A method for determining the rate of desorption of free radicals from latex particles into the continuous phase in emulsion polymerization
A technology of emulsion polymerization and free radicals, applied in the field of emulsion polymerization, can solve problems such as limited promotion, doubtful applicability of macroscopic mass transfer theory, and extremely complicated modeling work
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
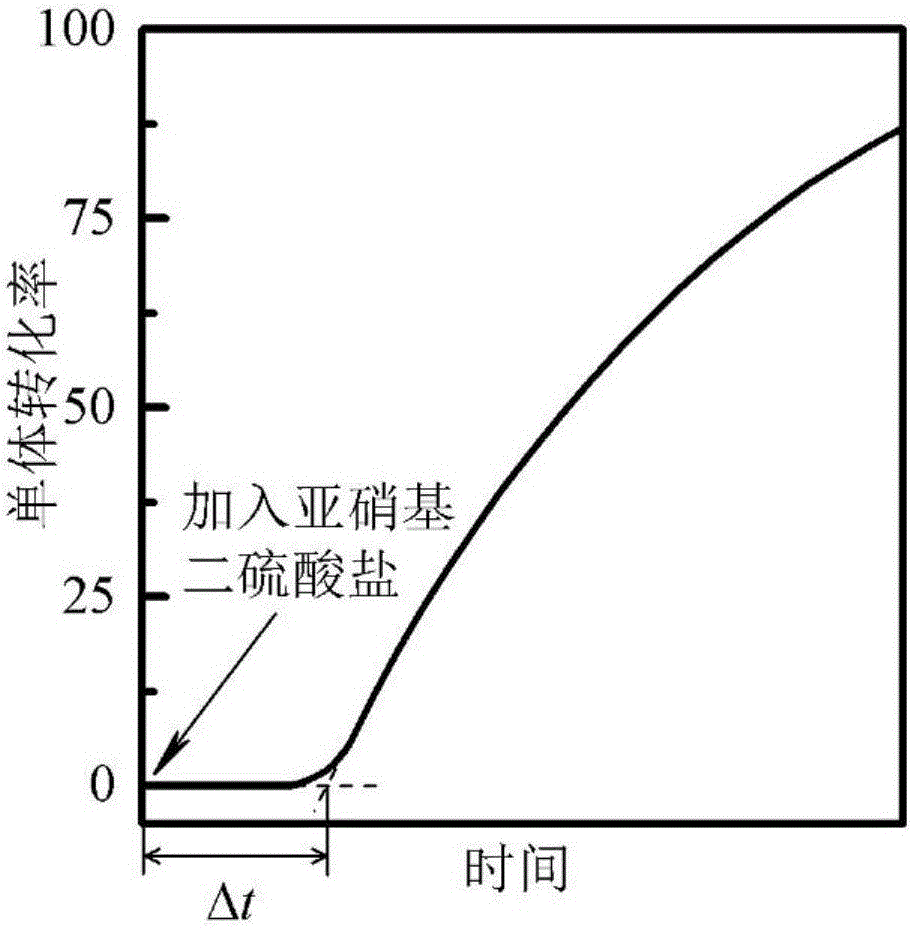
[0086] Mix 850g of water, 30g of methanol, 20g of formamide, 96g of butyl acrylate, 1g of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide, 1g of n-hexadecene, 1g of potassium hydrogen phthalate and 1g of benzoyl peroxide, The emulsion is formed by mechanical stirring, and the emulsion is put into a calorimetric reactor, and nitrogen gas is introduced to exclude oxygen, and then the temperature is raised to start the reaction. The reaction temperature was 90°C, and the polymerization rate was monitored after the polymerization started. When the reaction was carried out for 20 minutes, 1 mL of 1.1 wt % potassium nitrosodisulfate aqueous solution was added to the system. The duration of the polymerization rate decline stage was determined to be 160s, and P was optimized according to formulas 1-3. d =0.87, and then calculated according to formula 4 to obtain the apparent rate R of primary free radical desorption from latex particles into the continuous phase da =7.03×10 -6 mol / (L s), the absolu...
Embodiment 2
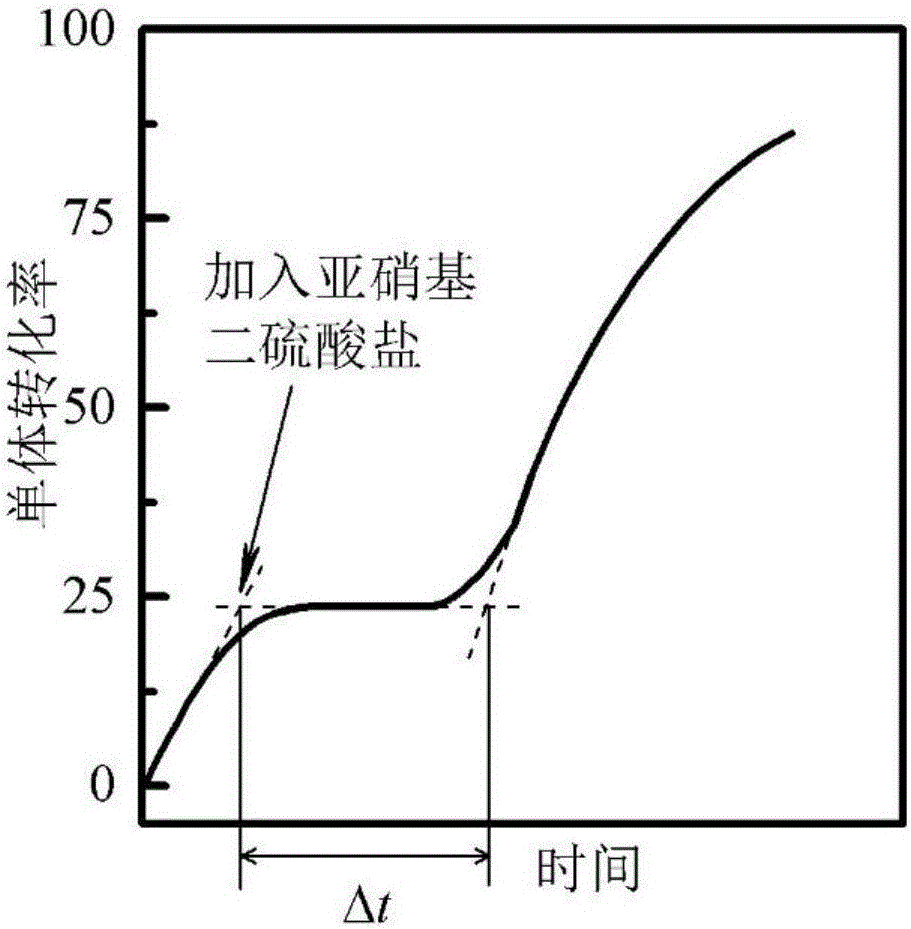
[0088] 350g of water, 50g of α-methylstyrene, 199g of sodium lauryl sulfate, 1g of silica with an average size of 1nm, 230g of n-pentanol, 50g of suberic acid, 9g of n-octadecane, and 8g of n-hexadecanol , 1g of 8-hexadecane, 2g of borax, 50g of hydroxybutyl azobisisobutyrate (initiator 1) and 50g of methyl azobisisobutyrate (initiator 2) were mixed and stirred mechanically to form an emulsion. The emulsion was put into a 2000mL glass jacketed reactor, nitrogen gas was introduced to remove oxygen, and then the temperature was raised to start the reaction. The reaction temperature was 25°C. After the polymerization started, the polymerization rate and polymer molecular weight were monitored by gravimetric method and viscosity method, respectively. When the reaction was carried out for 10 minutes, 50 mL of a 30 wt % aqueous solution of sodium nitrosodisulfate was added to the system. The measured duration of the polymerization rate decline phase and the duration of the polymer ...
Embodiment 3
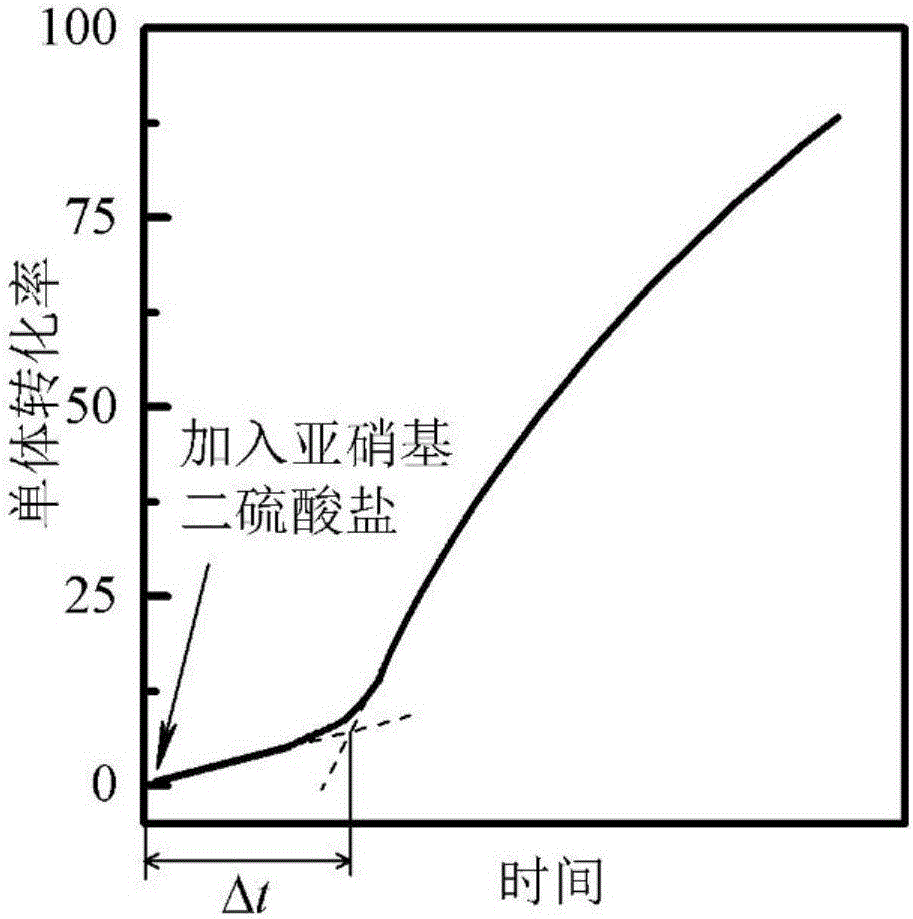
[0090] Mix 980g of water, 10g of ethanol, 9.98g of stearyl methacrylate, 0.01g of Tween 80 and 0.01g of azobisisobutyronitrile, disperse and form an emulsion through an ultrasonic cell pulverizer while mechanically stirring, and put the emulsion into 2000mL glass-jacketed reaction kettle, nitrogen-argon mixed gas is introduced to exclude oxygen, and then the temperature is raised to start the reaction. The reaction temperature was 60°C, and the polymerization rate was monitored by gas chromatography after the polymerization started. At the beginning of the reaction, 1mL of 0.1wt% ammonium nitrosodisulfate solution was added to the system. The duration of the polymerization rate decline stage was measured to be 3120s, and P d =0.91, and then calculated according to formula 4 to obtain the apparent rate R of primary free radical desorption from latex particles into the continuous phase da =7.03×10 -9 mol / (L s), the absolute rate R of primary free radicals desorbing from latex...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com