Enzymatic method for preparing statins intermediates
A compound and statin technology, which is applied in the field of enzymatic preparation of statin compound intermediates, can solve the problems of large amount of enzyme used, affecting extraction yield, high production cost, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0097] Preparation of formula I compound and statin compound
[0098] As used herein, the structural formula of the compound of formula I is It is the most important intermediate of statins and is usually synthesized by chemical methods.
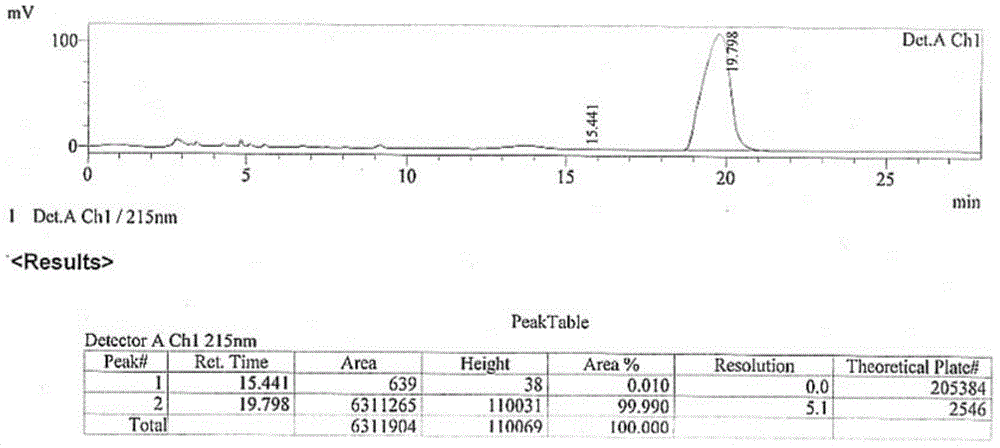
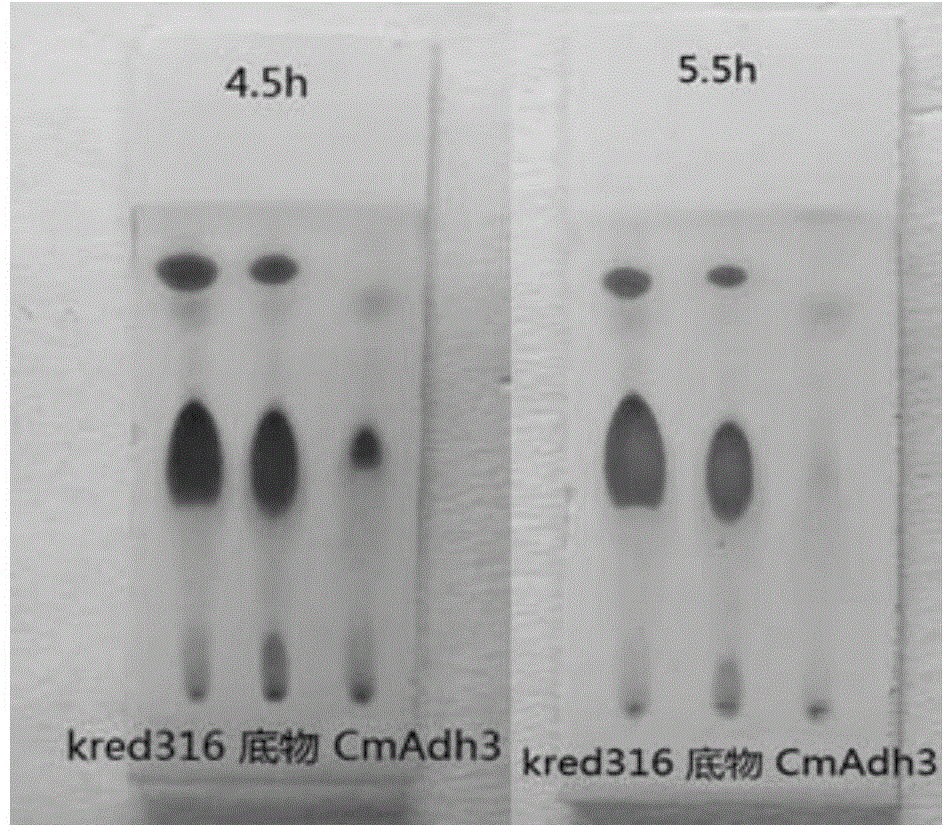
[0099] The present invention provides a kind of method of biosynthetic formula I compound, specifically, described method comprises the steps: (a) in the regeneration system of coenzyme factor (as NADPH) and coenzyme factor (as glucose dehydrogenase GDH and glucose) In the presence of alcohol dehydrogenase CmADH3, the compound of formula III is catalytically reduced to generate the compound of formula II; (b) the compound of formula II is reacted with 2,2-dimethoxypropane to form the compound of formula I. The compound of formula I obtained by this method has very high purity, the content of diastereomer is only 0.0106%, and the content of enantiomer is only 0.01%. Wherein, R of the compounds of formula I, formula II, and formula III is a...
Embodiment 1
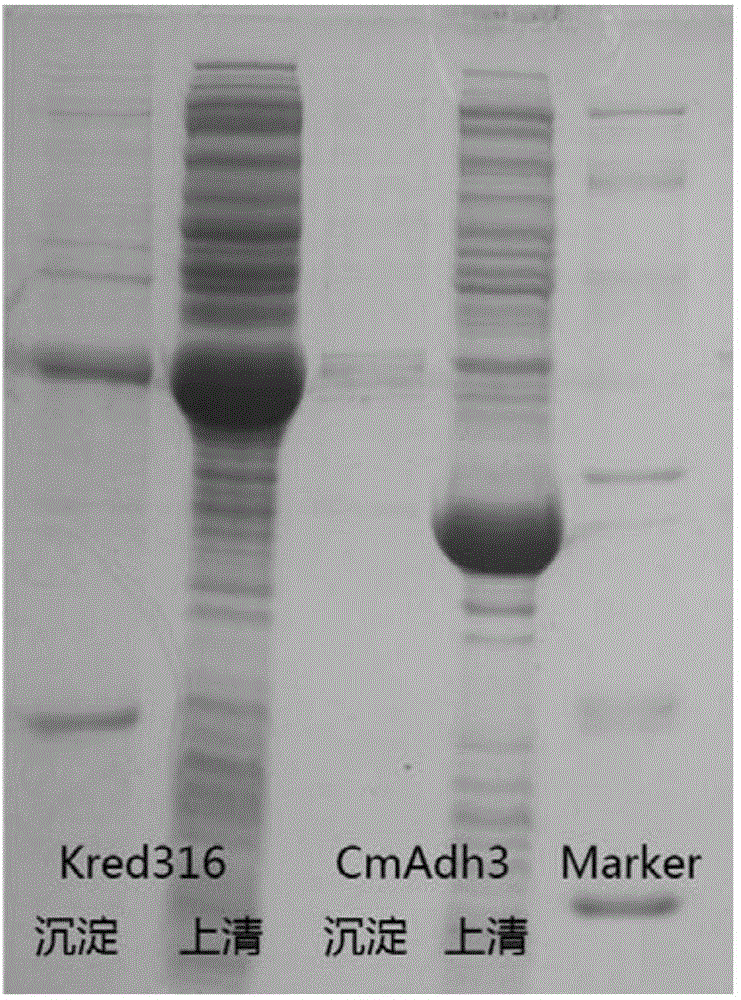
[0124] Construction of embodiment 1 CmADH3 expression strain
[0125] For the protein sequence of alcohol dehydrogenase CmADH3 derived from Candida magnoliae (NCBI accession number: ABB91667), the codons suitable for expression in Escherichia coli were optimized, and the gene sequence was synthesized completely, and enzymes were designed at both ends NdeI and BamHI sites were cut, and subcloned into the corresponding sites on the vector pET24a (purchased from Novagen) to obtain the recombinant plasmid pET24a-CmADH3.
[0126] The constructed recombinant plasmid pET24a-CmADH3 was transformed into Escherichia coli expression host BL21(DE3) by calcium chloride method to obtain BL21(DE3) / pET24a-CmADH3.
[0127] Codon-optimized gene sequence (SEQ ID NO.:3):
[0128]
[0129]
[0130] Protein sequence (SEQ ID NO.1):
[0131]
Embodiment 2
[0132] Example 2 Construction of KRED316 expression strain
[0133] According to the gene sequence of the reported carbonyl reductase mutant derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Chinese patent application number: 200780036841.6, SEQ ID NO.315), the sequence was synthesized from the whole gene, and restriction sites NdeI and BamHI were designed at both ends, and It was subcloned into the corresponding site on the vector pET24a (purchased from Novagen) to obtain the recombinant plasmid pET24a-KRED316.
[0134] The constructed recombinant plasmid pET24a-KRED316 was transformed into Escherichia coli expression host BL21(DE3) by calcium chloride method to obtain BL21(DE3) / pET24a-KRED316.
[0135] The gene sequence is as follows:
[0136]
[0137]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com