Rice wine brewing method using lactobacillus plantarum to degrade ethyl carbamate (EC)
A technology of urethane and Lactobacillus plantarum is applied in the directions of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, bacteria, etc., and can solve the problems of cumbersome process steps, time-consuming and laborious enzyme activity, and difficulty in obtaining.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0033] (2) Preparation of enzyme solution:
[0034] Lactobacillus plantarum ACCC10171 was inoculated in an Erlenmeyer flask containing 50 mL of MRS medium, and after 2 days of fermentation at 30°C, the fermentation broth was centrifuged, and the obtained cells were ultrasonically crushed at 4°C for 20 minutes, and the supernatant was the enzyme liquid. Store the obtained enzyme solution at 4°C.
[0035] (3) Principle of Enzyme Activity Determination:
[0036] Under certain conditions, after the enzyme solution of the strain reacts with the substrate (3% EC, pH 4.4), after using the terminator, chromogenic agent I, and chromogenic agent II respectively, the depth of its color within a certain range It is directly proportional to the activity of the enzyme, and the colorimetry is performed at 625nm to calculate the activity of the enzyme.
[0037] Among them, chromogen I: Weigh 15g of phenol and 0.625g of sodium nitroferricyanide and dilute to 250mL with ultrapure water;
[0...
Embodiment 1
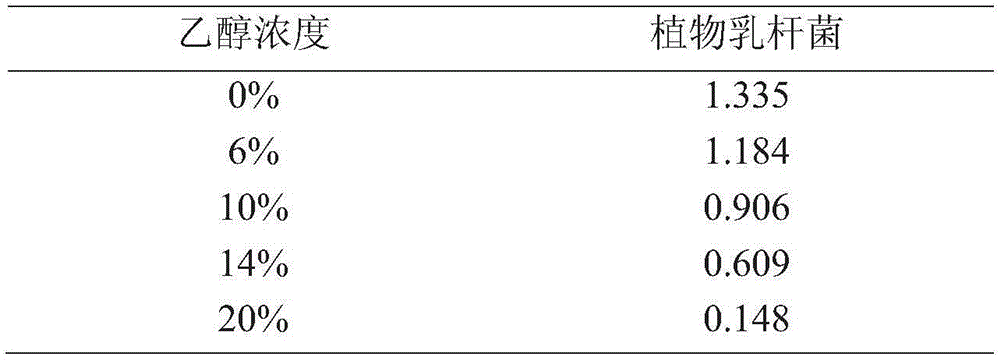
[0075] In the experimental group, Lactobacillus plantarum ACCC10171 was added on the 10th day of fermentation. The control group was not subjected to any treatment. Samples were taken and analyzed every 5 days to measure the activity of EC degrading enzymes in the fermentation broth. The results are shown in Table 1.
[0076] From the results, it can be seen that the activity of ethyl carbamate degrading enzyme in the control group of natural fermentation is almost zero, while the experimental group added with Lactobacillus plantarum (Lactobacillus plantarum) ACCC10171 has significant enzyme activity, indicating that Lactobacillus plantarum (Lactobacillus plantarum) ACCC 10171 does have the ability to degrade EC.
[0077] Table 1 The effect of adding Lactobacillus plantarum (Lactobacillus plantarum) ACCC10171 on the enzyme activity of EC degrading enzymes in rice wine fermentation
[0078]
Embodiment 2
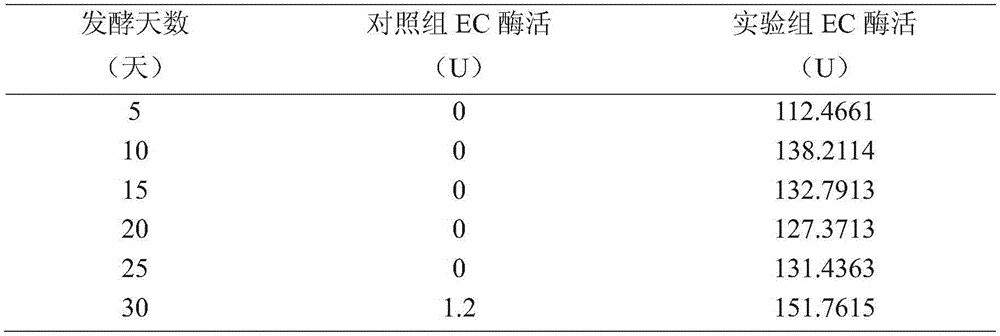
[0080] The experimental group added Lactobacillus plantarum ACCC10171 on the 10th day of fermentation, and the control group received no treatment. Samples were taken and analyzed every 5 days to determine the content of EC in the fermentation broth. The results are shown in Table 2.
[0081] It can be seen from the results that the content of ethyl carbamate in the experimental group added with Lactobacillus plantarum (Lactobacillus plantarum) ACCC10171 was lower than that of the naturally fermented control group, and in the late stage of fermentation, after 20 days, the level of EC was significantly reduced. It can be seen that the addition of Lactobacillus plantarum can inhibit the production of EC.
[0082] Table 2 Effect of adding Lactobacillus plantarum (Lactobacillus plantarum) ACCC10171 on EC content in rice wine fermentation
[0083]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com