Cultivation method for wheat rich in Se, Zn and Fe
A cultivation method and wheat technology are applied in the cultivation field of selenium-enriched zinc-iron wheat, which can solve the problems of low utilization rate of selenium and zinc, complicated operation, limited absorption capacity and the like, and achieve relatively low price, good solubility, and effective absorption. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Field implementation site: Weigang Town, Bozhou City, Anhui Province. The soil is wheat field soil developed on the basis of sandy loam, with 6.2% soil organic matter, 55 mg / kg of hydrolyzed nitrogen, 17 mg / kg of available phosphorus, and 138 mg / kg of available potassium.
[0024] Wheat for testing: the wheat variety is Wanmai 52.
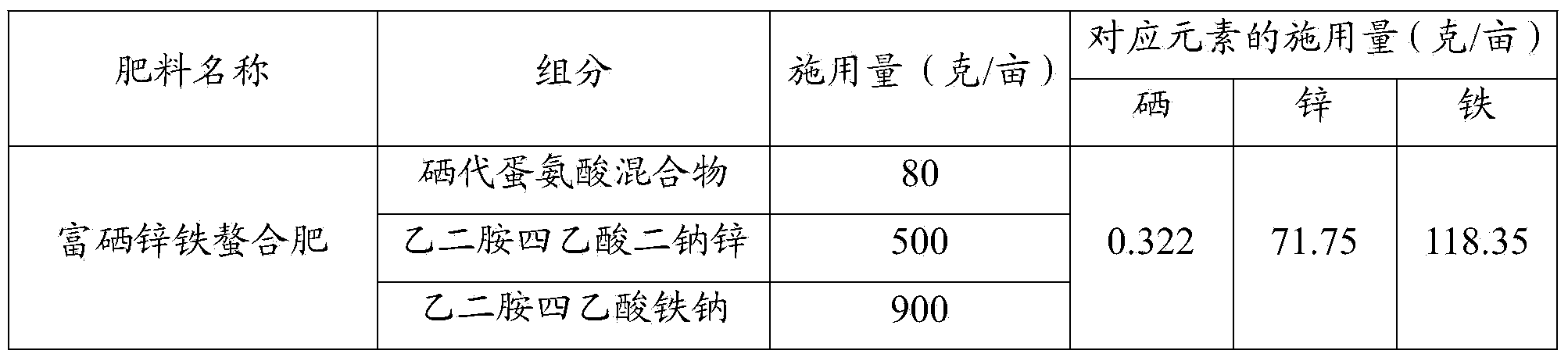
[0025] In this example, the wheat was sown on October 12, fertilized and irrigated conventionally, jointing began on March 15 of the following year, shallow water was poured on March 17 to keep the soil moist, and every other row of wheat was excavated at a depth of 10 to 15 cm on the same day Mix the wheat compound fertilizer and selenium-enriched zinc-iron iron chelate fertilizer and apply them to the ditch, and then cover with wet soil. In the control group, only wheat compound fertilizer was applied.
[0026] Wheat compound fertilizer consists of ammonium bicarbonate, superphosphate and potassium chloride. The application rate of ammon...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Field implementation location: Damiao Town, Guoyang County, Anhui Province. The soil is wheat field soil developed on the basis of sandy loam. The soil organic matter is 6.5%, hydrolyzed nitrogen is 59 mg / kg, available phosphorus is 19 mg / kg, and available potassium is 157 mg / kg.
[0036] Wheat for testing: The wheat variety is Zhengmai 7698.
[0037] In this example, the wheat was sown on October 19, fertilized and irrigated conventionally, jointing began on March 18 of the following year, shallow water was poured on March 20 to keep the soil moist, and every other row of wheat was excavated at a depth of 10 to 15 cm on the same day In the furrows, the experimental group and the control group were all applied with the same fertilizer as in Example 1. The specific application rate of selenium-rich zinc-iron chelate fertilizer was shown in Table 2-1. Other fertilizer components and application rates and production process and implementation Same as Example 1, the content...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Field implementation location: Damiao Town, Guoyang County, Anhui Province. The soil is wheat field soil developed on the basis of sandy loam. The soil organic matter is 6.6%, hydrolyzed nitrogen is 59 mg / kg, available phosphorus is 22 mg / kg, and available potassium is 149 mg / kg.
[0046] Wheat for testing: The wheat variety is Zhengmai 7698.
[0047] In this embodiment, wheat was sown on October 19, conventionally fertilized and irrigated, and jointing began on March 18 of the following year. On March 20, every other row was excavated with 10-15 cm deep grooves, and wheat compound fertilizer and selenium-enriched zinc Mix the iron chelate fertilizer and apply it to the ditch, and then cover it with wet soil. The control group was fed with wheat compound fertilizer and selenium-enriched chelate fertilizer. The specific application rates of selenium-rich zinc-iron chelate fertilizer and selenium-rich chelate fertilizer are shown in Table 3-1. Other fertilizer components...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com