Bacillus subtilis for degrading AFB1 (Aflatoxius B1)
A technology of Bacillus subtilis and microbial strains, applied in the direction of bacteria, microorganism-based methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve problems such as difficult large-scale production, unstable effects, and loss of nutrients
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0017] Example 1. Isolation of Bacillus subtilis Taishan
[0018] The starch-rich Taishan soil was collected, treated in a water bath at 80°C for 1 hour, and then diluted and coated on a starch-containing plate medium (beef extract 5.0g, peptone 10.0g, sodium chloride 5.0g, soluble starch 5.0g, agar) 20g and distilled water 1000ml pH=7.2) were cultured for 1-3 days and observed after culturing. Then carry out primary screening and purification, and identify whether it is Bacillus subtilis by using a microscope to carry out Gram staining identification. Then re-screen, determine its amylase activity, and finally determine the strain.
[0019] Experimental process: pouring plate - preparation of gradient dilution - coating - culture - primary screening - re-screening - purification - preservation
[0020] (1) Preparation of soil dilution
[0021] Take soil samples near the flower beds in Tianwai Village, Mount Tai, remove 5 cm of the surface layer, and take 5-15 cm. Sampling...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Example 2. Identification of Bacillus subtilis Taishan
[0035](1) Taishan Bacillus subtilis was cultured on BPY agar plate (5g of beef extract, 10g of peptone, 5g of sodium chloride, 5g of glucose, 5g of yeast extract powder, 15g of agar and 1L of distilled water, pH=7.0) at 37°C for 48h Afterwards, its shape and structure were observed by optical microscope.
[0036] (2) Design of primers for PCR amplification of 16S rDNA sequence
[0037] Eubac27F: AGA GTT TGA TCC TGC CTC AG;
[0038] Eubac1492R: GGA TAC CTT GTT ACG ACT T
[0039] (3) PCR reaction system: 10×PCR buffer (containing 20mmol / L Mg2+) 5μl, 20umol / L dNTP 4μl, 0.1OD / ml primer 1μl, 5u / μl Taq enzyme 1μl, ddH2O33μl, total DNA template 50μl.
[0040] Reaction conditions: denaturation at 94°C for 5 min; denaturation at 94°C for 1 min, annealing at 48.2°C for 1 min, extension at 72°C for 2 min, 35 cycles; extension at 72°C for 10 min. After the reaction, 5 ul of the PCR product was electrophoresed in 1% agaros...
Embodiment 3
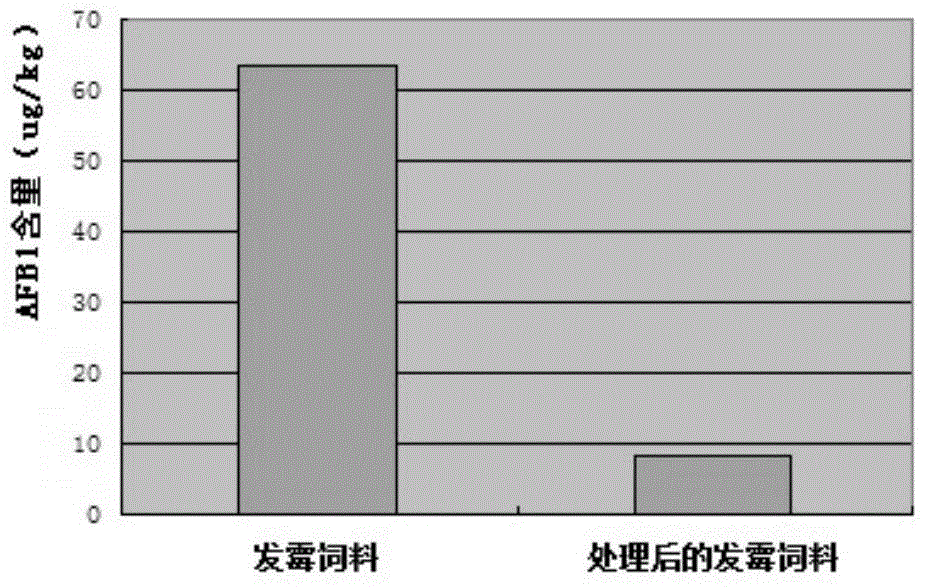
[0041] Example 3. Determination of Taishan Bacillus subtilis Degradation Aflatoxin Active Component
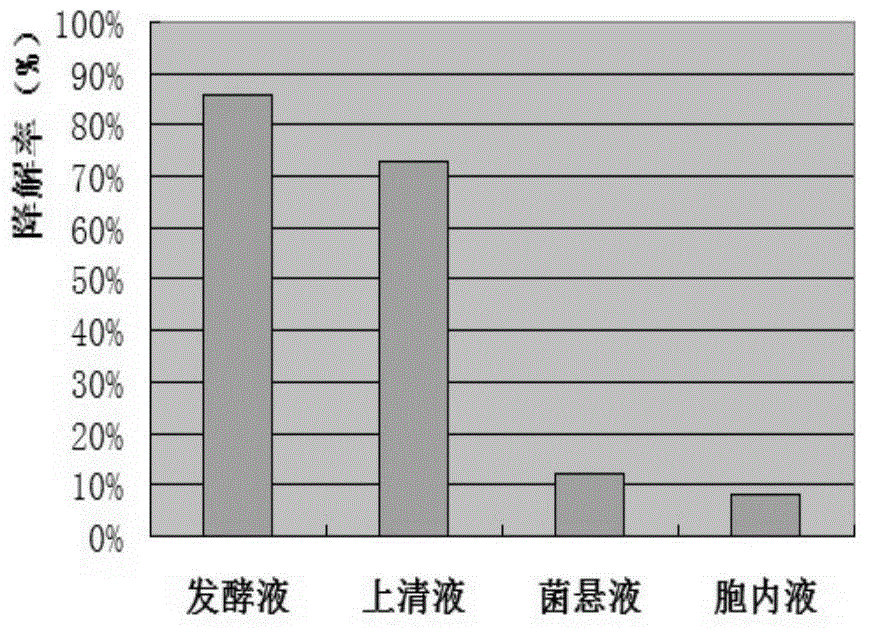
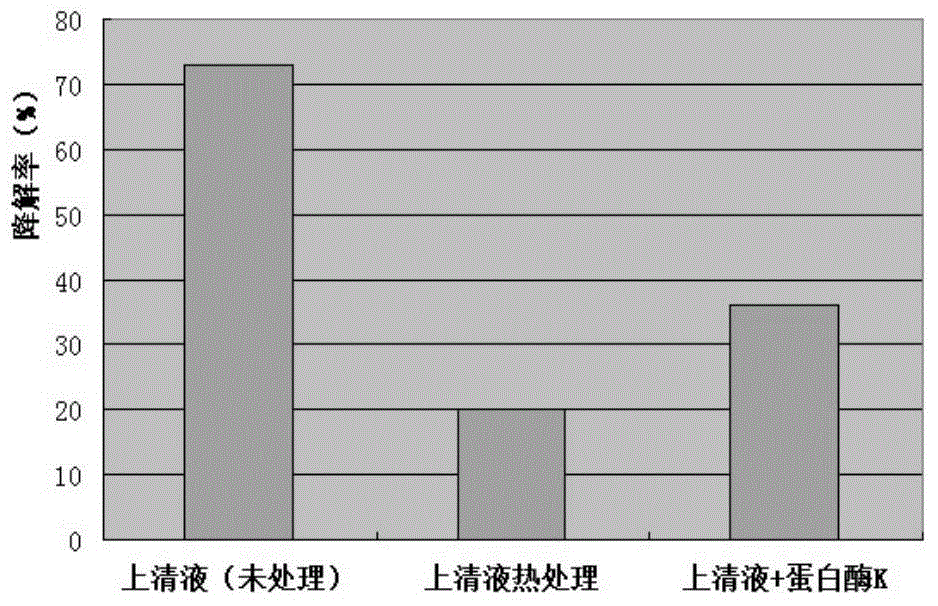
[0042] Pick Taishan Bacillus subtilis and culture it in 50ml BPY liquid medium for 8 hours, then inoculate the bacterium solution in 100ml BPY liquid medium with 6% inoculum amount, shake the flask for 24 hours at 37°C and 180r / min to obtain Bacillus subtilis Bacillus fermentation broth. Take 5ml of fermentation broth, centrifuge at 4°C for 20min (8000r / min), separate the supernatant and bacteria, and store the supernatant at 4°C for later use; wash the centrifuged bacteria with distilled water, then centrifuge, take the bacteria and add 5ml of distilled water to prepare The bacterial suspension was obtained for later use; then take 5ml of fermentation broth, centrifuge at 4°C for 20min (8000r / min), separate the supernatant and bacteria, add 5ml of distilled water to the bacteria, perform ultrasonic crushing on the cells, freeze and centrifuge the centrifuged supernatant The ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com