Deep phosphorous removal method for low-phosphorous water
A deep, crystal seed technology, applied in the field of deep phosphorus removal of secondary treatment effluent and landscape water, can solve the problems of unstable biological phosphorus removal process, high sludge moisture content, complex process flow, etc., to save investment and The effect of running cost, good treatment effect and simple process flow
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
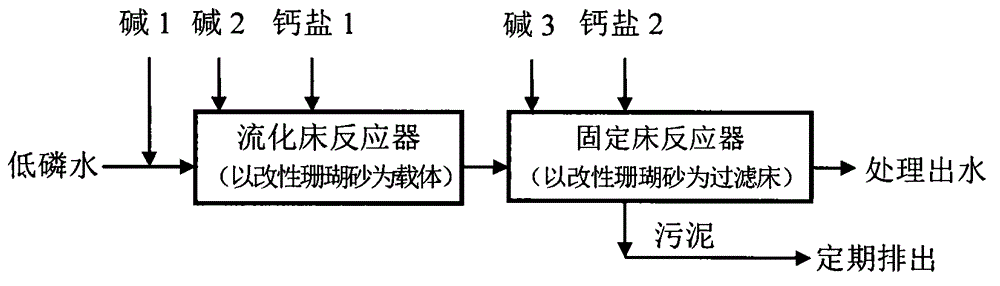
[0056] The specific operating parameters are: first-stage fluidized bed reactor: the total effective volume is 3.8L, and 350g of 0.3-0.1mm modified coral sand is put into it. The average influent flow rate is 15.72L / d, the hydraulic retention time is 5.46h, and the aeration rate is 200L / h. Secondary fixed-bed reactor: 4.17kg of modified coral sand of 0.45-1.0mm is input, the sand layer is 12cm high, the effective volume of the sand bed is 3.19L, the average influent flow rate is 16.71L / d, and the hydraulic retention time of the sand layer is 4.58h . The raw water is the secondary treatment effluent of domestic sewage, with an average TP=3.27mg / L. Calcium chloride is the calcium source, in the reactor [Ca 2+ ]=80~150mg / L, adjust the pH in the range of 8.5~10.0 with 0.1M NaOH.
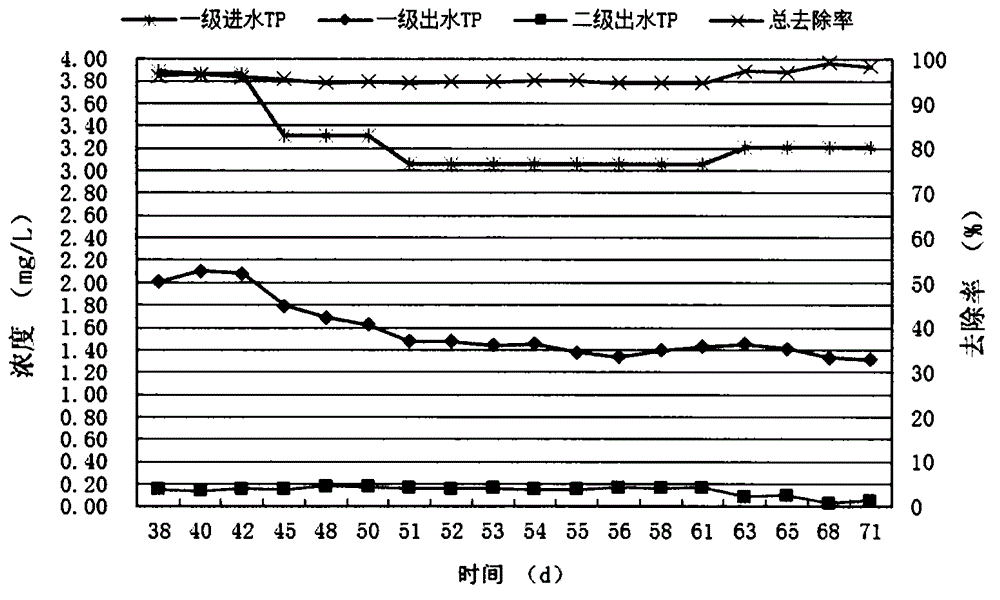
[0057] The operation effect is as follows figure 2 Shown: The total removal rate of the series system is 96.33%. The average influent TP of the primary reactor is 3.27mg / L, the average effluent TP ...
Embodiment 2
[0059] The specific operating parameters are: Secondary fixed bed reactor: input 4.17kg of 2.5-1.0mm modified coral sand, the height of the sand layer is 12cm, the effective volume of the sand bed layer is 3.19L, the average water flow rate is 16.6L / d, the sand layer The hydraulic retention time is 4.63h. The raw water is a landscape water body in a residential area, with an average TP=1.19mg / L. With calcium chloride as calcium source, [Ca 2+ ]=80~150mg / L, adjust the pH in the range of 8.5~10.0 with 0.1M NaOH.
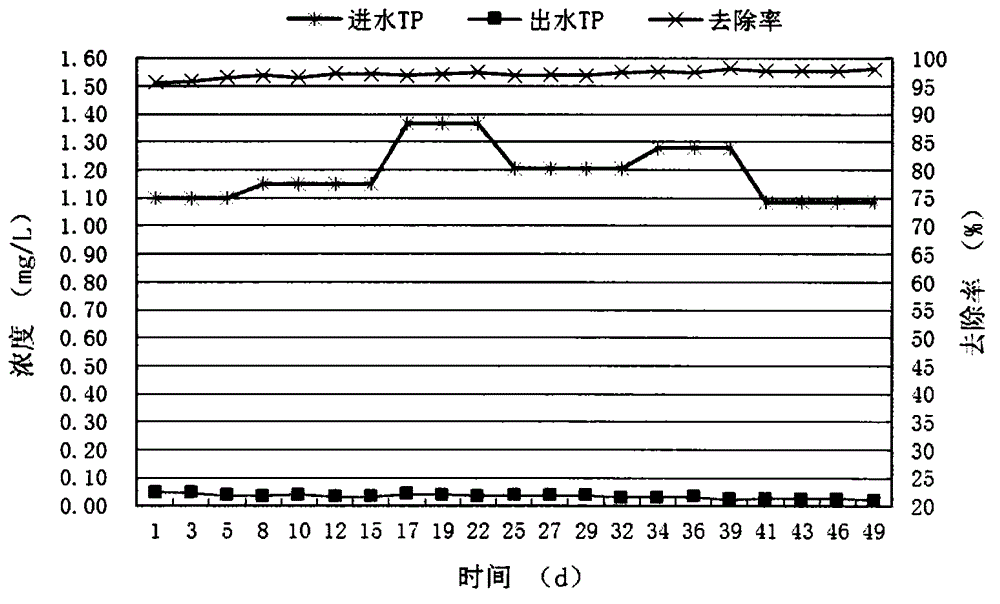
[0060] The operation effect is as follows image 3 Shown: The reactor can run continuously and stably for a long time, and the average removal rate of TP is 97.16% within 50 days of continuous monitoring. The average influent TP of the reactor is 1.19mg / L, the average effluent TP is 0.034mg / L, and the pH of the effluent is always within the range of 8.5 to 7.5, stably reaching the standard limit of surface water category III (lakes and reservoirs TP≤0.05mg / L) value...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com