Preparation method of biological composite material using titanium alloy as implant
A technology of composite materials and titanium alloys, applied in prosthetics, medical science, etc., can solve the problems of low bonding strength and easy falling off, and achieve the effect of improving bonding strength, realizing program control, and avoiding the loss of materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] S1: Pretreat the medical titanium alloy substrate, which is in the form of a thin sheet with a diameter of 14mm and a thickness of 1.5mm. The substrate is successively polished with 150#, 400#, 800#, 1200# and 1500# metallographic sandpaper to remove surface oxidation membrane, followed by ultrasonic cleaning with acetone and alcohol respectively;
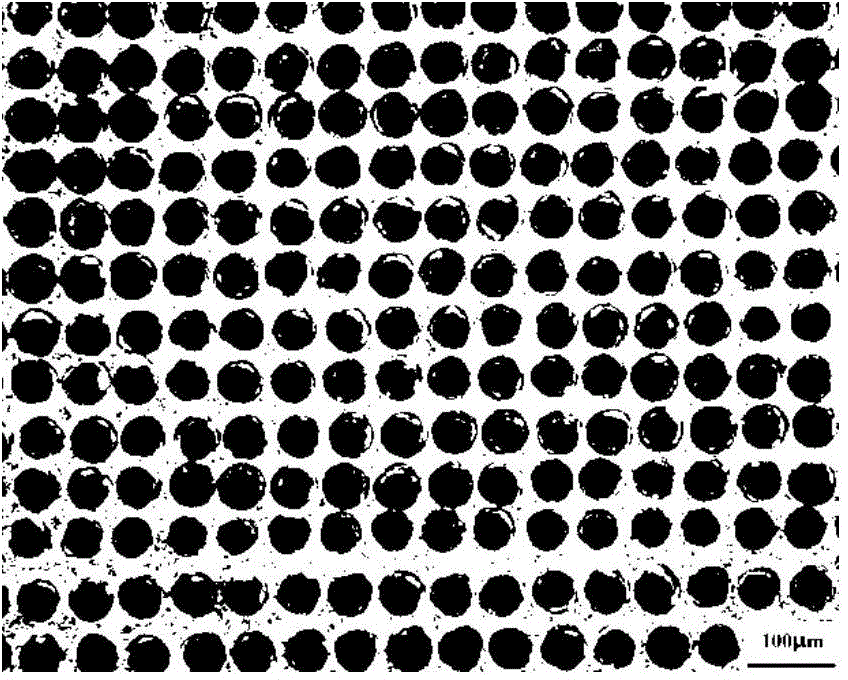
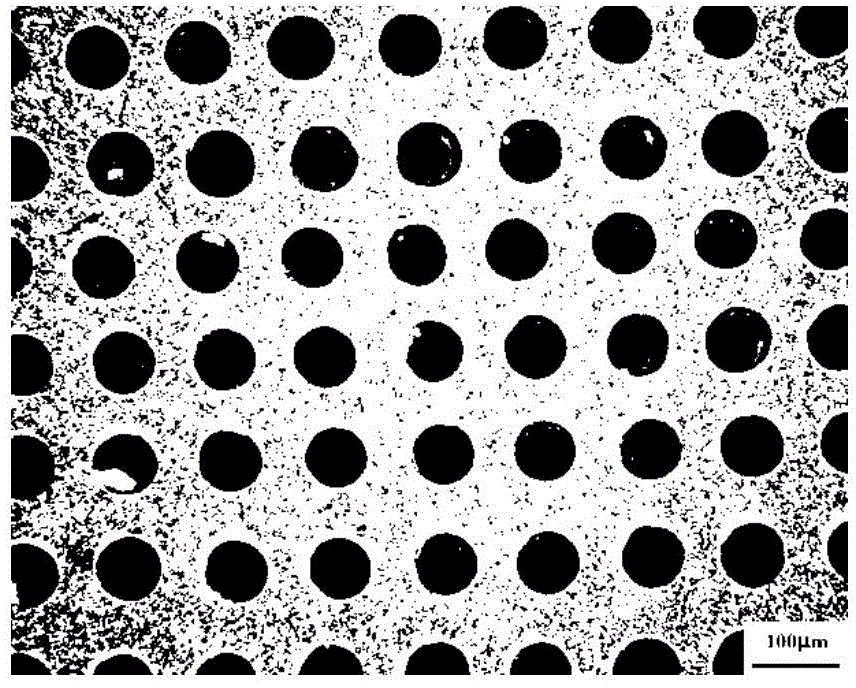
[0036] S2: Perform laser microporation treatment on the surface of the medical titanium alloy substrate obtained in S1, wherein the medical titanium alloy substrate obtained in S1 is placed in a 20W optical fiber laser processing platform with optomechanical integration, and its wavelength is 1.064 μm. Lens F=100mm, adjust the process parameters of laser processing, that is, the average laser power is 16W, the laser pulse width is 200ns, the laser frequency is 25KHz, the single pulse energy is 0.8mJ, and the laser action time is 0.3ms when processing a microhole. In the computer system that controls the laser processing, set...
Embodiment 2
[0041] This embodiment is the same as Embodiment 1, the difference is:
[0042]S2: Perform laser microporation treatment on the surface of the medical titanium alloy substrate obtained in S1, wherein the medical titanium alloy substrate obtained in S1 is placed in a 20W optical fiber laser processing platform with optomechanical integration, and its wavelength is 1.064 μm. Lens F=100mm, adjust the process parameters of laser processing, that is, the average laser power is 16W, the laser pulse width is 200ns, the laser frequency is 25KHz, the single pulse energy is 0.8mJ, and the laser action time is 0.7ms when processing a microhole. In the computer system that controls laser processing, set the hole spacing to 100 μm, adjust the laser processor to obtain the focal length, place the substrate at the focal point, turn on the equipment, and process, the prepared micropore diameter is 80.00 μm, and the micropore depth is 44.335 μm. Microporous medical titanium alloy with a microp...
Embodiment 3
[0044] This embodiment is the same as Embodiment 1, the difference is:
[0045] S2: Perform laser microporation treatment on the surface of the medical titanium alloy substrate obtained in S1, wherein the medical titanium alloy substrate obtained in S1 is placed in a 20W optical fiber laser processing platform with optomechanical integration, and its wavelength is 1.064 μm. Lens F=100mm, adjust the process parameters of laser processing, that is, the average laser power is 16W, the laser pulse width is 200ns, the laser frequency is 25KHz, the single pulse energy is 2.00mJ, and the laser action time is 1ms when processing a microhole. In the computer system that controls laser processing, set the hole spacing to 120 μm, adjust the laser processor to obtain the focal length, place the substrate at the focal point, turn on the equipment, and process. Microporous medical titanium alloy with hole center distance of 120 μm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com