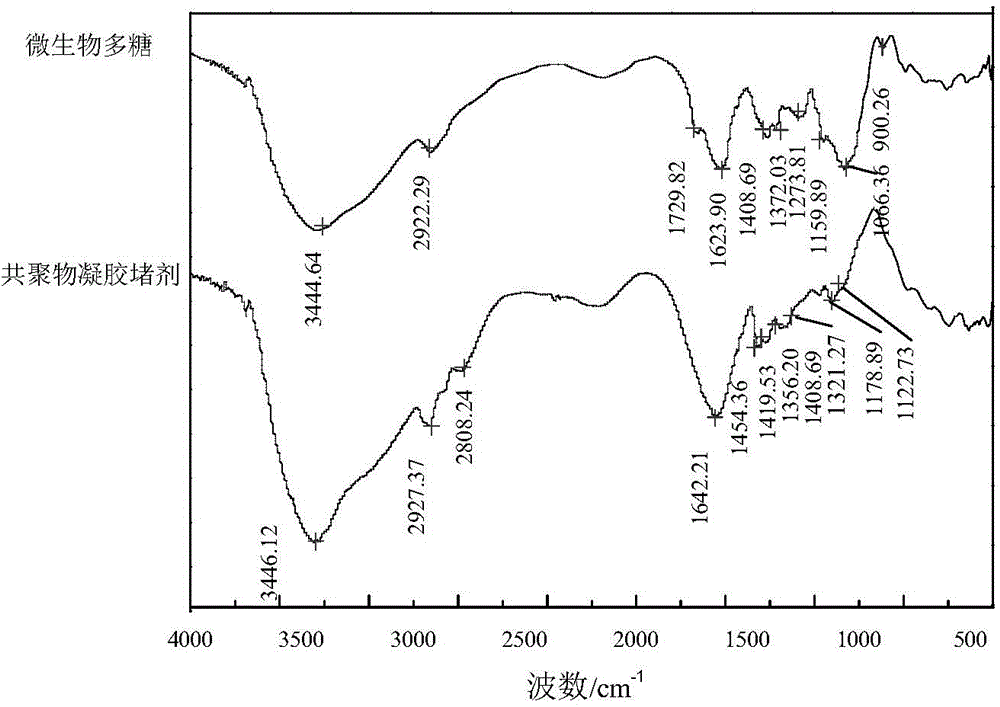
Method for preparing microbial polysaccharide modified copolymer gel plugging agent
A microbial polysaccharide and gel plugging agent technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, drilling compositions, etc., can solve problems such as poor temperature and salt resistance and erosion resistance, damage to operators and formations, short production cycle, etc. , to achieve good salt resistance and shear resistance, high sweep efficiency, and improved mobility ratio
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Prepare xanthan gum with distilled water into a solution with a mass fraction of 0.1% and stir evenly, then add 2.5 g of acrylamide (the mass ratio of xanthan gum to acrylamide is 1:10), 0.0825 g of N,N'-methylene Base bisacrylamide (accounting for 3% of the total mass of xanthan gum and acrylamide), feed nitrogen into the system, add Na 2 SO 3 0.0294g, (NH 4 ) 2 S 2 o 8 0.0532g (this initiation system accounts for 3% of the total mass of xanthan gum and acrylamide, wherein Na 2 SO 3 with (NH 4 ) 2 S 2 o 8 The molar ratio is 1:1), stirred evenly and reacted in a constant temperature water bath at 50°C for 8 hours to form a gel.
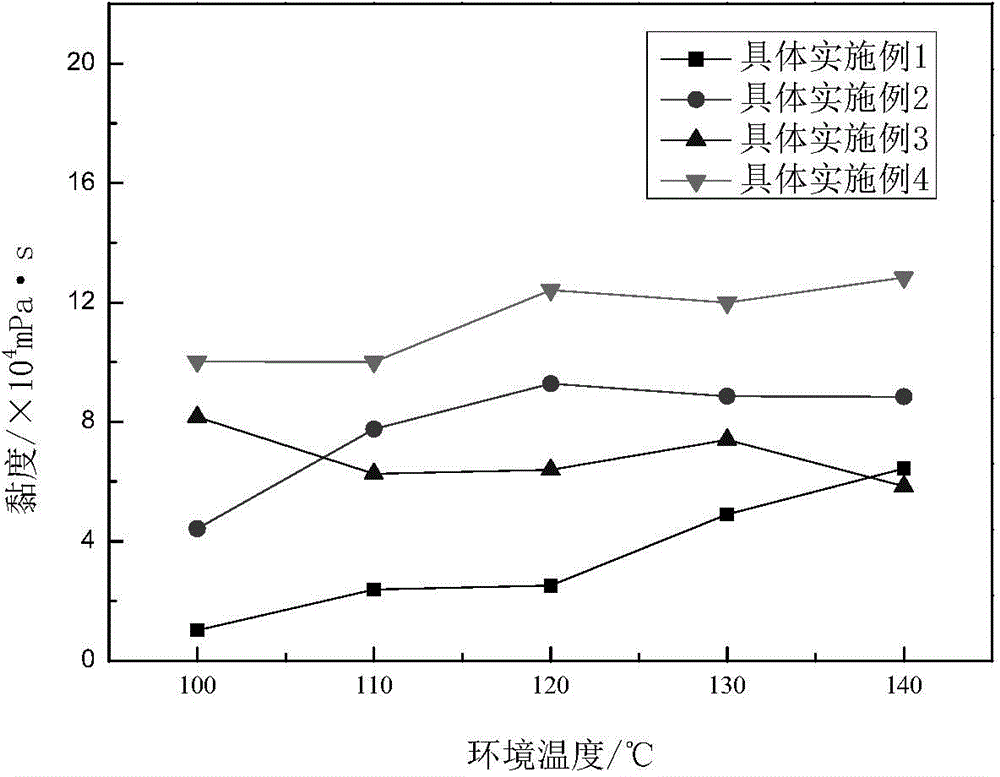
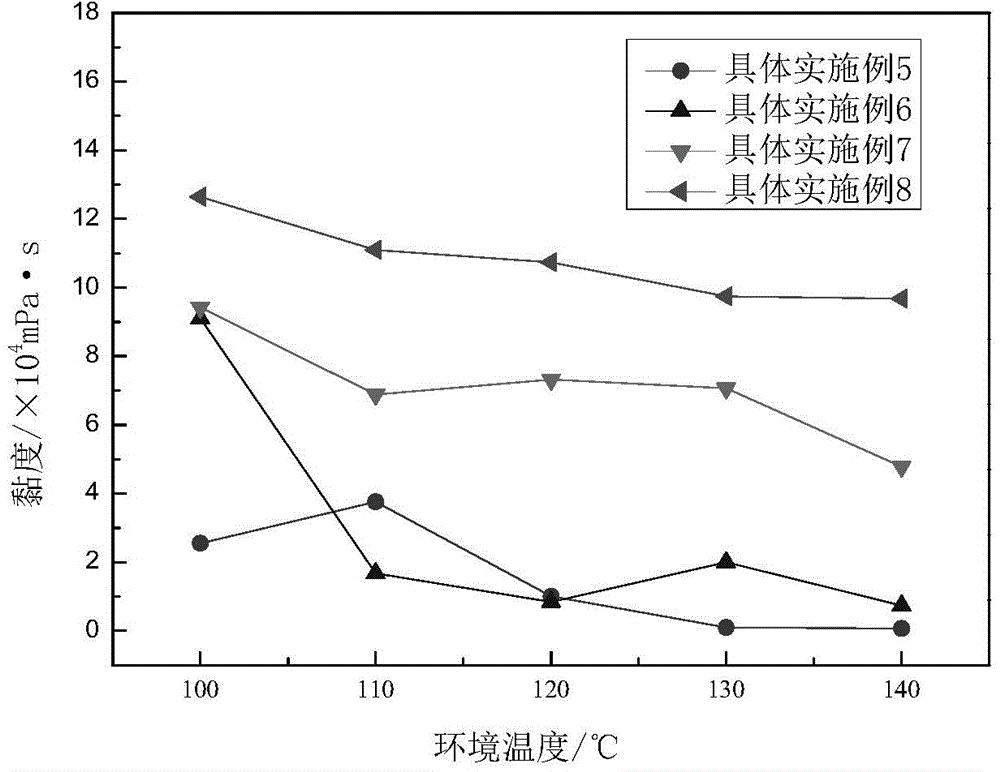
[0032] Measure the viscosity of the gel with NDJ-8S viscometer 3.68×10 4 mPa·s, the effect of temperature and salinity on the gel strength of the copolymer is shown in the attached figure 2 And attached Figure 4 shown.
[0033] From figure 2 Specific Example 1 Influence curve of temperature on copolymer gel strength, it can be...
Embodiment 2
[0036]Xanthan gum is mixed with distilled water and is the solution that mass fraction is 0.3% and stirs evenly, adds the 2-acrylamido-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid of 5.0g successively (xanthan gum and 2-acrylamido-2- The mass ratio of methylpropanesulfonic acid is 1:20), 0.0525g of N,N'-methylenebisacrylamide (1% of the total mass of xanthan gum and 2-acrylamido-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid %), feed nitrogen into the system, add Na in turn 2 SO 3 0.0373g, (NH 4 ) 2 S 2 o 8 0.0676g (this initiating system accounts for 2% of the total mass of xanthan gum and 2-acrylamido-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid, wherein Na 2 SO 3 with (NH 4 ) 2 S 2 o 8 The molar ratio is 1:1), stirred evenly and reacted in a constant temperature water bath at 50°C for 8 hours to form a gel.
[0037] Measure the viscosity of the gel with NDJ-8S viscometer 4.26×10 4 mPa·s, the effect of temperature and salinity on the gel strength of the copolymer is shown in the attached figure 2 And attached ...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Chitosan was formulated with distilled water into a solution with a mass fraction of 1% and stirred evenly, followed by adding 15g of acrylamide (the mass ratio of chitosan to acrylamide was 1:15), 0.8g of N,N'-methylene base bisacrylamide (accounting for 5% of the total mass of chitosan and acrylamide), feed nitrogen into the system, add initiator (NH 4 ) 2 [Ce(NO 3 ) 6 ] 0.64g (the initiation system accounts for 4% of the total mass of chitosan and acrylamide), stirred evenly and reacted in a constant temperature water bath at 50°C for 8h to form a gel.
[0042] Measure the viscosity of the gel with NDJ-8S viscometer 8.64×10 4 mPa·s, the effect of temperature and salinity on the gel strength of the copolymer is shown in the attached figure 2 And attached Figure 4 shown.
[0043] From figure 2 In specific example 3, the influence curve of temperature on the copolymer gel strength can be seen that as the ambient temperature increases, the gel viscosity increas...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com