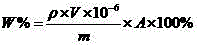Method for chemically analyzing content of boron nitride in nickel-based powder material
A technology of nickel-based powder and boron nitride, applied in the direction of material excitation analysis, etc., can solve the problems of particle size, uneven composition, difficulty in boron nitride content, etc., and achieve the effect of high accuracy and small external influence factors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Embodiment one : Determination of boron nitride content in Y boron C-2 composite rod
[0023] 1. Instruments and equipment used in the experiment
[0024] Inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometer: German SPECTRO ARCOS
[0025] Ultrapure water machine: Shanghai Youpu UPR-I-10T+UPT-II-10T combined type
[0026] Electronic balance: Sartorius CP124S (weighing range 0.1mg ~ 220g).
[0027] 2. Reagents used in the experiment
[0028] Ultrapure water (homemade)
[0029] Concentrated nitric acid ρ1.42g / mL, analytically pure
[0030] Hydrochloric acid ρ1.19 g / mL analytically pure
[0031] Mixed acid: hydrochloric acid + nitric acid + water = 2+1+2
[0032] Mixed acid: hydrochloric acid + nitric acid = 2 + 1
[0033] Anhydrous Sodium Carbonate Analytical Pure
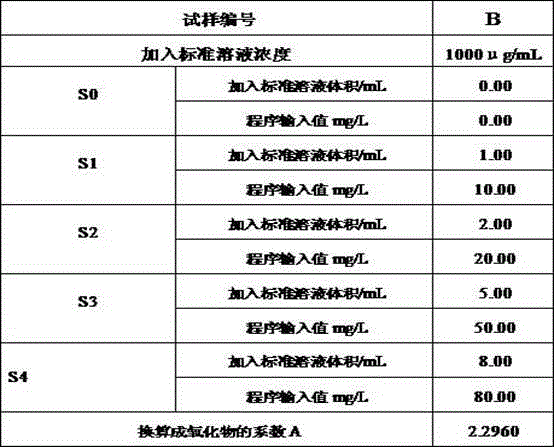
[0034] Boron standard solution 1000 μg / mL.
[0035] 3. Test procedure
[0036] 3.1 Sample processing
[0037] The sample was hammered into a fine powder with a hammer, and the fine powder was pa...
Embodiment 2
[0075] Embodiment two , Comparison of various methods for the determination of boron nitride content in the same batch of nickel-based composite spraying materials
[0076] The boron content in the same batch of nickel-based composite spraying materials was measured by plasma atomic emission spectrometry (ICP-AES), X-ray fluorescence spectrometry (XRF), gravimetric method, and volumetric method, and converted into boron nitride content. The results are shown in Table 7.
[0077] Table 7 Experimental data of boron nitride content determined by different methods
[0078] experiment method J-YT01-13032001 J-YT01-12120401 ICP-AES 12.21、12.25 11.54、11.66 XRF 12.15、12.28 11.79、11.62 gravimetric method 12.38、12.22 11.56、11.73 Kjeldahl method 12.19、12.28 11.55、11.62
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com