Method for detecting residual quantity of orthocide in vegetables and fruits
A detection method, the technology of captandan, is applied in the detection of captanidan residues in vegetables and fruits, and the detection of pesticide residues. The effect of improving sensitivity, improving recovery, and easy operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
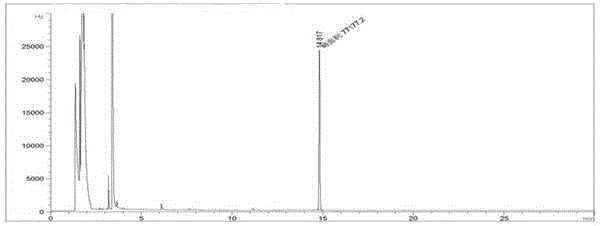
[0043] Example 1: Detection of captan residues in apples
[0044] (1) Sample pretreatment
[0045] Weigh 10.0 g of well-mixed apples into an Erlenmeyer flask, add 8 mL of acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer (pH=4) solution and mix well, add 100 mL of acetone to homogenize and extract for 3 minutes, filter with suction, and transfer the filtrate to a flat bottom flask In the filter residue, add 50 mL of acetone to homogenize extraction for 3 min, filter with suction, and combine the filtrate. Concentrate to about 30mL. Transfer the concentrated solution to a separatory funnel containing 50 mL of 10% sodium chloride solution, rinse the flat-bottomed flask with 50 mL of petroleum ether and transfer to the separatory funnel, shake vigorously for 2 minutes, stand for separation, and take the upper organic layer over anhydrous sodium sulfate Phase in the flat-bottomed flask, the lower aqueous phase was extracted again with 30 mL petroleum ether, the organic phases were combined, concentr...
Embodiment 2
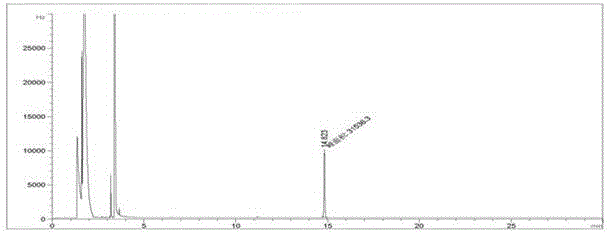
[0068] Example 2 Detection of captan residue in cucumber
[0069] (1) Sample pretreatment
[0070] Weigh 15.0 g of well-mixed cucumber into an Erlenmeyer flask, add 8 mL of acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer (pH=2.6) solution and mix well, add 60 mL of acetone to homogenize and extract for 3 minutes, filter with suction, and transfer the filtrate to a flat bottom flask In the filter residue, add 30 mL of acetone to homogenize extraction for 3 min, filter with suction, and combine the filtrate. Concentrate to about 30mL. Transfer the concentrated solution to a separatory funnel containing 50 mL of 10% sodium chloride solution, rinse the flat-bottomed flask with 50 mL of petroleum ether and transfer to the separatory funnel, shake vigorously for 2 minutes, stand for separation, and take the upper organic layer over anhydrous sodium sulfate Phase in the flat-bottomed flask, the lower aqueous phase was extracted again with 30 mL petroleum ether, the organic phases were combined, conce...
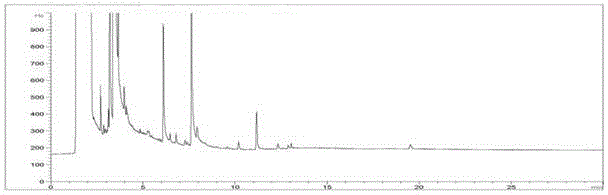
Embodiment 3
[0083] Add 8 mL of acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer solution (pH=4.8) and mix well, add 100 mL of acetone for homogenization and extract for 3 min, filter with suction, transfer the filtrate to a flat-bottomed flask, and add 50 mL of acetone to the filter residue for homogenization and extract for 3 min. Filter with suction and combine the filtrate. Concentrate to about 30mL. Transfer the concentrated solution to a separatory funnel containing 50 mL of 10% sodium chloride solution, rinse the flat-bottomed flask with 50 mL of petroleum ether and transfer to the separatory funnel, shake vigorously for 2 minutes, stand for separation, and take the upper organic layer over anhydrous sodium sulfate Phase in the flat-bottomed flask, the lower aqueous phase was extracted again with 30 mL petroleum ether, the organic phases were combined, concentrated to about 3 mL, and then passed through the column. The Florisil cartridge is pre-leached with 5 mL of n-hexane, the concentrated solut...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Column length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The inside diameter of | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Film thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com