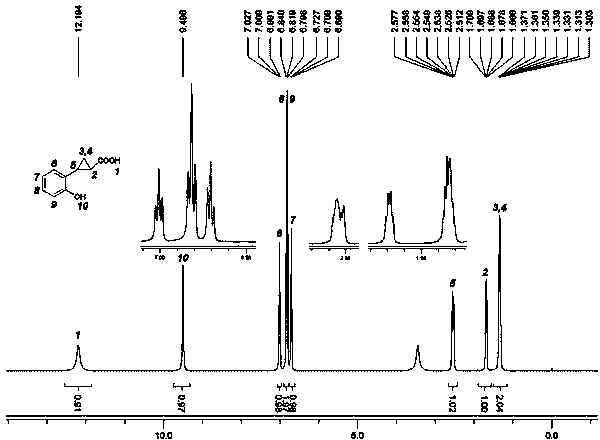
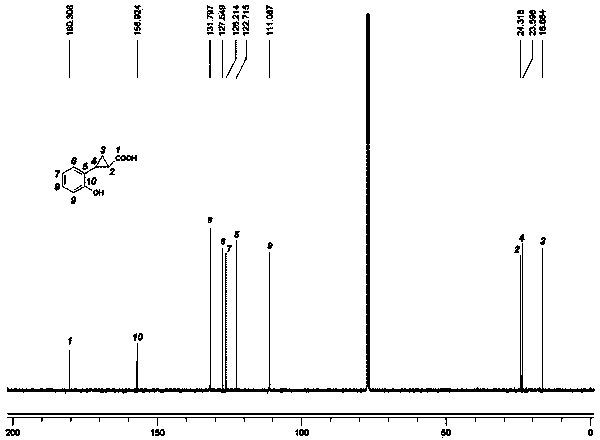
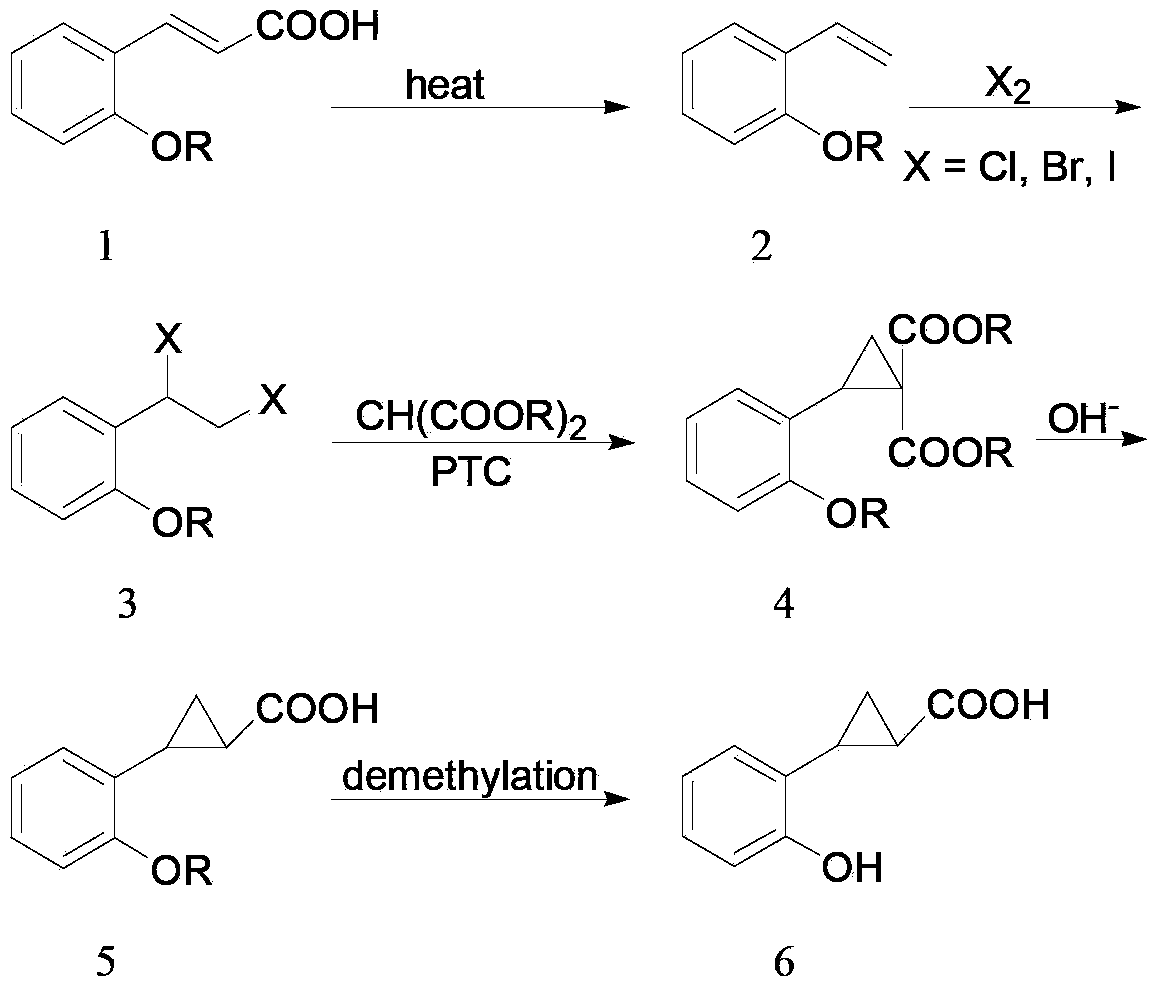
Preparation method of 2-(o-hydroxyphenyl)cyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid
A technology of o-hydroxyphenyl and cyclopropane, which is applied in the field of preparation of 2-cyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid, can solve the problems of expensive reagent TMSOI, difficulty in large-scale preparation, and poor reaction yield, and achieve low cost of raw materials and reagents , easy to large-scale industrial production, ideal yield effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] The synthetic route of the 2-(o-hydroxyphenyl)cyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid of the present embodiment is as follows:
[0032]
[0033] (A) Synthesis of o-methoxystyrene (compound 2)
[0034] In a dry 100mL single-necked bottle, add o-methoxycinnamic acid (compound 1, 25g, 0.14mol), potassium hydroxide (17g, 0.3mol) and 60mL of ethylene glycol in sequence. The mixture was heated to reflux for 1 hour, followed by distillation to collect fractions at 140-150°C. When the temperature rose to 180°C, the distillation was stopped. 15.6 g of a light yellow oil was obtained, namely o-methoxystyrene (compound 2), with a yield of 83%. The GC purity is 95%, and it can be directly used in subsequent reactions without purification. (B) Synthesis of 1-o-methoxyphenyl-1,2-dibromoethane (compound 3)
[0035] In a 150 mL round bottom flask, compound 2 (13.4 g, 0.1 mol) and 100 mL of chloroform were added. Under stirring, slowly add 50 mL of chloroform solution containing bromine (...
Embodiment 2
[0044] The same as Example 1, the difference is that this example investigated the reaction temperature, reaction time, reaction solvent, and different bases in the step (A) of Example 1. The influence of different bases on the reaction to generate compound 2 (ie conversion rate), the results are shown in the table 1 shows:
[0045] The impact of different reaction conditions on the yield of compound 2 in table 1
[0046]
Embodiment 3
[0048] Same as Example 1, the difference is that this example examines different reaction temperatures, reaction times, and reaction solvents in Step (B) of Example 1, compound 2: Br 2 The effect of the molar ratio on the reaction to generate compound 3 (i.e. conversion rate), the results are shown in Table 2:
[0049] The impact of different reaction conditions on the yield of compound 3 in table 2
[0050]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com