Patents
Literature
52 results about "Vascular tissue engineering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Vascular substrate without cell in vascular tissue and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a blood vessel matrix for removing cell components in vascular tissue and a preparing method thereof. The invention provides a method which can remove the cell components in the vascular tissue and protect the structural integrity of the cell matrix at utmost. The method comprises the steps of cell extraction, detergent removing and enzyme treatment. The blood vessel cell removing matrix prepared by the invention has the advantages of excellent mechanical strength, proper porosity and low cytotoxicity and can successfully implant cells into the cell matrix, thereby providing a favorable tissue stent for the blood vessel tissue engineering.
Owner:XUANWU HOSPITAL OF CAPITAL UNIV OF MEDICAL SCI
Bioreactor for vascellum tissue engineering
InactiveCN101294131APromote growthRealize internal rotation inoculationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHuman bodyHemodynamics
The invention discloses a bioreactor in vascular tissue engineering, which comprises a hemodynamics simulating device, a 3D bracket and culture chambers. The hemodynamics simulating device is a pulsating flow control device; the culture chambers are serially connected with each other in the pulsating flow control device and include hermetically matched rotary devices and a sealed cavity; the rotary device includes a rotary rod having the 3D bracket fixed thereon and a drive device for rotating the rotary rod; and the rotary rod is located in the sealed cavity. The bioreactor can provide a pulsating flow simulating environment of human body facilitating growth, proliferation and differentiation of cells by adopting the pulsating flow control device for providing the dynamic effect simulating human heart. In the culture chambers, cells are inoculated in the internally-rotating 3D bracket, and secondary cell inoculation can be further executed to achieve convenient taking and dropping of cells, so that the cells can uniformly adhered on the 3D bracket, thus obviating the contamination of the reactor connected with the 3D bracket, on which the cells are inoculated through rotation.
Owner:NAT INST FOR THE CONTROL OF PHARMA & BIOLOGICAL PROD
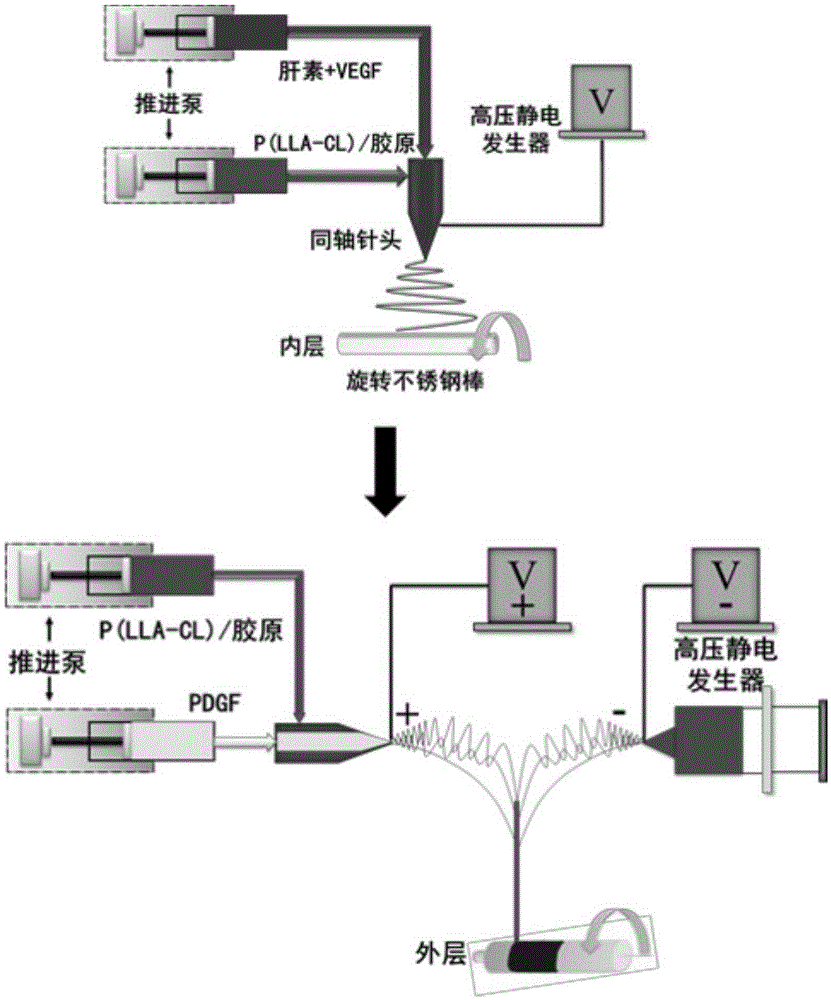
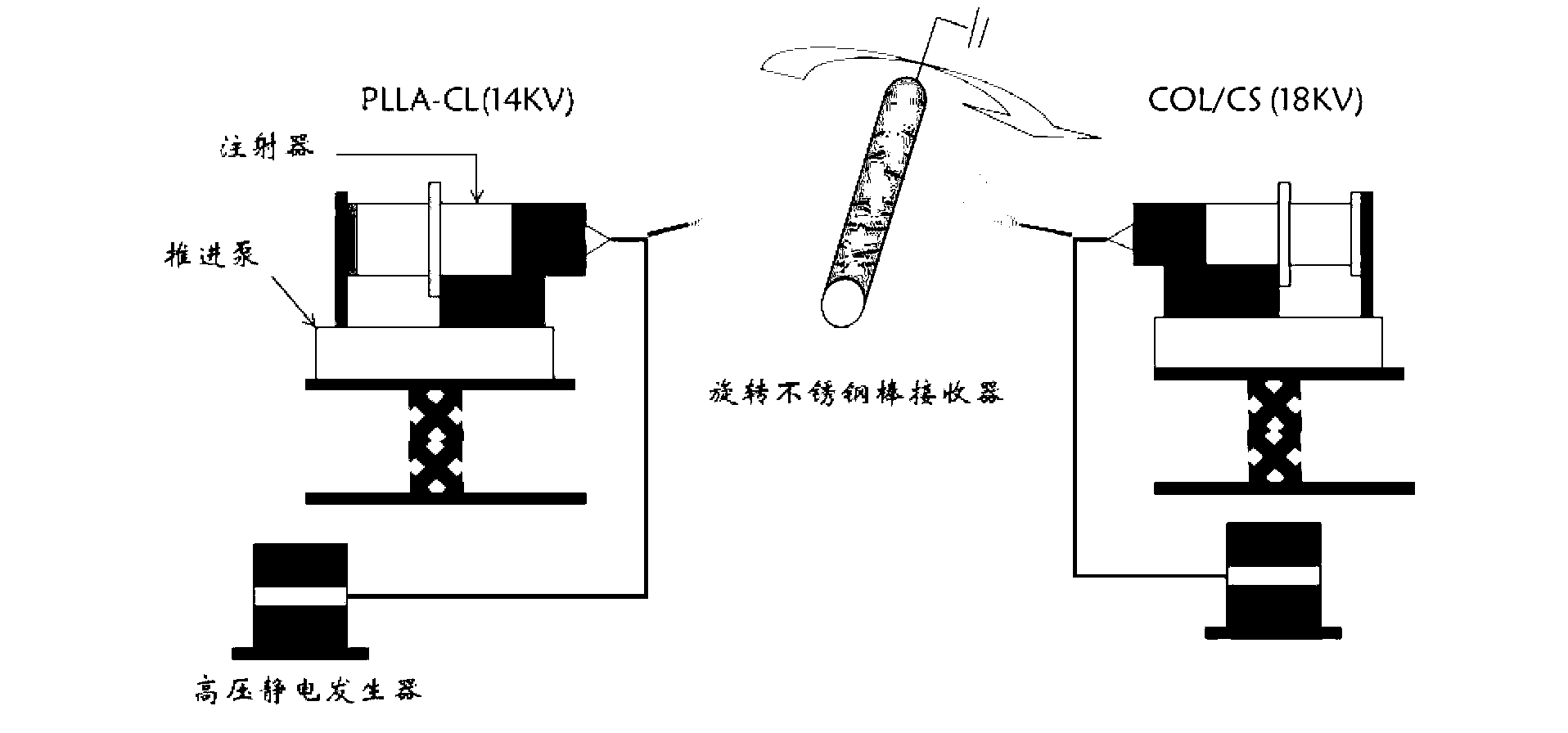
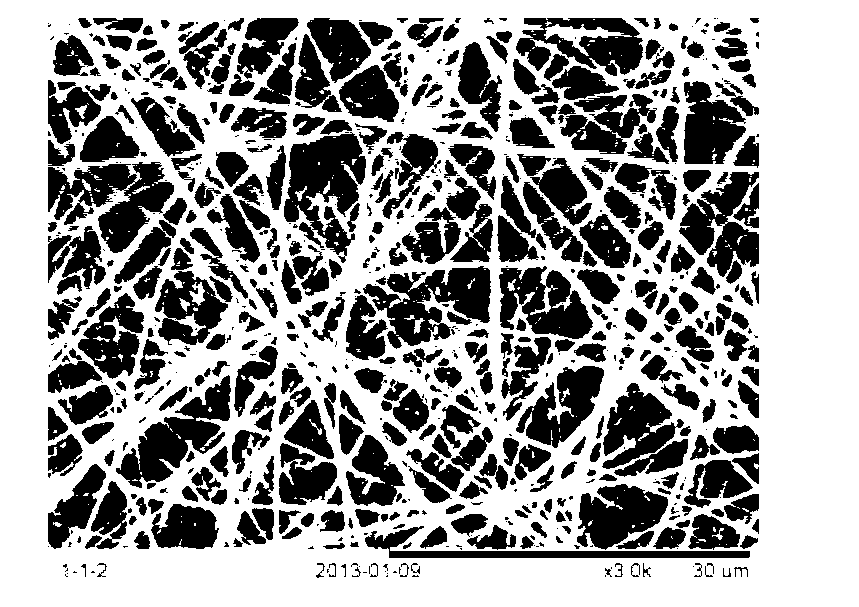
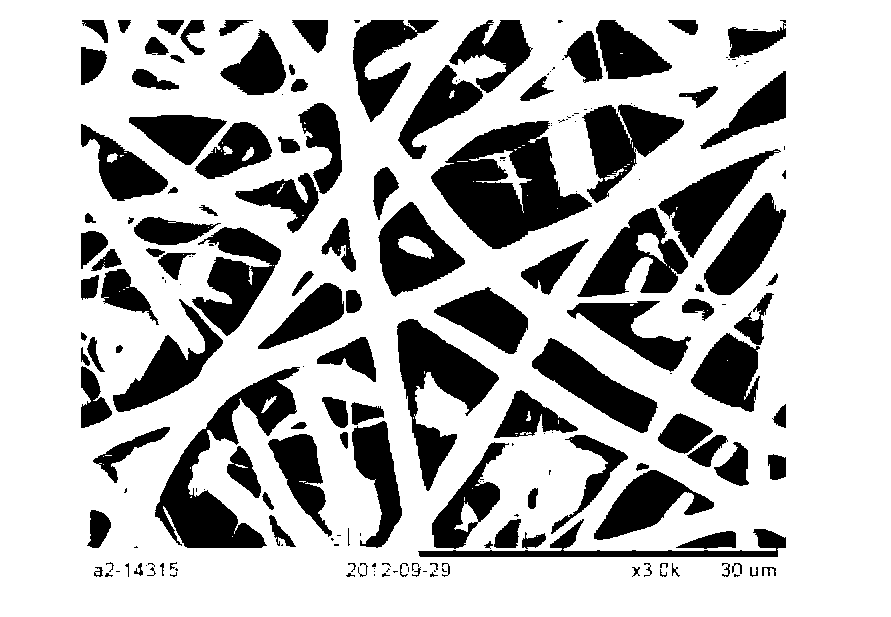
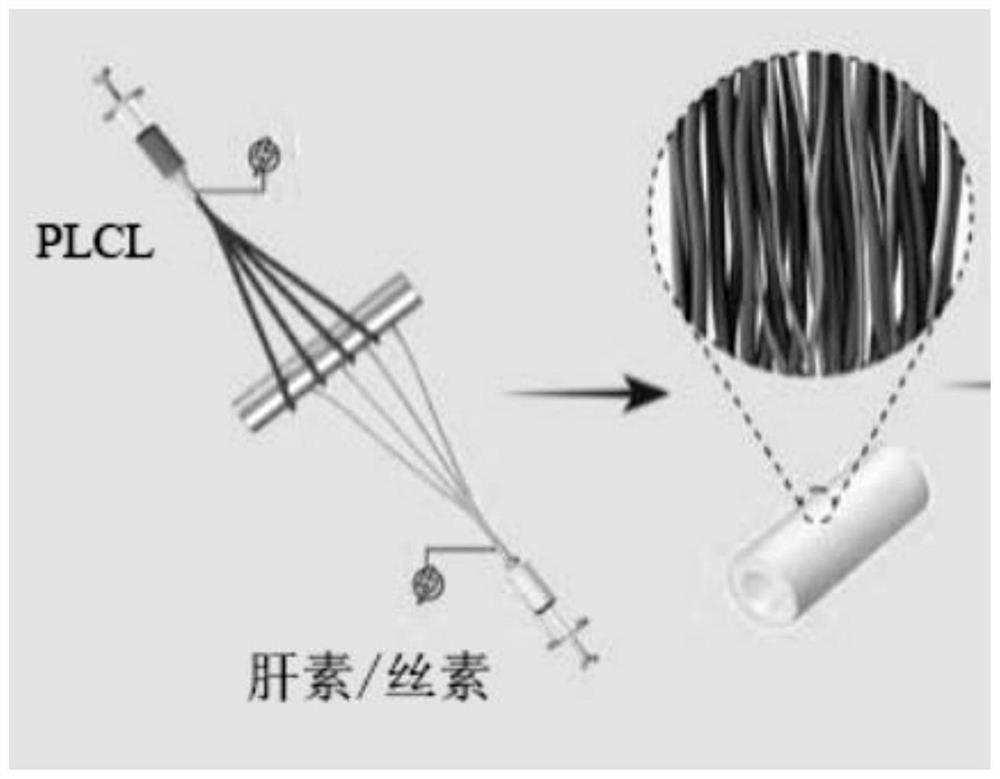
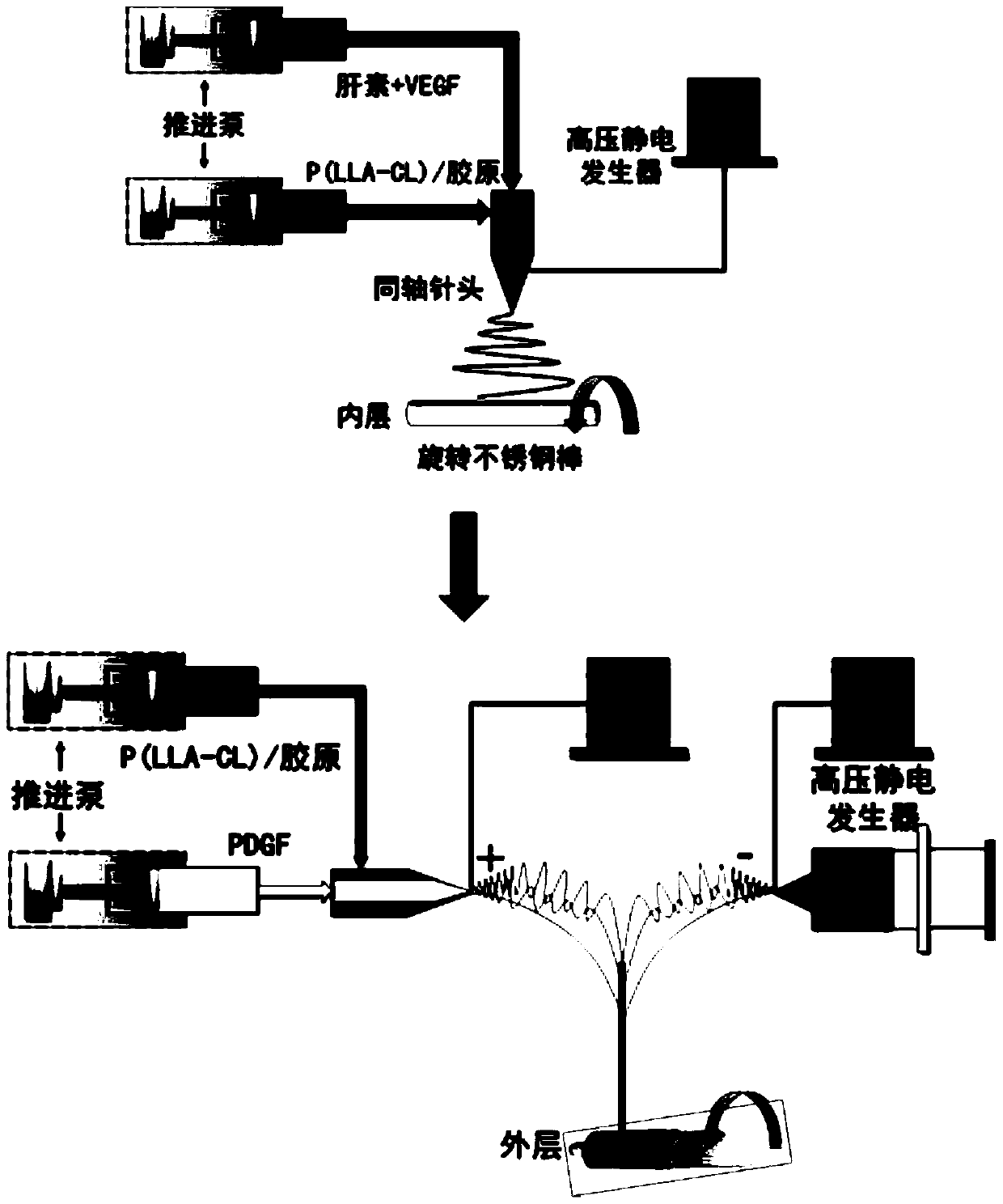
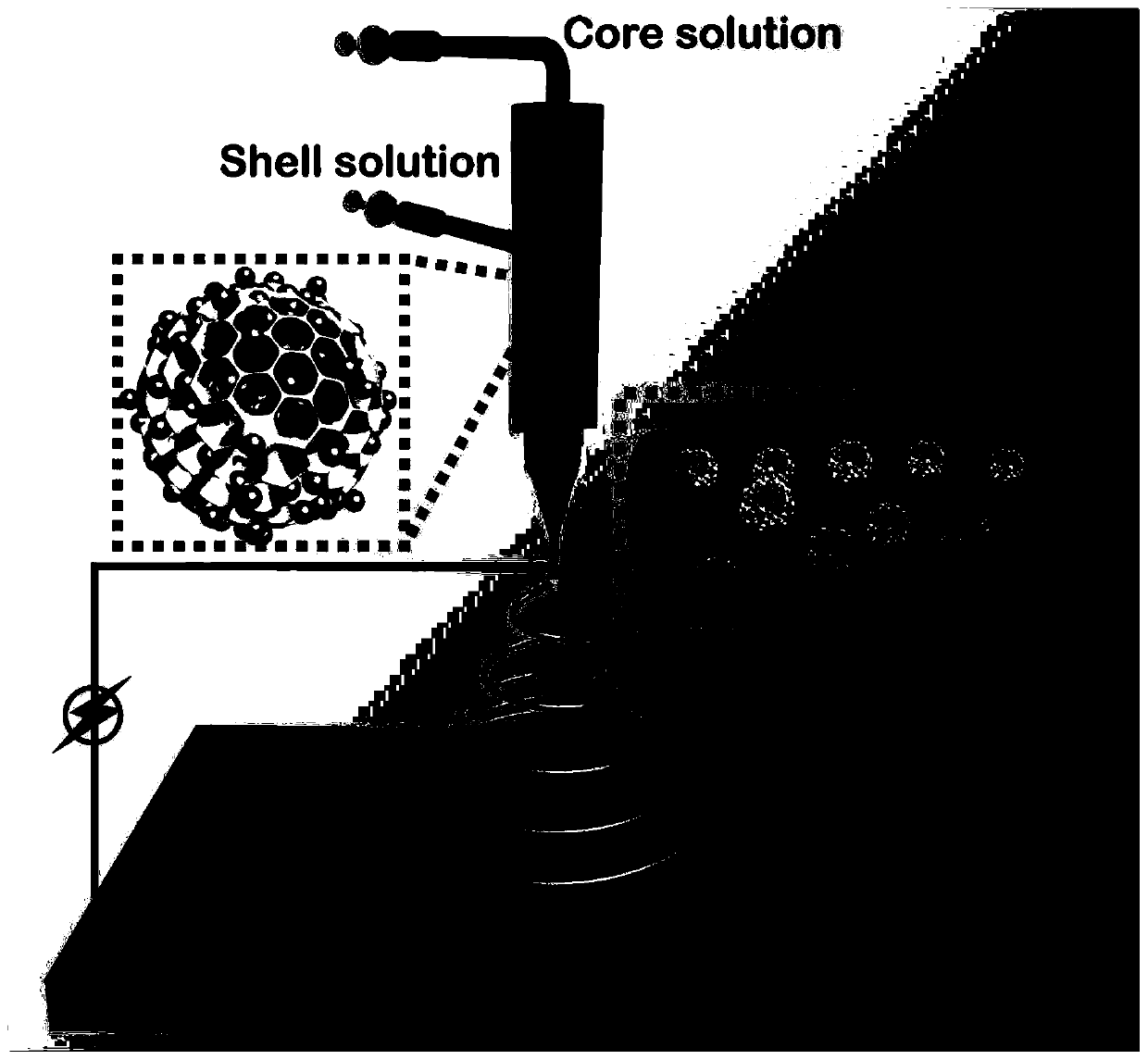
Preparation method of heparin and twin factor synergistically regulated P(LLA-CL)/collagen bilayer intravascular stent
ActiveCN105233339ARapid endothelializationPromote growthStentsPharmaceutical containersCross-linkBlood Vessel Tissue
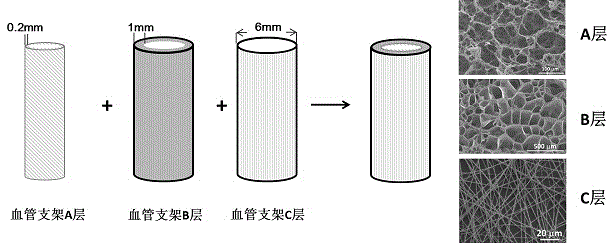
The invention relates to a preparation method of a heparin and twin factor synergistically regulated P(LLA-CL) / collagen bilayer intravascular stent. The method comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing P(LLA-CL) with collagen in a solvent to obtain a composite spinning solution; dissolving heparin sodium and VEGF in a dilution solution to obtain an internal layer supported medicine solution; dissolving PDGF in the dilution solution to obtain an external layer supported medicine solution; carrying out coaxial electrostatic spinning with the internal layer supported medicine solution as a core layer and the spinning solution as a shell layer to obtain a intravascular stent internal layer; and carrying out bidirectional conjugate electrostatic spinning with the external layer loaded medicine solution as a core layer and the spinning solution as a shell layer to obtain an intravascular stent external layer, continuously receiving the intravascular stent external layer at the outer side of the intravascular stent internal layer to obtain a bilayer intravascular stent, and cross-linking to obtain the heparin and twin factor synergistically regulated P(LLA-CL) / collagen bilayer intravascular stent. The intravascular stent provided by the invention has excellent mechanical performances and biocompatibility, has natural blood vessel simulating components, structure and functions, is in favor of realizing in situ regeneration of blood vessel tissues and reconstruction of a multilayer structure, and has important applications in the blood vessel tissue engineering.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
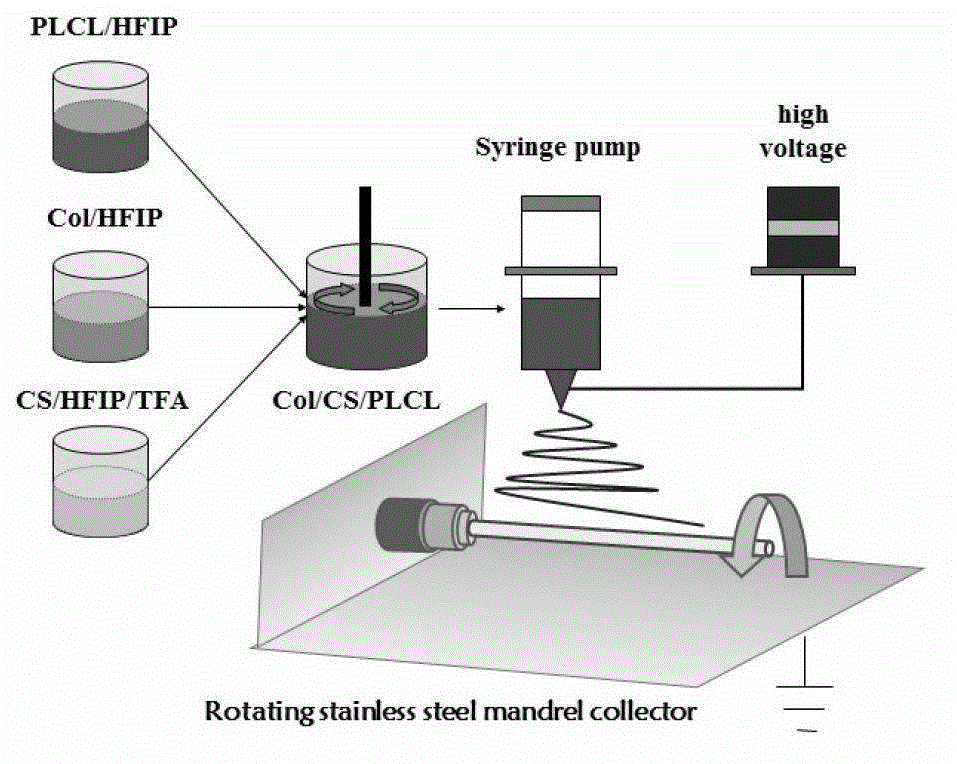
Preparation method for protein-polyose-polylactic acid polycaprolactone vascular stent
InactiveCN103147225AGood balance mechanicsWell balanced biocompatibilityNon-woven fabricsProsthesisBiocompatibility TestingVascular tissue engineering
The invention relates to a preparation method for a protein-polyose-polylactic acid polycaprolactone vascular stent. The method comprises the following steps: (1) completely dissolving chitosan into a hexafluoroisopropanol and trifluoroacetic acid mixed solution to obtain a chitosan solution; (2) completely dissolving collagen into hexafluoroisopropanol to obtain a collagen solution; (3) completely dissolving polylactic acid polycaprolactone into hexafluoroisopropanol to obtain a polylactic acid polycaprolactone solution; and (4) mixing and stirring the chitosan solution, the collagen solution and the polylactic acid polycaprolactone solution to obtain a protein-polyose-polylactic acid polycaprolactone spinning solution, and then achieving static spinning to obtain the protein-polyose-polylactic acid polycaprolactone vascular stent. The prepparation materials have superior biocompatibility and mechanical property; and the designed multi-component composite biological material has a broad application prospect, and the preparation method is simple and feasible and is mainly used in small-caliber vascular tissue engineering.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Preparation method of microfluidic three-dimensional gel chip model
InactiveCN105381826AFast preparationCheap manufacturingLaboratory glasswaresEngineeringVascular tissue engineering
The invention discloses a preparation method of a microfluidic three-dimensional gel chip model and belongs to the field of biological micro-processing. A preparation process comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a micro-fiber columnar mold; (2) embedding the prepared mold into a three-dimensional biological gel; (3) dissolving the mold and constructing a micro-channel in the three-dimensional biological gel so as to form the microfluidic three-dimensional gel chip model. A method for constructing a microfluidic chip in the three-dimensional biological gel is realized and the method has a simple preparation process; the size and space structure of the formed micro-channel can be adjusted according to actual requirements. The microfluidic three-dimensional gel chip model can be used for research in the fields of tissue microenvironments, vascular tissue engineering, 3D drug delivery and screening and the like.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Vascular tissue engineering reactor having vas stretch and pulsating flow pouring functions
ActiveCN101372663AWith rotation functionEnhanced mass transferBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsVascular tissueBlood Vessel Tissue
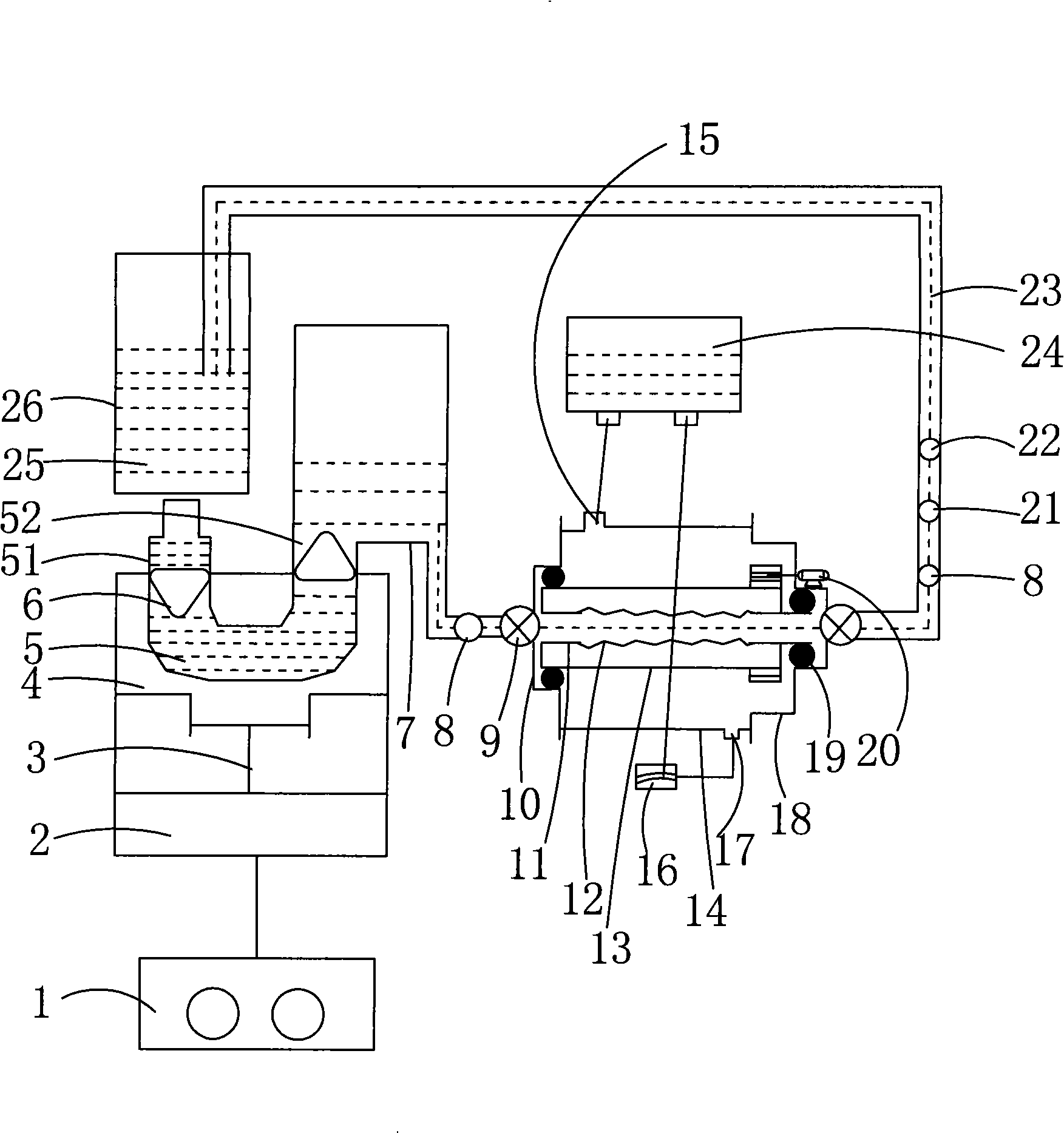
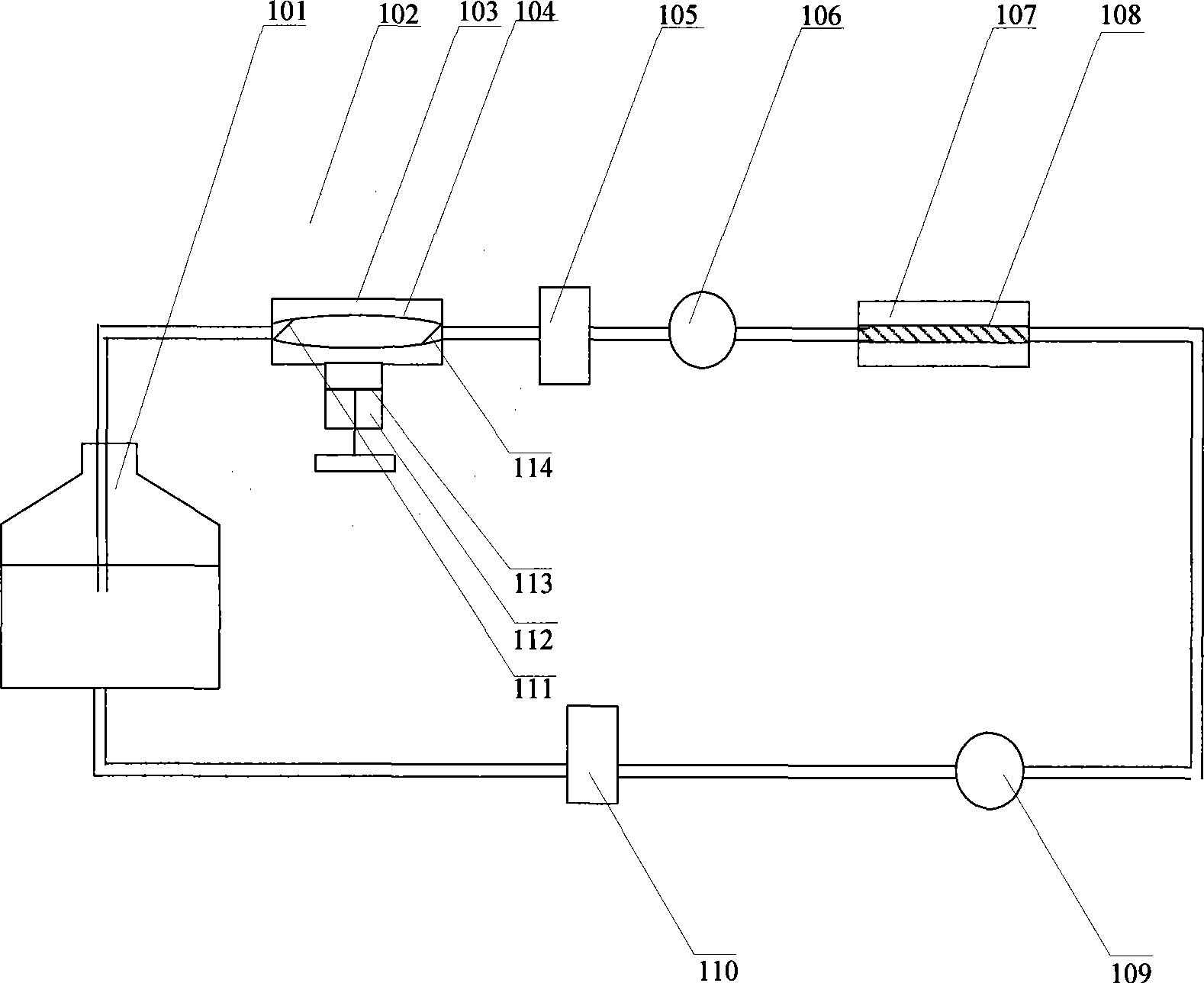
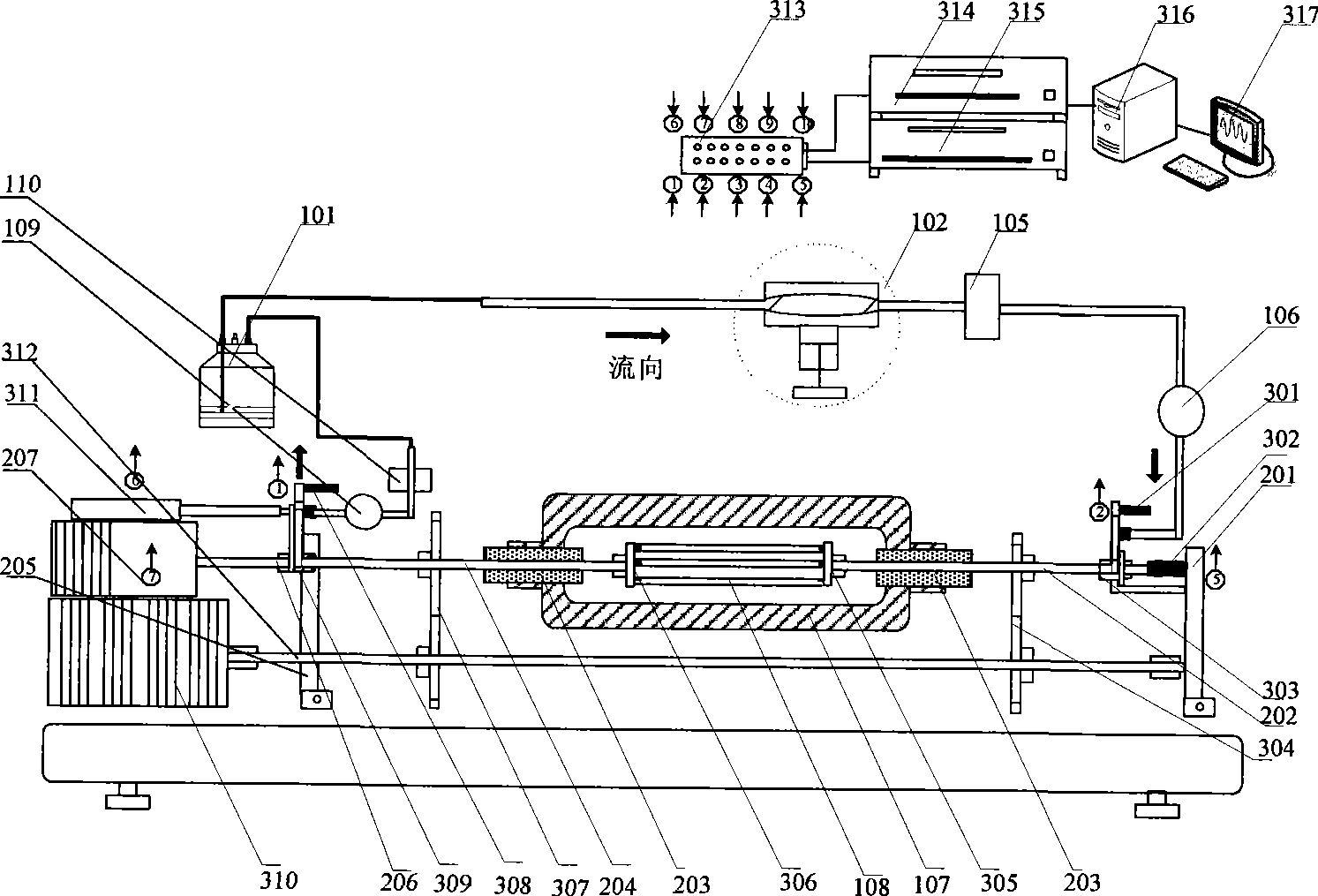
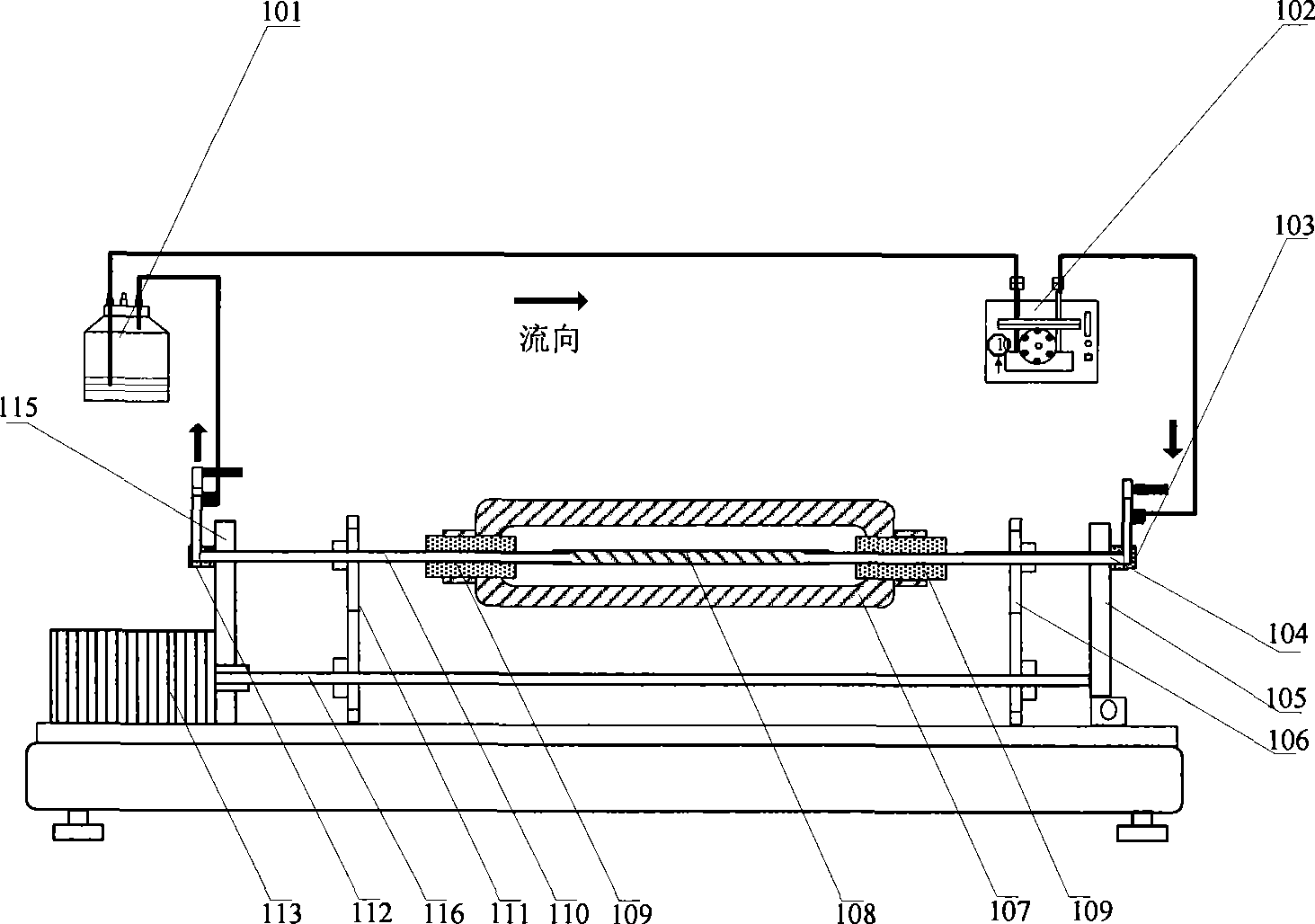
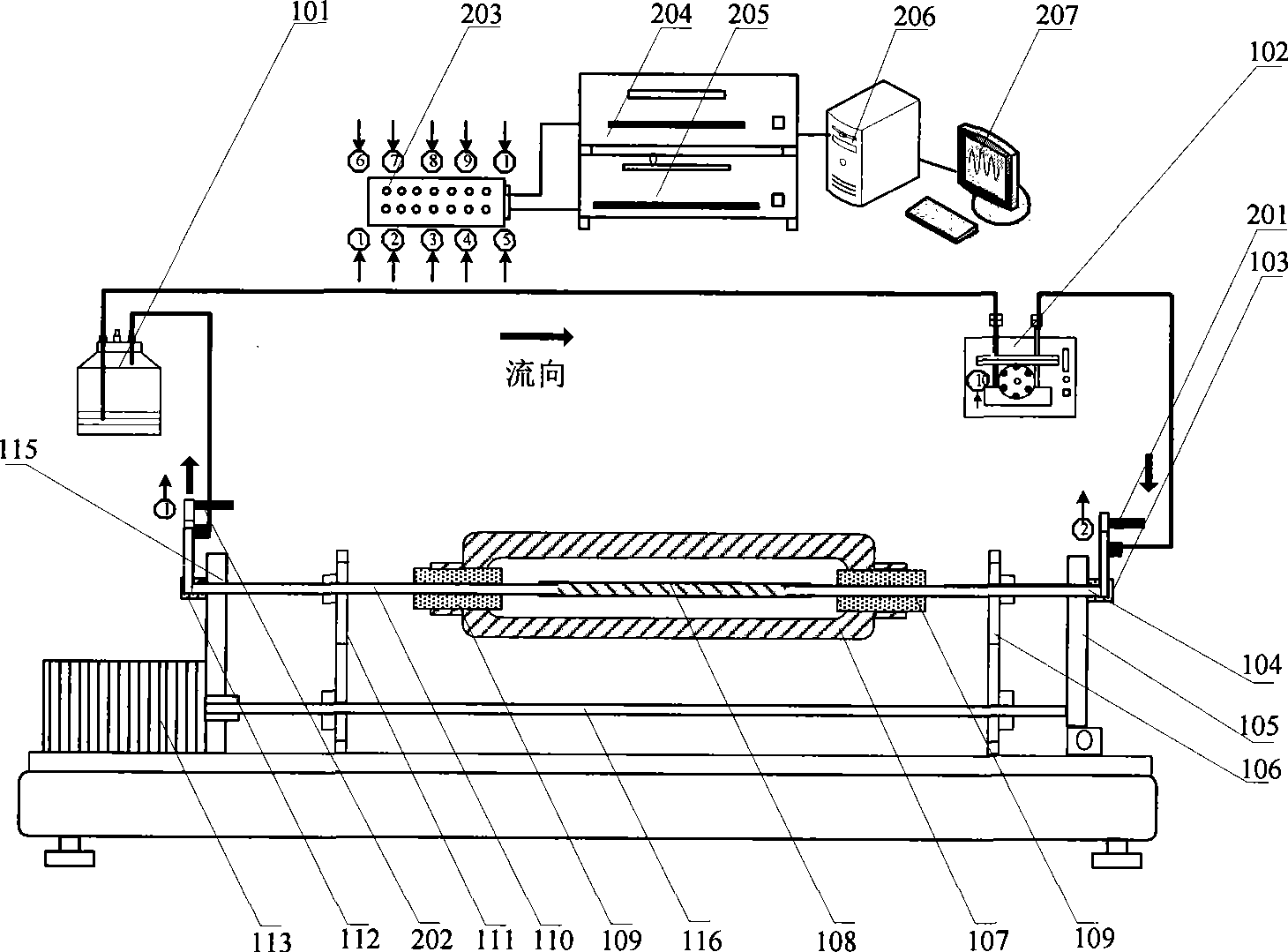
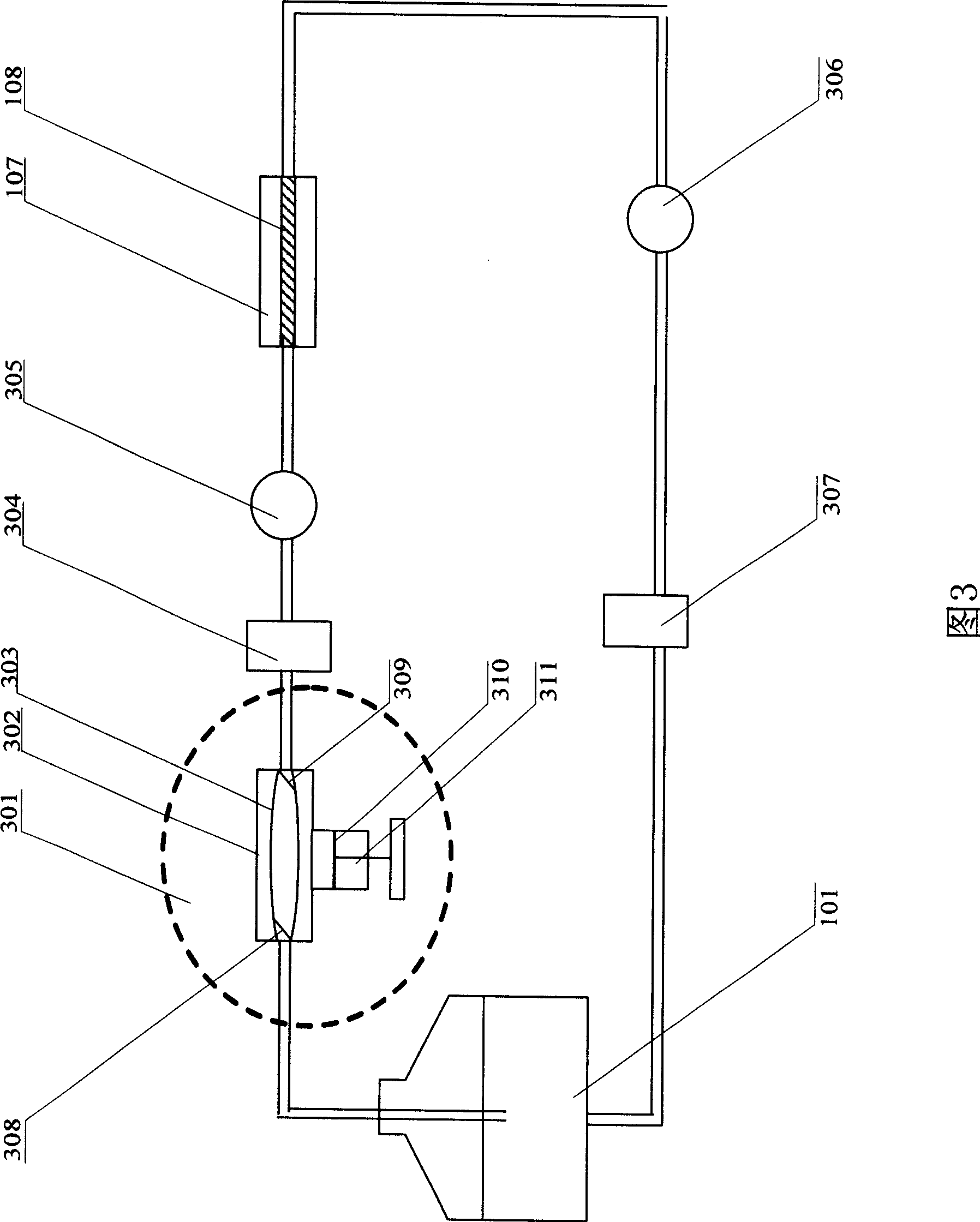
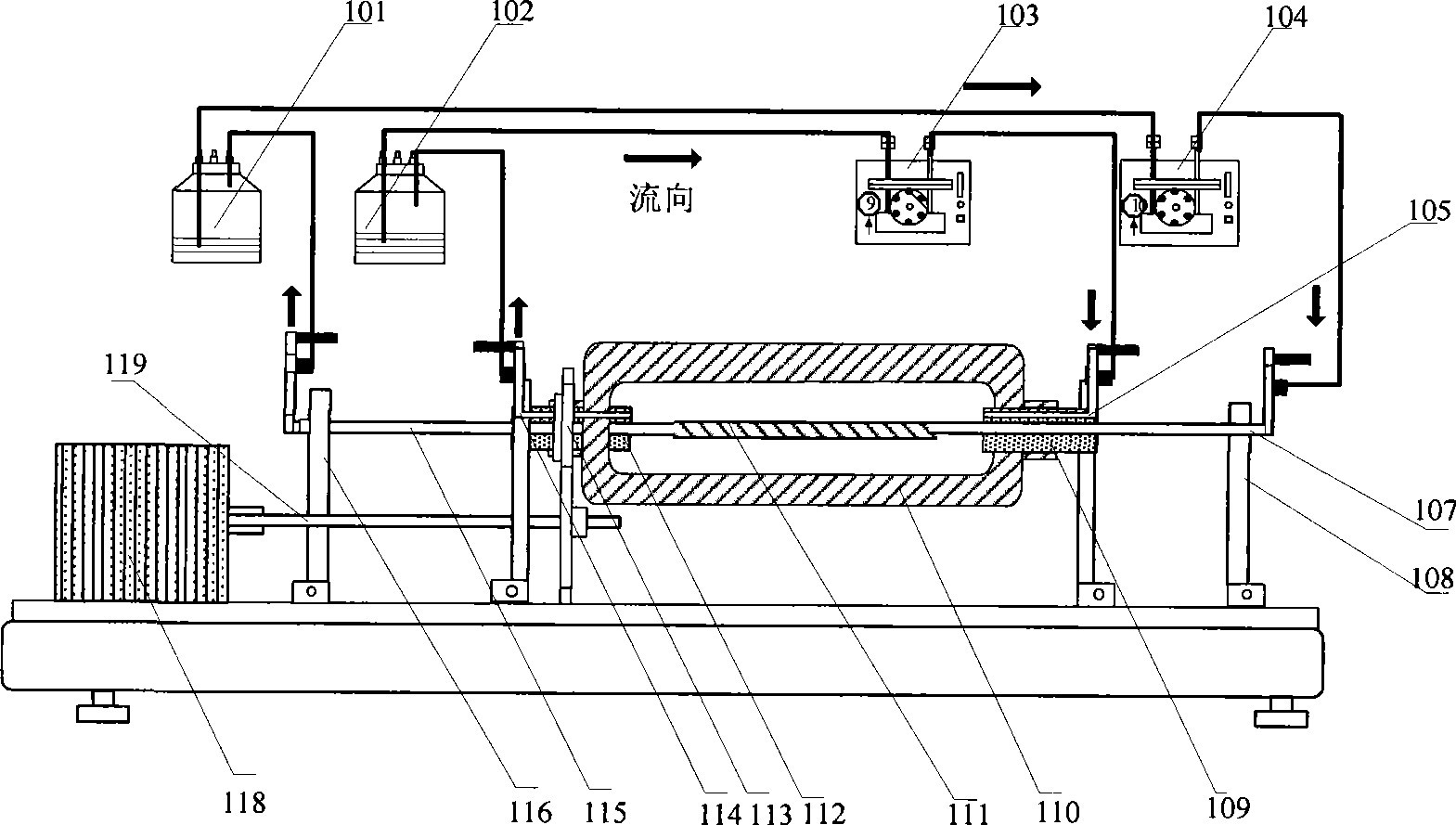
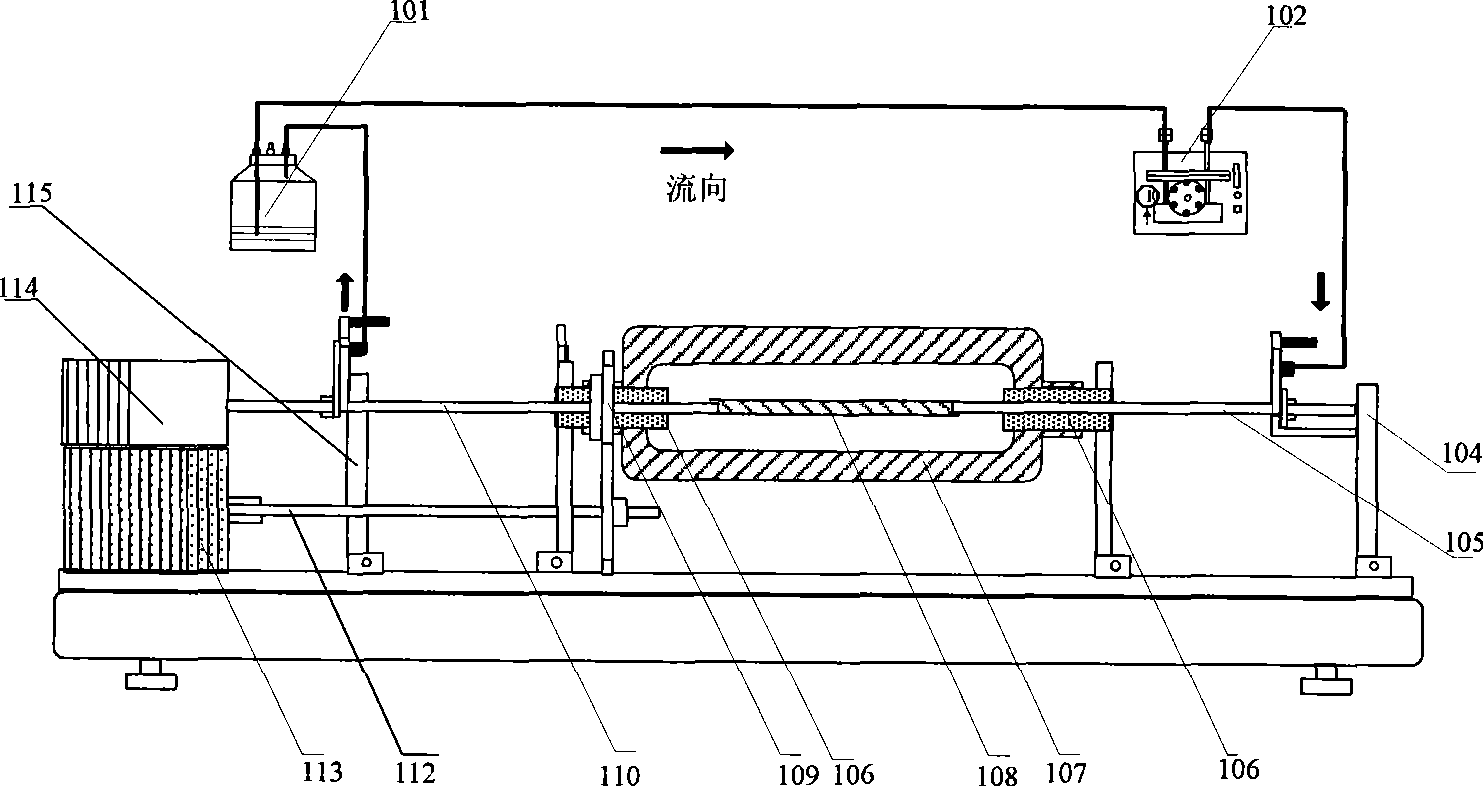
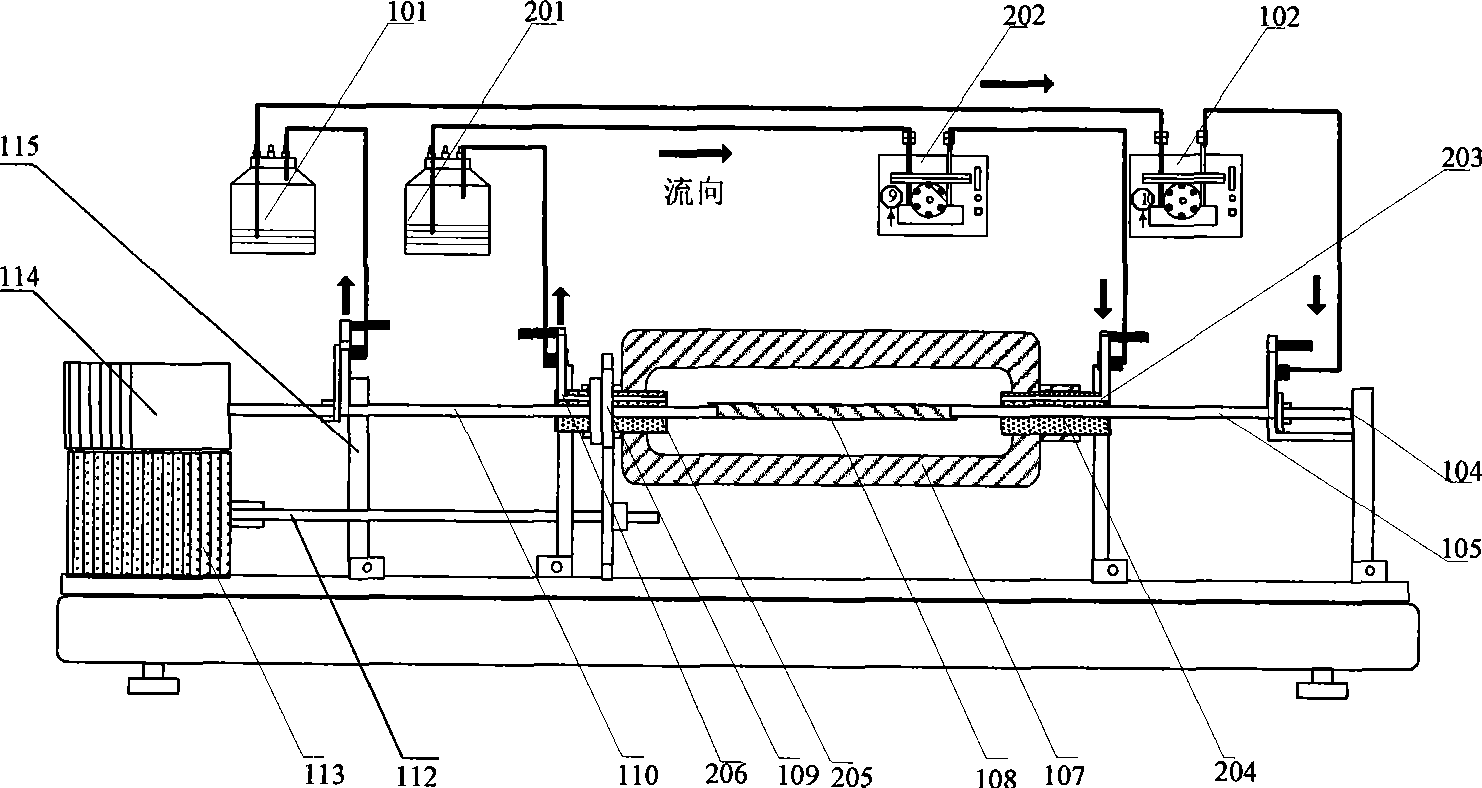
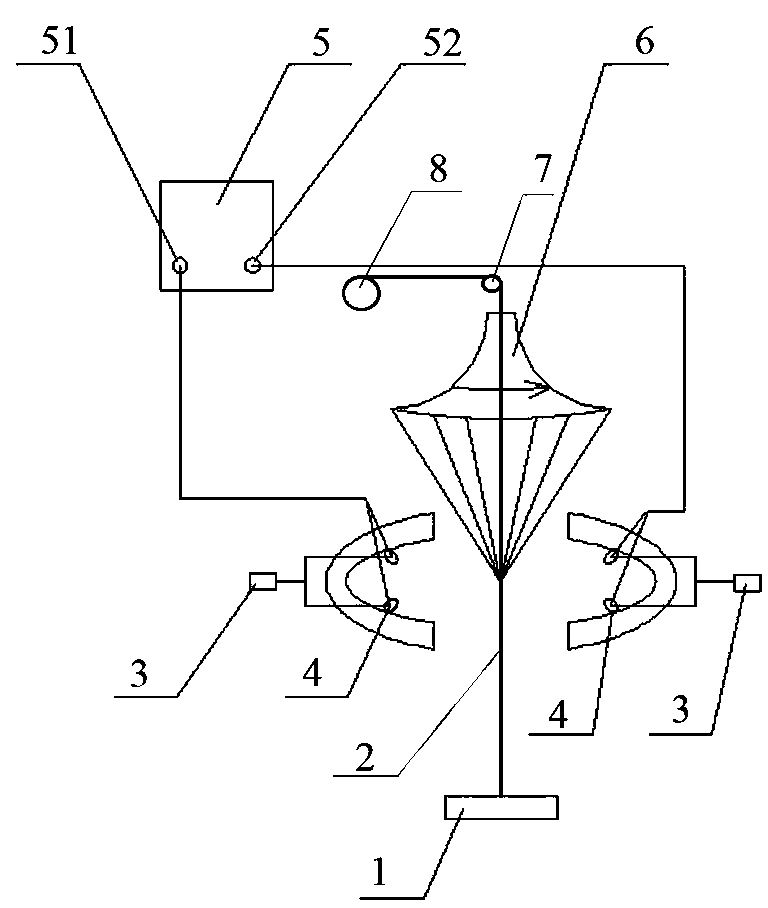
The invention relates to a vascular tissue engineering reactor which is characterized by comprising intravascular perfusion liquid storage bottles (101) which are connected with each other in sequence by pipelines, a pulsation source (102) which is taken as an intravascular perfusion liquid driving device, a culture cavity inlet pipeline (202) of an intravascular perfusion circuit, and a vascular tissue culture cavity (107), wherein, one end of an inlet pipeline (104) of the culture cavity enters the vascular tissue culture cavity (107), and is connected with one end of a vascular tissue (108) to be cultured so as to cause the culture solution from the perfusion liquid storage bottle (101) to flow into the vascular tissue (108). The reactor further comprises a culture cavity outlet pipeline (204) of the intravascular perfusion circuit, one end of the culture cavity outlet pipeline (204) enters the vascular tissue culture cavity (107), and is connected with the other end of the vascular tissue (108) to be cultured so as to export the culture solution from the inner part of the vascular tissue (108).
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +1
Pourable vascular tissue engineering reactor having rotating function
ActiveCN101372660ARealize the pulsation functionRealize axial push-pull functionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPerfusion CultureRotation function
The invention discloses a vascular tissue engineering reactor with rotation function. The reactor overcomes the disadvantages that the common arterial tissue engineering reactors can not simultaneously supply the vascular tissue with the culture conditions of intravascular perfusion and vascular rotation, and the mass transfer performance is poor. The vascular tissue engineering reactor comprises a liquid storage bottle, a liquid driving device, a vascular tissue culture cavity, a linear motor, a step motor, a vascular tissue transmission device, and the like, realizes the vascular tissue rotation in the course of intravascular perfusion culture, and has good mass transfer performance.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +1
Preparation method of caprolactone lactate copolymer/collagen/chitosan small-caliber intravascular stent
ActiveCN103266421AFavorable for three-dimensional ingrowthLarge apertureNon-woven fabricsProsthesisBiocompatibility TestingVascular tissue engineering
The invention relates to a preparation method of a caprolactone lactate copolymer / collagen / chitosan small-caliber intravascular stent, and the preparation method comprises the following steps of: dissolving a caprolactone lactate copolymer into a solvent to obtain a caprolactone lactate copolymer spinning solution; dissolving collagen into the solvent to obtain a collagen spinning solution; dissolving chitosan into the solvent to obtain a chitosan spinning solution; and carrying out bidirectional electrostatic spinning by taking the caprolactone lactate copolymer spinning solution as a component I and a mixed solution of the collagen spinning solution and the chitosan spinning solution which have the volume ratio of 5-10:1 as a component II to obtain the caprolactone lactate copolymer / collagen / chitosan small-caliber intravascular stent. The biomaterial designed into a multicomponent gradient symmetrical structure has the advantages of better mechanical property and excellent biocompatibility and especially has the advantages of potential on accelerating cell three-dimensional ingrowth and important application in small-caliber vascular tissue engineering.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Preparation method of composite nanometer fiber small-diameter intravascular tissue engineering stent material
InactiveCN101653624AGood physical and mechanical propertiesGood chemical stabilityStentsProsthesisFiberCell adhesion
The invention relates to the field of tissue engineering, in particular to a preparation method of a composite nanometer fiber small-diameter intravascular tissue engineering stent material. The technical scheme is achieved as follows: formic acid is used as a common solvent; RGD-recombinant spider silk protein, polycaprolactone and chitosan are mixed in a mass ratio of 1:8:1 according to the requirements of an intravascular stent to prepare a spinning solution with the concentration of 20-30 percent (w / v); electrospinning process parameters are as follows: the diameter of a cross section of acylindrical rotating shaft is 3-6 mm, the rotating speed is 1,500-3,000rpm, the curing distance is 15-30 cm, the voltage is 50-150kV, the extrusion speed is 3-7ml / h and the temperature is 45-50 DEG C. The small-diameter intravascular stent has favorable cell adhesion-promoting capability, anticoagulant property and mechanical property for resisting physiological environment and can be clinicallyapplied as a small-diameter intravascular tissue engineering stent.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
Adjustable pouring type vascular tissue engineering reactor having rotating cultivation cavity
ActiveCN101372661ARealize the pulsation functionGood blood pressureBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsVascular tissueBlood Vessel Tissue
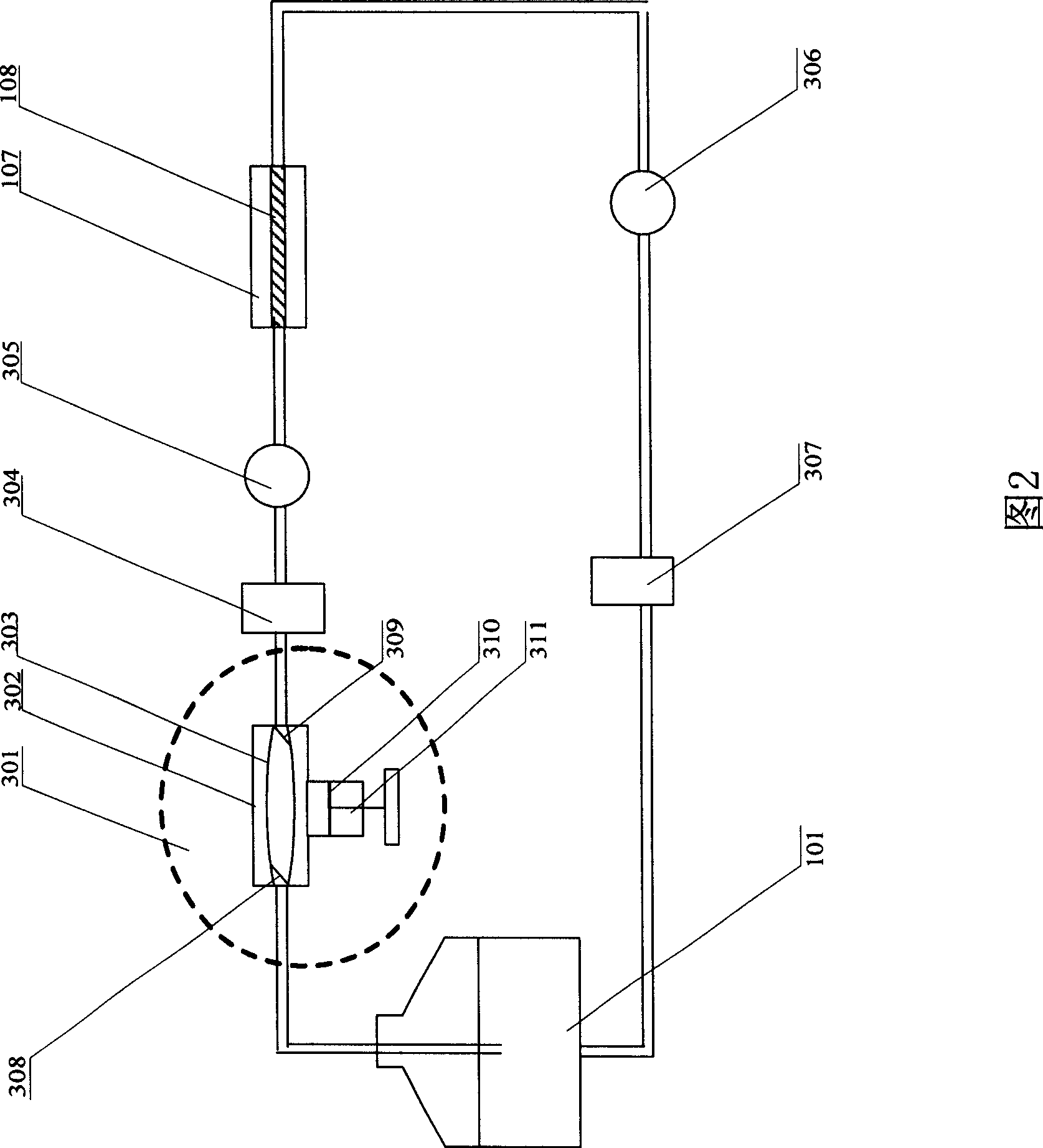
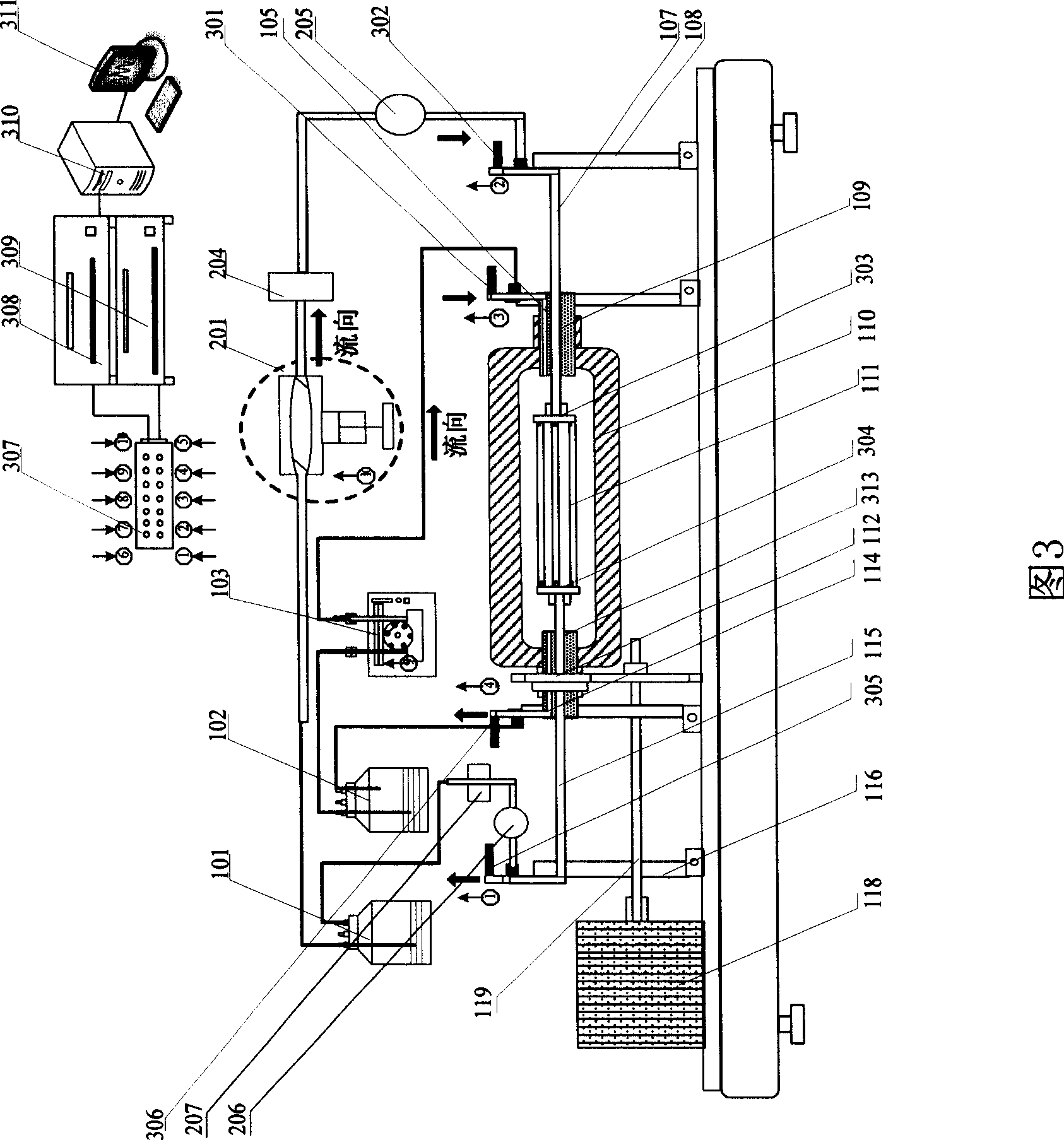
The invention provides a vascular tissue engineering reactor which has the functions of culture cavity rotation, dual perfusion inside and outside vascular tissues and intravascular nutrient solution pulsation. The reactor can simultaneously realize the intravascular perfusion of the culture solution, the extravascular perfusion of the culture solution, the rotation of a culture cavity, the reciprocating tension of blood vessels in culture along the axial direction and any combination thereof. In addition, the reactor can realize multi-blood vessels culture at the same time and handling, recording and / or displaying of the pressure data.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +1
Adjustable pouring type vascular tissue engineering reactor having cultivation cavity rotation and vas stretch functions
ActiveCN101372662ARealize the pulsation functionRealize axial push-pull functionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsVascular tissueBlood Vessel Tissue
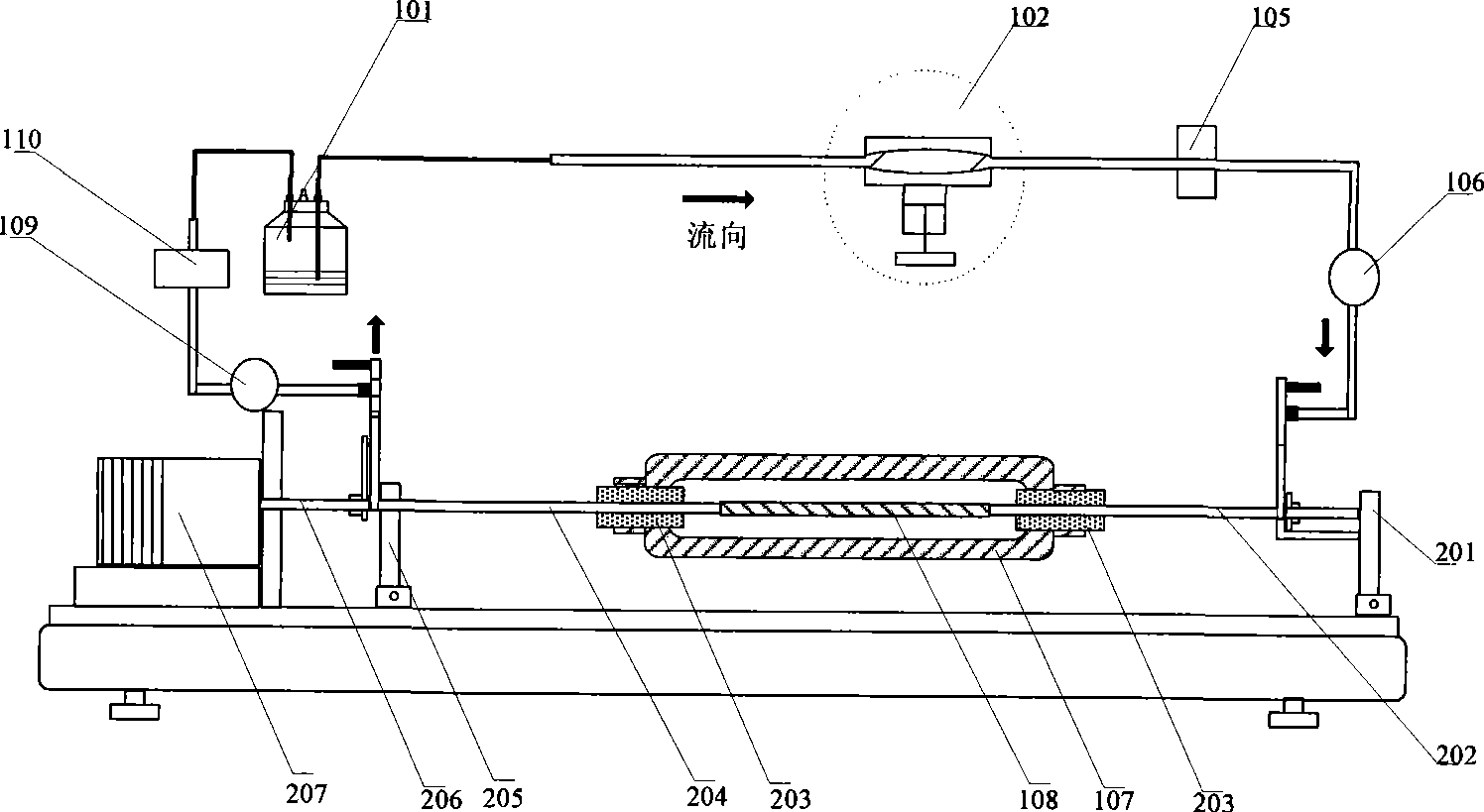
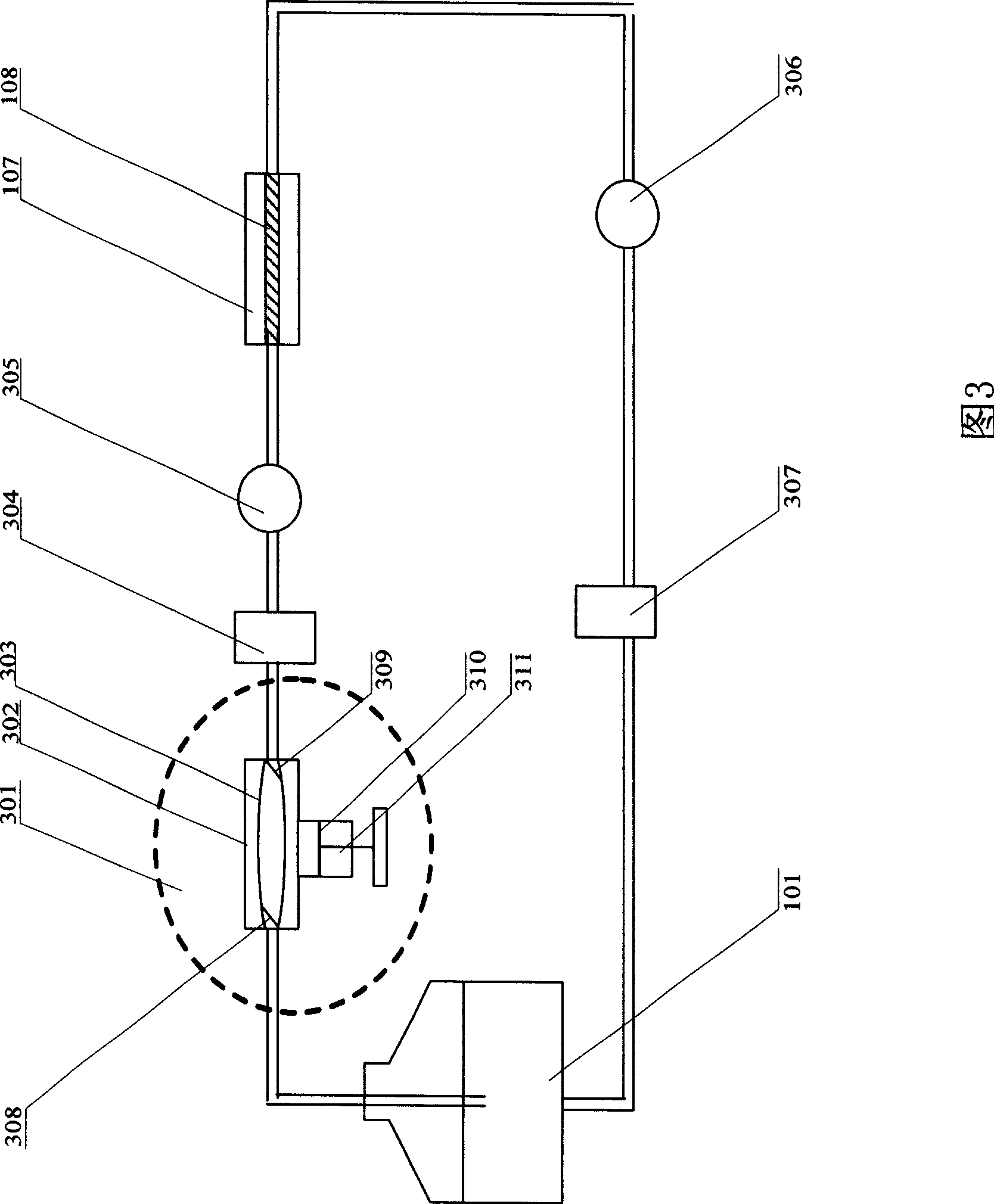
The invention relates to a vascular tissue engineering reactor which comprises intravascular perfusion circuits (101, 102, 105, 110), a vascular tissue culture cavity (107), a culture cavity rotation driving motor (113) with the rotation driving force which is transferred to the culture cavity (107) to cause the culture cavity to rotate, a vascular reciprocating tension driving device (114) with the reciprocating driving force which acts on a vascular tissue (108) arranged between an outlet pipeline (110) and an inlet pipeline (105) of the culture cavity of the intravascular perfusion circuit to cause the vascular tissue (108) to receive the reciprocating tension along the axial direction. The vascular tissue engineering reactor can simultaneously realize intravascular perfusion of the culture solution, extravascular perfusion of the culture solution the rotation of the culture cavity, the reciprocating tension of the blood vessels in culture along the axial direction, the pulsation of nutrient solution in the vascular tissue in culture and any combination thereof.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +1
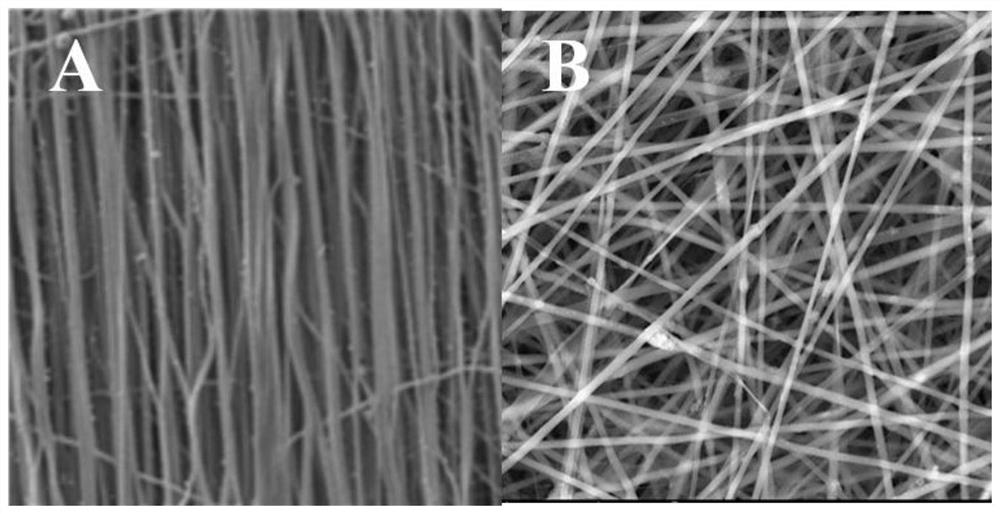
Method for preparing sulfated silk fibroin vascular tissue engineering scaffold by using electrostatic spinning
InactiveCN102652841AGood cell compatibilityLong-term stable anticoagulantSurgeryPharmaceutical containersFiberVascular tissue engineering
The invention relates to a sulfated silk fibroin vascular tissue engineering scaffold prepared by using electrostatic spinning and belongs to the field of biological medical materials. The sulfated silk fibroin vascular tissue engineering scaffold is prepared through the following steps of: dissolving a silk fibroin and sulfated silk fibroin sponge in hexafluoroisopropanol, so as to prepare a 7-10% mixed silk fibroin and sulfated silk fibroin solution; filling the solution in an injector, applying a 10-30kV voltage, and receiving fibers by using a rotary metal rod, wherein the receiving distance is 10-25 cm, the diameter of the selected receiving rod is 3-5 mm, the rotating speed is 200-1000 rpm (revolutions per minute), and the propelling speed of the injector is 0.03-0.05 mm / s, so as to obtain a tubular tissue engineering scaffold with the thickness of 0.1-1 mm and the internal diameter of 3-5 mm; then inducing the silk fibroin to convert to a beta laminated structure by using a 90-100% methanol solution to soak the scaffold, so that the tissue engineering scaffold can be prevented from being dissolved in water by virtue of improving mechanical properties. The vascular tissue engineering scaffold prepared by the invention has excellent cell compatibility and long-term and stable anti-blood coagulation property, has controllable caliber, and can be used for maintenance of small-caliber blood vessels and establishment of tissue engineering and hemodialysis access. The preparation method provided by the invention has the advantages of simplicity in operation and low cost, and can be used for realizing commercial production.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
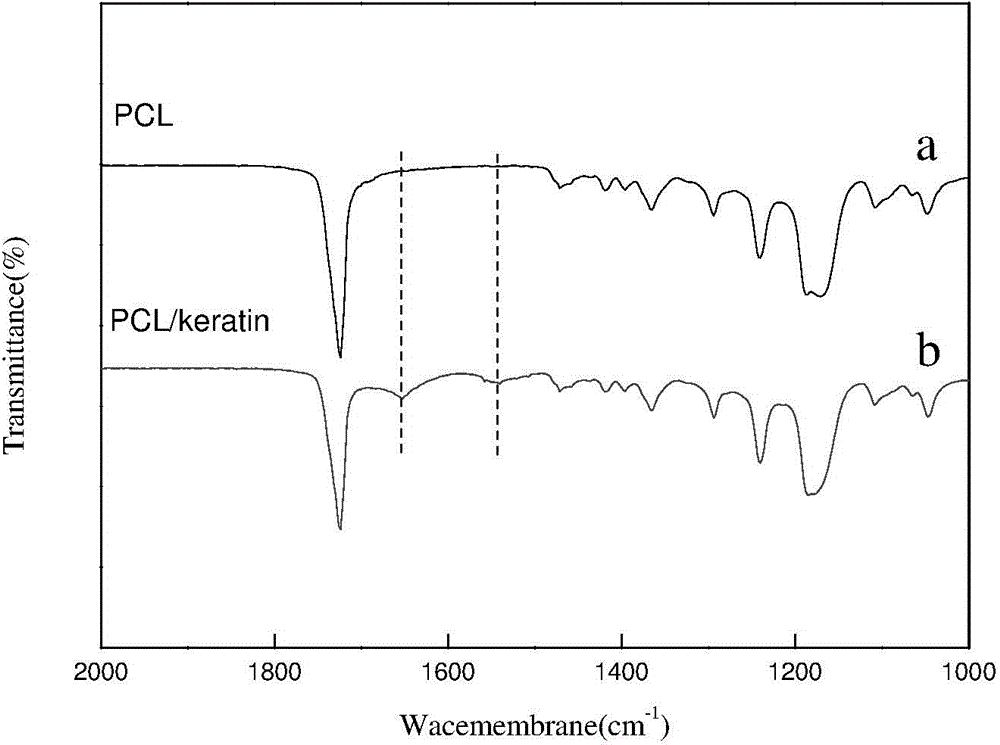
Preparation method of polymer/keratin composite anticoagulation vascular tissue engineering scaffold
ActiveCN104784758AReduce restenosisAvoid stickingPharmaceutical containersMedical packagingFiberSmooth muscle
The invention discloses a method for constructing an anticoagulation vascular tissue engineering scaffold by utilizing keratin. The method for constructing the anticoagulation vascular tissue engineering scaffold by utilizing keratin comprises the following steps: extracting keratin, stabilizing the extracted keratin, and carrying out blended spinning on the extracted keratin and a biodegradable polymer to prepare a composite fiber diaphragm. The prepared composite fiber diaphragm is taken as a vascular tissue engineering scaffold, and NO release is realized by utilizing keratin having a capability of in situ catalyzing or inducing an endogenous NO donor to release No; and further blood compatibility and cytocompatibility of the scaffold are improved, growth of smooth muscles is inhibited, and finally in-situ vascularization is realized. The method can be used for preparing the vascular tissue engineering scaffold and also can be used for preparing other medical devices in contact with blood.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
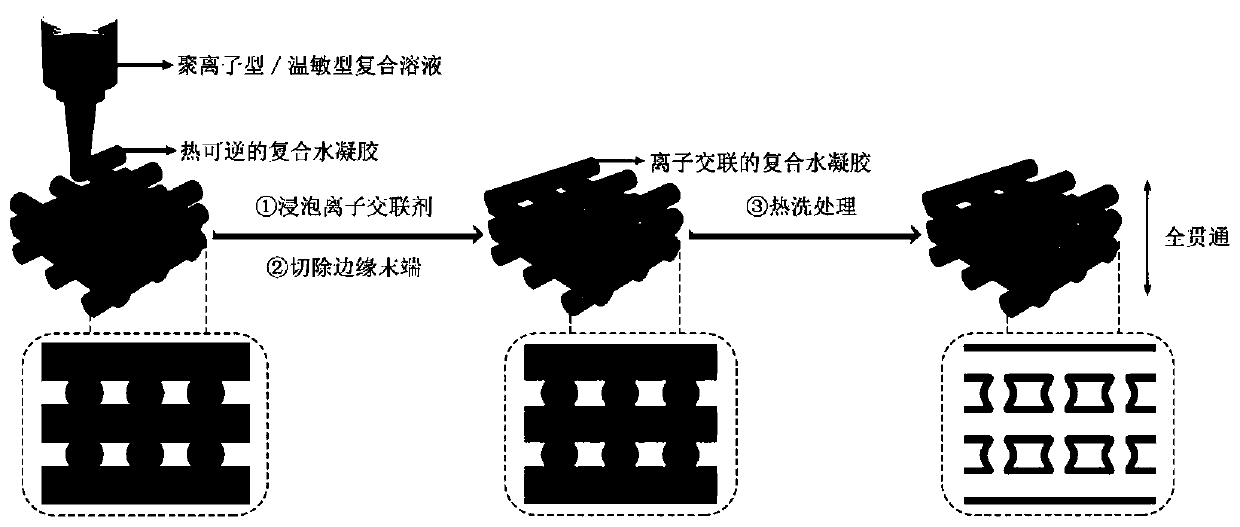
3D printed all-through tubular hydrogel support and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110421835AWide variety of sourcesLow priceAdditive manufacturing apparatusAdditive manufacturing with liquidsCross-linkHydrogel scaffold
The invention discloses a 3D printed all-through tubular hydrogel support and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps that a, a polyion type / thermo-sensitive type complex solution is prepared and poured into a 3D printing material cylinder; b, printing parameters are set, and printing is conducted on a low-temperature platform to obtain a heat-reversible composite hydrogel support; c, the support is soaked in an ionic cross-linking agent aqueous solution for a period of time and then taken out; and d, after the edge tail end of the support is removed and then thesupport is soaked in deionized water for thermal washing treatment to obtain the hydrogel support with an all-through tubular structure. According to the support and the method, based on the difference of the thermal stability of the composite hydrogel before and after ion crosslinking, the spatial effect of 3D printing and the time effect of ion diffusion are combined, the process is simple, theprepared tubular hydrogel support has good structural connectivity and size regulation and control, and has a potential application prospect in the field of vascular tissue engineering.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Medicament coating material and preparation method
InactiveCN101934093AEasy to synthesizeInhibit aggregationCoatingsProsthesisBiocompatibility TestingVascular tissue engineering
The invention relates to the field of vascular tissue engineering, in particular to a medicament coating material which can be used in vascular tissue engineering and intervened in a stent and a preparation method. The coating material has the characteristics of degradability and an effect on promoting the growth of endothelial cells and inhibiting platelet adhesion. The coating material takes a polymer material which has good biocompatibility as a medicament carrier, and takes an effective extracts such as ferulic acid and derivatives thereof of a traditional Chinese medicament angelica sinensis. The preparation method has the following processes of: fully dissolving the medicament carrier and a medicament with a solvent; and using after mixing uniformly by ultrasonic sound. The medicament coating material can be prepared by a solution pouring method, wherein uniformly dissolved solution is poured in glass ware; volatilizing the solvent for 24 hours at the temperature of between 20 and 25 DEG C in vacuum to form a film; continuing heating for volatilizing the solvent thoroughly for 48 hours; and sterilizing for later use. The coating material has the effects on inhibiting the platelet adhesion and prompting the growth of endothelial cells, and can be used in the field of vascular tissue engineering and intervened in a degradable medicament coating on a stent surface.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Degradable tubular polymeric multipore foaming material and its preparation method
A degradable tubular high-molecular porous foam material used as the porous cell scaffold of blood vessel tissue or nerve tissue engineering is prepared from a high-molecular material through use of combined mould. Its advantages are high porosity up to 90% and uniform distribution of pores.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Mammary artery derived cells and methods of use in tissue repair and regeneration
An isolated mammalian internal mammary artery-derived cell is disclosed. Furthermore, methods of isolating the mammalian internal mammary artery-derived cell are disclosed. The cell is useful in tissue engineering technologies, specifically in vascular tissue engineering.
Owner:ADVANCED TECH & REGENERATIVE MEDICINE
Polyamino acidic elastic vascular tissue engineering stent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104524641AAccelerate the remodeling processGood biocompatibilitySurgeryNon-woven fabricsBiocompatibilityVascular tissue engineering
The invention discloses a polyamino acidic elastic vascular tissue engineering stent and a preparation method thereof; an inner layer is formed by compounding -NH<3+> in polysaccharide with -COO- in polyamino acid in an electrostatic compounding manner; an intermediate layer is a chemical crosslinking stent layer; an outer layer is an electrostatic spinning net; and the electrostatic spinning net is prepared from a poly(epsilon-caprolactone)-b-polyamino acid ester segmented copolymer through an electrostatic spinning method. According to the invention, the complex structure and the mechanical property of normal vessels are simulated; on one hand, the stent has good biocompatibility; the compliance of the stent can be well matched with a host vessel; on the other hand, the intermediate layer of stent has relatively good elasticity; under the dynamic stimulation of a vascular bioreactor, the stent can better bear wall-crossing pressure and resilience of a blood flow to a vascular wall; furthermore, the stent is deformed periodically, so that self remodelling can be strengthened; therefore, a regenerated blood vessel is closer to a normal blood vessel in tissue constitution; and furthermore, the polyamino acidic elastic vascular tissue engineering stent has excellent biomechanical property.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Method for preparing vascular tissue engineering stent material carried with pravastatin sodium
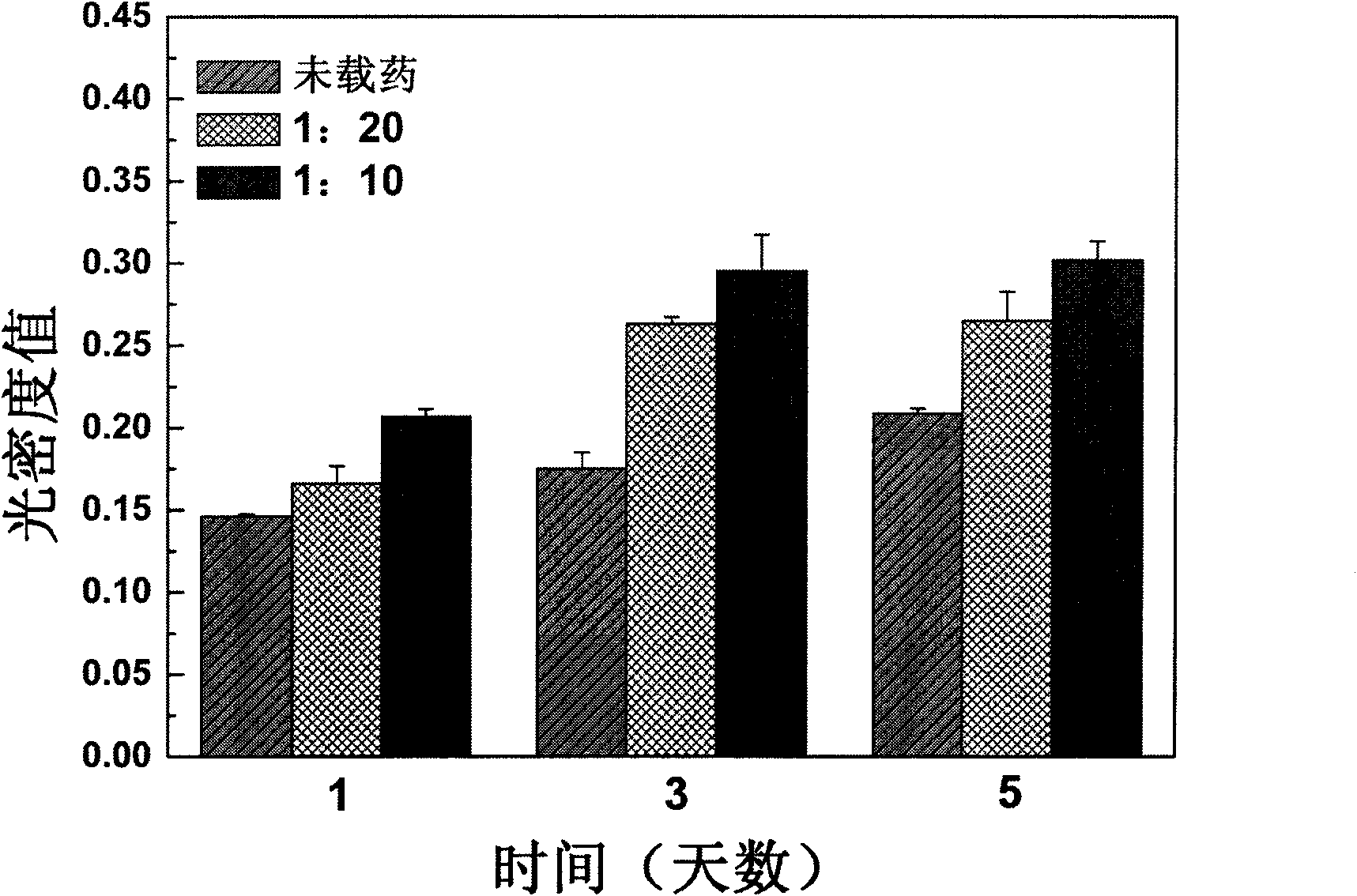
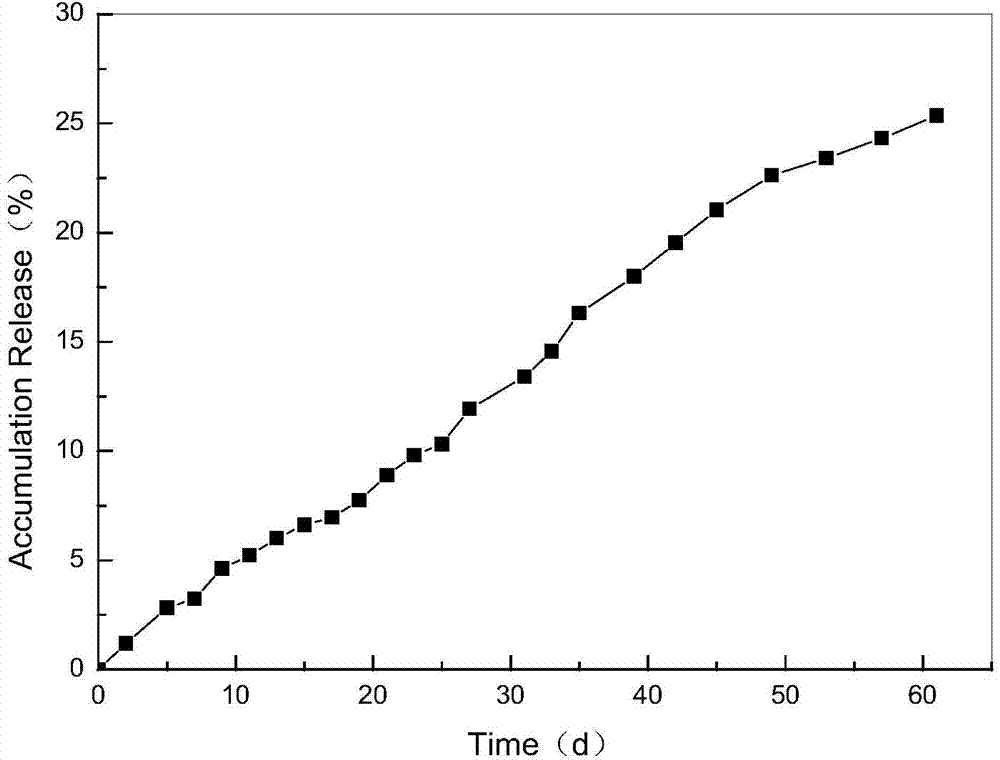
The invention relates to a method for preparing a vascular tissue engineering stent material carried with pravastatin sodium. The method consists of the following steps: (1) preparing chitosan solution and gelatin salutation; (2) preparing cross-linking agent solution; (3) mixing the chitosan solution, the gelatin salutation and the cross-linking agent solution, then adding chitosan microspheres entrapping pravastatin sodium, performing uniform mixing, pouring the mixture into a vascular stent mold, performing freeze-drying and then performing demolding; (4) repetitively washing the vascular stent after demolding and then performing freeze-drying. The vascular tissue engineering stent material carried with pravastatin sodium prepared by adopting the method has a pore diameter of 10-600mu m, the chitosan microspheres entrapping pravastatin sodium are well dispersed in the stent and the release time reaches more than 60 days.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of hollow fiber used for blood vessel tissue engineering
InactiveCN103638555ASmall water fluxIncrease water fluxHollow filament manufactureConjugated synthetic polymer artificial filamentsHollow fibreFiber
The invention relates to a preparation method of a hollow fiber used for the tissue engineering. The hollow fiber is prepared through a phase transition of a PCL / PLGA mixture, has an appropriate tensile strength and can be used for a regeneration technology of blood vessels having small diameters. The hollow fiber can also be mixed and dissolved after processing, the obtained mixed and dissolved material has an appropriate mechanical properties for operation, and can satisfy the smallest mechanical demands of the blood vessels having small diameters. The hollow fiber has a wide application prospect in the tissue engineering field because of its excellent performances.
Owner:WUXI ZHONGKE GUANGYUAN BIOMATERIALS
Method for inducing umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into endothelial cells
InactiveCN102776150AArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsVascular tissue engineeringBiomedicine
Belonging to the field of biomedicine, the invention relates to a method for paeoniflorin to induce umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into endothelial cells and application thereof. In the invention, the paeoniflorin has a structure as shown in formula (I). The induction differentiation steps of the method comprise: inducing the umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells respectively in a beta-mercaptoethanol medium with a concentration of 1-100micromoles / L and a retinoic acid 5%DMEM medium with a concentration of 1-100micromoles / L for 24h, then shifting the cells into a paeoniflorin-containing endothelial cell conditioned medium, half of the solution is changed every two days. And after 10-14d of induction, umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell derived endothelial cells can be obtained. In the invention, the application of the paeoniflorin and the method can promote differentiation of the umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells, improve the differentiation efficiency, and can be used in cell transplantation treatment of ischemic vascular diseases. The obtained endothelial cells can be further prepared into cell preparations to be used for ischemic vascular disease treatment, and seed cell application of vascular tissue engineering.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
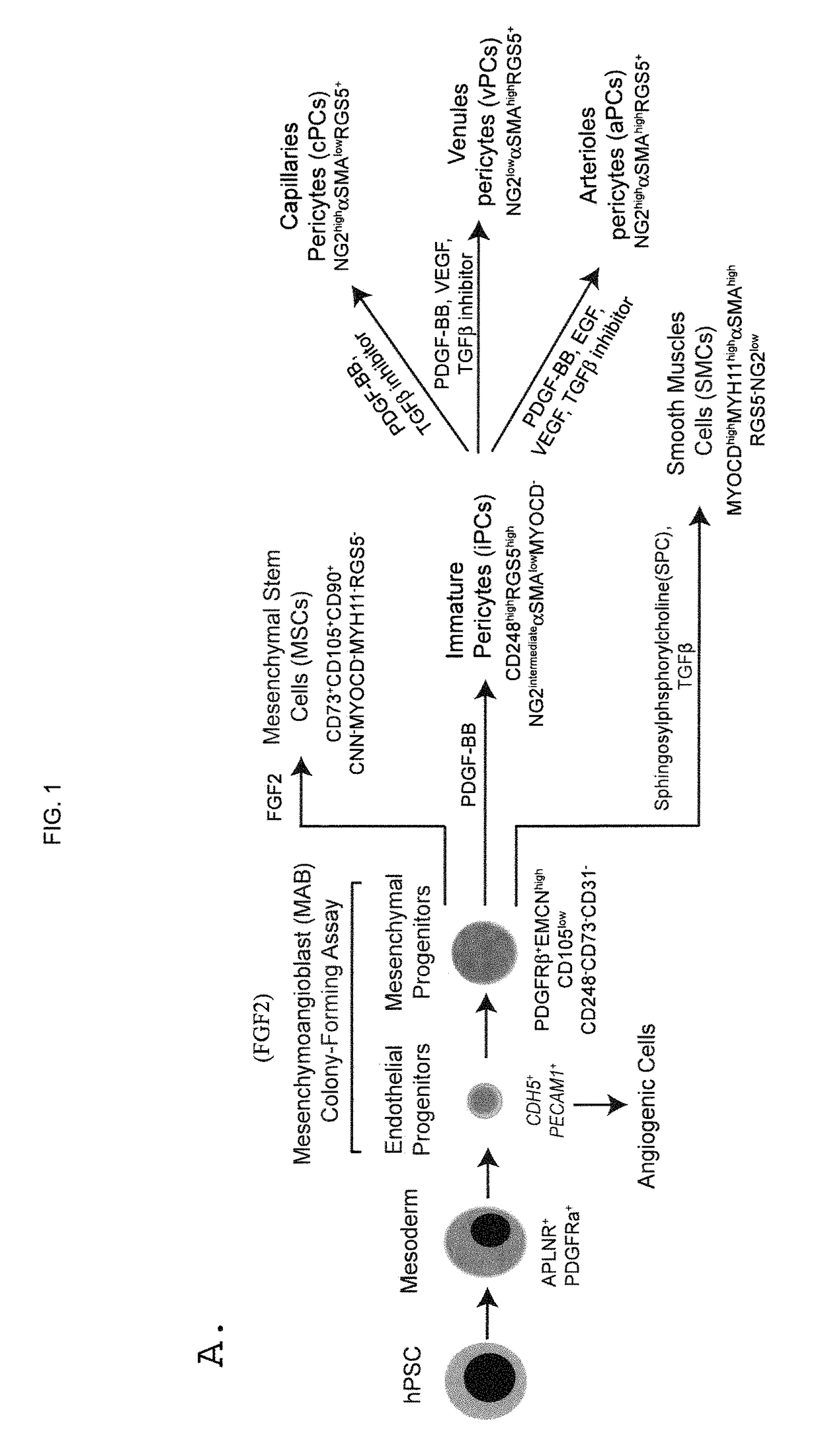
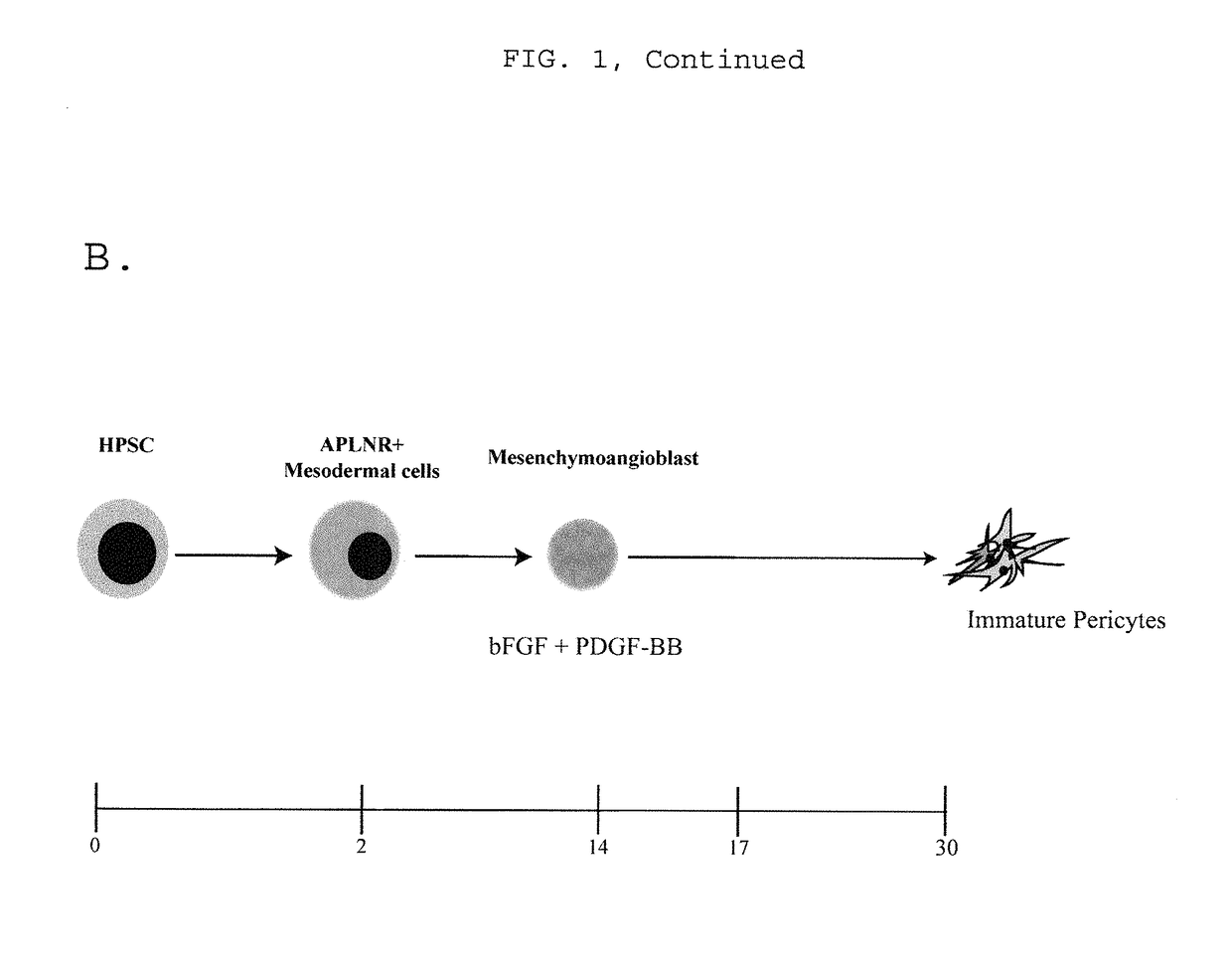
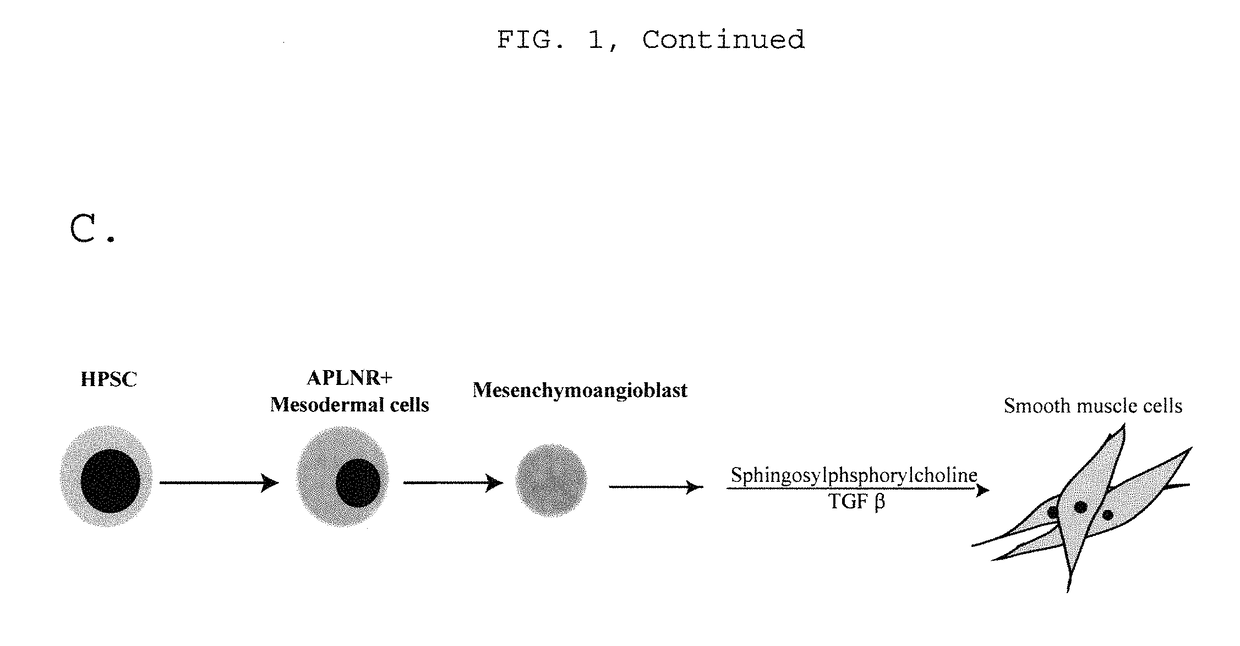
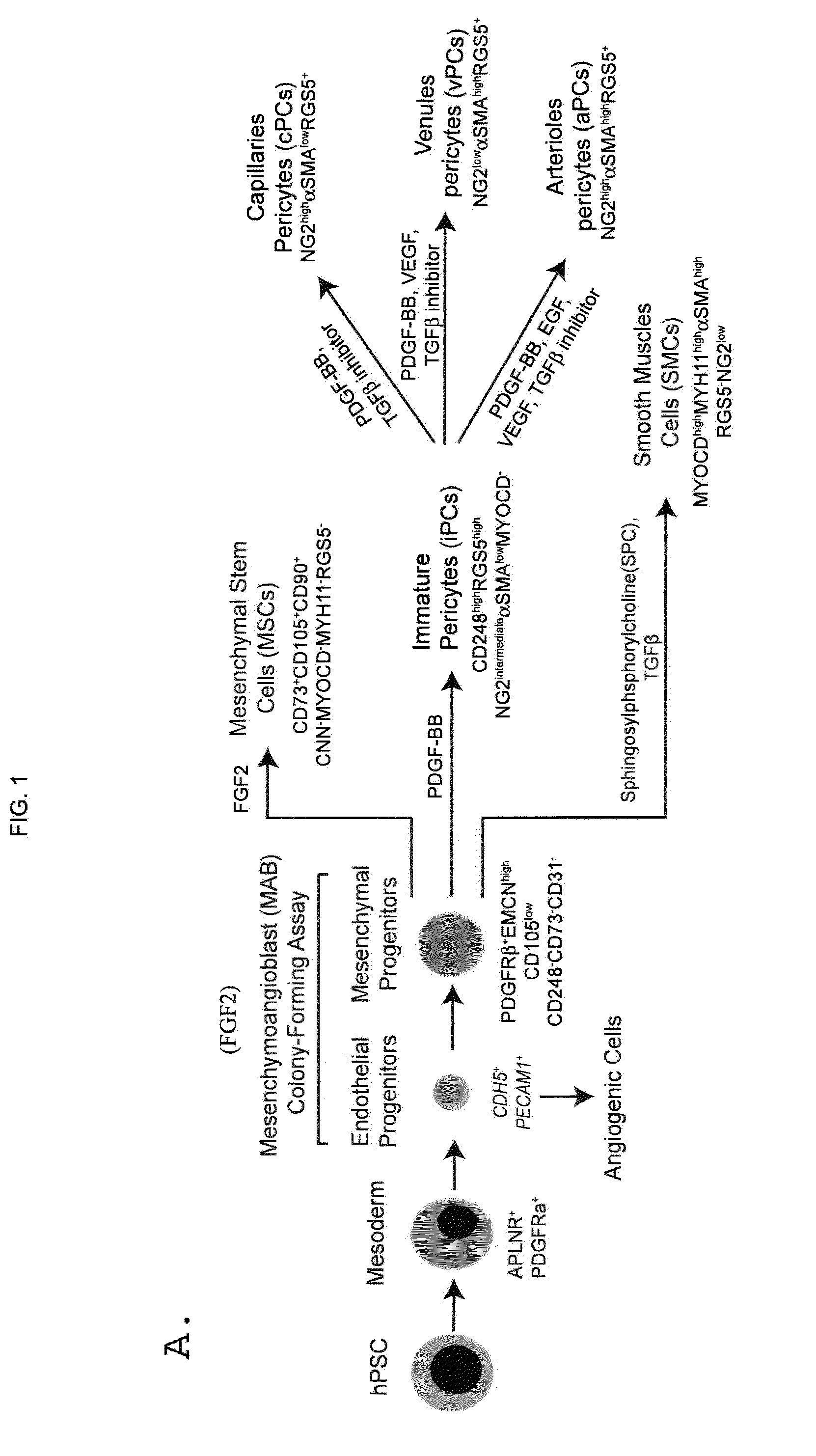
Generating vasculogenic cell populations
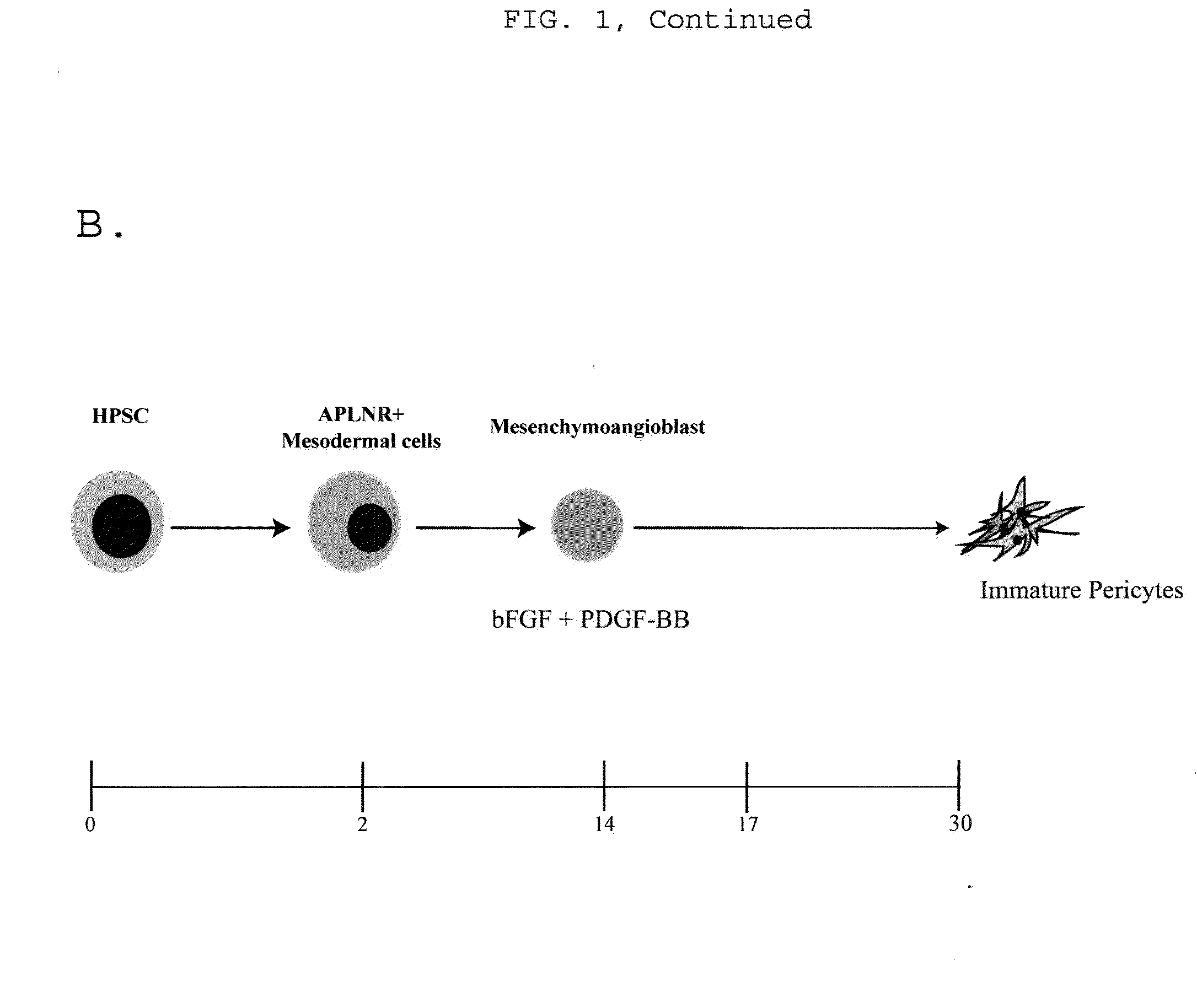
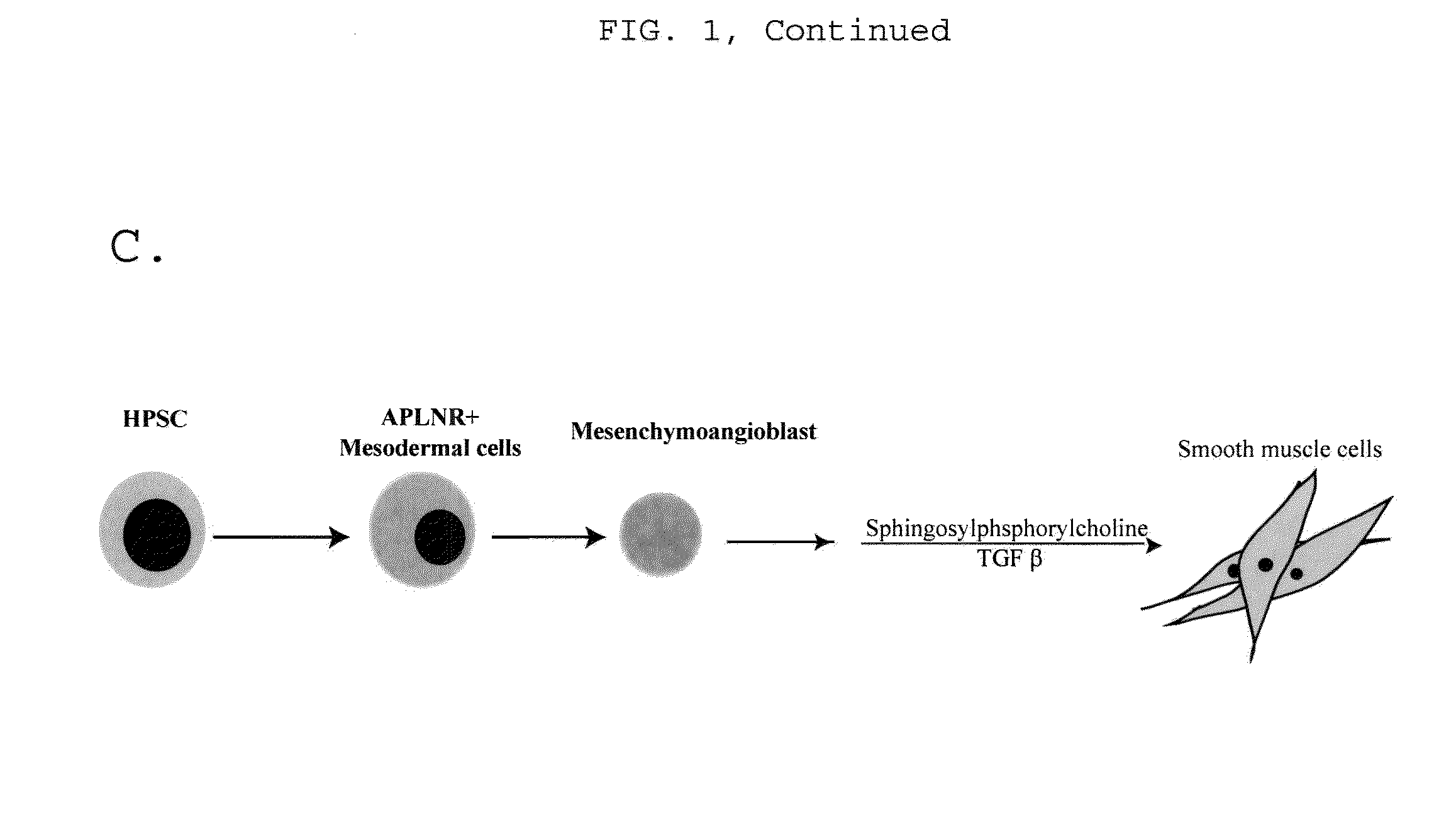
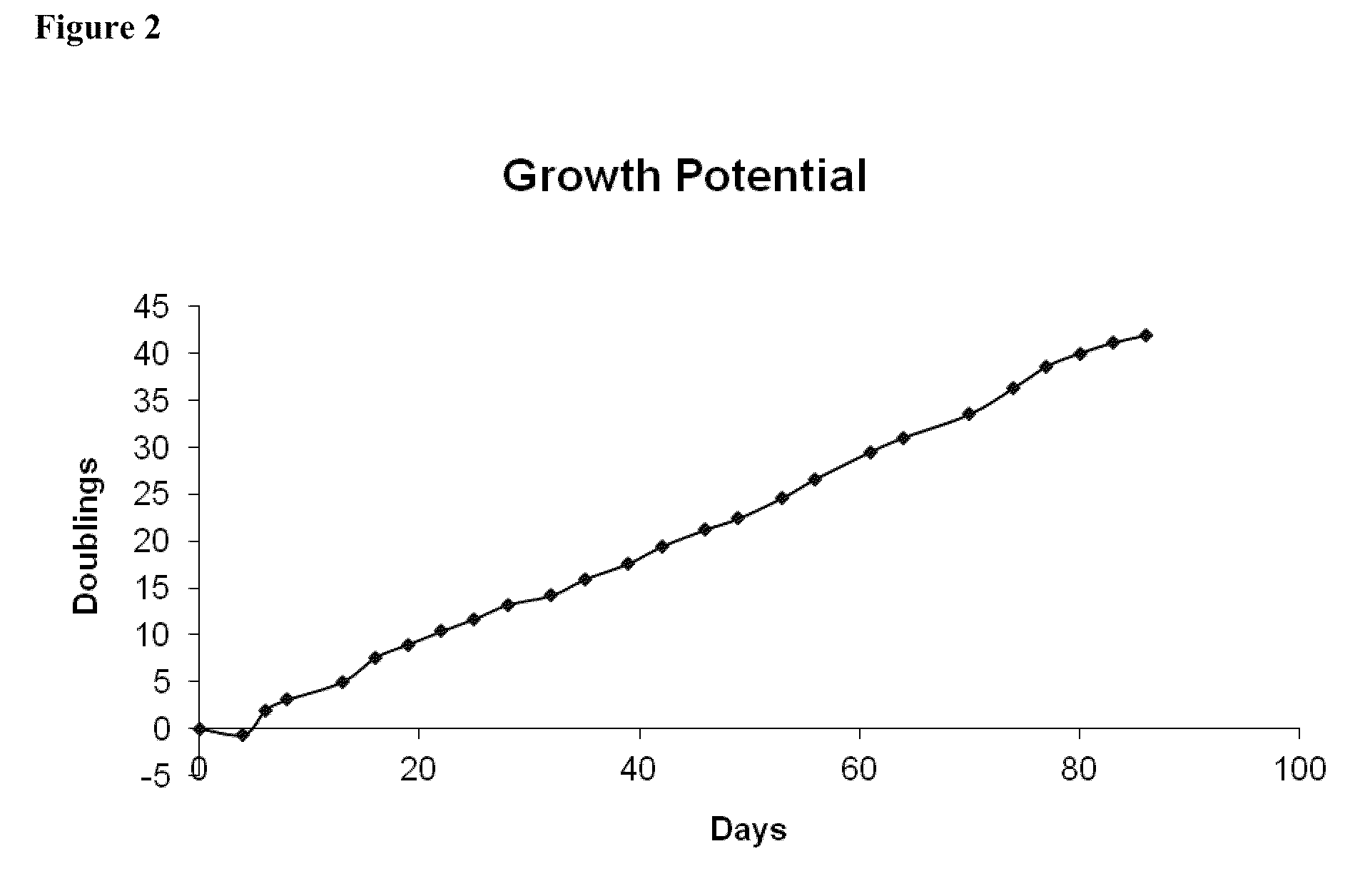
ActiveUS9868939B2Culture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsProgenitorVascular tissue engineering
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Generating vasculogenic cell populations
ActiveUS20140369968A1Promote differentiationBiocideCulture processVascular tissue engineeringBiomedical engineering
The present invention relates generally to methods and compositions useful for therapeutic vascular tissue engineering. In particular, the present invention provides methods for generating substantially pure populations of vasculogenic cells from human mesenchymal progenitors, and methods and compositions for clinical applications in the field of regenerative medicine.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Mammary artery derived cells and methods of use in tissue repair and regeneration
ActiveUS8323972B2Cell dissociation methodsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsTissue repairMammary artery
An isolated mammalian internal mammary artery-derived cell is disclosed. Furthermore, methods of isolating the mammalian internal mammary artery-derived cell are disclosed. The cell is useful in tissue engineering technologies, specifically in vascular tissue engineering.
Owner:ADVANCED TECH & REGENERATIVE MEDICINE
Tissue engineering of blood vessels
InactiveUS9179996B2Increase pressureThickening of a vessel wallBlood vesselsBlood vessel spasmReference device
Owner:DTHERAPEUTICS
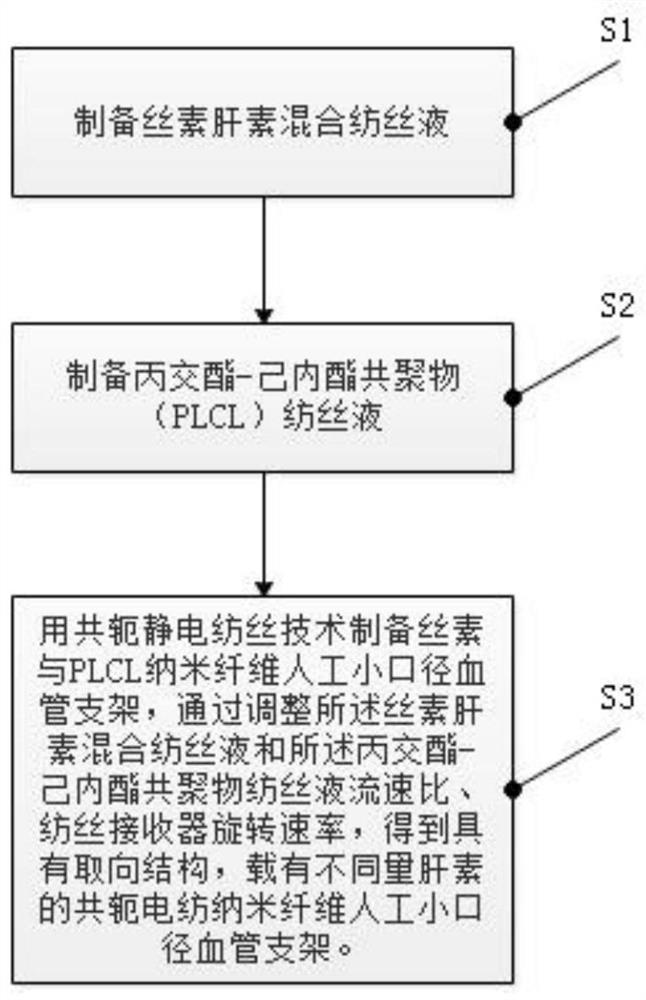
Preparation method of conjugate electrospinning nanofiber artificial small-caliber intravascular stent and product
ActiveCN111850818AGuaranteed activityRelease stabilitySurgeryPharmaceutical containersElectrospun nanofiberLactide
The invention discloses a preparation method of a conjugate electrospinning nanofiber artificial small-caliber intravascular stent. The preparation method comprises the following steps that S1, a fibroin and heparin mixed spinning solution is prepared; S2, a lactide-polycaprolactone copolymer (PLCL) spinning solution is prepared; and S3, the fibroin and PLCL nanofiber artificial small-caliber intravascular stent is prepared through the conjugate electrospinning technology, and the conjugate electrospinning nanofiber artificial small-caliber intravascular stent is obtained by adjusting the flowspeed ratio of the fibroin and heparin mixed spinning solution and the lactide-polycaprolactone copolymer spinning solution and the rotating speed of a spinning receiver. The method for preparing theconjugate electrospinning nanofiber artificial small-caliber intravascular stent is simple and efficient in operation and low in price; the small-caliber intravascular stent has good mechanical properties and biocompatibility; and compared with a nanofiber stent prepared by a common electrospinning method, the small-diameter intravascular stent has larger porosity, cells can be migrated into thestent more easily, tissue regeneration is promoted, and the stent has extremely good application prospects in vascular tissue engineering.
Owner:无锡市觉新生物科技有限公司
A preparation method of p(lla-cl)/collagen double-layer vascular stent coordinated by heparin and gemini factor
ActiveCN105233339BRapid endothelializationPromote growthStentsPharmaceutical containersDrugs solutionVascular tissue
The invention relates to a method for preparing a P(LLA-CL) / collagen double-layer vascular stent coordinated and regulated by heparin and gemini, comprising: mixing P(LLA-CL) and collagen in a solvent to obtain a composite spinning Silk liquid; dissolving heparin sodium and VEGF in the diluent to obtain the drug solution loaded on the inner layer; dissolving PDGF in the diluent to obtain the drug solution loaded on the outer layer; the drug solution loaded on the inner layer is the core layer, and the spinning solution is the shell The inner layer of the stent is obtained by coaxial electrospinning; the drug solution loaded on the outer layer is the core layer, and the spinning solution is the shell layer, and the outer layer of the stent is obtained by bidirectional conjugate electrospinning, which is continuously received in the inner layer of the stent On the outside, a double-layer vascular stent was obtained, cross-linked, and obtained. The vascular stent of the present invention has excellent mechanical properties and biocompatibility, can mimic the components, structures and functions of natural blood vessels, and is beneficial to the in situ regeneration of vascular tissues and the reconstruction of multilayer structures, and is of great importance in vascular tissue engineering. Applications.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Double-layer small-caliber nanofiber tissue engineering blood vessel stent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109172871ASmall caliberCaliber adjustablePharmaceutical delivery mechanismBlood vesselsYarnBlood Vessel Tissue
The invention discloses a double-layer small-caliber nanofiber tissue engineering blood vessel stent and a preparation method thereof. The double-layer small-caliber nanofiber tissue engineering bloodvessel stent comprises an inner layer of a tissue engineering blood vessel stent and an outer layer of the tissue engineering blood vessel stent, wherein the inner layer of the tissue engineering blood vessel stent and the outer layer of the tissue engineering blood vessel stent are sequentially electrospun to obtain a core-spun yarn on the core yarn, and after the electrospinning is completed, the core yarn of the core-spun yarn is extracted to obtain a tissue engineering blood vessel stent. As the blood vessel tissue engineer stent material with micro and small caliber has a multi-layer structure and composition of the bionic natural blood vessel to a certain extent, the blood vessel tissue engineer stent material has good biocompatibility, is not easy to generate thrombus and has sufficient viscoelasticity so that the blood vessel tissue engineering stent material can withstand the pressure in the blood vessel for a long time.
Owner:ZHONGYUAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE
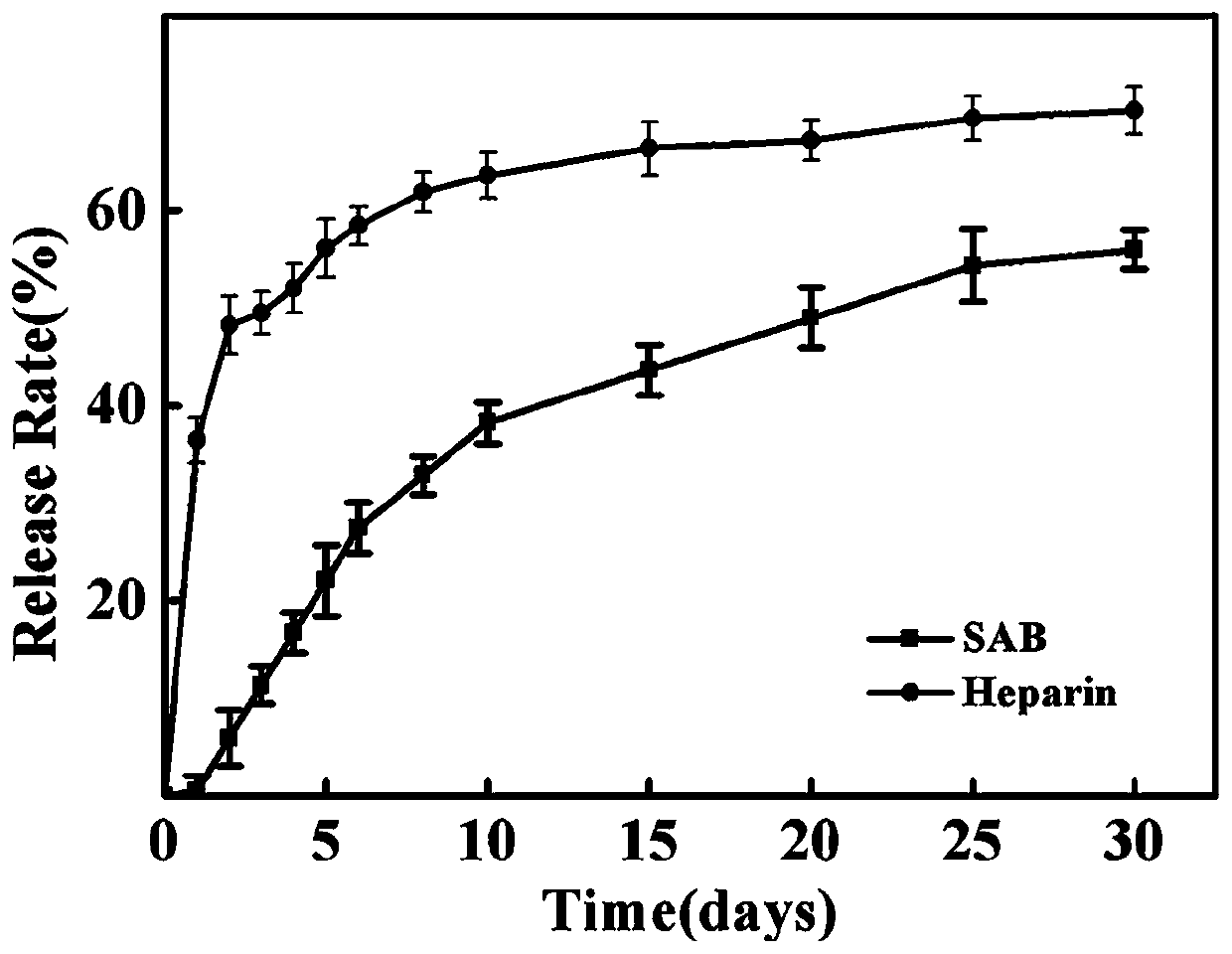
Nanofiber jointly modified by SAB and heparin and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN110409014AImprove adhesionPromote proliferationConjugated cellulose/protein artificial filamentsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismFiberMedicine
The invention relates to a nanofiber jointly modified by SAB and heparin and preparation and application thereof. The fiber comprises a shell layer which comprises SAB-MSN and a high molecular polymer, and a core layer which comprises the heparin. The method comprises the steps of preparation of SAB-MSN, preparation of a shell layer spinning solution, preparation of a core layer solution and preparation of the nanofiber. The method is simple and efficient, and the price is low. The core layer and the shell layer of the nanofiber carry drugs simultaneously, and the double sustained release effect can be achieved; the good biocompatibility and blood compatibility are achieved, and the nanofiber has excellent application prospects in vascular tissue engineering.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV +1
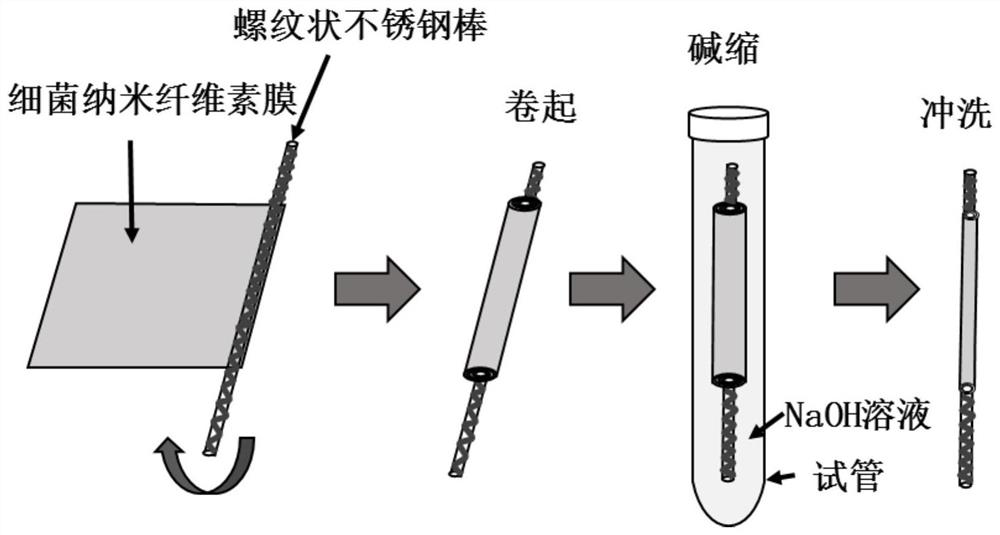
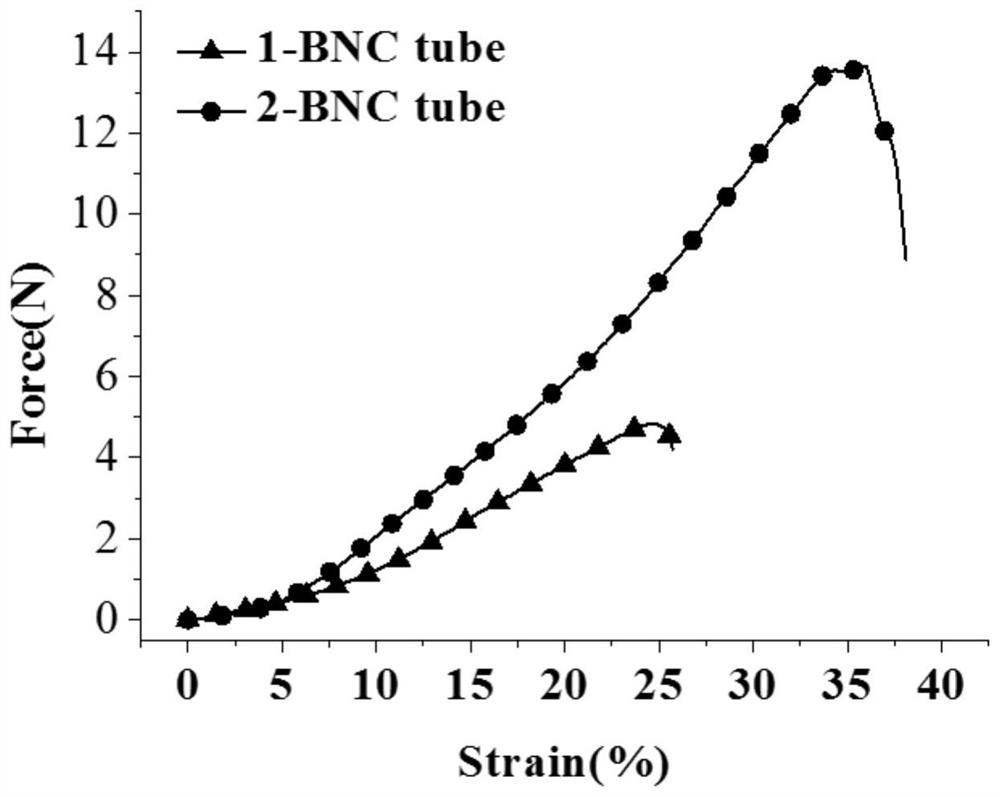
Bacterial nanocellulose base tube with inner surface texture modification and preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to a bacterial nanocellulose base tube modified with inner surface texture, and a preparation method and application thereof. Condensed and pickled. The bacterial nanocellulose base tube of the invention has controllable mechanical and mechanical properties, has a shape memory function, and can impart bacteriostatic activity, etc.; the inner surface texture of the tube-shaped material can improve cell adhesion, migration and growth, and is used in vascular tissue engineering, It has good application prospects in the fields of nerve repair and urethral repair.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com