Low cost clean nondestructive transfer method of large area of graphene
A graphene and large-area technology, applied in the field of graphene transfer, can solve the problems of destroying the structural integrity of graphene, unfavorable for continuous scale transfer, graphene surface pollution, etc., to achieve easy operation, short transfer cycle, avoid pollution effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
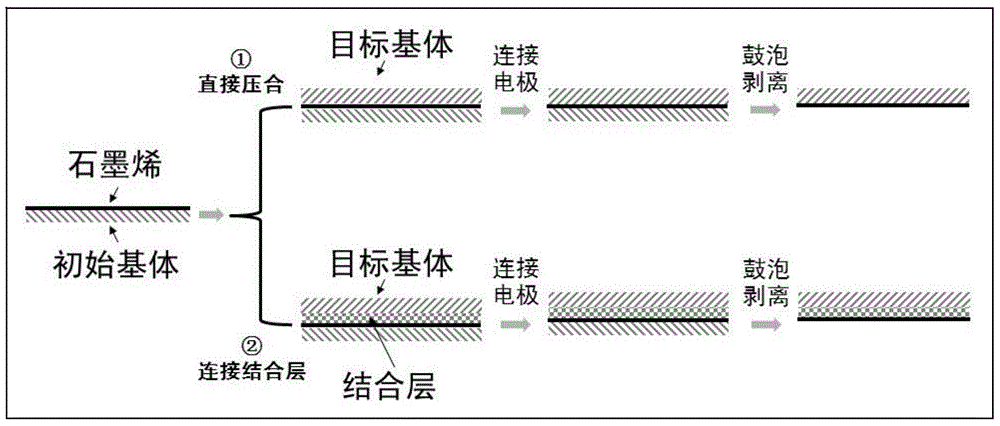
[0040] Metal copper foil is used as the initial substrate, polyethylene terephthalate film is used as the target substrate, and electrostatic force is used as the binding force. Graphene is grown on metal copper foil by CVD method (in this embodiment, the metal copper foil can be replaced with copper sheets or copper plates of different specifications, single crystal or polycrystalline, and the thickness is greater than 10 μm). After the copper foil grown with graphene is cooled, use an electrostatic generator to generate electrostatic force on the copper foil (or on the surface of polyethylene terephthalate film) (the voltage for generating static electricity is not less than 0.1kV), and use a roller Copper foil / graphene and polyethylene terephthalate film are pressed together by electrostatic force (pressure less than 1MPa) by pressing or plate pressing. Connect "polyethylene terephthalate / graphene / copper foil" to the negative pole of the constant current power supply, and u...
Embodiment 2
[0042] The difference from Example 1 is:
[0043] The graphene on the growing copper foil and the polyethylene terephthalate film are directly pressed together by roll-to-roll roll pressing (or plate pressing), the pressure is less than 1MPa, and the hot pressing temperature is 100-180°C .
[0044] In this embodiment, the electrolyte is 2mol / L NaOH aqueous solution, the operating temperature of the electrolysis process is 40-50°C, the voltage used in the electrolysis process is 5-10 volts, and the current is 3 amperes; the gas generated by the electrolysis is hydrogen.
Embodiment 3
[0046] The difference from Example 1 is:
[0047] Adopt different materials (in this embodiment, metal copper foil can be changed into foils of metals such as nickel, platinum, ruthenium, iridium and alloys thereof (copper-nickel alloy, molybdenum-nickel alloy, gold-nickel alloy, etc.) Combined metal films, and metal carbides such as titanium carbide, molybdenum carbide, and tungsten carbide, or other semiconductors such as Si) are used as the initial substrate, and graphene is grown on its surface by different methods.
[0048] In this embodiment, the electrolyte is 3 mol / L NaOH aqueous solution, the operating temperature of the electrolysis process is 40-50° C., the voltage used in the electrolysis process is 10-12 volts, and the current is 4 amperes; the gas generated by the electrolysis is hydrogen.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| electron mobility | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com