Patents
Literature
72 results about "Respiratory Process" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A Respiratory Process involves the function of components of the respiratory tract involved in breathing, which include the nose, throat, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs.
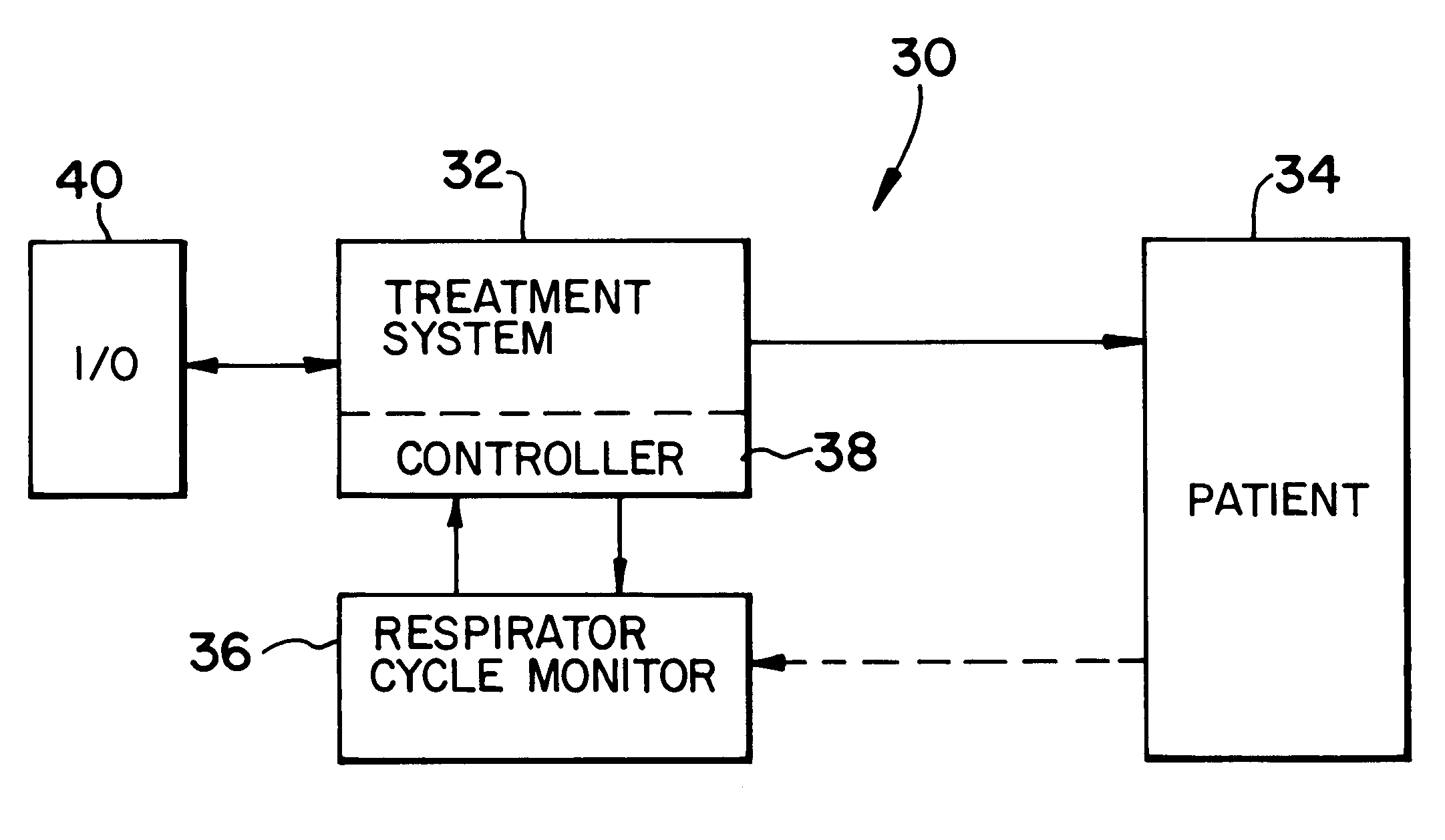
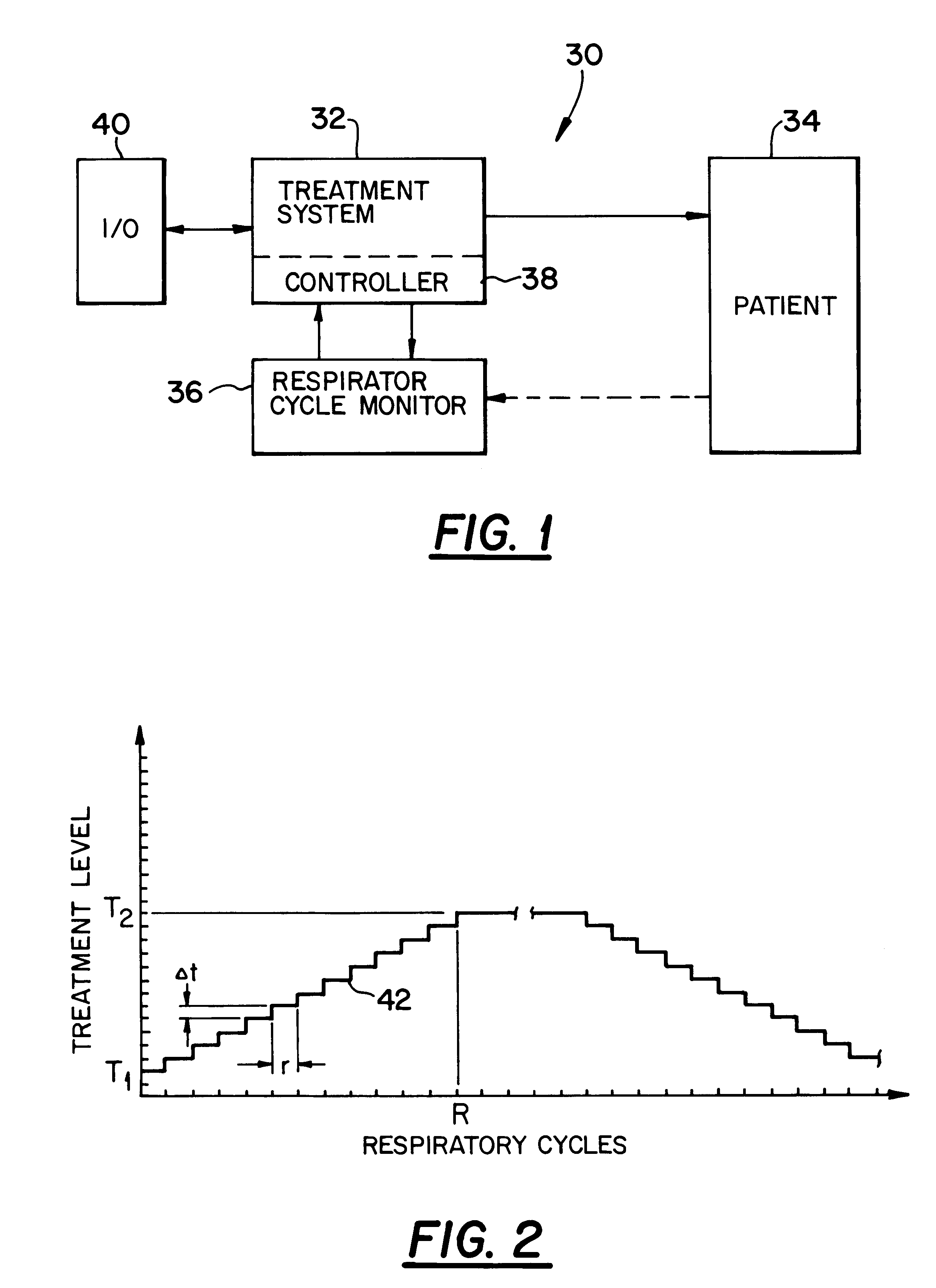
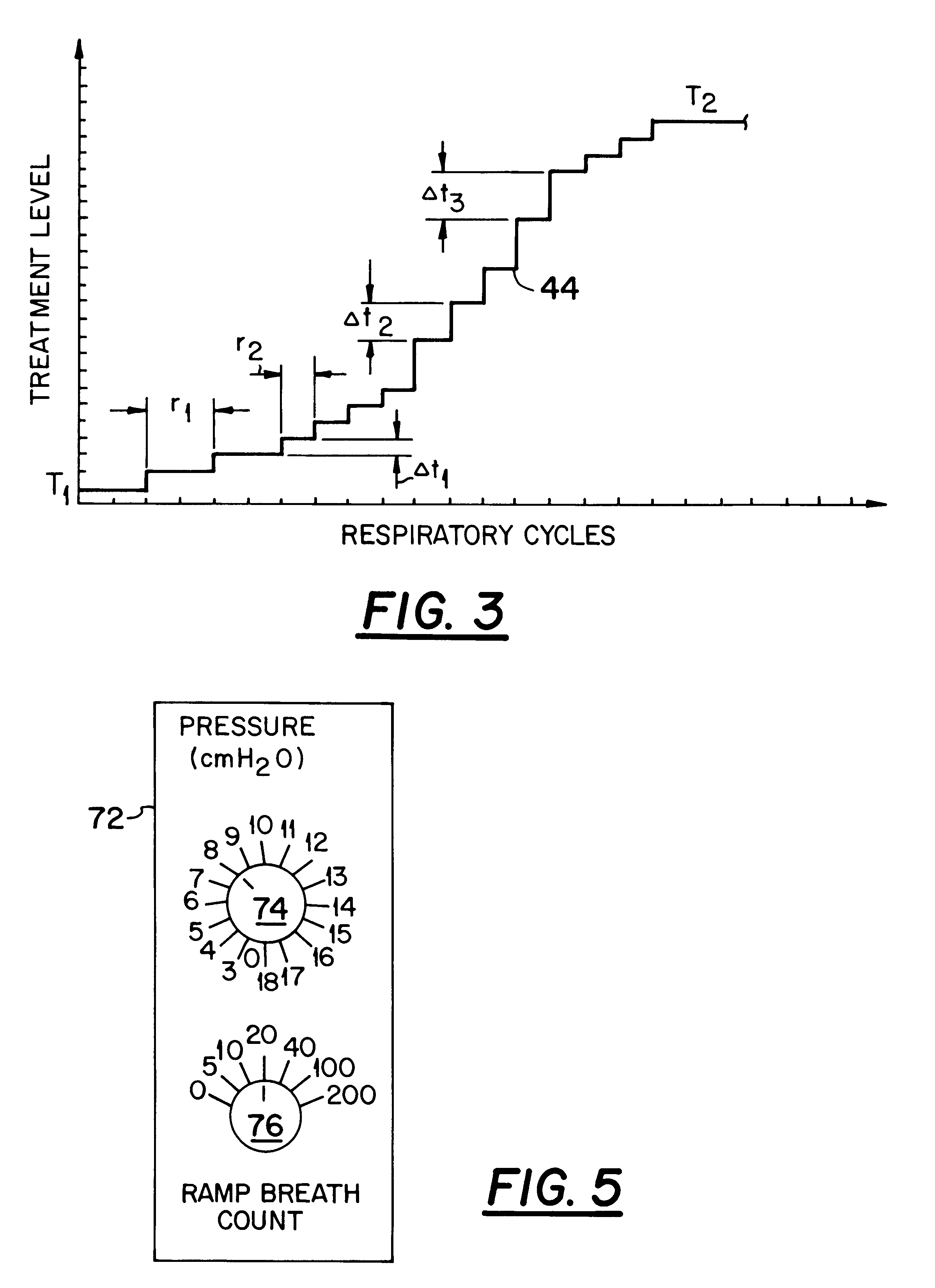
Breath-based control of a therapeutic treatment
A system and method for providing a therapeutic treatment, such as a flow of breathing gas, to a patient at variable treatment levels. A respiratory cycle monitor detects the patient's respiratory cycles and a control unit incrementally adjusts the treatment level from a first predetermined level to a second predetermined level over a first predetermined number of respiratory cycles. The amount of the incremental adjustment and the frequency of such adjustments over the course of the first predetermined number of respiratory cycles can be controlled to achieve a desired change in the therapeutic treatment over the course of the patient's respiration.
Owner:RIC INVESTMENTS LLC
Method for continuous measurement of flux of gases in the lungs during breathing
ActiveUS20050217671A1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAutonomous breathingEngineering
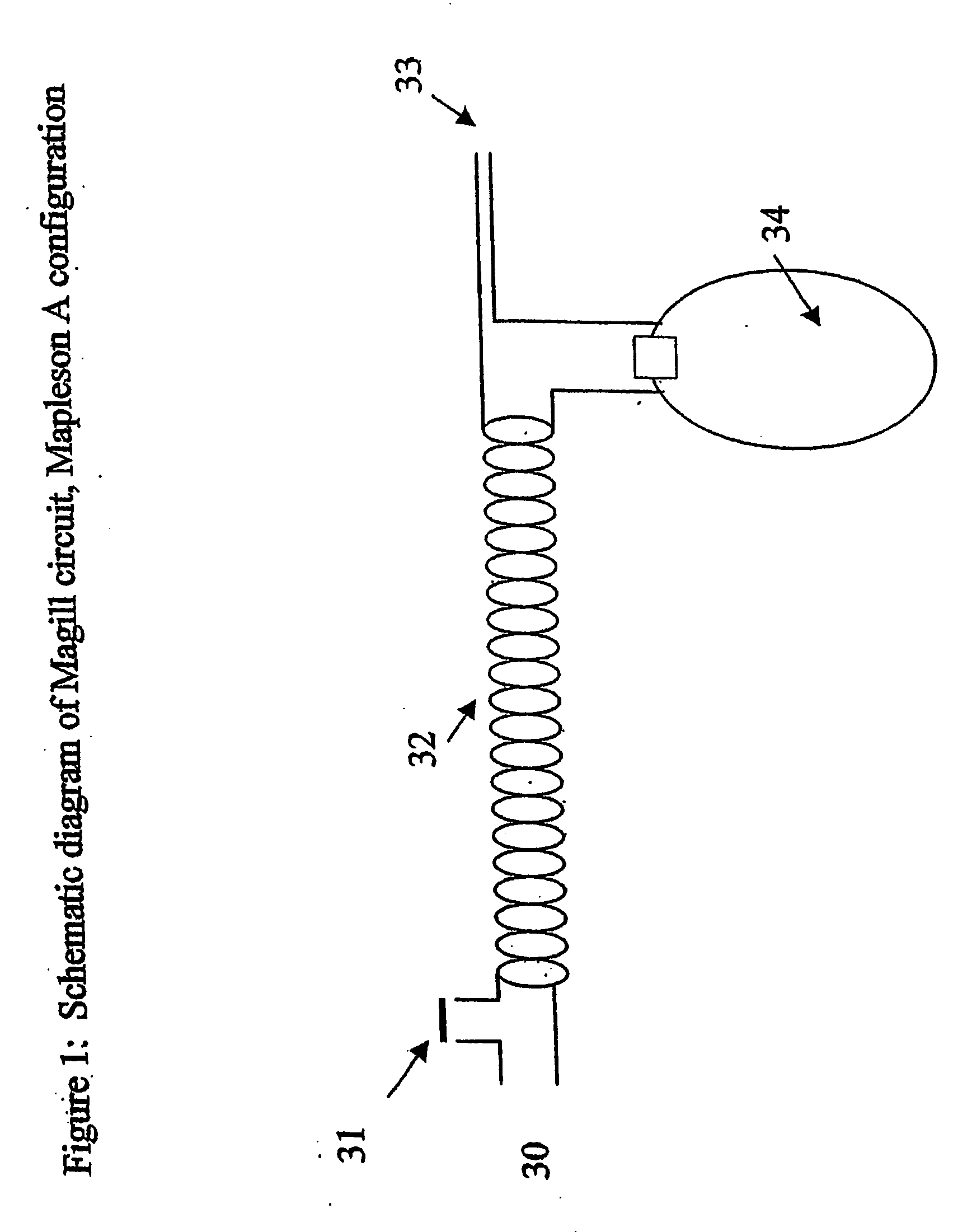
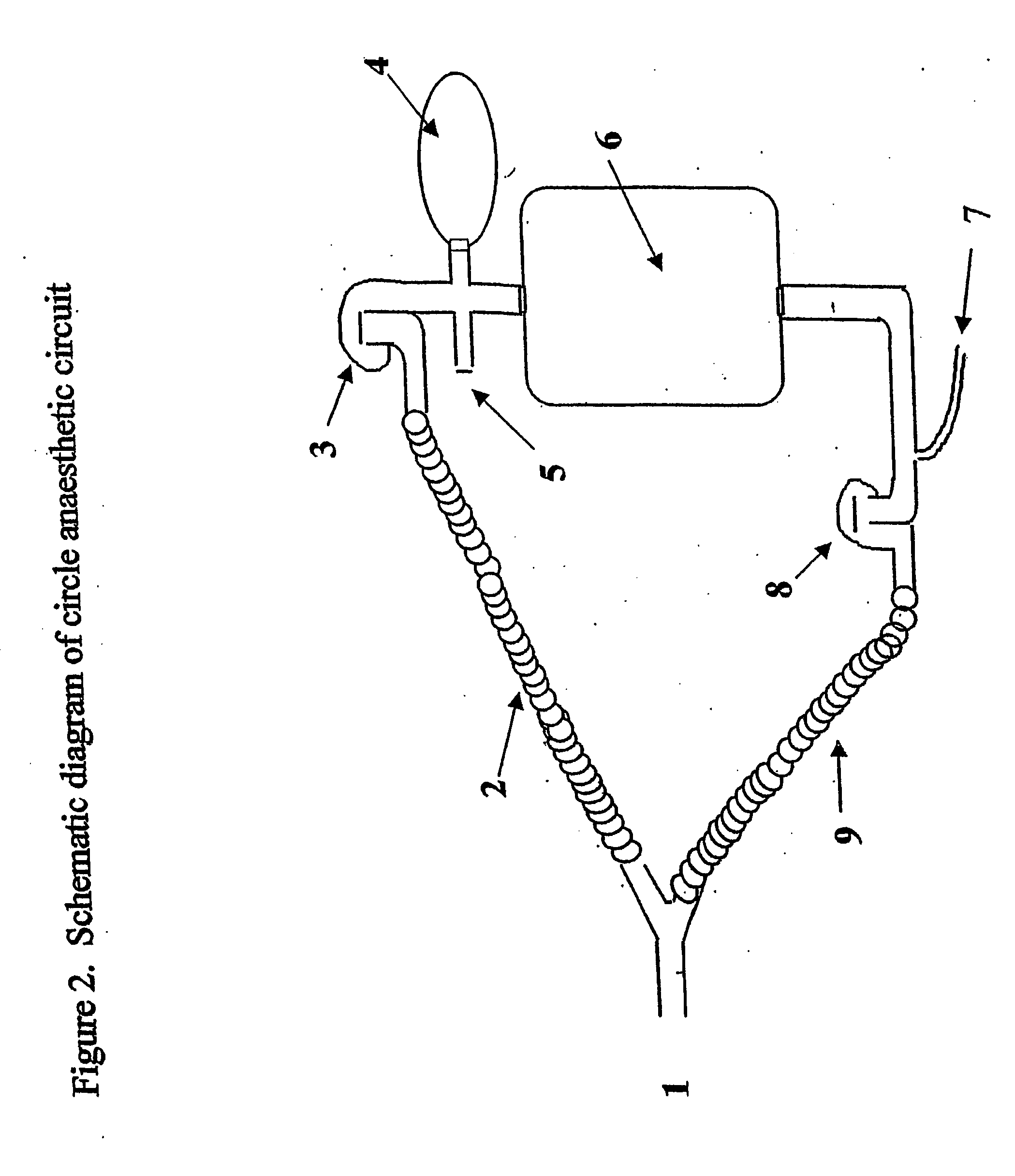
A method of calculating the flux of any gas (x) in a CBC circuit for a ventilated or a spontaneous breathing subject, for example said gas(x) being; a) an anesthetic such as but limited to; i)N2O; ii) sevoflurane; iii) isoflurane; iv) halothane; v) desflurame; or the like b) Oxygen; c) Carbon dioxide; or the like utilizing the following relationships; Flux of gas(x)=SGF (FSX−FEX) wherein SGF=Source of gas flow into the breathing circuit (CBC circuit) in liters / minute as read from the gas flow meter as set by the anesthesiologist; FSX=Fractional concentration of gas X in the source gas (which is set by the anesthesiologist); FEX=Fractional concentration of gas X in the end expired gas as determined by a portable gas analyzer, or the like.
Owner:THORNHILL SCI INC
Real time ultrasound monitoring of the motion of internal structures during respiration for control of therapy delivery
InactiveUS20060241443A1Organ movement/changes detectionChiropractic devicesHelical computed tomographyReal time ultrasound
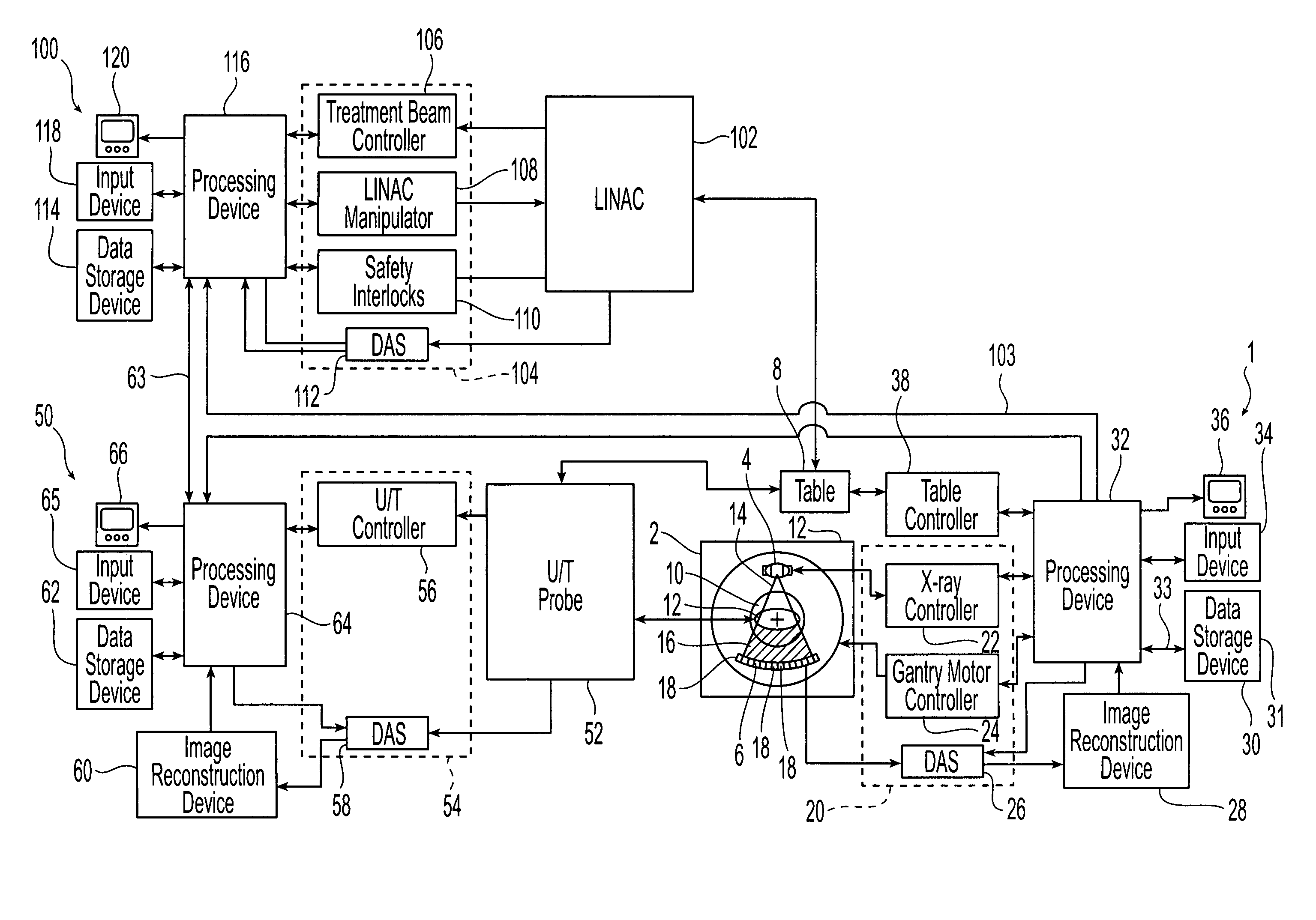
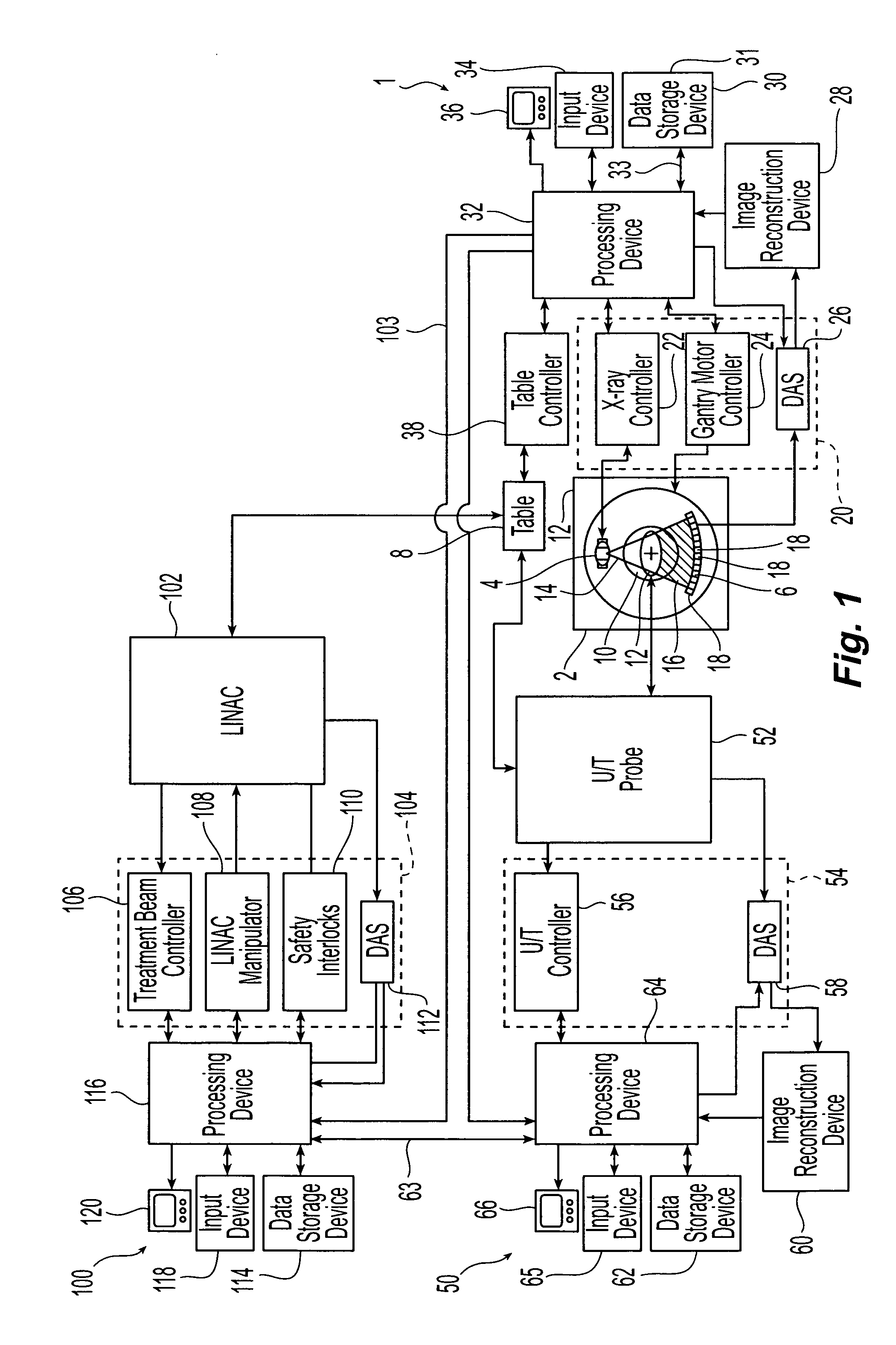
A method of targeting therapy such as radiation treatment to a patient includes: identifying a target lesion inside the patient using an image obtained from an imaging modality selected from the group consisting of computed axial tomography, magnetic resonance tomography, positron emission tomography, and ultrasound; identifying an anatomical feature inside the patient on a static ultrasound image; registering the image of the target lesion with the static ultrasound image; and tracking movement of the anatomical feature during respiration in real time using ultrasound so that therapy delivery to the target lesion is triggered based on (1) movement of the anatomical feature and (2) the registered images.
Owner:CIVCO MEDICAL INSTR CO
Dental appliance for improving airflow through nasal-pharyngeal airway
ActiveUS20040177852A1Increase airflowReduce airflow resistanceRespiratorsBreathing filtersNasopharyngeal airwayNasal dilators
A dental device comprises an intraoral nasal dilator and a mandibular repositioner working synergistically as an anti-snoring device. The device has a lower segment of thermoplastic material which is formed to fit over the lower teeth and is connected to an upper section of molded material extending between the upper jaw and the upper lip by a wire connector. The wire connector has mechanisms allowing adjustment of the lower jaw positioning. A wire extension with acrylic pads at end is bonded in the midline of the flange and extends out so that the pads stretch the tissue of the lip and lateral nasal walls preventing collapse during respiration while the anterior repositioning of the lower jaw maintains opening of the posterior pharyngeal airway during sleep functioning as an anti-snoring device. Additional applications of the intraoral nasal dilator include incorporation into sports mouth guards using a variety of materials.
Owner:ABRAMSON MARK
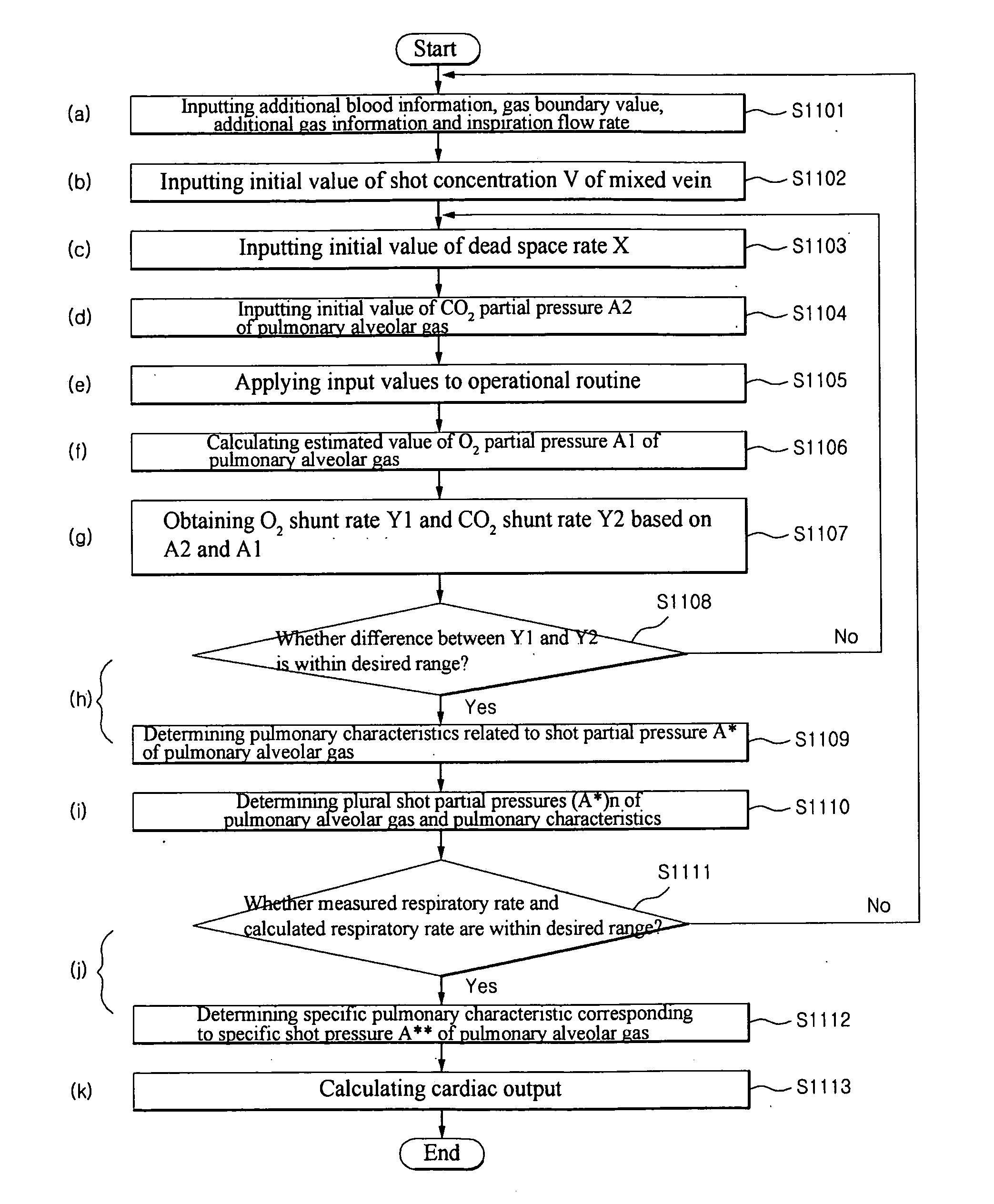
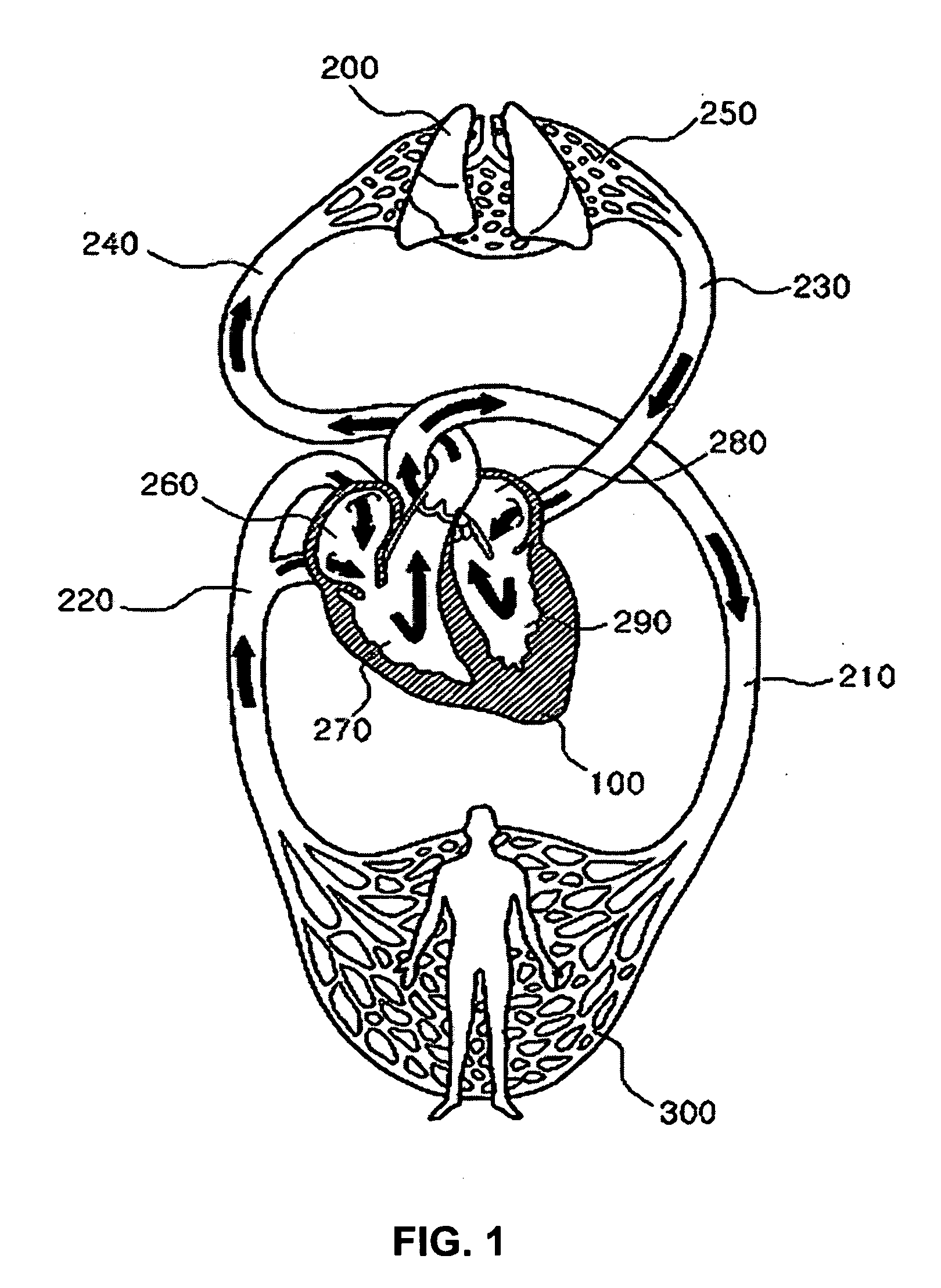
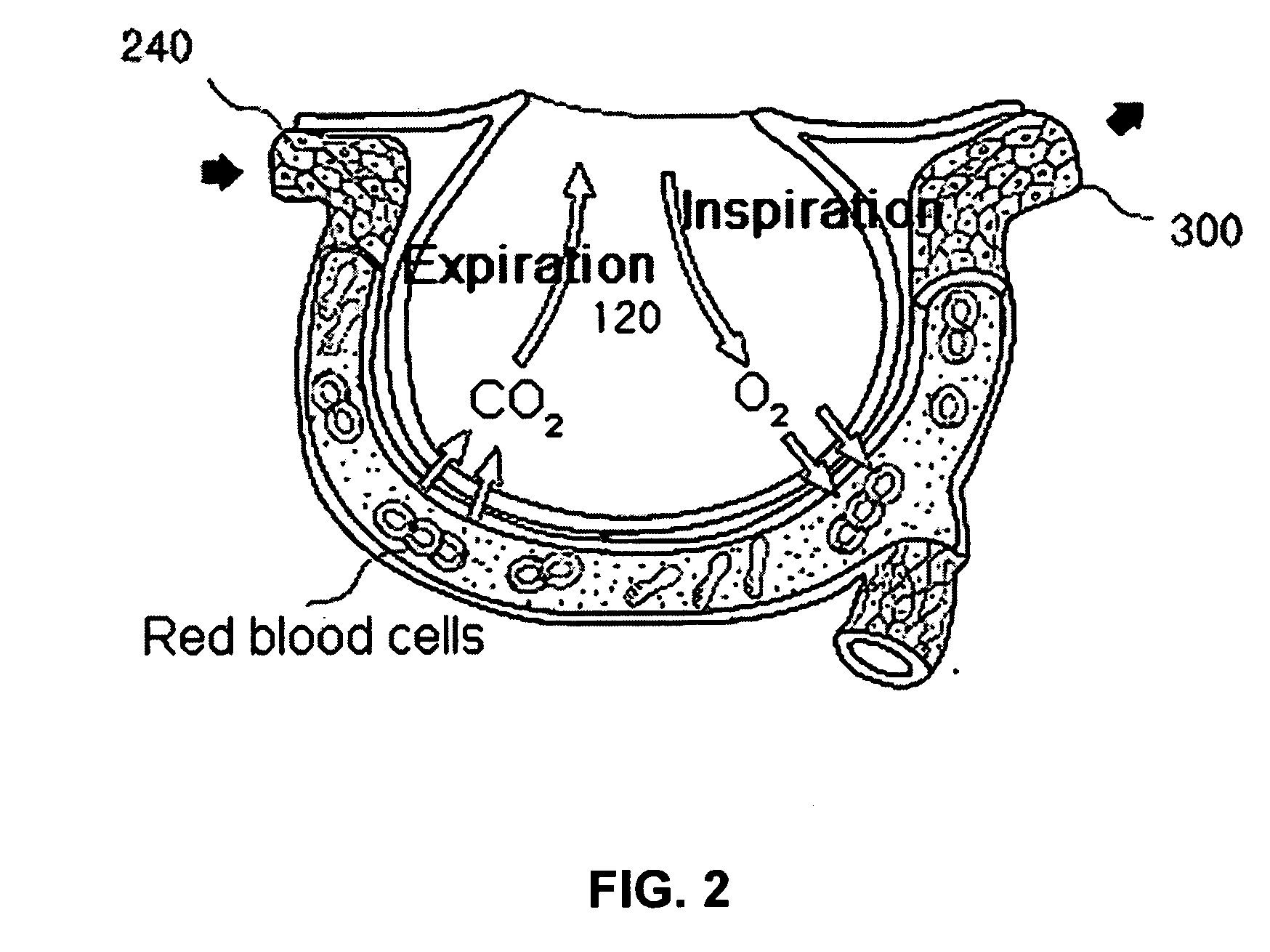
Method and display apparatus for non-invasively determining pulmonary characteristics by measuring breath gas and blood gas
InactiveUS20100179392A1Solve the real problemSensorsBlood flow measurementPulmonary vasculatureLung structure
A method for non-invasively determining pulmonary characteristics by measuring breath gas and blood gas and a display apparatus for the same, and for estimating major physiological characteristics, such as respiratory characteristics of lungs-pulmonary circulation system, cardiac functional characteristics, structural characteristics of lungs, etc. by applying primary measurement parameters obtained from ventilation gas and blood during breathing; and a display apparatus useful for the same.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Scientific respiration for self-health-care
I. Discovery of the Right Respiratory Science. Owing to the discovery of "Haldane effect", we comprise this Invention. This effect says, "The deoxygenation of the blood increases its ability to carry CO2.". So that we understand why most people are by exercise to promote health, it is with big muscles-contraction to have the "Deoxygenation of the Blood" as in exercise by walking, jogging or running to consume O2 5-15 times more than sitting in quiet, but few people know why and how is the right way. Especially as we see, a lot of professional athletes usually early died of heart diseases, because there is not the right respiratory science and process until today. II. The Right Respiratory Science and Process. We cite the right respiratory theories from the right related science as: "Haldane effect", "Gas Diffusion Law" and the "Relations between Respiration and Autonomic Nervous Functions". In addition to promote health, life and welfare for common people, it is to prevent from and control of many traditional functional diseases standing as rheumatism, cold and heart diseases, etc. The invented respiratory process is that, exhaling be long and slow; Inhaling be short and shallow once no longer than 1 second, by elasticity of breathing organs after exhaling; in case for more O2 required as in sport, it just speeds the breathing rate and keeps other breathing technics the same.
Owner:CHANG YUNG CHI
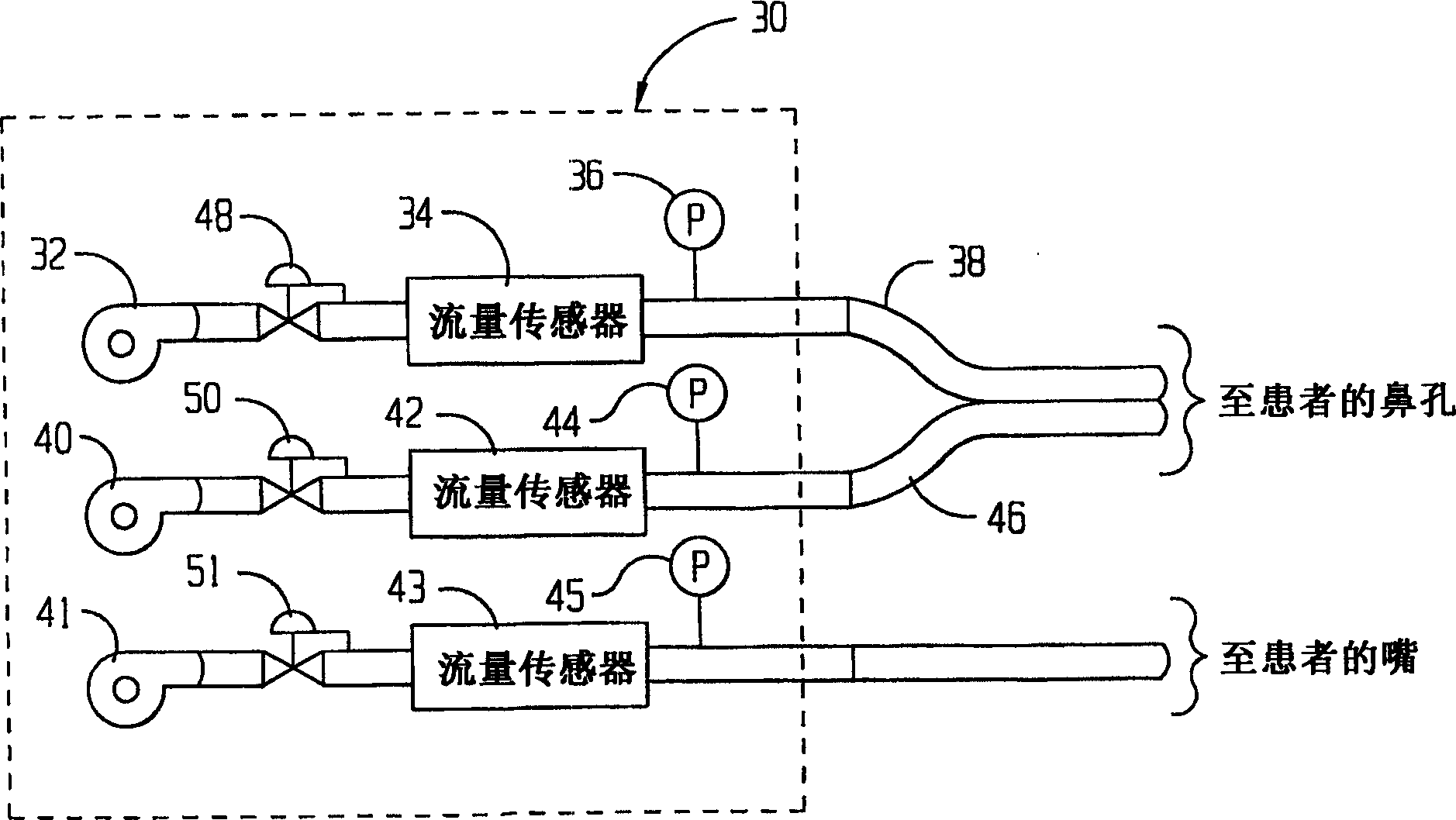
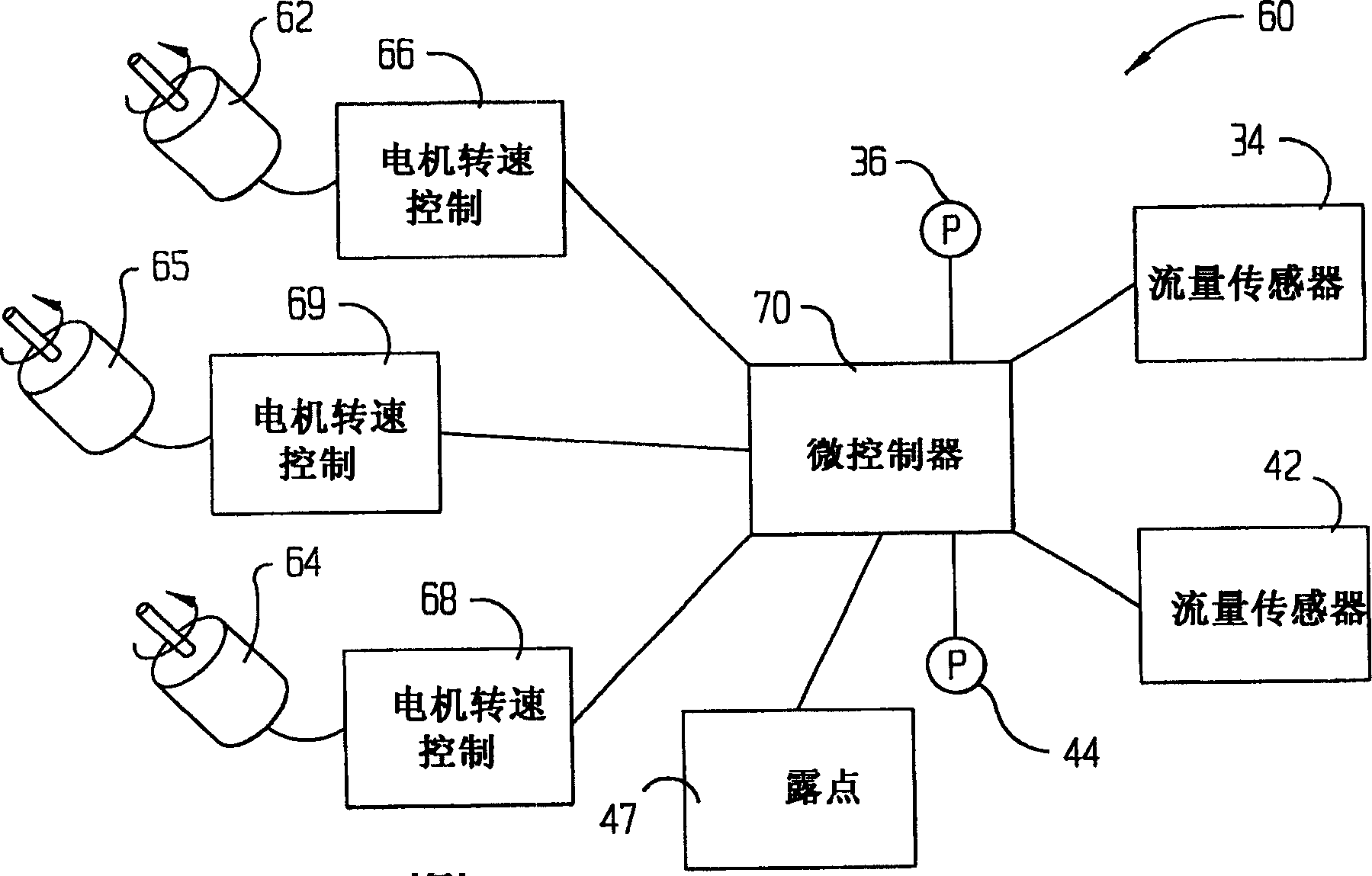
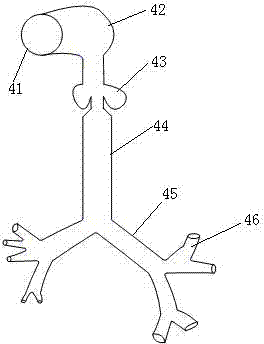
Method and system of individually controlling airway pressure of a patient's nares
A method and system of individually controlling positive airway pressure of a patient's nares. Some exemplary embodiments may be a method comprising applying therapeutic gas pressure within a first naris of a patient during respiration, and applying therapeutic gas pressure within a second naris of the patient during the respiration. The therapeutic gas pressures applied to each naris are different.
Owner:ACOBA LLC
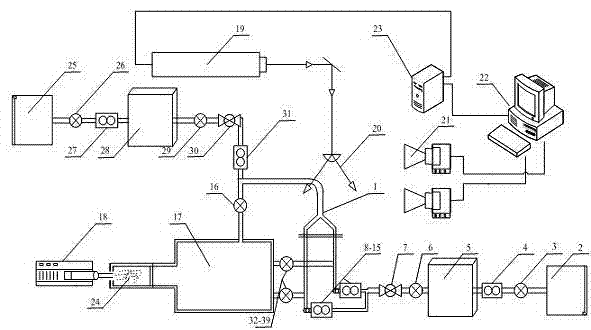
Method and experimental device for measuring flow field of human upper respiratory tract based on particle image velocimetry (PIV) technology
ActiveCN102564728AAccurate measurementAerodynamic testingHydrodynamic testingResearch ObjectScattering effect
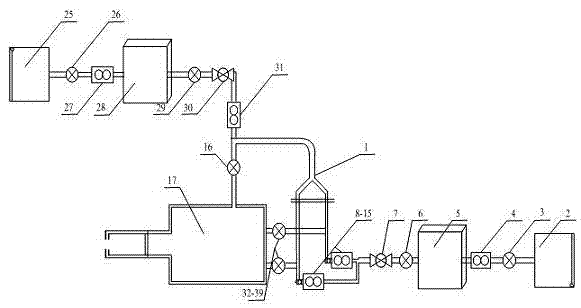
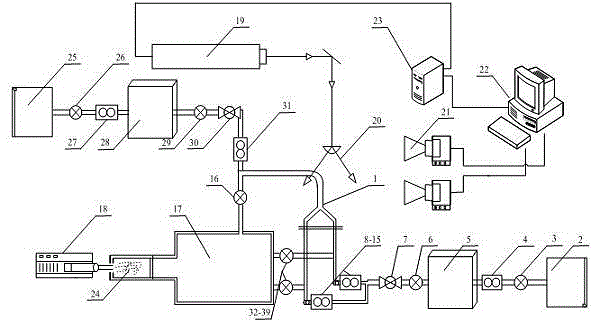
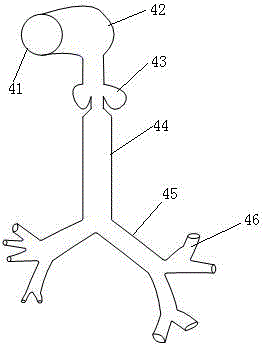
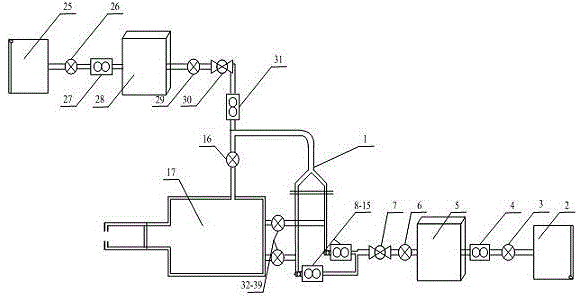
The invention discloses a method and an experimental device for measuring the flow field of a human upper respiratory tract based on a particle image velocimetry (PIV) technology. According to the invention, a true human upper respiratory tract model is taken as a research object, and the pumping effect of a vacuum pump is utilized to ensure that gas forms a channel in the model so as to simulate the respiratory process of a human lung. The method comprises the following steps of: scattering trace particles in the flow field, irradiating the flow field of the human upper respiratory tract model by using a sheet light source generated by a laser, aligning an area to be measured in a direction vertical to the sheet light source by using a cross-frame charge coupled device (CCD) camera, recording images of the particles during double pulse laser exposure according to the scattering effect of the trace particles on light, transmitting the images into a computer, computing and analyzing, solving the velocity of a fluid in the flow field of the human upper respiratory tract model by an autocorrelation or cross-correlation algorithm, and thus obtaining the characteristics of a vortex structure of the airflow of the flow field of the human upper respiratory tract during inspiration, an evolution form of the vortex structure, and the change and a distribution form of shear stress at the same time.
Owner:SANITARY EQUIP INST ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI PLA
Predictive respiratory monitor and system
ActiveUS20180129786A1Easy to detectTelemedicineMedical automated diagnosisCrowd sourcingComputer module
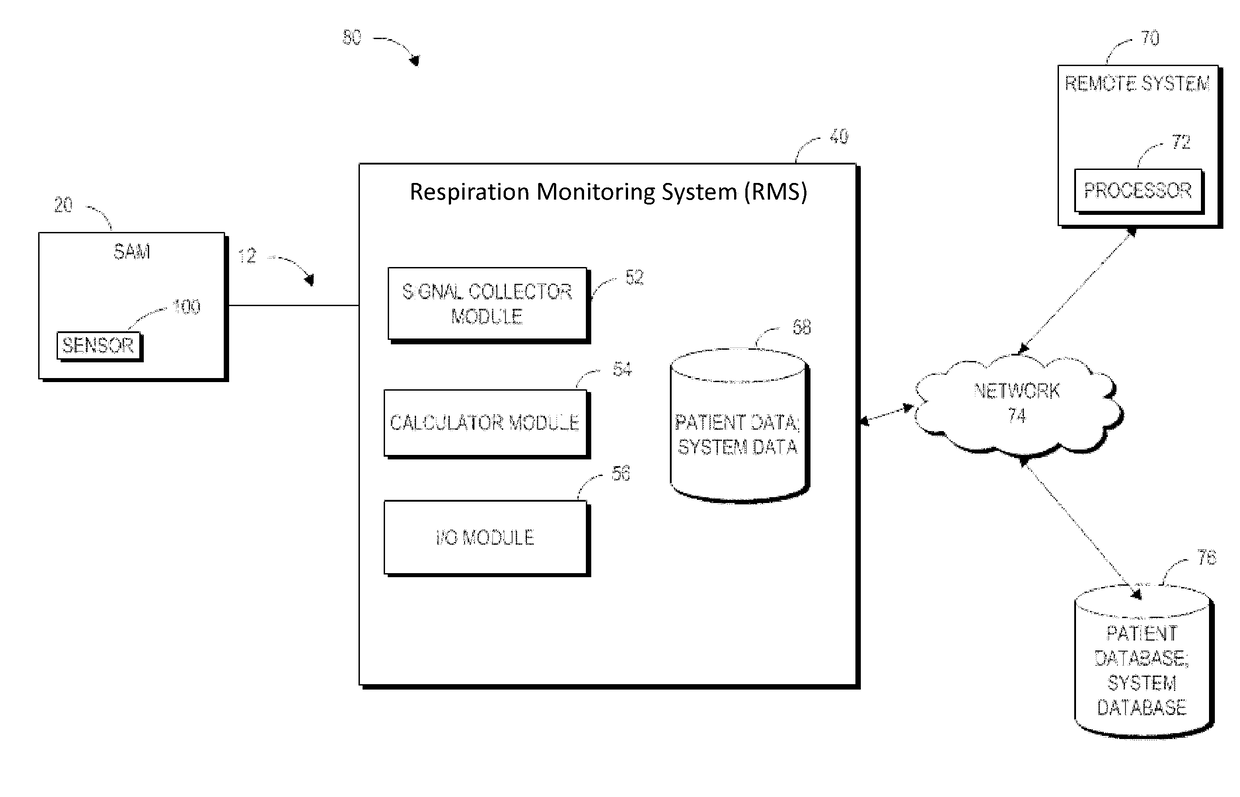
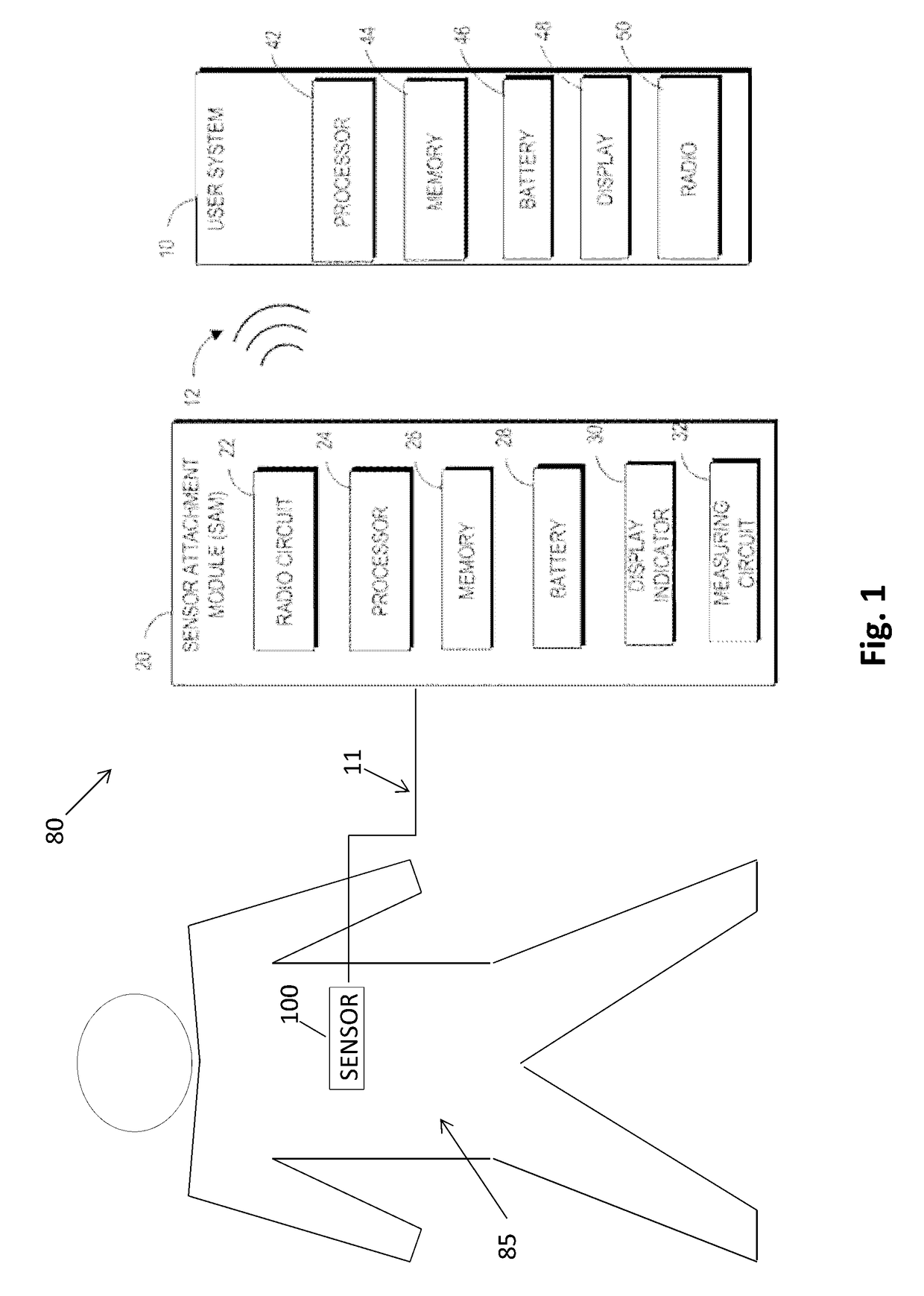
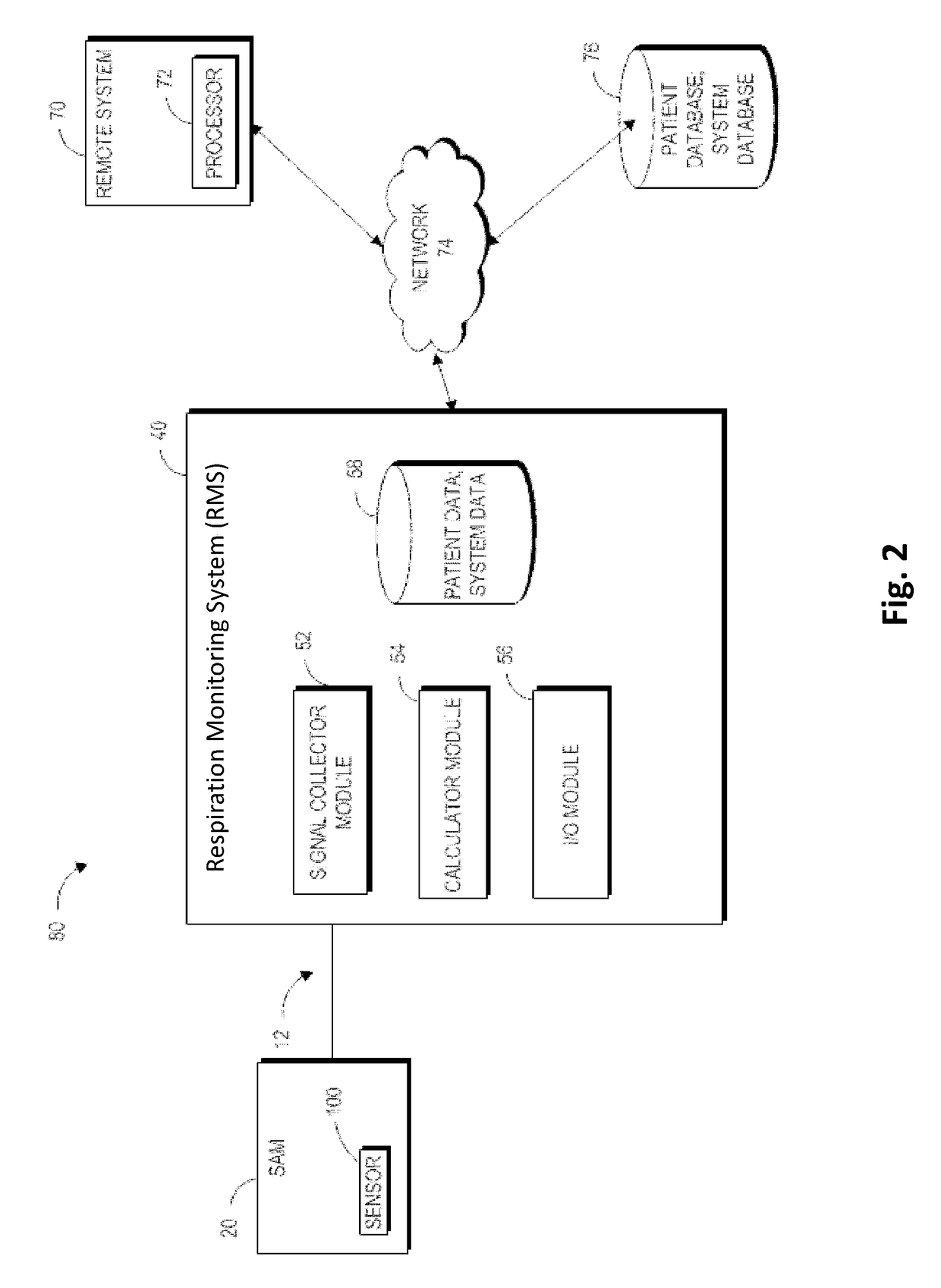
A mobile medical device for monitoring a respiratory condition in a subject, the medical device including: a sensor configured to be adhered to the skin of a patient, the sensor configured to yield a resistance signal that is modulated by movements of a chest of a patient during respiration; a sensor attachment module configured to receive the signal from the sensor and to output data to a mobile electronic device an indication of an adverse respiratory event. Also disclosed is a server for integrating data collected from a plurality of the mobile medical devices and a crowd-sourced respiration advisory system including a plurality of the mobile medical devices and a server for integrating data collected by the mobile medical devices.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Semi-physical simulation system for pressure adjustment of oxygen mask respiratory chamber
ActiveCN105974823AShorten the development cycleReduce mistakesSimulator controlApplication objectOxygen mask
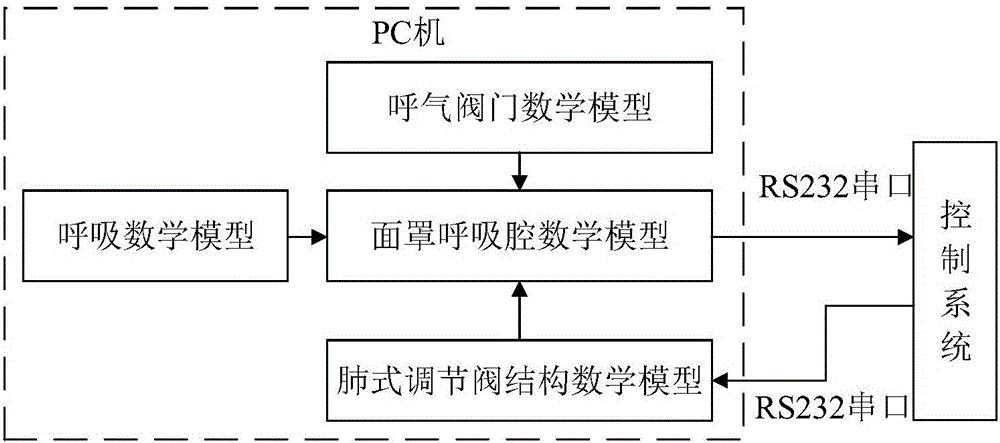
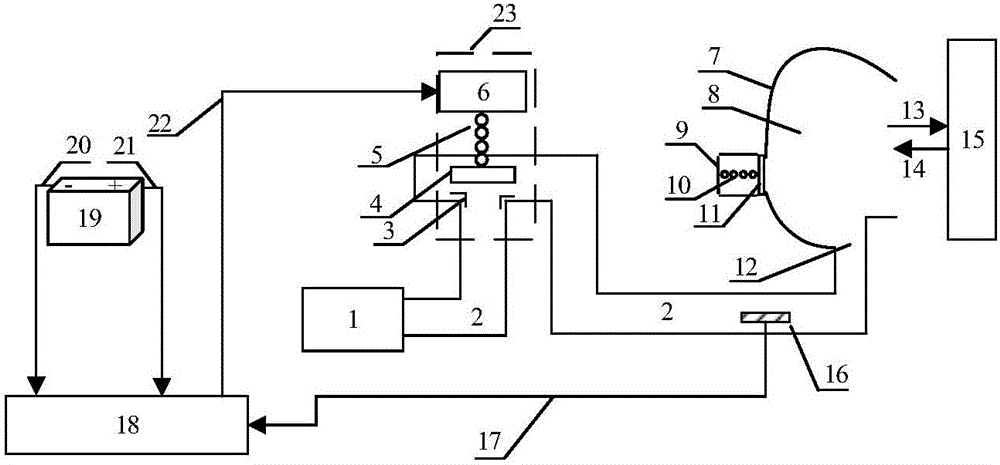
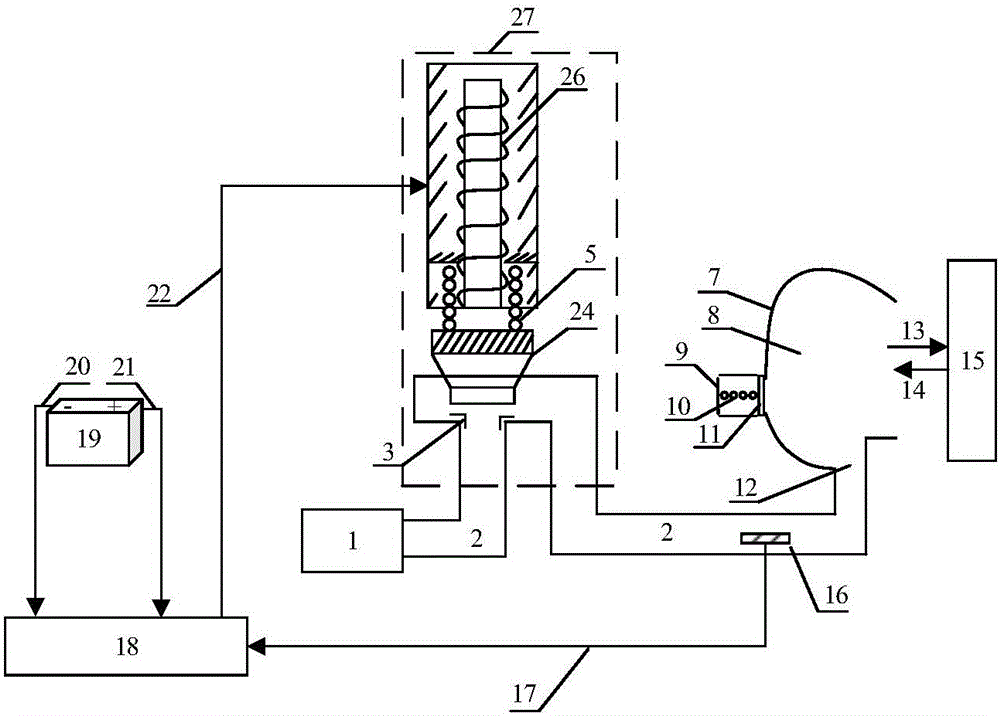
The invention provides a semi-physical simulation system for pressure adjustment of an oxygen mask respiratory chamber. A lung type regulating valve structure mathematical model, a respiratory valve mathematical model, a respiratory mathematical model and a mask respiratory chamber mathematical model are realized by a Matlab platform in a PC, and are respectively used for describing gas flow characteristics in a lung type regulating valve structure, a respiratory valve, a breathing process and a mask respiratory chamber. An STM32F407IGT6 microprocessor is used as control of the control system in the semi-physical simulation system, thereby operating a control algorithm. The PC communicates with the control system through an RS232 serial port. The semi-physical simulation system is obtained through comparing efficiencies of different control algorithms in the control plan development process of an oxygen mask respiratory chamber pressure regulator. The semi-physical simulation system has advantages of flexible structures of a control algorithm and an application object, high interface universality, etc. The semi-physical simulation system has advantages of realizing advanced problem finding and in-time settlement, shortening development period of a control solution, and saving cost.
Owner:雁翔和泰(深圳)科技有限公司
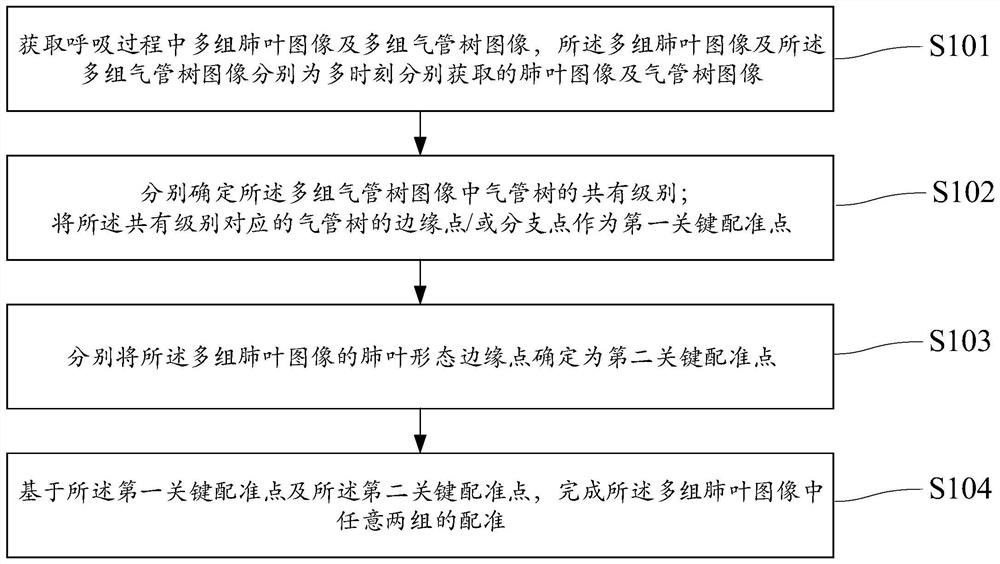
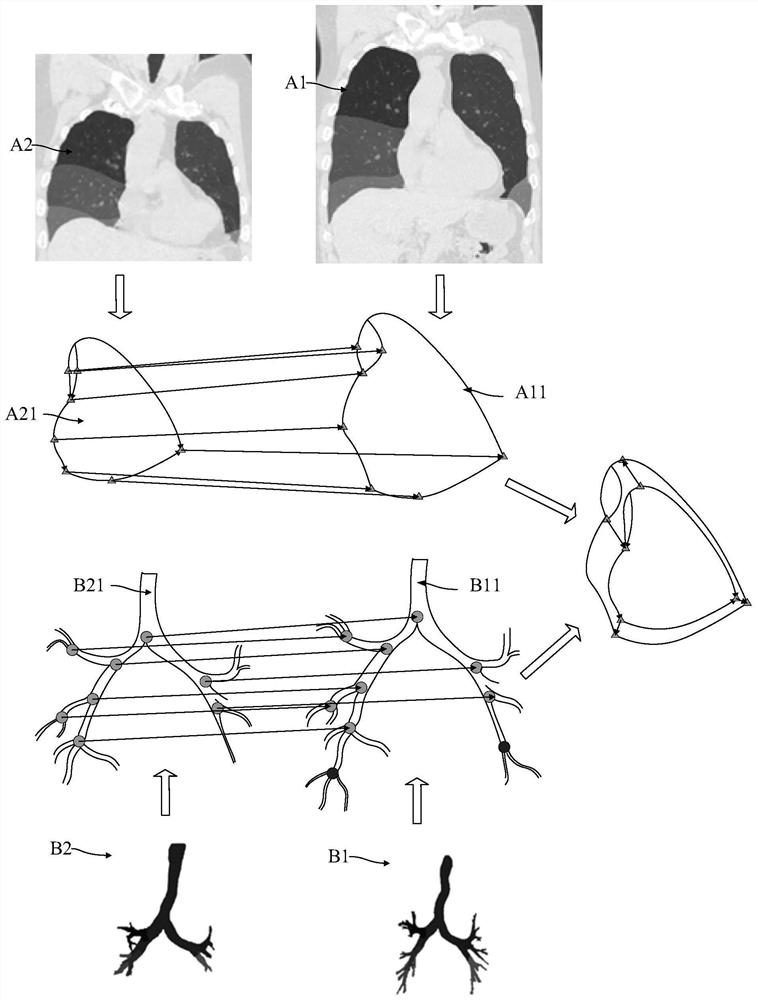
Lung lobe and tracheal tree-based registration method and device and storage medium
The invention relates to a lung lobe and tracheal tree-based registration method and device and a storage medium., and relates to the field of image processing. The method comprises the steps: obtaining a plurality of groups of lung lobe images and a plurality of groups of tracheal tree images in a breathing process, and enabling the plurality of groups of lung lobe images and the plurality of groups of tracheal tree images to be respectively lung lobe images and tracheal tree images obtained at a plurality of moments; determining common levels of tracheal trees in the plurality of groups of tracheal tree images respectively; taking an edge point / or a branch point of the tracheal tree corresponding to the common level as a first key registration point; determining lung lobe form edge points of the multiple groups of lung lobe images as second key registration points; and based on the first key registration point and the second key registration point, completing registration of any twogroups in the multiple groups of lung lobe images. The problem that lung lobe registration cannot be carried out or lung lobe registration is inaccurate at present is solved.
Owner:SHENZHEN TECH UNIV
Method and device for displaying focus in real time, electronic equipment and storage medium
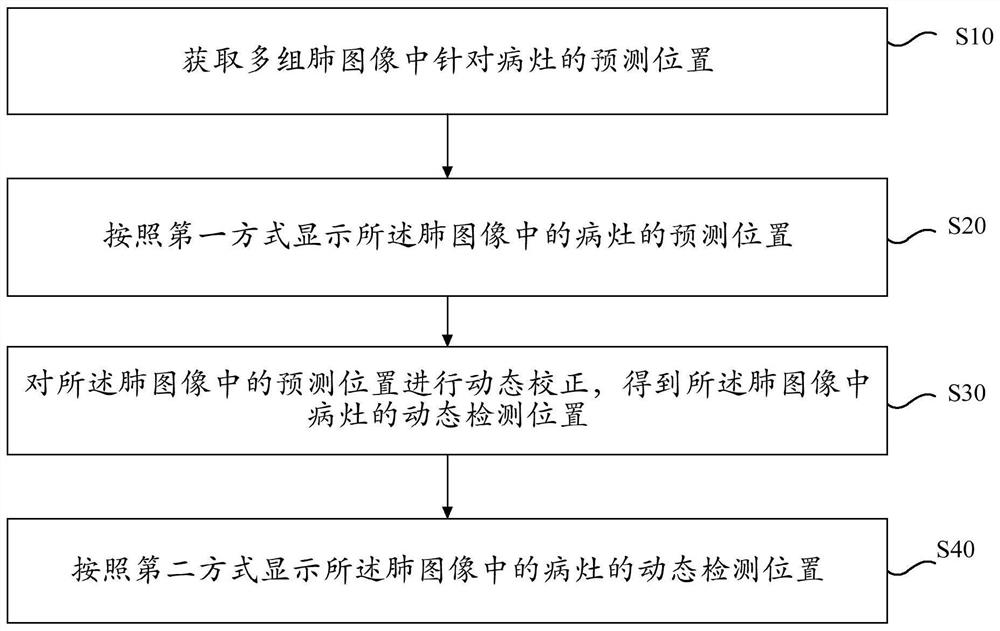
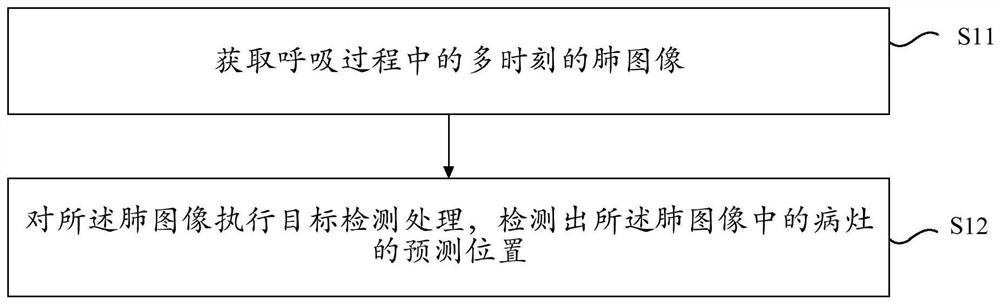
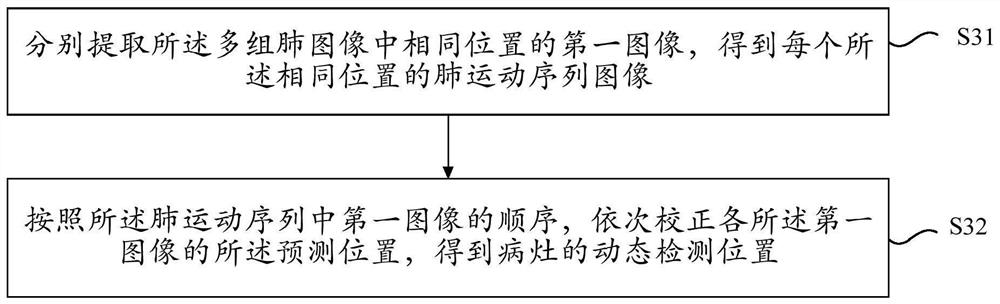
ActiveCN111724361ADoes not affect general observationDoes not affect detectabilityImage enhancementImage analysisEngineeringReal time display
The invention relates to a method and device for displaying a focus in real time, electronic equipment and a storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining a prediction position for thefocus in a plurality of groups of lung images, wherein the plurality of groups of lung images are lung images obtained at a plurality of moments in a breathing process; displaying a predicted position of a lesion in the lung image according to a first mode; performing dynamic correction on the prediction position in the lung image to obtain a dynamic detection position of a focus in the lung image, the dynamic correction being related to multi-moment information of the lung image; and displaying the dynamic detection position of the focus in the lung image in a second mode. According to the embodiment of the invention, the balance between the detection time and the detection precision is difficult to achieve under the condition of not influencing the discrimination and observation of thelesion in the medical image.
Owner:SHENZHEN TECH UNIV
Method and experimental device for measuring flow field of human upper respiratory tract based on particle image velocimetry (PIV) technology
ActiveCN102564728BAccurate measurementAerodynamic testingHydrodynamic testingResearch ObjectScattering effect
The invention discloses a method and an experimental device for measuring the flow field of a human upper respiratory tract based on a particle image velocimetry (PIV) technology. According to the invention, a true human upper respiratory tract model is taken as a research object, and the pumping effect of a vacuum pump is utilized to ensure that gas forms a channel in the model so as to simulate the respiratory process of a human lung. The method comprises the following steps of: scattering trace particles in the flow field, irradiating the flow field of the human upper respiratory tract model by using a sheet light source generated by a laser, aligning an area to be measured in a direction vertical to the sheet light source by using a cross-frame charge coupled device (CCD) camera, recording images of the particles during double pulse laser exposure according to the scattering effect of the trace particles on light, transmitting the images into a computer, computing and analyzing, solving the velocity of a fluid in the flow field of the human upper respiratory tract model by an autocorrelation or cross-correlation algorithm, and thus obtaining the characteristics of a vortex structure of the airflow of the flow field of the human upper respiratory tract during inspiration, an evolution form of the vortex structure, and the change and a distribution form of shear stress at the same time.
Owner:SANITARY EQUIP INST ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI PLA
Carbon fiber/carbon composite material C-shaped artificial tracheal stent with high bioactivity and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a carbon fiber / carbon composite material C-shaped artificial tracheal stent with high biological activity and a preparation method thereof. The C-shaped artificial tracheal stent is composed of a single C-shaped tracheal stent unit, or is composed of two or more C-shaped tracheal stent units which are combined side by side or assembled into a continuous hollow tubular structure with an axial notch in the side wall. The main body of the C-shaped tracheal stent unit is a U-shaped or pear-shaped hollow banded structure , and the hollow is filled with bioactive materials. The tracheal stent has good biocompatibility and mechanical properties, high surface hardness and small friction coefficient, has a communicated space for blood supply, has a similar elastic modulus tocartilage, has a high goodness of fit with the biomechanical property of a tracheal port, particularly it is similar to a tracheal cartilage ring structure, and during the breathing process, througha C-shaped opening,the tracheal stent can be retracted or expanded to meet physiological functions.
Owner:HUNAN TANKANG BIOTECH CO LTD
Bio-based multifunctional freshness protection package
InactiveCN106275770AEasy to produceLow costSynthetic resin layered productsBagsSurface layerEngineering
The invention discloses a bio-based multifunctional freshness protection package, comprising a bag body, wherein an opening is formed in one side of the bag body, the bag body consists of a weight bearing layer, a blocking and separating layer and an adsorbing and freshness protecting layer from outside to inside, and the adsorbing and freshness protecting layer comprises a surface layer micro-foamed film body capable of slowing down water loss and adsorbing ethylene. As the freshness protection package consists of the weight bearing layer, the blocking and separating layer and the adsorbing and freshness protecting layer from outside to inside, a bio-based freshness protecting layer can not only lock water that is generated during the respiratory process of vegetables and fruits but also adsorb the ethylene that is generated during the respiration, the blocking and separating layer can reduce water loss, the weight bearing layer can buffer external extrusion so as to reduce damage, and therefore the freshness protection and storage time for the vegetables and the fruits is prolonged greatly, and meanwhile the freshness protection package has the advantages of simplicity and convenience for production and low cost.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN ZHENHONG PACKAGING TECH
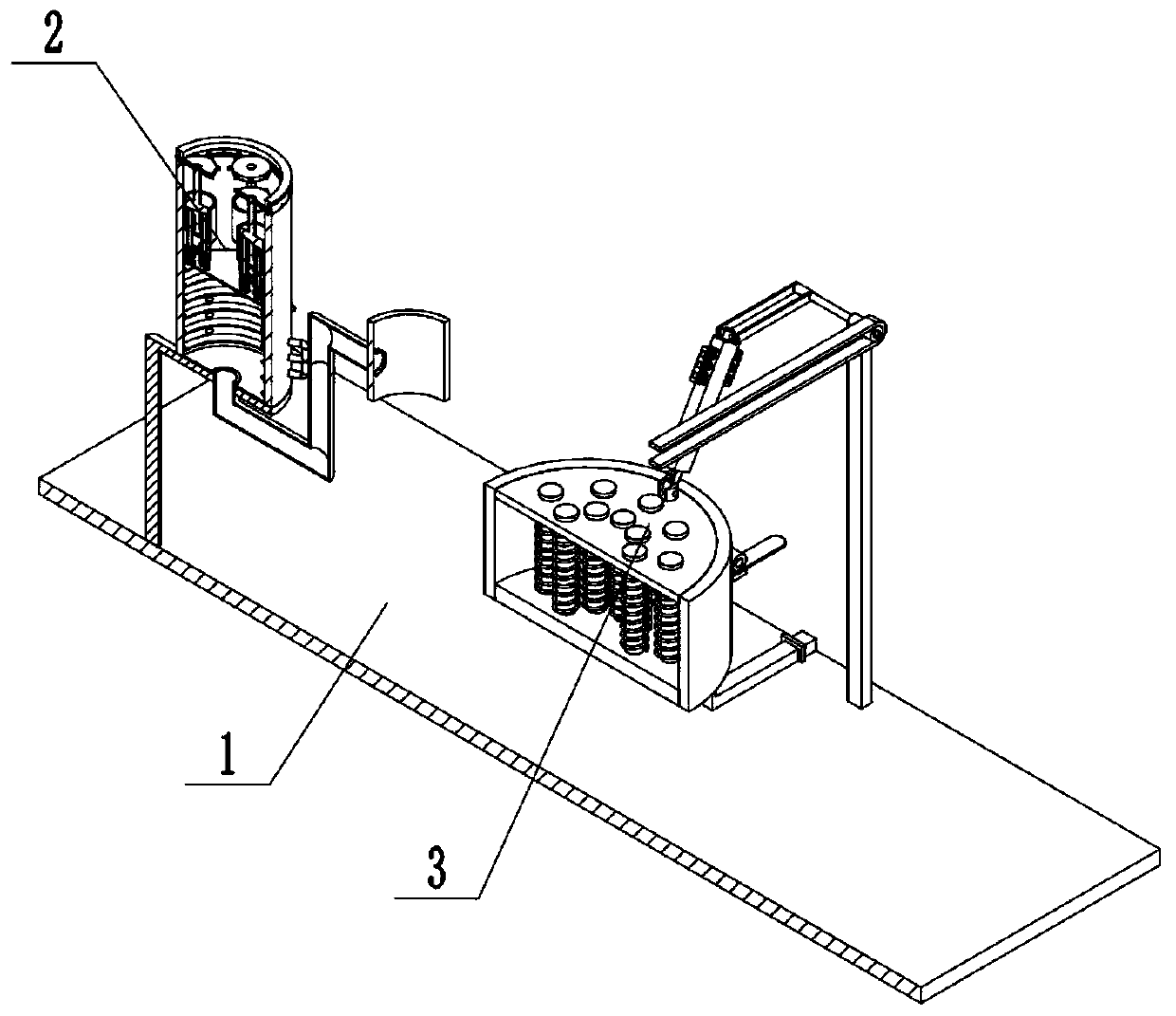
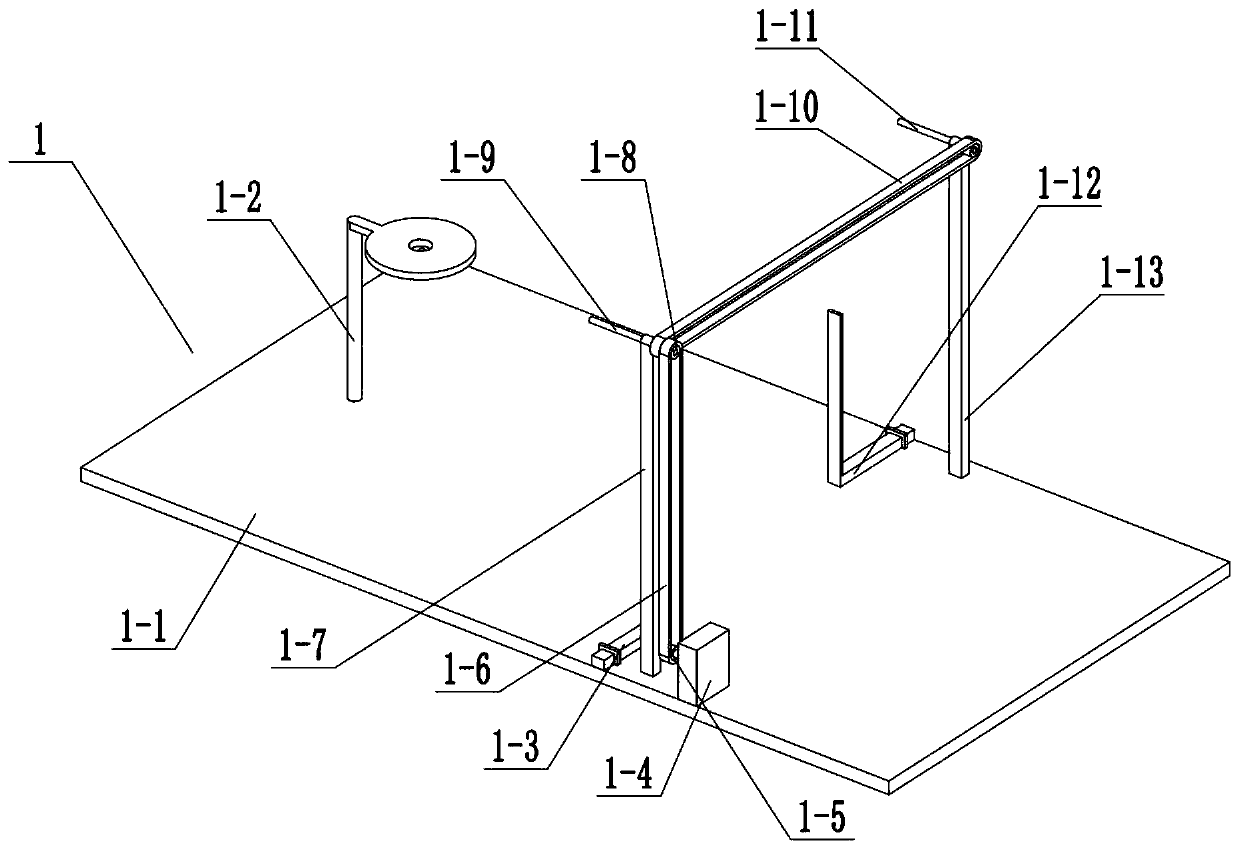
Autonomous respiration control system suitable for CT scanning
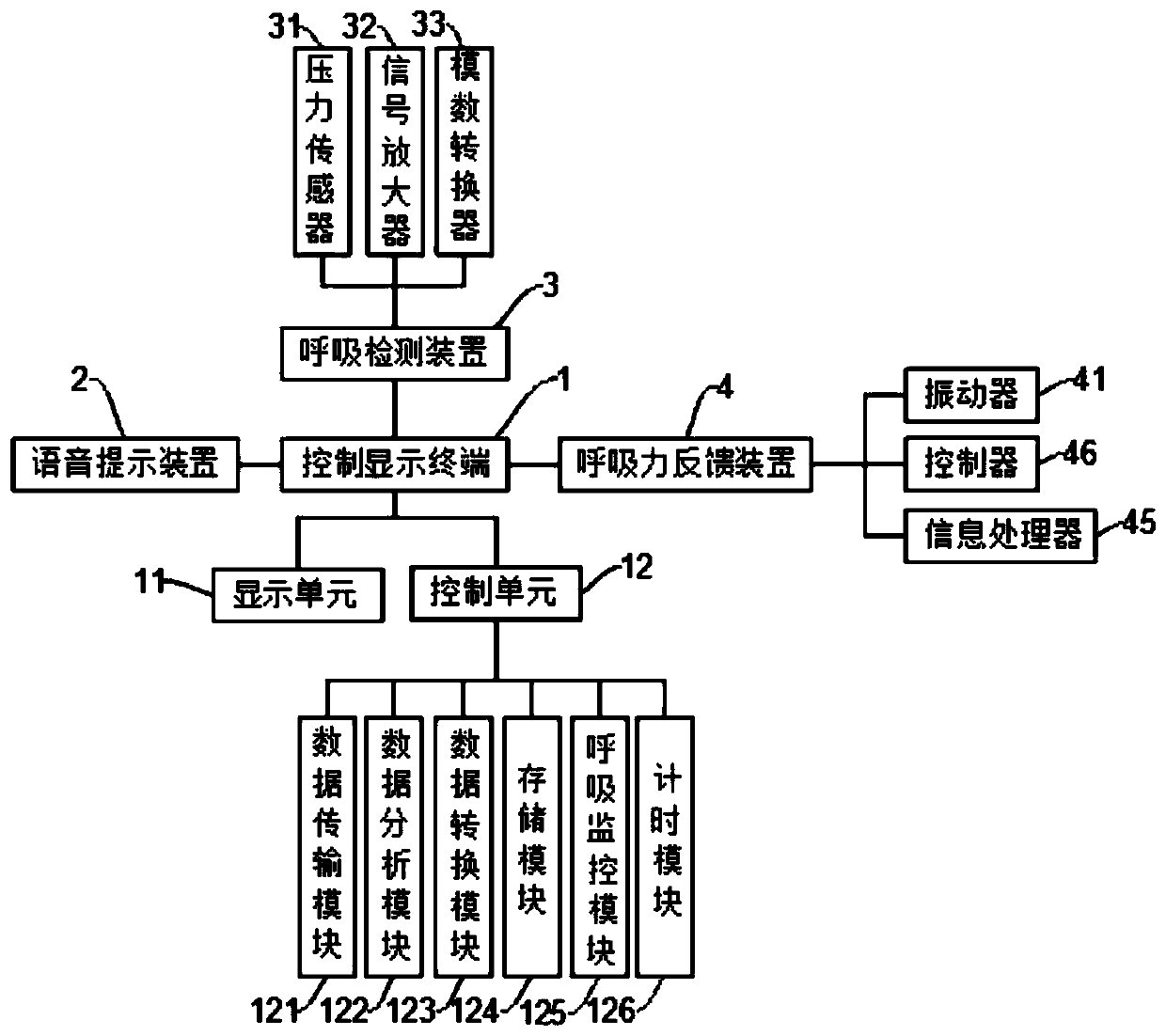
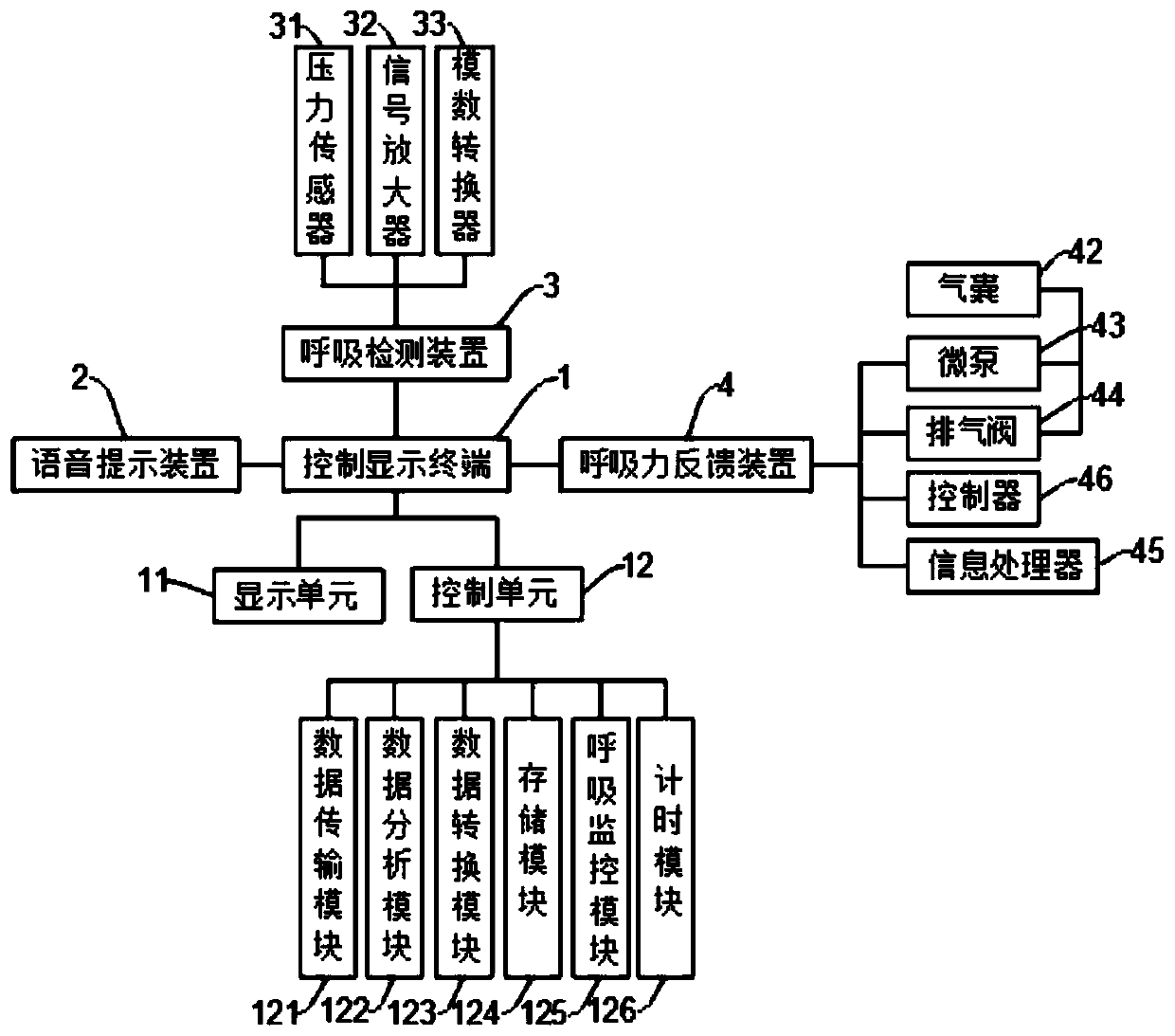
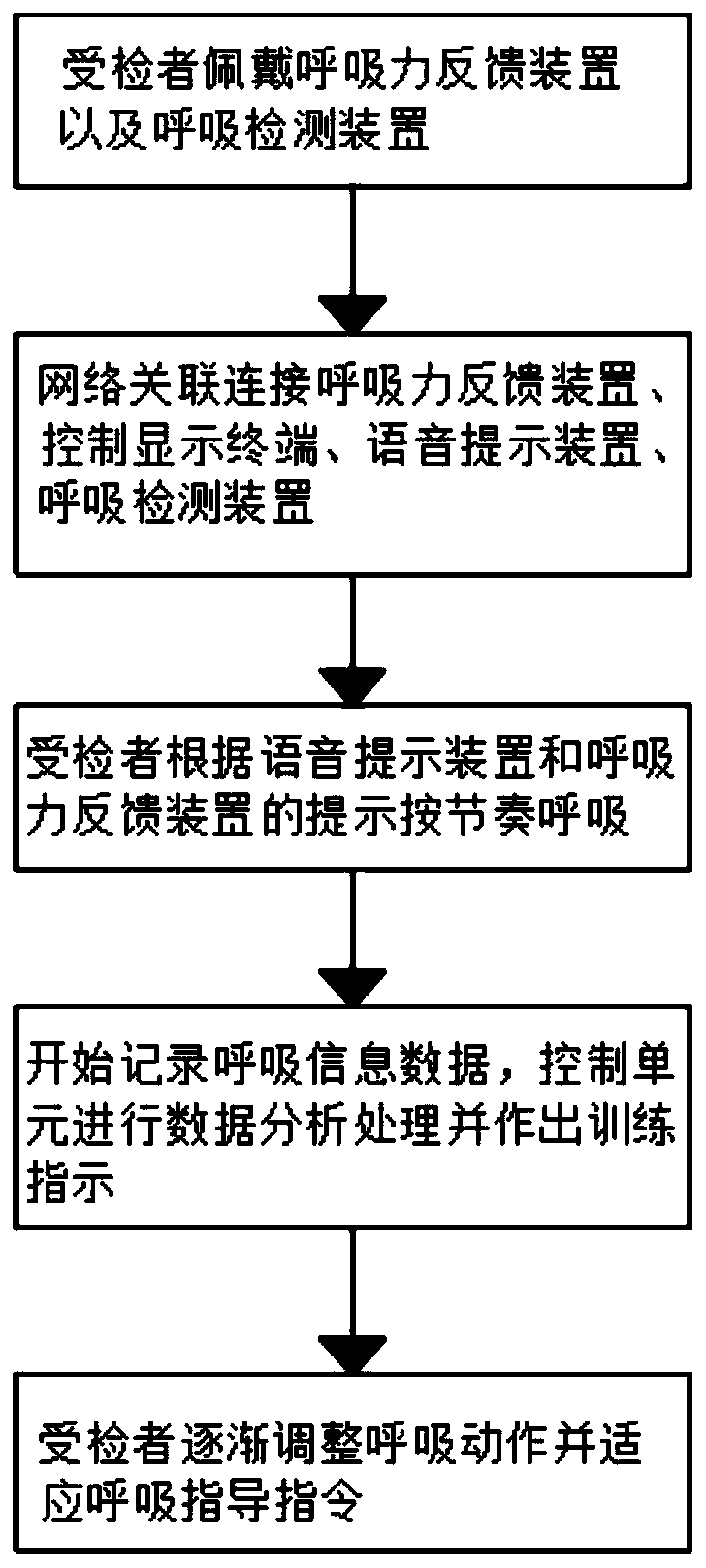
PendingCN111513750AReduce psychological burdenImprove adaptabilityPatient positioning for diagnosticsRespiratory organ evaluationPhysical medicine and rehabilitationAutonomous breathing
The invention relates to simulated training equipment for adjusting respiration, in particular to an autonomous respiration control system suitable for CT scanning. The control system comprises a control display terminal, a voice prompt device, a respiration detection device and a respiratory force feedback device; the control display terminal sends a respiration guidance instruction to the voiceprompt device and send a somatosensory feedback signal to the respiratory force feedback device, and the respiratory force feedback device executes a somatosensory feedback action according to the somatosensory feedback signal; the respiration detection device is adopted to detect a pressure signal generated in the respiration process, the pressure signal is analyzed and output by the control display terminal, and respiration action which does not conform to the respiration guidance instruction is corrected, so that a subject exercises to self-adjust the respiration frequency in the simulatedtraining process; and the wearable respiration force feedback device is adopted to execute the somatosensory feedback action, the respiration rate is adjusted according to the somatosensory feedback action, and the respiratory action can be correctly adjusted after multiple times of training of a subject.
Owner:CANCER CENT OF GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
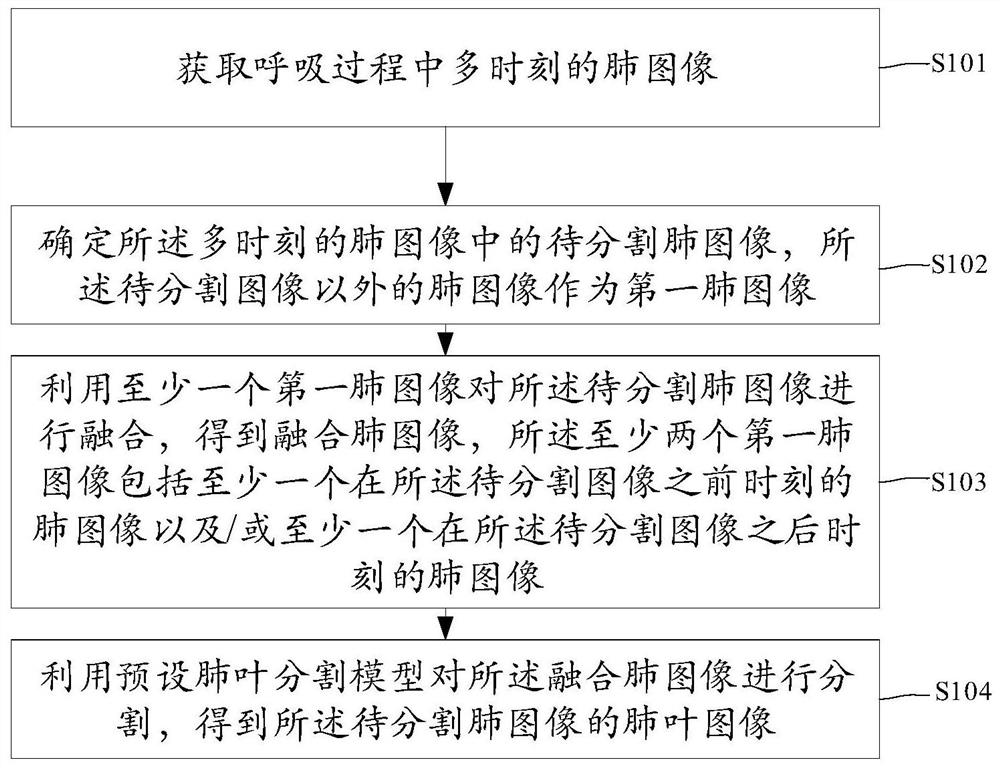
Lung lobe segmentation method and device and storage medium
ActiveCN111724360ASolve the problem of poor segmentation effectImage enhancementImage analysisLung lobeImaging processing
The invention discloses a lung lobe segmentation method and device and a storage medium, and relates to the field of medical image processing, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining lung imagesat multiple moments in a breathing process; determining a to-be-segmented lung image in the multi-moment lung image, wherein the lung image except the to-be-segmented image is used as a first lung image; fusing the to-be-segmented lung image by using at least one first lung image to obtain a fused lung image, the at least two first lung images comprising at least one lung image at a moment beforethe to-be-segmented image and / or at least one lung image at a moment after the to-be-segmented image; and segmenting the fused lung image by using a preset lung lobe segmentation model to obtain a lung lobe image of the lung image to be segmented. The problem that the segmentation effect is poor due to the fact that feature information of lungs (leaves) is insufficient at present is solved.
Owner:SHENZHEN TECH UNIV
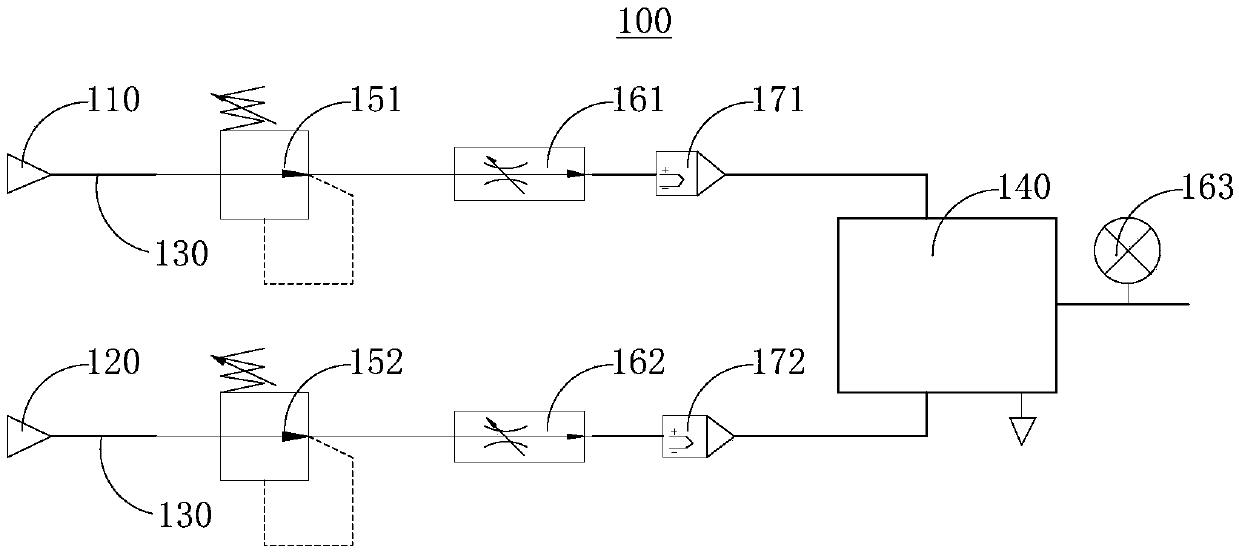
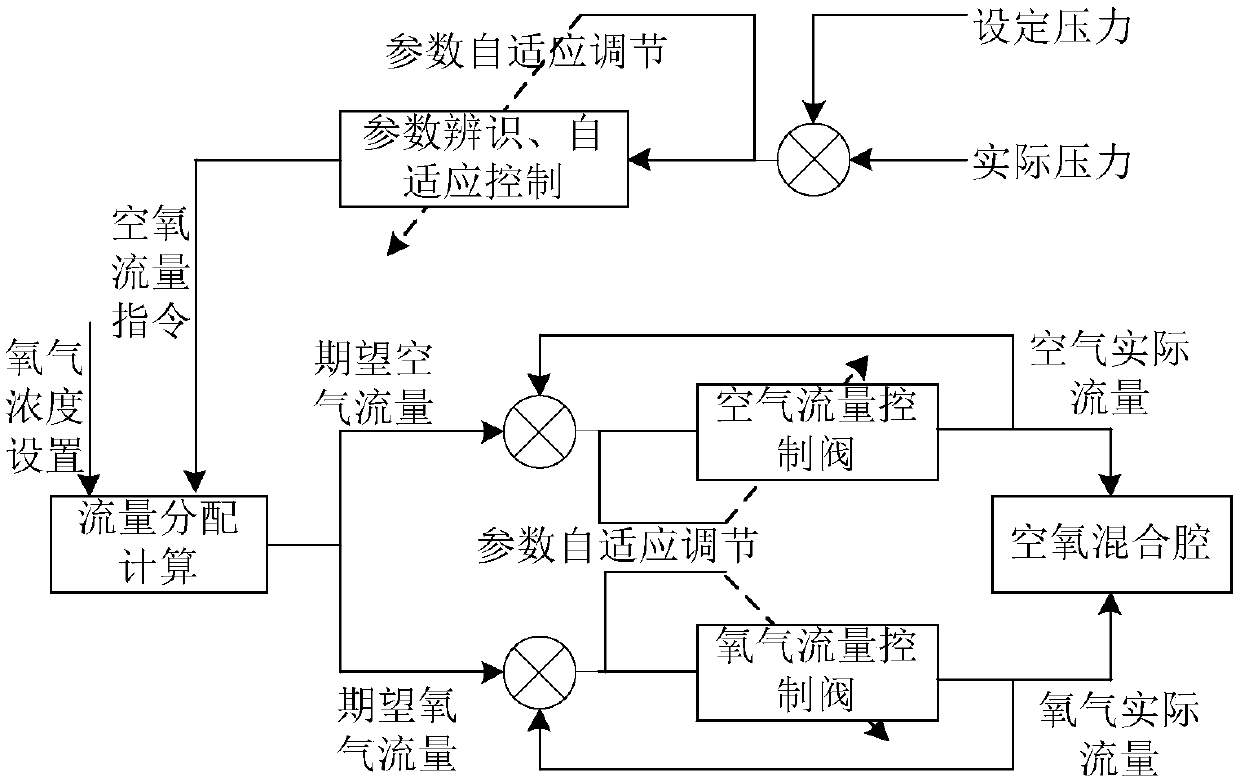
Adaptive pressure and oxygen concentration control method
The application relates to an adaptive pressure and oxygen concentration control method. The adaptive pressure and oxygen concentration control method comprises the steps of S10, carrying out online identification on respiratory process dynamic parameters, and respectively calculating a linearized gas path damping coefficient Rrs and a linearized dynamic smoothing coefficient Crs; S20, estimatingadaptive parameters theta according to the linearized gas path damping coefficient Rrs and the linearized dynamic smoothing coefficient Crs; S30, calculating the air-oxygen mixed flow control signal ue in combination with the adaptive parameters theta to implement pressure adaptive control; and S40, calculating an air flow control signal uea and an oxygen flow control signal ueo in combination with the adaptive parameters theta to achieve adaptive control over oxygen concentration. The adaptive pressure and oxygen concentration control method synchronizes the pressure maintenance process withthe oxygen concentration maintenance process. The adaptive pressure and oxygen concentration control method is simple and easy to implement, and can ensure the simultaneous adjustment of the pressureand the oxygen concentration without increasing the complexity of a ventilator, thereby ensuring the clinical use effect of the ventilator.
Owner:SHENZHEN COMEN MEDICAL INSTR
Newborn rescue table
The invention relates to the field of medical treatment, in particular to a newborn rescue table which can blow air into the body of a newborn through a breathing assembly to complete the breathing process in newborn rescue. The cardiopulmonary resuscitation process in neonatal rescue can be completed through a cardiopulmonary resuscitation assembly; the use position in newborn rescue can be adjusted; the newborn rescue table comprises a bottom plate assembly, the breathing assembly and the cardiopulmonary resuscitation assembly, the use position of the cardiopulmonary resuscitation assembly is adjusted according to the actual condition; a pressing outer frame is subjected to manual pulling, the pressing outer frame drives a side wall rack to move between an adjusting gear I and the matched outer frame; the transverse use position of the cardio-pulmonary resuscitation assembly is adjusted, meanwhile, the pressing outer frame is vertically pulled along a first rectangular sliding rod Iin a sliding mode, the distance between the cardio-pulmonary resuscitation assembly and the bottom plate body is changed under the action of the first rectangular sliding rod I and a second adjustinggear, and then the use height of the cardio-pulmonary resuscitation assembly is adjusted.
Owner:商丘市第一人民医院
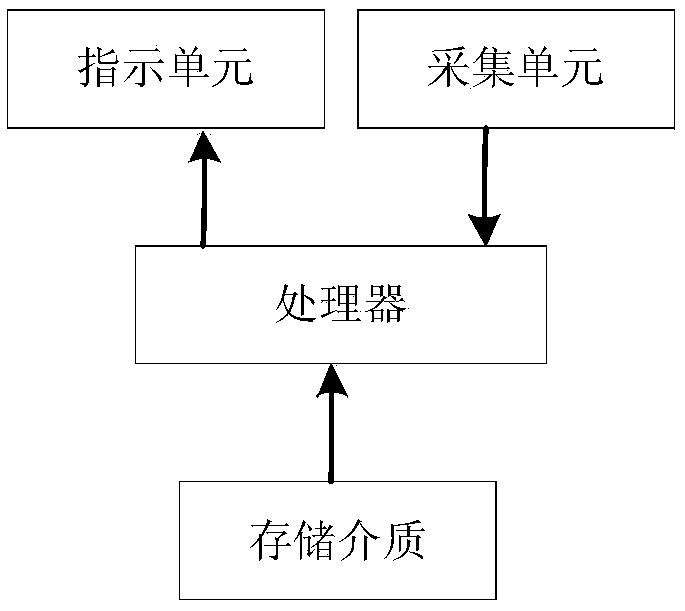
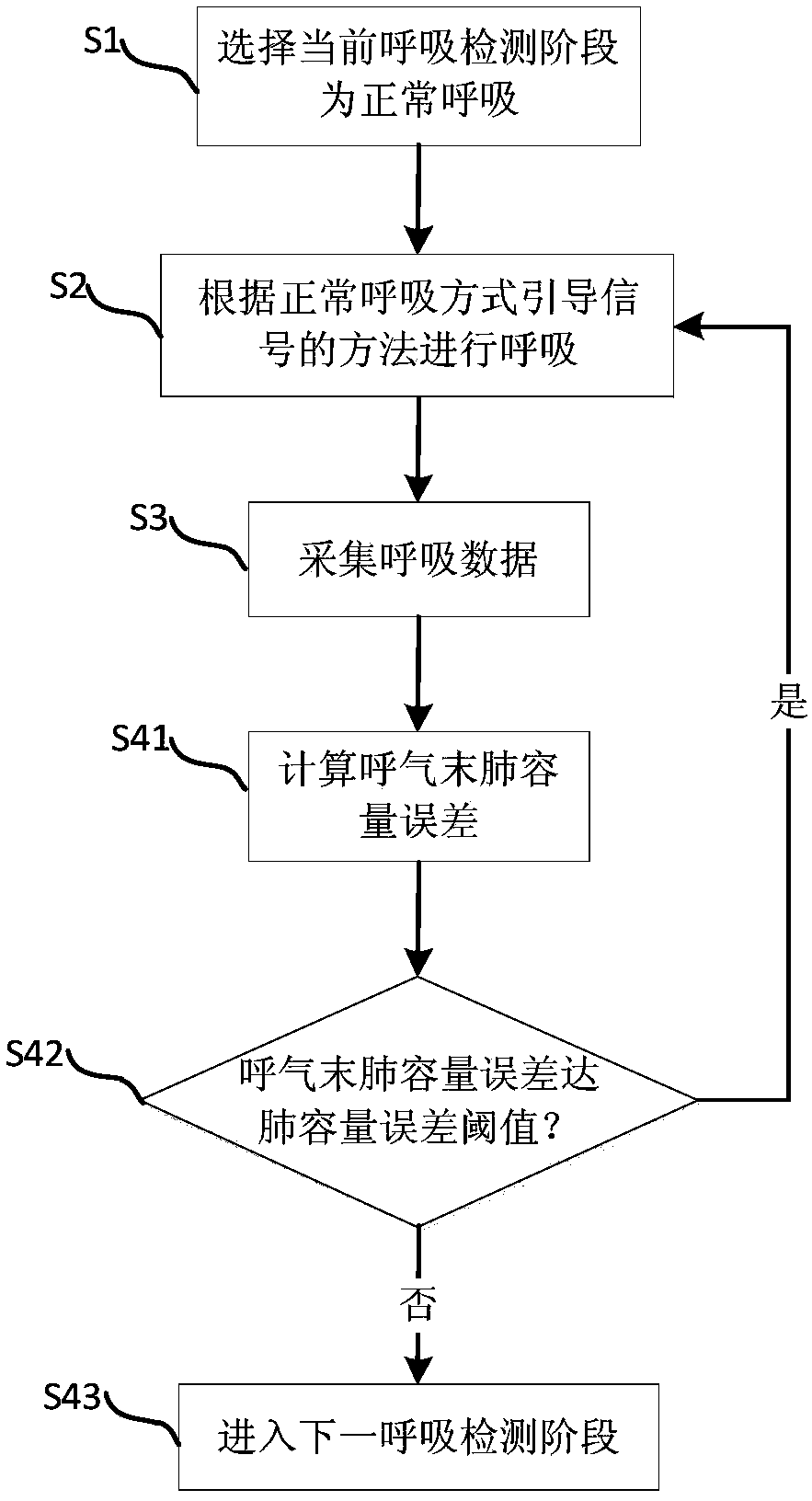
Lung function testing system and method
InactiveCN108968964AAvoid invalid situationsImprove accuracyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsIntensive care medicinePulmonary function testing
The invention provides a lung function testing system. The system comprises an indicating unit, a collecting unit, a processor and a storage medium; the indicating unit is used for outputting respiratory mode guiding signals; the collecting unit is used for collecting respiratory data in the respiratory process of a testee; the processor is connected with the indicating unit and the collecting unit; the storage medium is used for storing multiple instructions, wherein when the instructions are executed by the processor, the processor calculates the respiratory data and compares the data with apreset condition to obtain a processing result, and the indicating unit is controlled to output the respiratory mode guiding signals according to the processing result. The invention further providesa lung function testing method. By arranging the indicating unit on the lung function testing system, the indicating unit outputs the respiratory mode guiding signals to guide the testee in respiration, the difference in artificial guidance is reduced, and the application range of lung function testing is greatly expanded.
Owner:SHENZHEN MEIHAO CHUANGYI MEDICAL TECH
Pulmonary percutaneous puncture navigation method and system
ActiveCN113893033AHigh precisionReduce the risk of tumor punctureSustainable transportationSurgical needlesImage segmentationSkin tumours
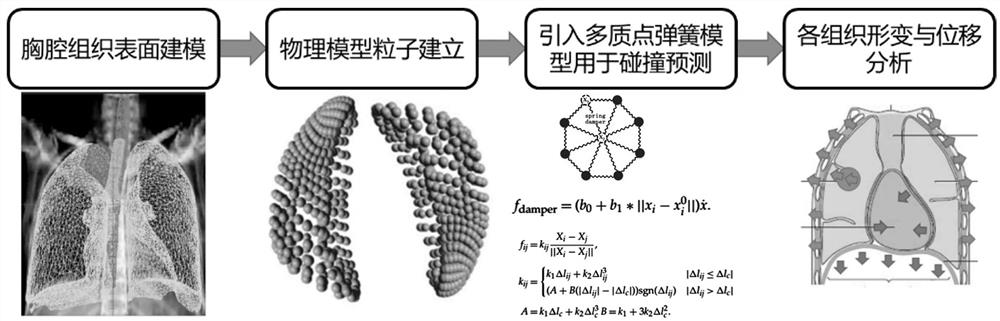
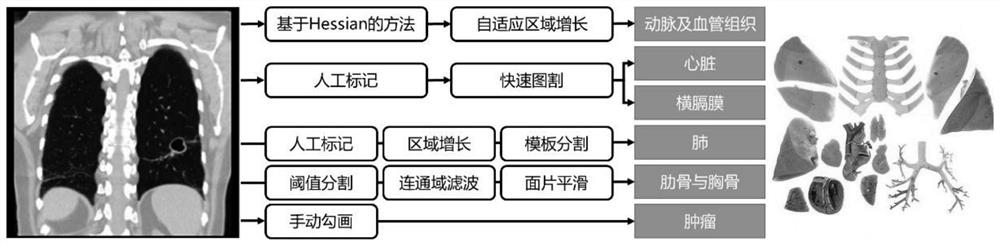
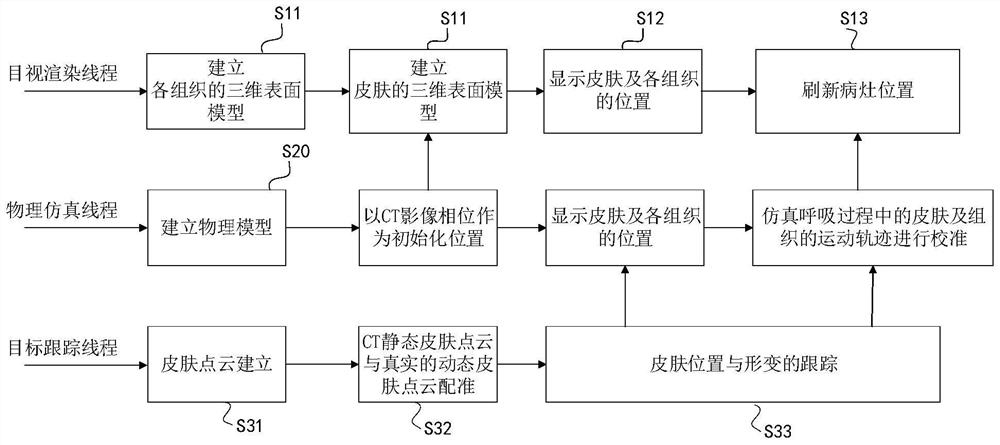
The invention provides a pulmonary percutaneous puncture navigation method. The method comprises the following steps: inputting pulmonary static image data of a target patient, and obtaining a three-dimensional surface model of skin and tissues by adopting an image segmentation method; establishing a physical model by using the three-dimensional surface model, and simulating movement tracks of the skin and each tissue in a respiration process; and matching the simulated movement tracks with a real-time respiration scene of the patient, and performing linked real-time virtual-real-fused display on the skin and each tissue. According to the method, under the condition that only static CT image data exist, the movement tracks of the skin and all the tissues in the respiration process are simulated; the movement tracks are matched with an actual respiration position of the patient and a real position is displayed; when a skin surface model in a CT image is matched with an actual skin surface, puncture reminding information is generated, and the tumor puncture precision is improved; and dynamic movement tracks of simulated skin, tumors and other tissues and actual respiration shapes are displayed in a linked mode, and doctors are helped to conduct high-efficiency and high-accuracy puncture.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
Heart rate monitoring device for heart disease patients
InactiveCN112957020AAvoid heart attack recurrenceEnhance myocardial contractilityElectrotherapySensorsEngineeringEmergency medicine
The invention relates to the technical field of heart rate monitoring, and discloses a heart rate monitoring device for heart disease patients. The heart rate monitoring device comprises monitoring seats; a wearing seat is movably connected to the outer surface of each monitoring seat; an air inlet is fixedly connected to the outer surfaces of the wearing seats; a rotating blade disk is rotatably connected to the position, located in each wearing seat, on the side surface of the air inlet; a first limiting rope is movably connected to the outer surface of each rotating blade disk; a telescopic rod is movably connected to the other end of each first limiting rope; an elastic seat is movably connected to the side surface of each telescopic rod; a bearing seat is fixedly connected to each of the upper side and the lower side of each telescopic rod; a second limiting rope is movably connected to the outer surface of each bearing seat; and a fixed pulley is rotationally connected into each monitoring seat. During use, a patient can be comfortably massaged in the breathing process, so that the patient is kept in a stable mood, and the phenomenon that the patient is stimulated to cause poor breath to cause heart disease relapse is avoided.
Owner:丛丽娟
Measuring method for lung electrical tomography
InactiveCN106821379AImprove imaging effectCompounds screening/testingDiagnostic recording/measuringTomographyOxygen
The invention relates to a measuring method for lung electrical tomography. The method comprises the steps that materials to be sucked into the lung are contained in a container, one of a heating device or dispersion devices including an ultrasonic device are selected according to different materials to be sucked into the lung, the materials to be sucked into the lung are mixed with oxygen or air and dispersed into the container, and when the lung electrical tomography is performed, a person to be tested sucks the materials dispersed into the container into the lung through the respiratory organ; the materials to be sucked into the lung can change the specific conductance of lung pulmonary alveoli in the respiratory process.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Carbon fiber C-ring tracheal stent and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a carbon fiber C-ring tracheal stent and a preparation method thereof. According to the method, carbon fiber bundles are woven into carbon fiber woven strips, then the carbon fiber woven strips are sequentially subjected to mold auxiliary baking shaping, medium ultrasonic treatment and DLC or F-DLC coating deposition, and the carbon fiber C-ring tracheal stent is obtained. The carbon fiber C-ring tracheal stent has good mechanical properties, the surface layer contains F active atoms, the biocompatibility is better, the surface layer is high in hardness, small in friction coefficient and not prone to being damaged, the carbon fiber C-ring tracheal stent has elastic modulus similar to cartilage, when the carbon fiber C-ring tracheal stent is connected with a tracheal port, the biomechanical property goodness of fit is high, biological fixation can be achieved, especially, the tracheal stent is similar to a tracheal cartilage ring structure, through a C-shaped opening, the tracheal stent can be contracted and extended in a breathing process, and requirements of physiological functions are met.
Owner:HUNAN TANKANG BIOTECH CO LTD
Method and apparatus for measurement of cardiopulmonary function
ActiveUS10799125B2Accurate measurementEliminate inaccuraciesRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsAnatomical dead spaceEngineering
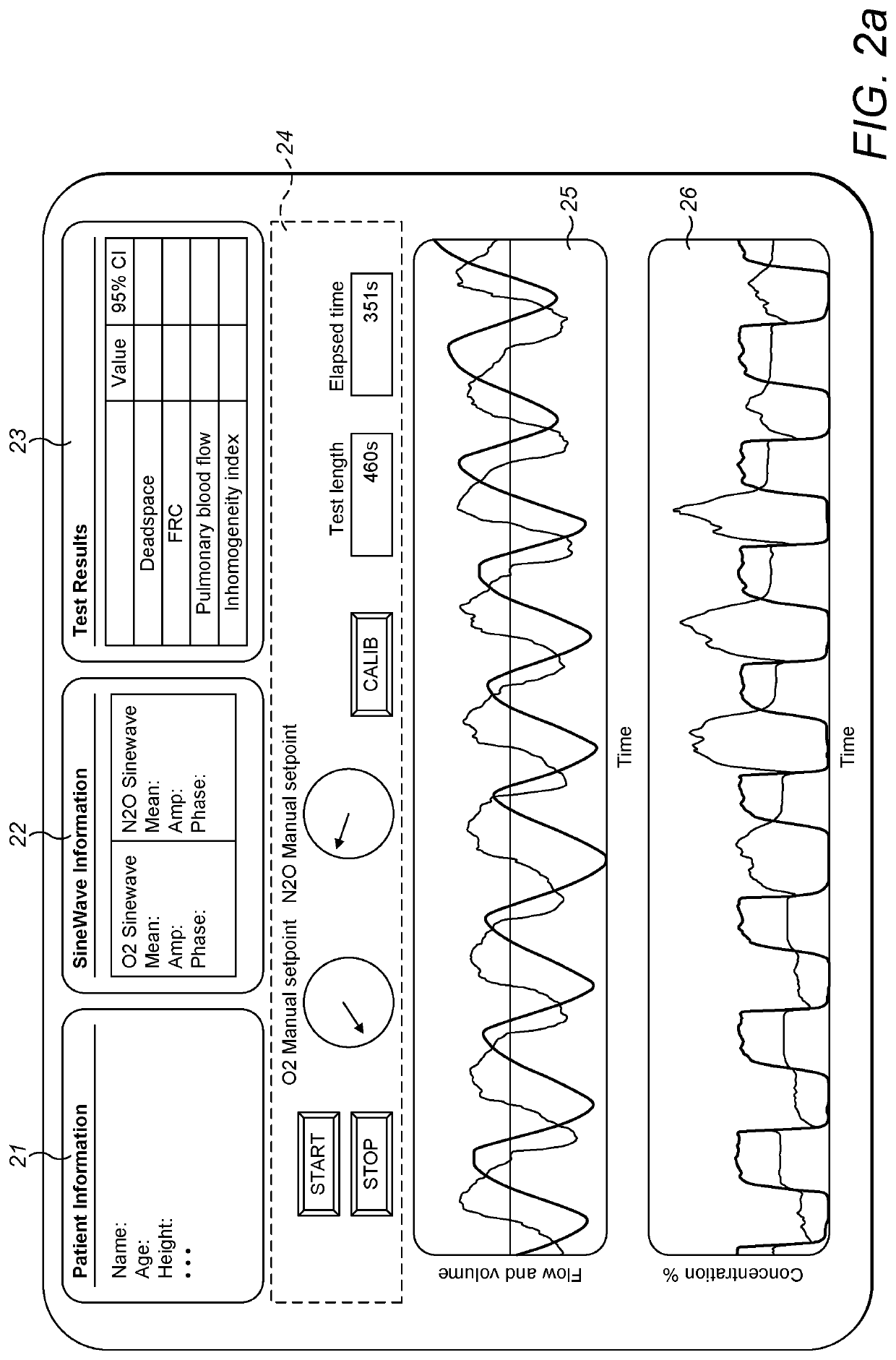
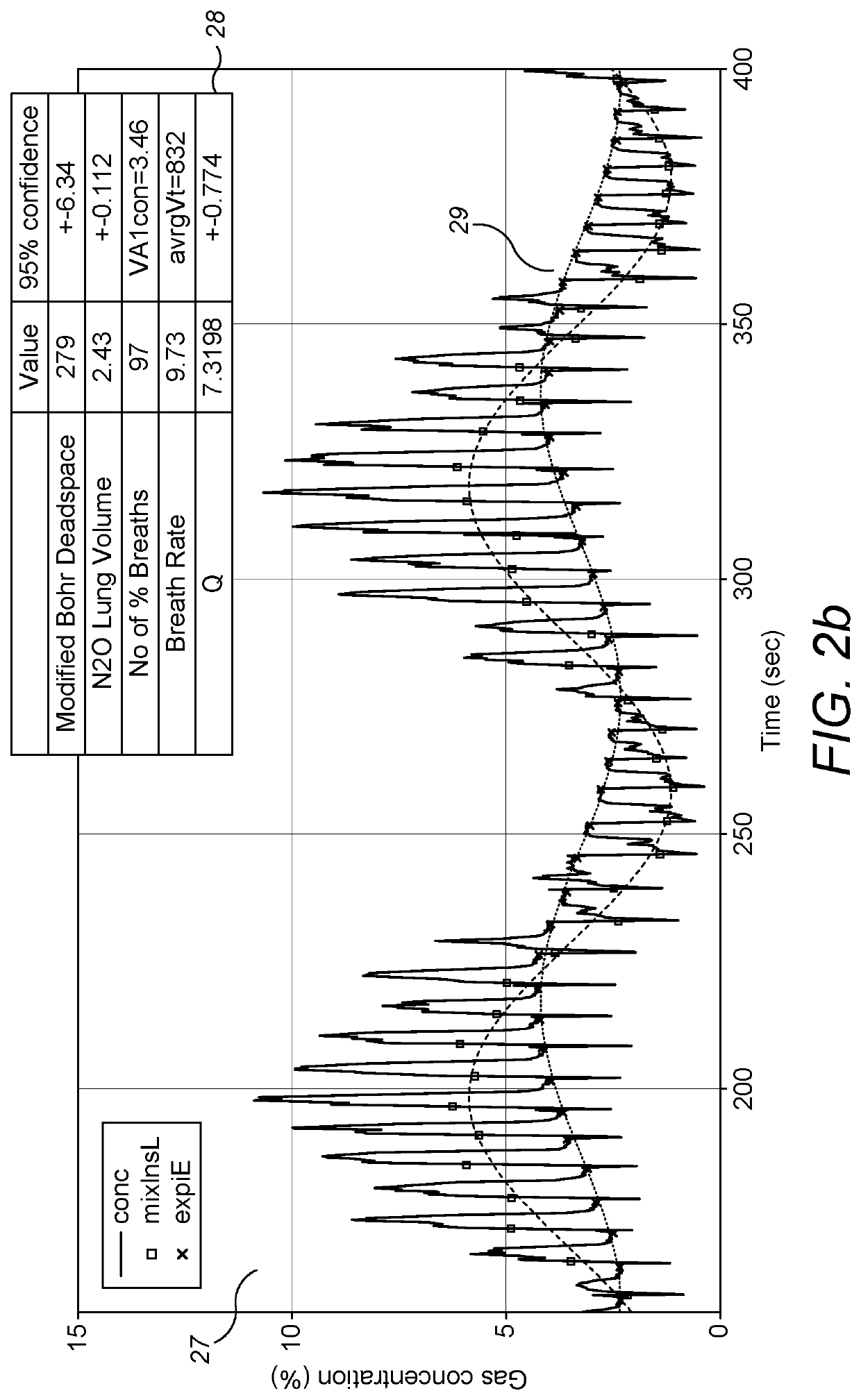
A method for measuring anatomical dead space in a lung, the method comprising: (a) providing, in a supply of inspired gas, at least one indicator gas for inhalation by a patient during a test, the concentration of the indicator gas being controlled such as to follow a sinewave pattern over successive breaths; (b) measuring, over successive breaths, the flow rate and concentration of the indicator gas during both inspiration and exhalation of the patient; (c) fitting sinewave envelopes to the measured concentration values of the indicator gas over the successive breaths and, from the fitted sinewave envelopes, determining the inspired concentration, the mixed expired concentration, and the end expired concentration in respect of the indicator gas for each breath; and (d) calculating the anatomical dead space for each of a plurality of inspirations based on a conservation-of-mass principle. Also provided is a test apparatus for carrying out such a method, and a computer program or set of instruction code which, when executed, causes a processor to implement such a method.
Owner:PHAN PHI ANH +2
A sterilizing type respiratory assisted therapeutic apparatus
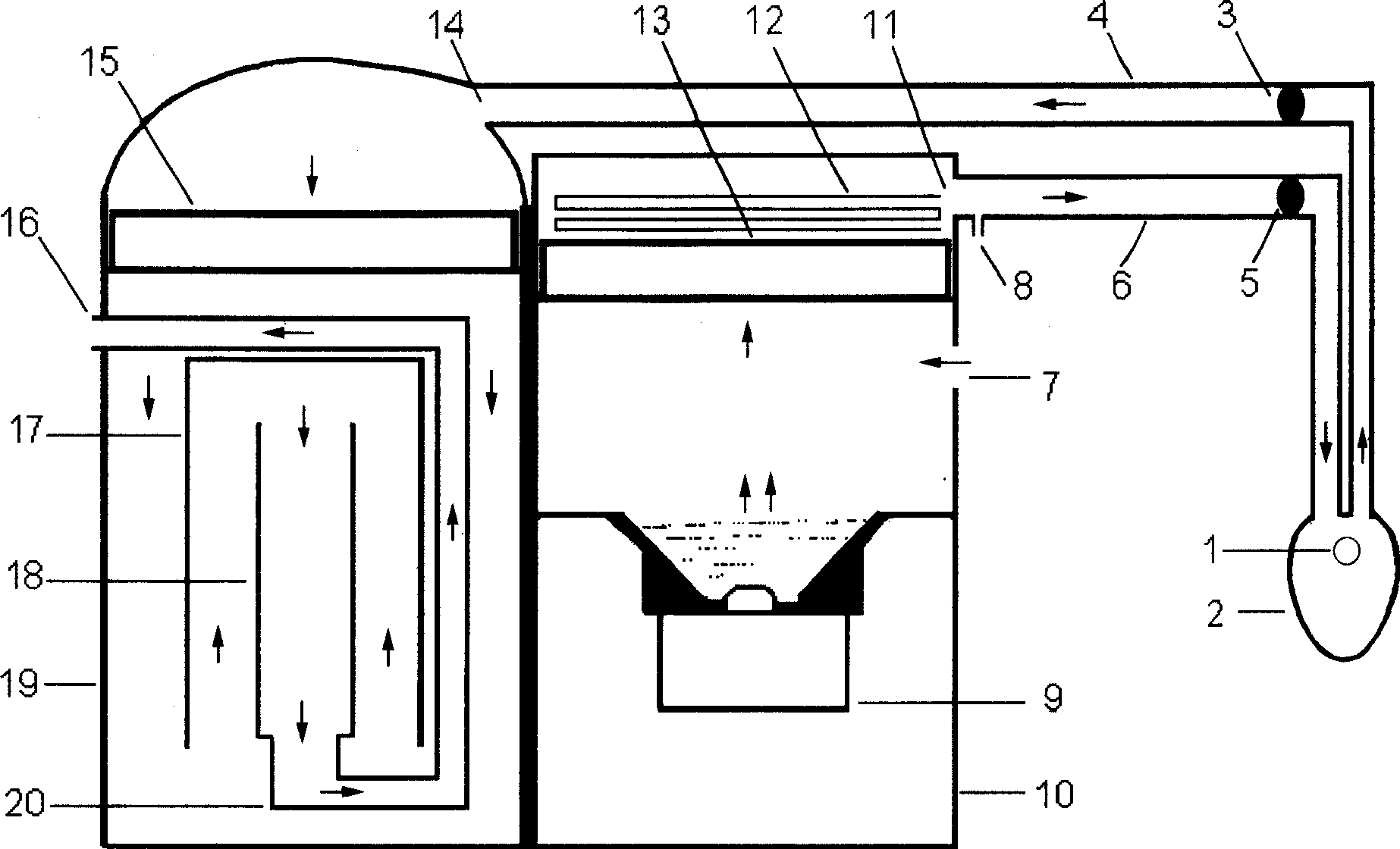
InactiveCN100464797CIntelligentAbsolute control of pollutionRespiratorsFire rescueDiseaseTopical treatment
A sterilization-type auxiliary respiratory machine for killing the pathogenic bacteria in the air exhalated by patient, helping respiration of patient and treating the local lung disease is composed of an air supplying case consisting of ultrasonic atomizer, fan and heating band for heating and moistening the air containing medicine, an exhaust case consisting of fan, thermal sterilizing tube, heat isolating ringand heat radiating tube, a respiratory mask, and two pipelines.
Owner:刘里远
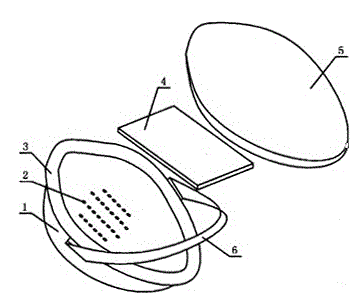
Multi-layer filtering mask
The invention discloses a multi-layer filtering mask. The multi-layer filtering mask comprises a supporting body, an elastic fixing belt, a filtering layer, a soft sponge and a dustproof layer; the supporting body is a plastic housing; uniformly-arranged through holes are arranged in the supporting body, corresponding to a mouth part and a nose part; the elastic fixing belt is connected to two sides of the supporting body; the filtering layer covers the through hole from the inner side and is adhered to the inner surface of the supporting body; the soft sponge is adhered to the outer edge of the supporting body, in contact with the face; the dustproof cover covers the filtering layer, and four edges of the dustproof layer are clamped between the soft sponge and the supporting body. The multi-layer filtering mask has the advantages that the filtering layer and the movably-connected dustproof layer form a filtering system for filtering air for breathing by a plurality of layers, so as to ensure the quality of the air for breathing, and the invasion of dust, bacteria and the like to a human body is also prevented; the multi-layer filtering mask is firm, durable, convenient to clean, and smooth to breath, and is particularly suitable for the place with high dust.
Owner:哈尔滨安赛福经贸有限公司
Respiratory rehabilitation apparatus
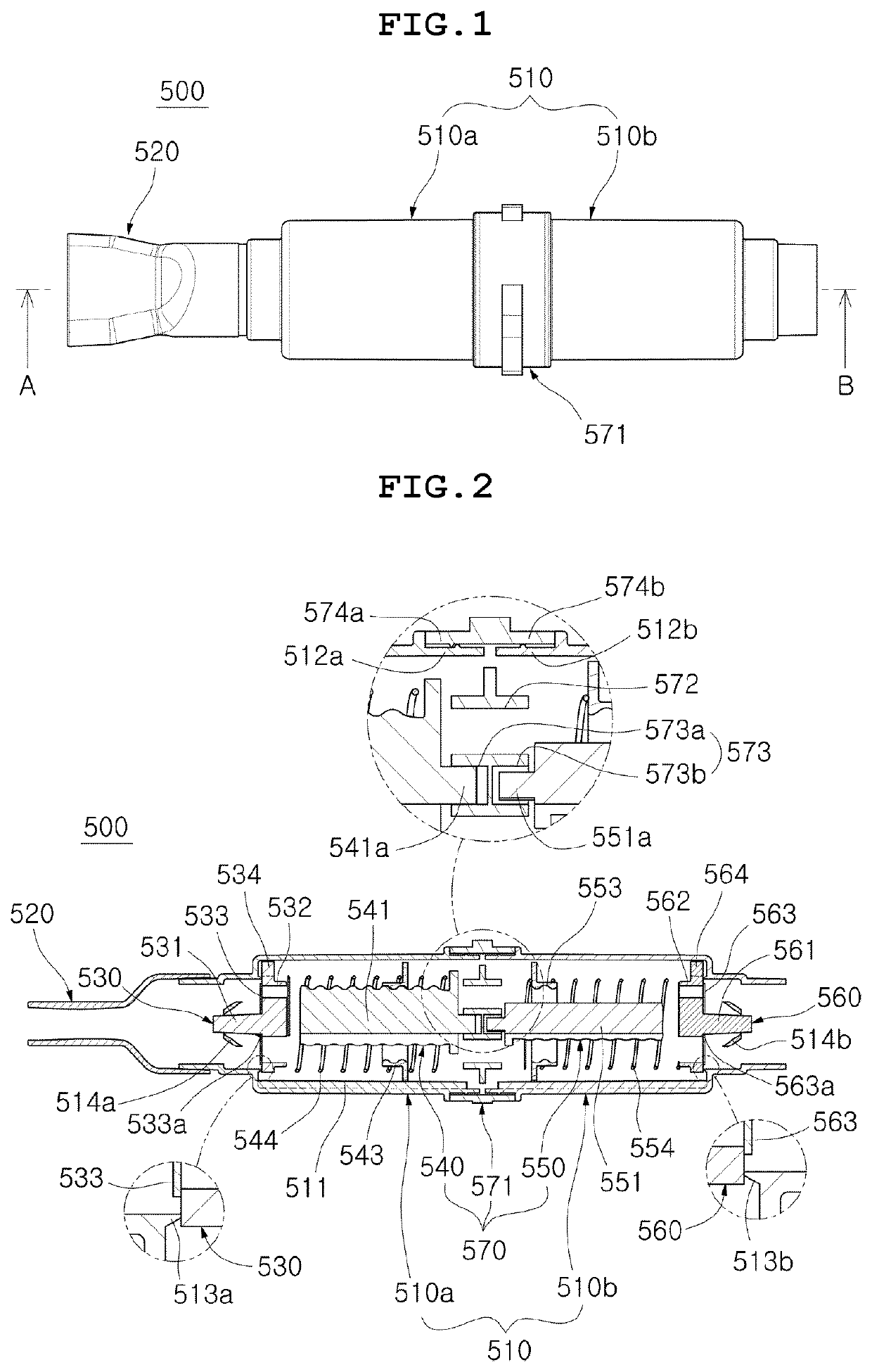
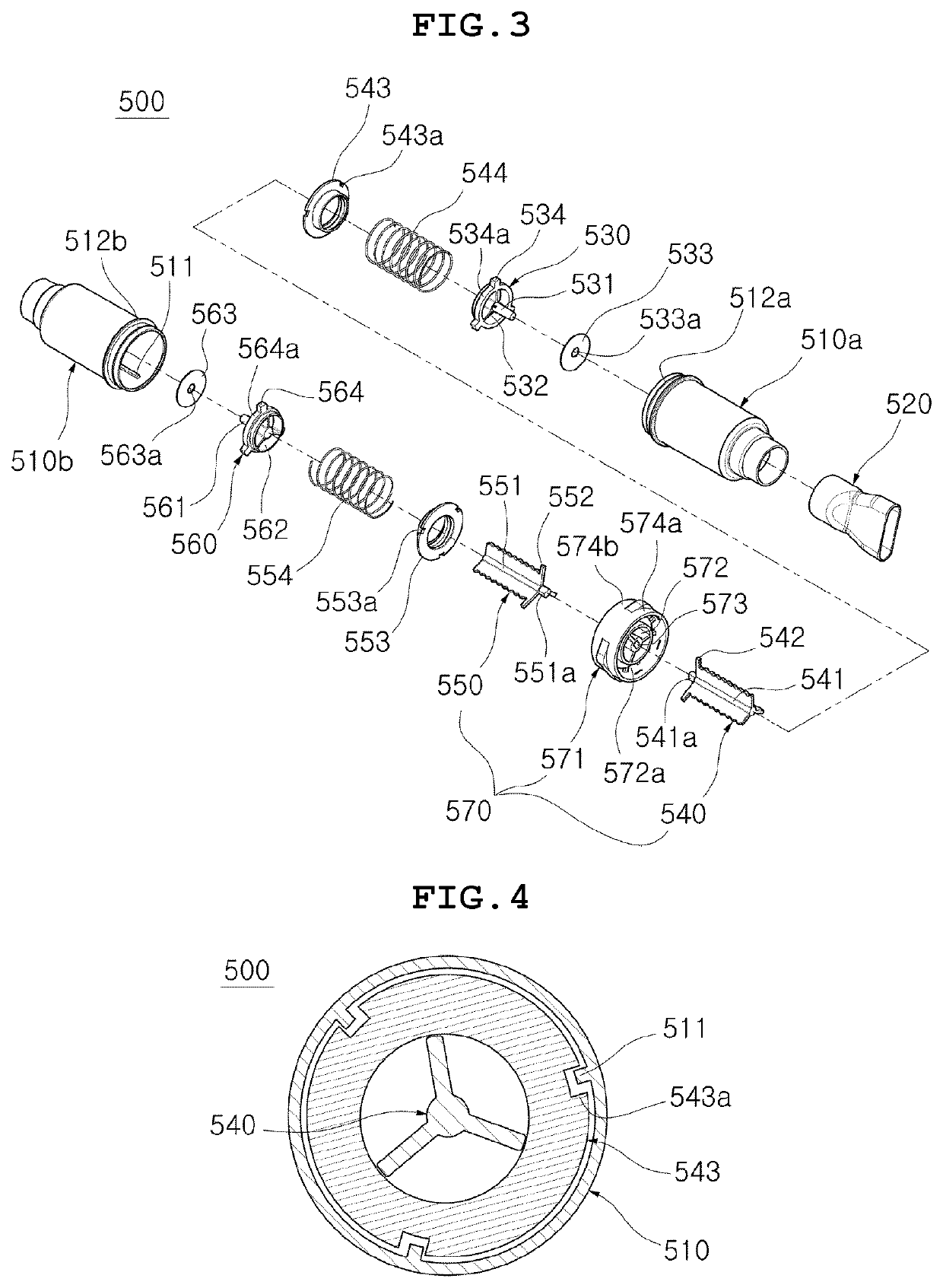
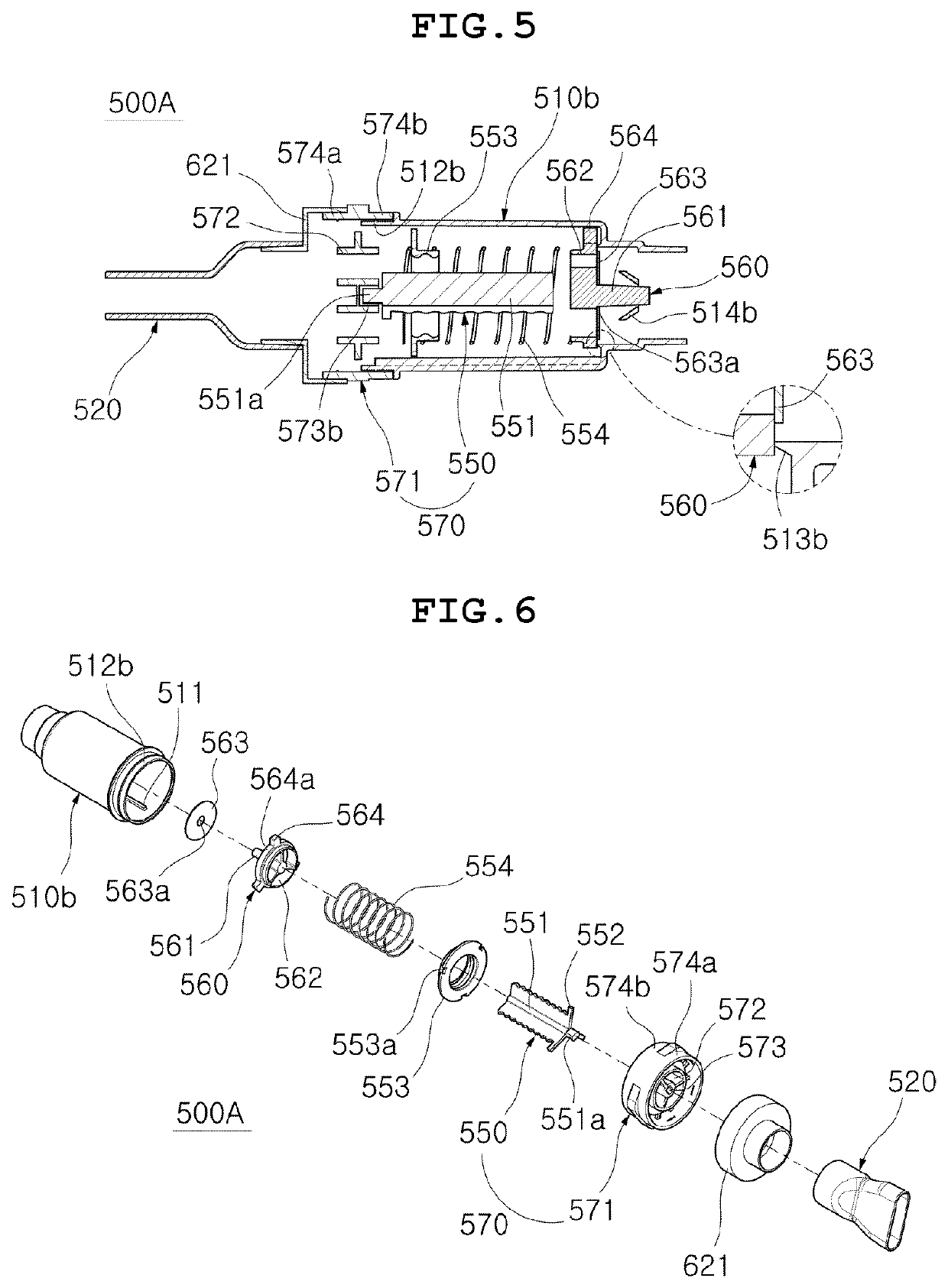
ActiveUS20210331035A1Small sizeEasy to carryResilient force resistorsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationRespiratory pressure
Disclosed is a respiratory rehabilitation apparatus having improved convenience of use, the respiratory rehabilitation apparatus including a housing defining an external appearance, the housing being formed to have a hollow shape, an adjustment rod including a housing-coupling part disposed at the center portion in a longitudinal direction of the housing, the housing-coupling part including a plurality of through-passages formed therethrough in a longitudinal direction, and a pair of rod body parts provided at opposite sides in a longitudinal direction of the housing-coupling part, the rod body parts including screw threads formed in outer circumferences thereof, a pair of stoppers formed to have a hollow shape so as to be coupled to the outer circumferences of the rod body parts, the stoppers including screw threads formed in inner circumferences thereof, the stoppers being configured to selectively adjust respiration pressure, a pair of pressurization-movement parts including protrusions formed at center portions thereof, the protrusions extending outwards in a longitudinal direction, and a plurality of respiration passages formed therethrough, the respiration passages extending in a longitudinal direction while surrounding the protrusions, the pressurization-movement parts being configured to be pressurized and moved inwards in a longitudinal direction of the housing by respiration pressure during respiration, a pair of elastic members disposed between the pressurization-movement parts and the stoppers so as to be selectively pressed, the elastic members surrounding the outer peripheries of the rod body parts, and a pair of diaphragms including a through-hole formed in center portions thereof to allow the protrusions to be inserted thereinto, the diaphragms being disposed to be in close contact with outer sides in a longitudinal direction of the pressurization-movement parts.
Owner:GH INNOTEK CO LTD
Bionic alpha internal pollution metering and monitoring device
InactiveCN112068177AAchieving alpha internal contamination doseUnderstanding Pollution DosageX-ray spectral distribution measurementDosimetersAir pumpElectric machinery
The invention relates to the field of alpha internal pollution monitoring, in particular to a bionic alpha internal pollution metering and monitoring device which comprises an intelligent trolley, a controller and a remote control platform in communication with the controller. An air pump controlled by a stepping motor and used for pumping air in a monitoring area is installed on the intelligent trolley chassis, the air outlet end of the air pump is connected with a monitoring bin through an air pipe A, any side wall of the monitoring bin is connected with an air pipe B, and an alpha energy spectrum obtaining and analyzing system used for monitoring the pollution dose in alpha in the monitoring bin is installed on the intelligent trolley chassis. The human body respiratory rate is preset in the controller, and the stepping motor controls the air pump to work based on the human body respiratory rate, so that the alpha internal pollution dose borne by the human body in the respiratory process is achieved, and data reference is provided for the dose borne by the human body.
Owner:THE ENG & TECHN COLLEGE OF CHENGDU UNIV OF TECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com