Polyamino acidic elastic vascular tissue engineering stent and preparation method thereof
A polyamino acid and vascular tissue technology, which is applied in non-woven fabrics, textiles and papermaking, medical science and other directions, can solve the problems that the mechanical properties of scaffold materials cannot meet clinical needs, the lack of mechanical strength of regenerated blood vessels, and the lack of mechanical properties of vascular tissue, etc. Achieve excellent biomechanical strength, good biocompatibility, and low biodegradability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
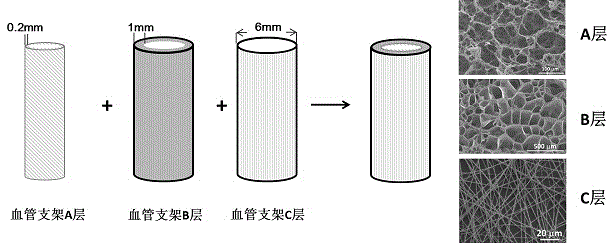
[0033] The purpose of the present invention is to provide a vascular tissue engineering scaffold material and a preparation method thereof, which can simulate normal blood vessels in terms of structure and mechanical properties. Include the following steps:
[0034] A) an inner layer, the inner layer is made of an electrostatic composite scaffold, and the electrostatic composite scaffold is electrostatically blended by polyamino acids and polysaccharides;
[0035] B) Middle layer made of chemically cross-linked gel scaffold based on poly((ε-caprolactone)- b -(ethylene glycol)- b -(ε-caprolactone)) tri-block copolymer is obtained by cross-linking polyamino acid to obtain polyamino acid / poly((ε-caprolactone)- b -(ethylene glycol)- b -(ε-caprolactone)) composite gel, through gradient dialysis and freeze-drying to obtain a porous scaffold;
[0036] C) an outer layer made of an electrospun mesh made of poly(ε-caprolactone)- b - Made of polyamino acid ester block copolymer.
...
Embodiment 1
[0046] The present embodiment provides the construction of vascular stent, comprising the following steps:
[0047] Vascular stent A) Construction of the inner layer: respectively prepare poly(L-glutamic acid) and chitosan aqueous solutions with a molar ratio of carboxyl and amino groups of 1:0.5, adjust the pH value to between the pKa values of the two, and obtain after blending The electrostatic composite floc solution is poured into a pre-prepared mold and freeze-dried to obtain a hollow porous inner layer support. The scaffold material exhibited a sponge-like morphology. The pore size distribution is 100-150 mm; the porosity is above 85%.
[0048] Vascular stent B) construction of the middle layer: prepare an elastic stent with a cross-linking degree of 50% in the middle layer. First, the poly((ε-caprolactone)- b -(ethylene glycol)- b -(ε-caprolactone)) (Mn: 1000-400-1000) triblock copolymer and poly(L-glutamic acid) (Mn: 100000) DMSO / DMF solution, followed by additi...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Vascular stent A) Construction of the inner layer: respectively prepare poly(L-glutamic acid) and chitosan aqueous solutions with a molar ratio of carboxyl and amino groups of 1:1, adjust the pH value to between the pKa values of the two, and obtain after blending The electrostatic composite floc solution is poured into a pre-prepared mold and freeze-dried to obtain a hollow porous inner layer support. The scaffold material exhibited a sponge-like morphology. The pore size distribution is 100-150 mm; the porosity is above 85%.
[0052] Vascular stent B) construction of the middle layer: prepare an elastic stent with a cross-linking degree of 50% in the middle layer. First, the poly((ε-caprolactone)- b -(ethylene glycol)- b -(ε-caprolactone)) (Mn: 1000-400-1000) triblock copolymer and poly(L-glutamic acid) (Mn: 100000) DMSO / DMF solution, followed by addition of catalyst, its EDC HCl: The molar ratio of DMAP is 1:0.1, stir to make it evenly dispersed, and pour the s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com