Method for producing glucaric acid by constructing recombinant yeast fermentation
A technology of glucaric acid and yeast, which is applied in the field of metabolic engineering, can solve the problems of inability to produce glucaric acid, etc., and achieve the effect of cheap medium, stable genetics and high expression level
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Example 1 Construction of recombinant Pichia pastoris GS115 / Udh
[0045] Using the genome of Pseudomonas putida KT2440 as a template, udh-F (sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.7), udh-R (sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.8) as primers to amplify the Udh gene , while using the pGAPZB plasmid as a template, G-F (sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.9), G-R (sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.10) as primers to amplify the GAP promoter. Using the fusion PCR method, the GAP promoter was fused with the Udh gene, and the restriction sites SacI and NotI were respectively introduced into the upstream and downstream of the fusion fragment through primers. The fusion fragment was double digested, connected to the expression vector pPIC9K with corresponding cuts, transformed into E.coliJM109, and the recombinant expression plasmid pPIC9K-GAP-Udh was identified under the premise of ensuring the correct reading frame, and compared by DNA sequencing , the recombinant sequence is correct. The recombinant plasmid...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Example 2 Construction of recombinant bacteria Pichia pastoris GS115 / Udh-MTI
[0047] Using the Pichia pastoris GS115 genome as a template, use primers M-F (sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.11), M-R (sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.12) to amplify the MIOX gene, and primers I-F (sequence shown in SEQ ID NO. 13), I-R (sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.14) amplifies the Ino1 gene. At the same time, using the pGAPZB plasmid as a template, primers T-F (sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.15) and T-R (sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.16) were used to amplify the Pichia pastoris constitutive promoter TEF. The obtained MIOX, TEF, and Ino1 genes were fused in sequence, and two restriction sites XhoI and XbaI were added to both ends of the fusion fragment by designing primers. After double digestion, it was connected to the expression vector pGAPZB with corresponding cuts, and transformed into E.coli TOP10. Under the premise of ensuring the correct reading frame, the recombinant expression plasmid pGAPZB-M...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Example 3 Fermentative production of glucaric acid by recombinant Pichia pastoris
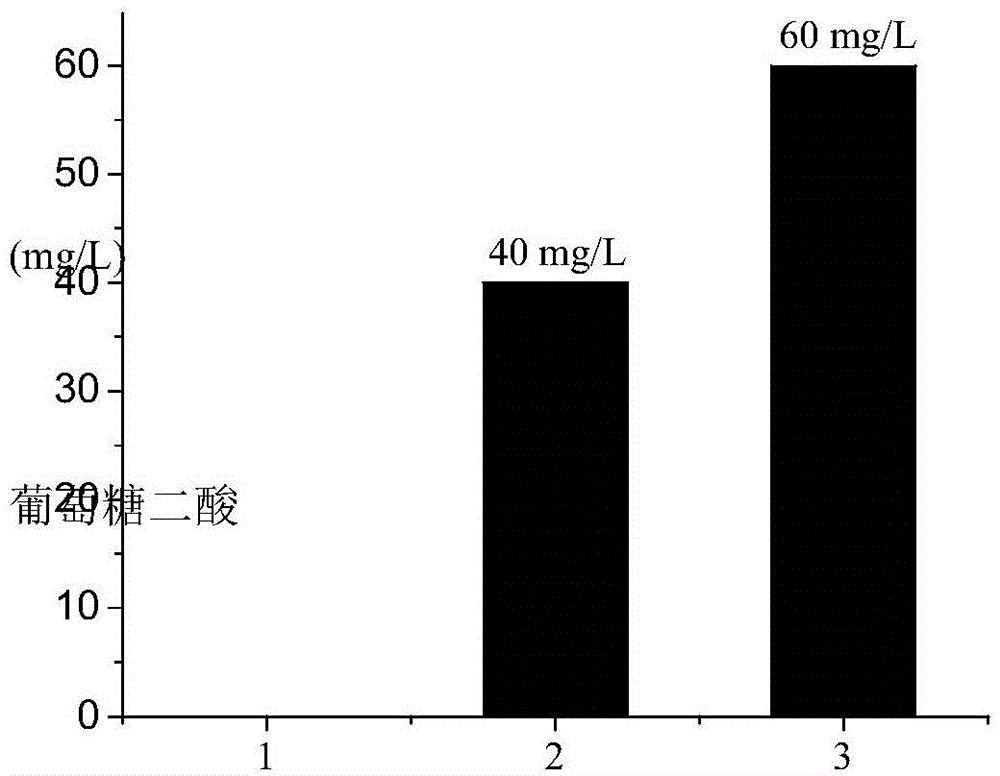
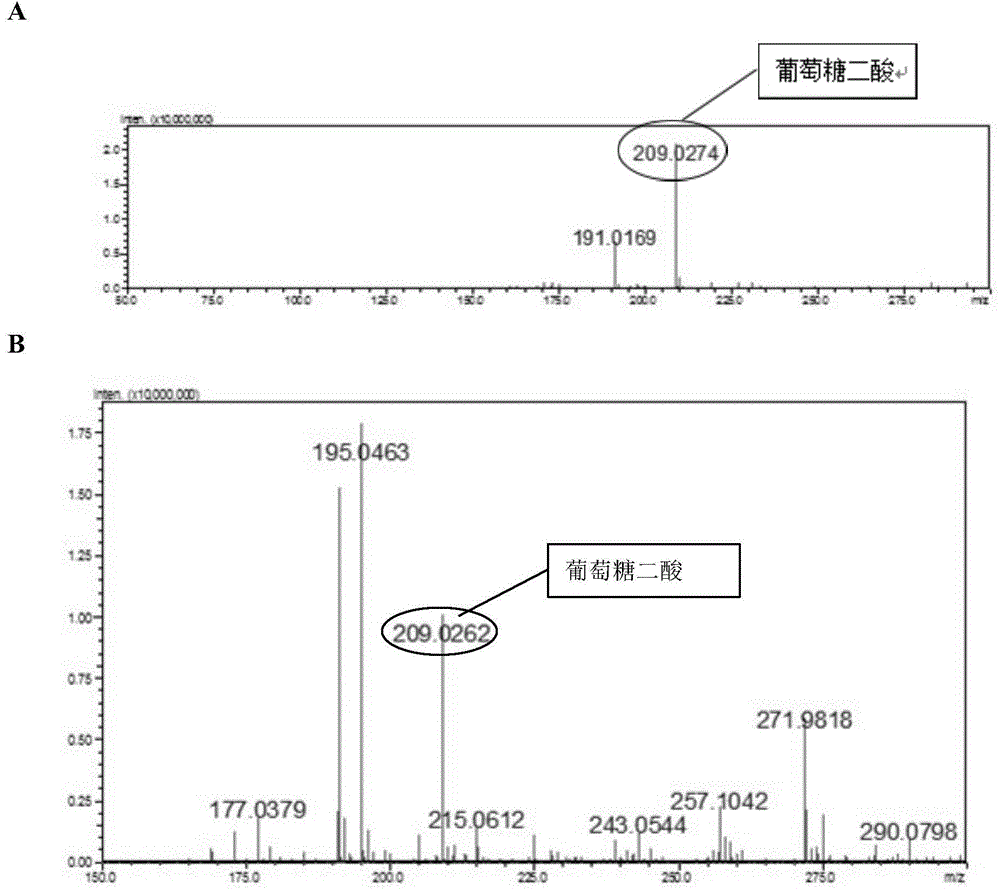
[0053] The recombinant strain Pichia pastoris GS115 / Udh-MTI was fermented. The single clone was inoculated in 25ml of YPD medium (yeast extract 10g / L, peptone 20g / L, glucose 20g / L), and cultured at 30°C and 200rpm for 24h. Inoculate 10% of the inoculum into 50ml (the capacity of the shaker flask is 500ml) fermentation medium for fermentation, and cultivate for 60 hours. The fermentation medium is divided into YPD medium and YPD-MI medium (60 mM inositol is added to YPD medium). After the cultivation, 1ml of the fermentation broth was centrifuged at 8000rpm for 10min, and the supernatant was filtered through a 0.22um filter membrane, and the product was detected by LC-MS. figure 2 It is the result of LC-MS detection of glucaric acid in the fermentation broth, wherein A is the standard sample of glucaric acid, and B is the recombinant Pichia pastoris fermentation broth. It can be seen ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com