Photolithographic methods
A photoresist layer and polymer technology, applied in the fields of manufacturing electronic equipment, photolithography methods and photoresist protective layer compositions, can solve the problems of unpredictable effective amount of alkaline quenchers and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
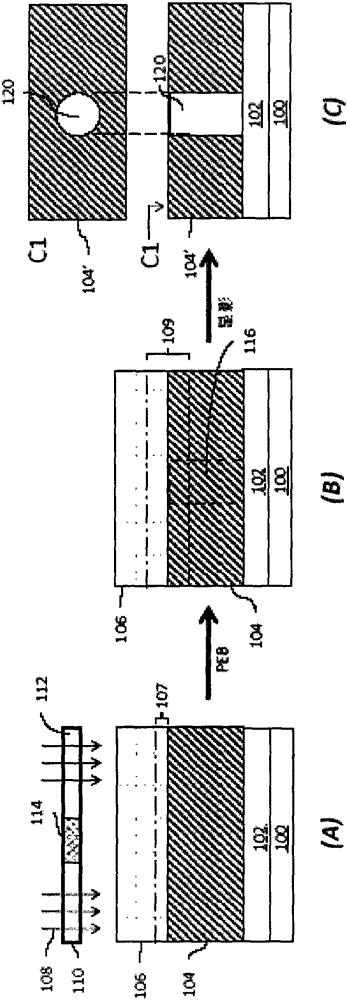
Image
Examples
Embodiment
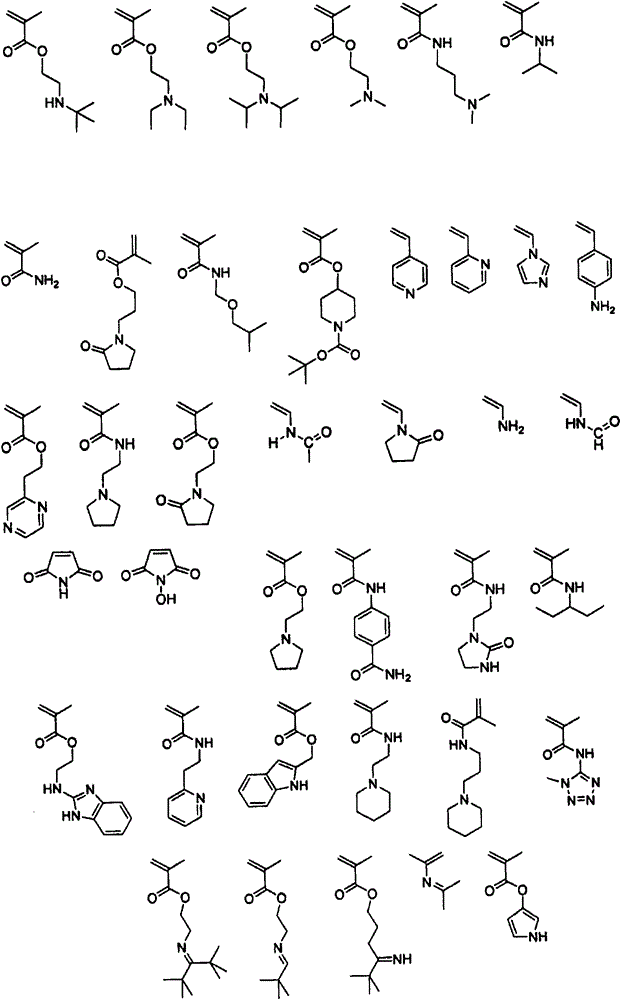
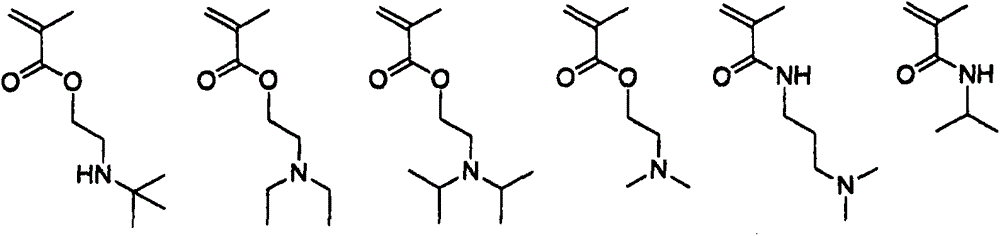
[0087] Synthesis of Photoresist Polymer (PP)
[0088] The structures of the monomers used in the synthesis of photoresist polymers along with their abbreviations are shown below:
[0089]
[0090] Synthesis of Poly(ECPMA / MCPMA / MNLMA / HADA)(PP-1)
[0091] The monomers ECPMA (5.092 g), MCPMA (10.967 g), MNLMA (15.661 g) and HADA (8.280 g) were dissolved in 60 g of propylene glycol monomethyl ether acetate (PGMEA). The monomer solution was degassed by bubbling nitrogen for 20 minutes. PGMEA (27.335 g) was added to a 500 mL three-neck flask equipped with a condenser and a mechanical stirrer, and degassed with nitrogen bubbling for 20 minutes. The solvent in the reaction flask was then warmed to 80°C. V601 (dimethyl 2,2-azobisisobutyrate) (0.858 g) was dissolved in 8 g of PGMEA, and the initiator solution was degassed with nitrogen gas bubbling for 20 minutes. The initiator solution was added to the reaction flask, and then the monomer solution was added dropwise to the r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com