 1~7;
[0092] The above-mentioned copper-based powder-dispersed c...
Embodiment 1
[0098] Copper powder 61, diamond powder 3, titanium diboride powder 2, alumina powder 4, silicon oxide powder 3, aluminum powder 3, chromium powder 2, molybdenum powder 2, nickel powder 4, tin powder 5, graphite powder 6, two Tungsten sulfide powder 5;
[0099] The preparation method is as follows:
[0100] ①Raw material mixing: mix all raw materials evenly;
[0101] ② Blank making: put the raw material powder mixed in step ① into the mold, press it with 15MPa on the hydraulic press, hold the pressure for 3min to form, and demould;
[0102] ③ Sintering: put the green body obtained in step ② into an inert atmosphere, and pressurize and sinter with nitrogen; the temperature of the nitrogen-filled pressurized sintering is 880° C., the pressure is 3 MPa, and the sintering time is 5 hours.
Embodiment 2
[0104] Copper powder 63, diamond powder 2, titanium diboride powder 2, silicon carbide powder 4, boron carbide 3, aluminum powder 3, chromium powder 2, molybdenum powder 2, nickel powder 3, tin powder 6, graphite powder 5, disulfide Tungsten powder 5;
[0105] Preparation method is the same as embodiment 1, and difference is:
[0106] ③ Sintering: put the green body obtained in step ② into an inert atmosphere, and pressurize and sinter with nitrogen; the temperature of the nitrogen-filled pressurized sintering is 880° C., the pressure is 3 MPa, and the sintering time is 5 hours.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com