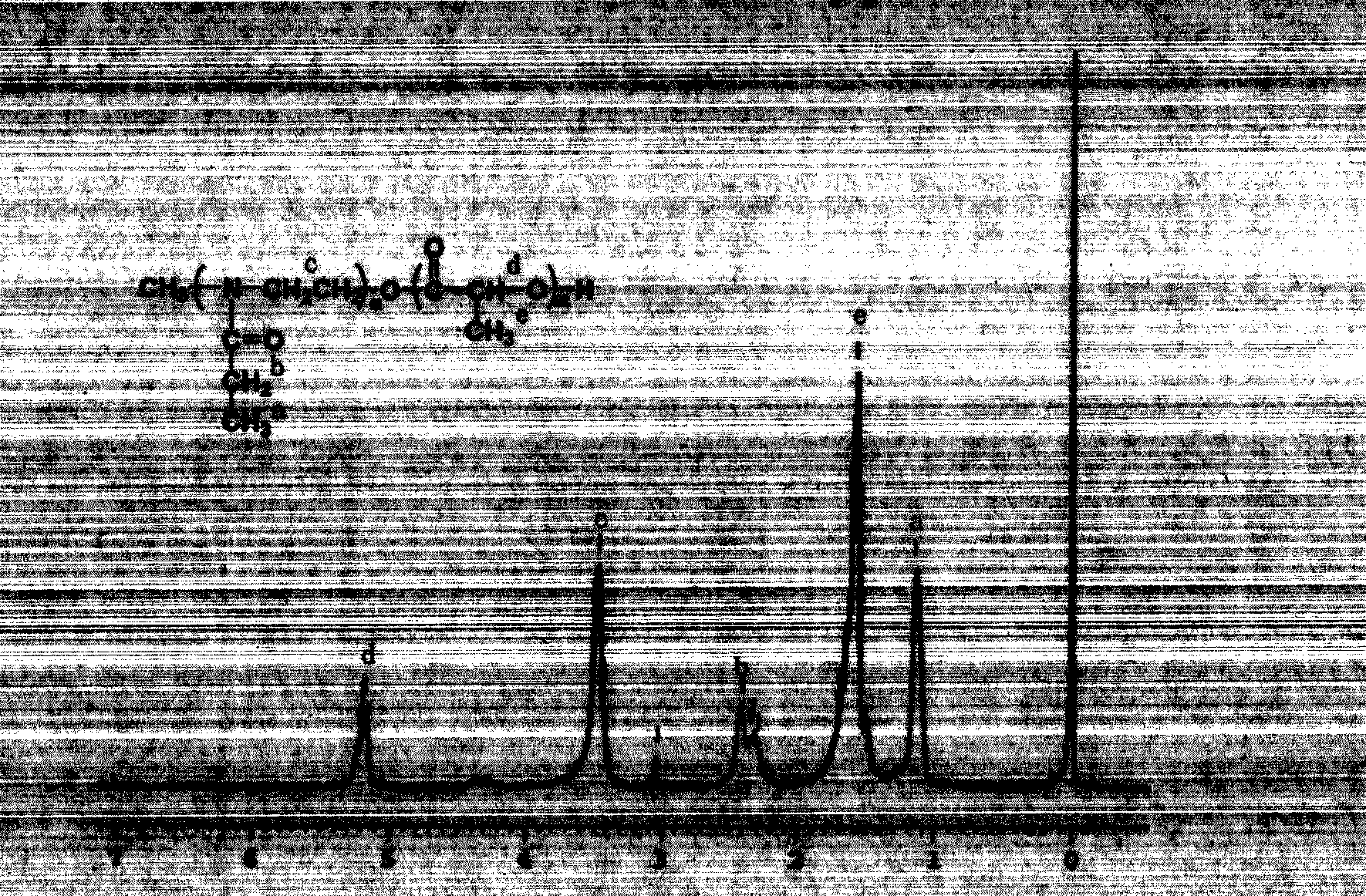
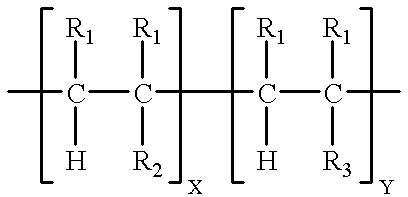
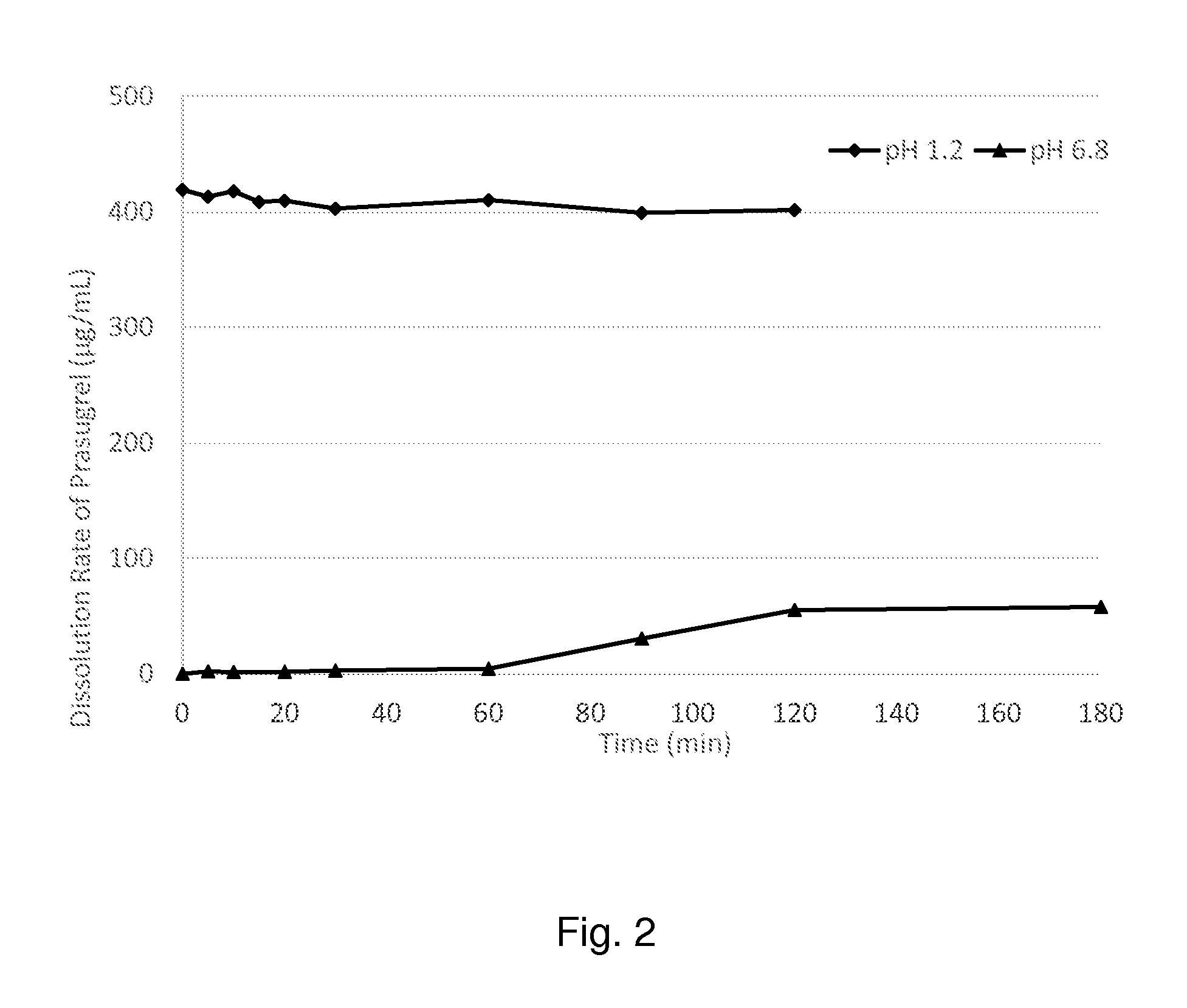
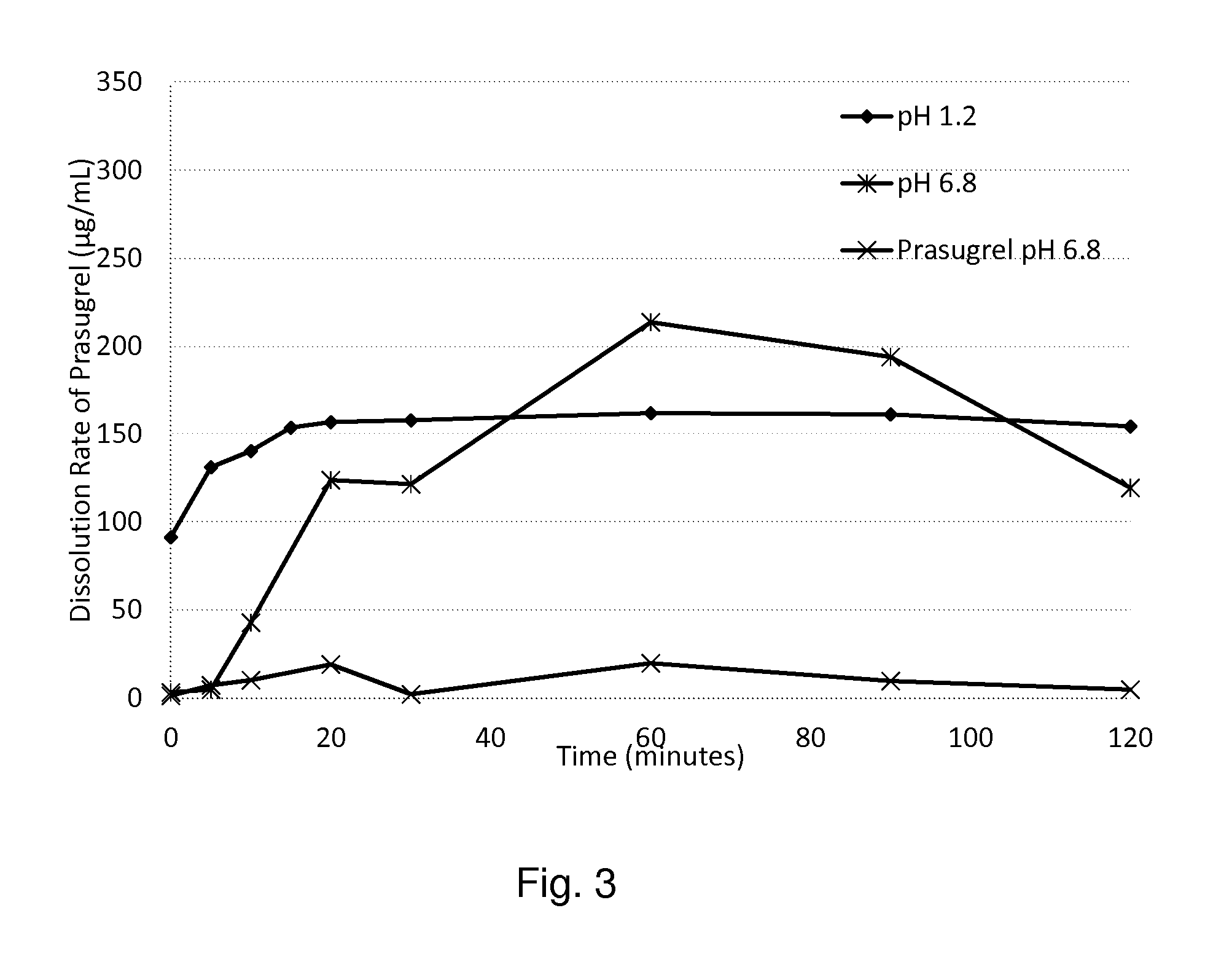
Patents
Literature
47 results about "PH-sensitive polymers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
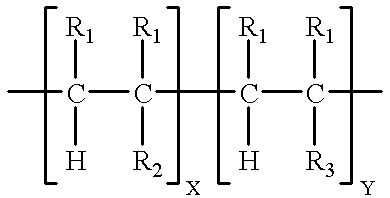
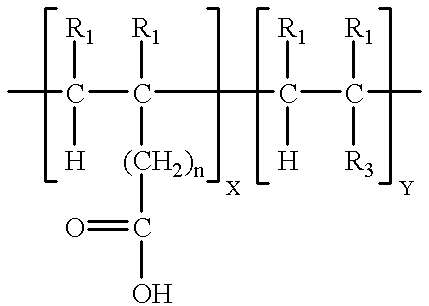
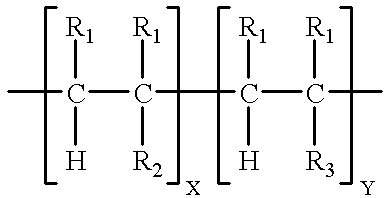
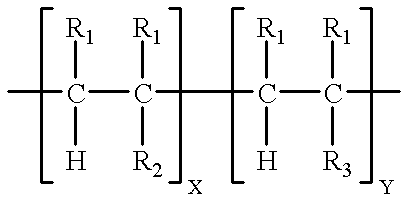
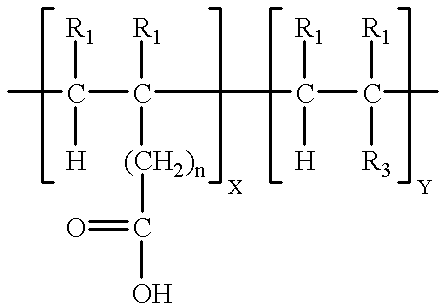
PH sensitive or pH responsive polymers are materials which will respond to the changes in the pH of the surrounding medium by varying their dimensions. Materials may swell, collapse, or change depending on the pH of their environment. This behavior is exhibited due to the presence of certain functional groups in the polymer chain. pH-sensitive materials can be either acidic or basic, responding to either basic or acidic pH values. These polymers can be designed with many different architectures for different applications. Key uses of pH sensitive polymers are controlled drug delivery systems, biomimetics, micromechanical systems, separation processes, and surface functionalization.
Ink to ink bleed and halo control using specific polymers in ink-jet printing inks
InactiveUS6281267B2Reduce bleedingReduce haloDuplicating/marking methodsInksPH-sensitive polymersPrinting ink
The ink set of this invention comprises at least two inks, one of which contains a pH sensitive polymer and preferably a self-dispersing pigment colorant. A second ink is provided which comprises incompatible inorganic or organic salts or has an appropriate pH. The polymer precipitates onto a medium upon contact with the second ink, thereby providing improved bleed and halo control.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Pharmaceutical formulations targeting specific regions of the gastrointesinal tract
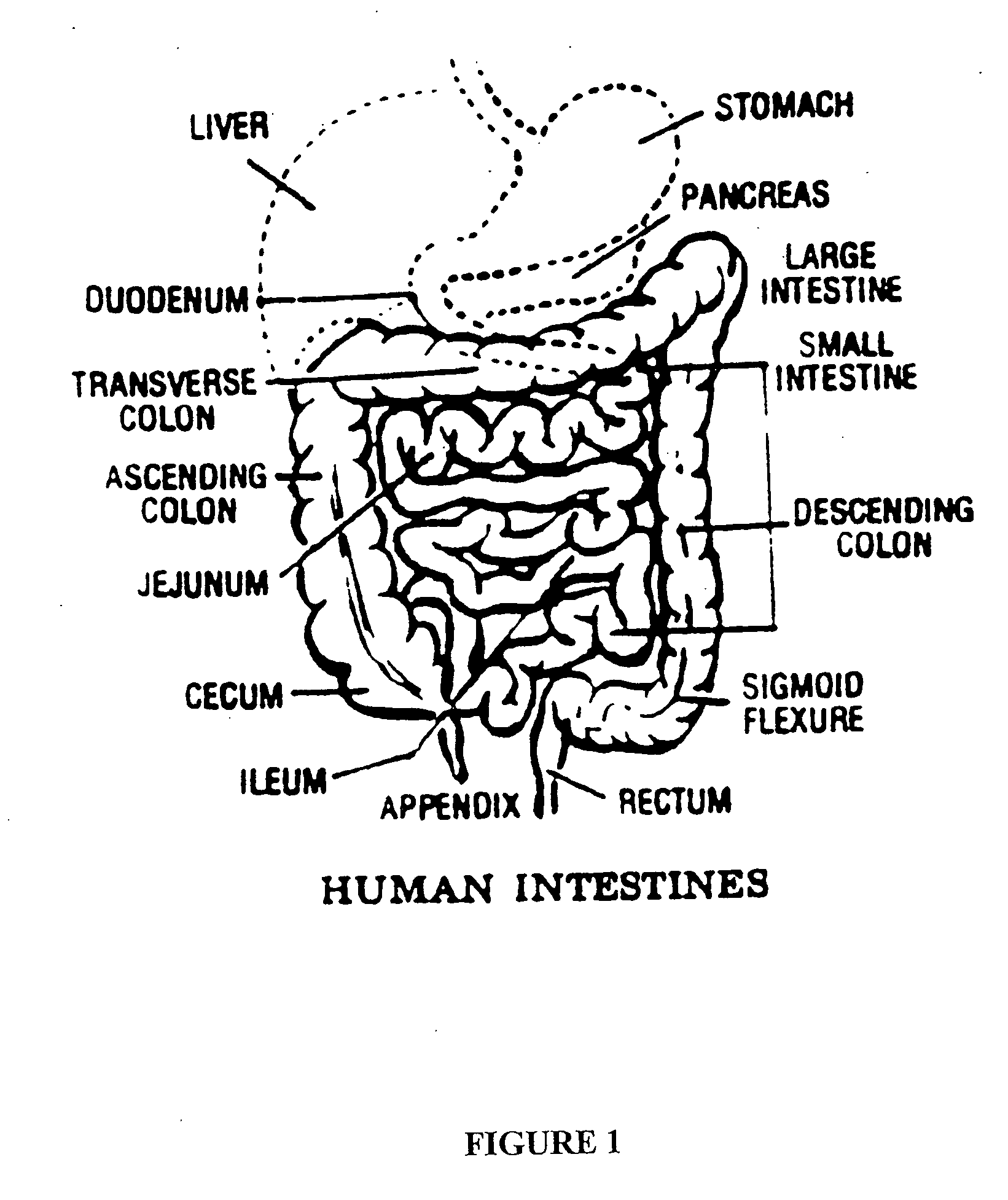
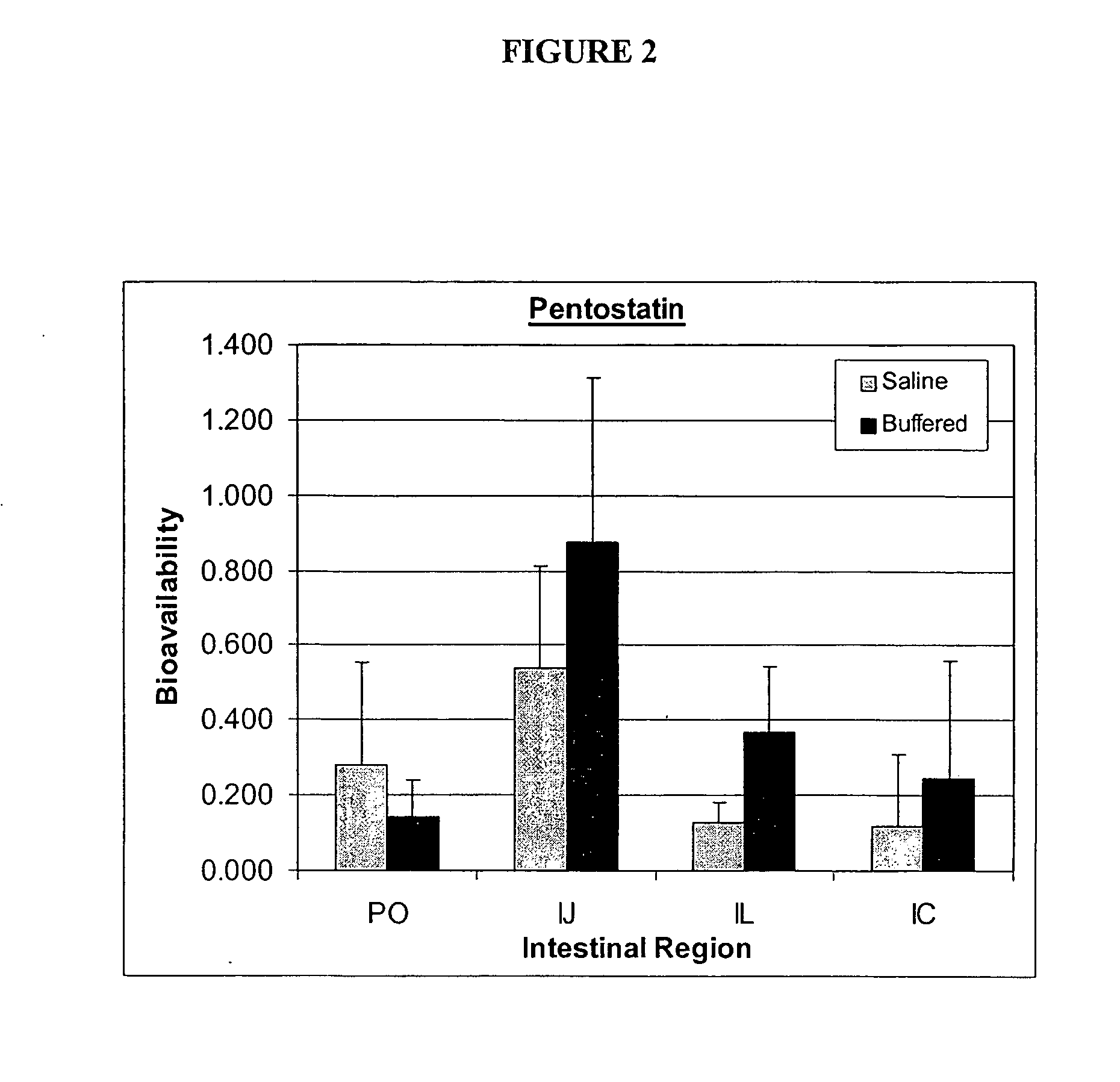
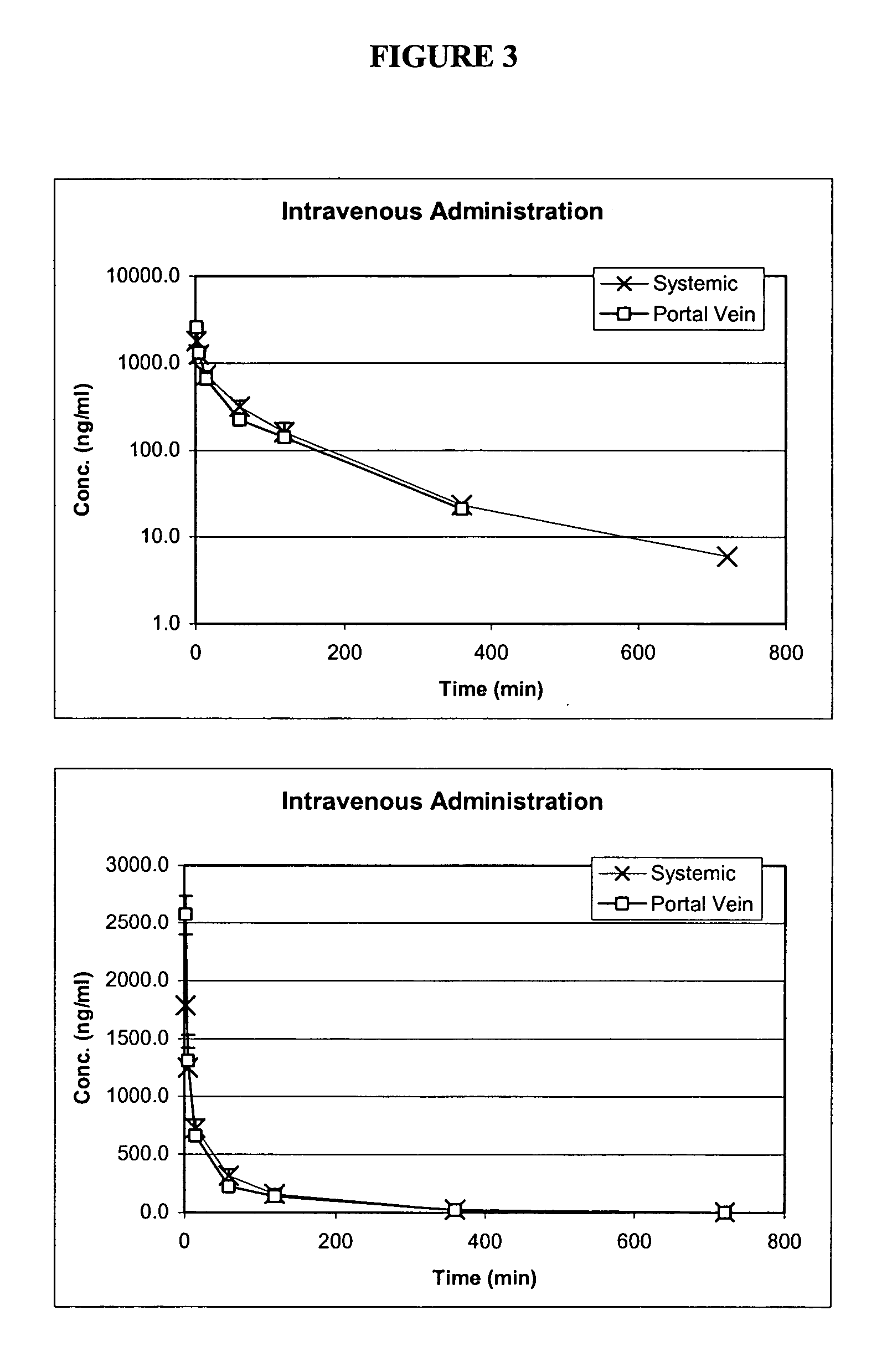
Oral formulations of pharmaceuticals are provided with enhanced bioavailability by targeting specific regions of the gastrointestinal tract. Particularly, water soluble and acid-labile drugs such as cytidine analogs (e.g., decitabine) and 2'-deoxyadenosine analogs (e.g., pentostatin) are formulated with pH-sensitive polymers so that these drugs are preferably absorbed in the upper regions of the small intestine, such as the jejunum. In addition, drugs with poor oral bioavailability such as camptothecin compounds (e.g., 9-nitro-camptothecin) can also be formulated using similar strategies in order to significantly improve their oral bioavailability. These formulations can be used to treat a wide variety of diseases or conditions, such hematological disorders, benign tumors, cancer, restenosis, inflammatory diseases, and autoimmune diseases.
Owner:MAYNE PHARMA USA
Taste masked pharmaceutical compositions comprising bitter drug and pH sensitive polymer
InactiveUS20050136114A1Improve palatabilityA large amountPowder deliveryDispersion deliveryPH-sensitive polymersLiquid oral
The present invention discloses pharmaceutical compositions comprising of pH sensitive polymers used for taste masking highly bitter drugs. The pH sensitive polymer acts as a reverse enteric coating, which is soluble in the acidic pH range 1.0 to 3.0 normally found in the stomach but is insoluble in the pH range 3.5 to 7 thus inhibiting the release of the bitter drug at the pH of saliva and also at the pH of reconstitution medium in case of liquid orals.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Inks containing glycol ethers and specific polymers for dry time and bleed improvements in ink-jet printing inks
InactiveUS6300391B2Faster rateImprove performanceDuplicating/marking methodsInksPH-sensitive polymersGlycol ethers
The ink set of this invention comprises at least two inks, one of which contains a pH sensitive polymer, a glycol ether, and preferably a self-dispersing pigment colorant. A second ink is provided which comprises incompatible inorganic or organic salts or has an appropriate pH. The polymer precipitates onto a medium upon contact with the second ink, thereby providing improved dry time as well as bleed and halo control.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Coating compositions for bitterness inhibition
InactiveUS7294347B2Mask bitternessImprove palatabilityPowder deliveryInksPH-sensitive polymersPh independent
The present invention discloses coating compositions with taste masking property, comprising a blend of pH sensitive polymers and optionally a pH independent polymer or a blend of the pH sensitive polymer and pH independent polymer used for taste masking of highly bitter drugs. The pH sensitive polymers used comprise the acid soluble polymers and the enteric polymers. The process for the preparation of taste masked pharmaceutical compositions of the bitter drugs comprising the said coating compositions is disclosed. The concomitant use of the polymers inhibits the release of the bitter drug at the pH of saliva. The said coating compositions deliver substantial amount of the bitter drug immediately with improved palatability.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
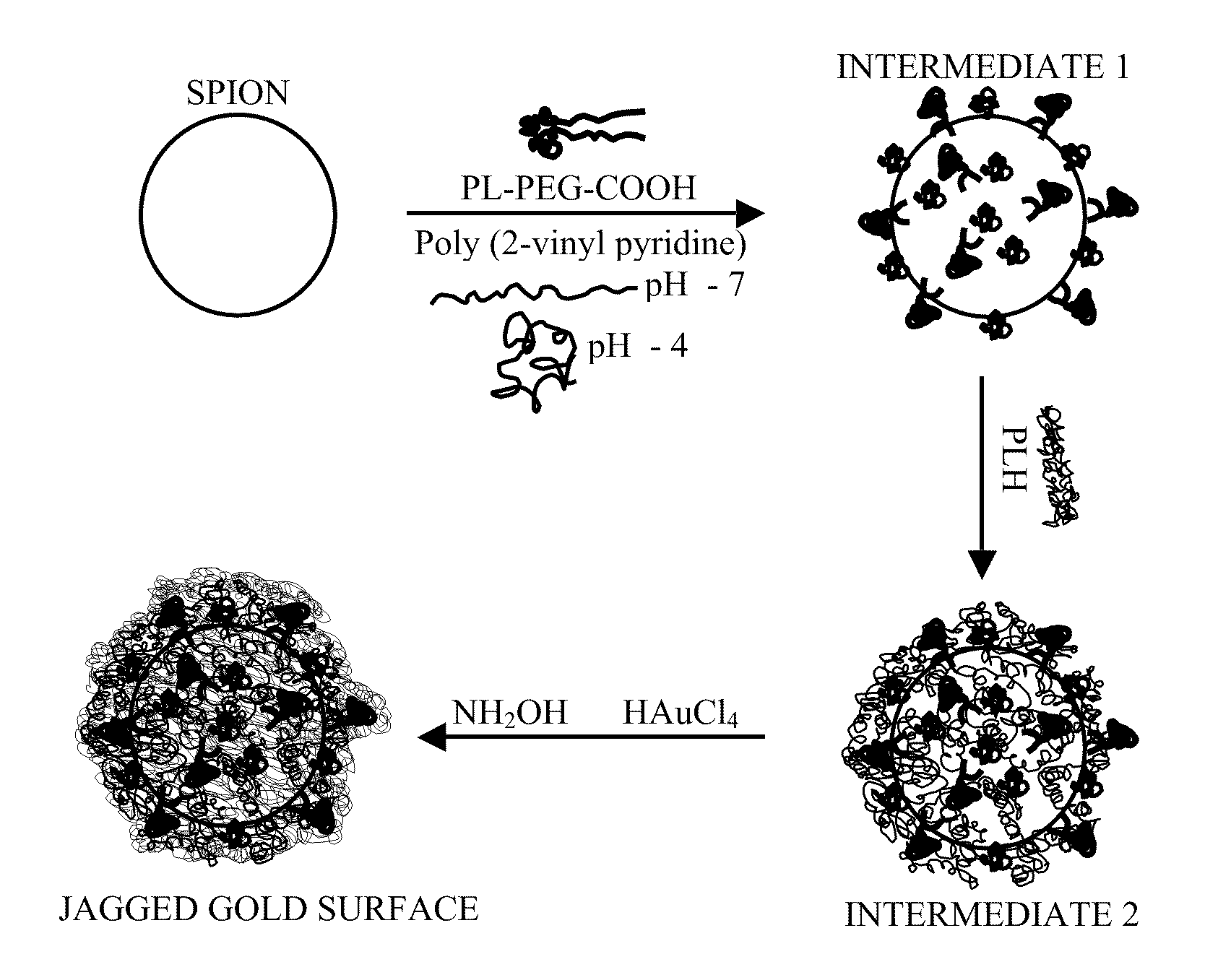
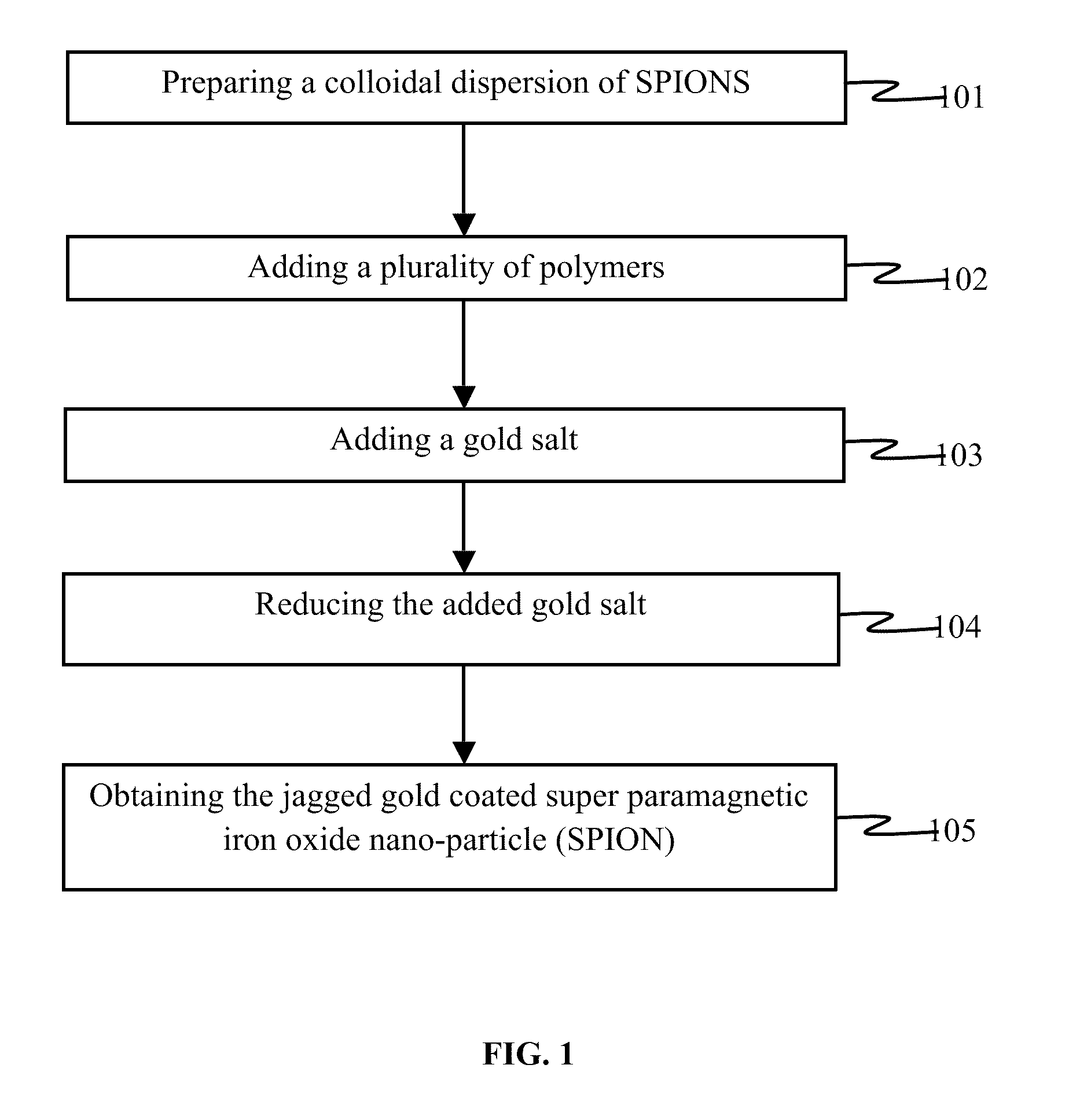
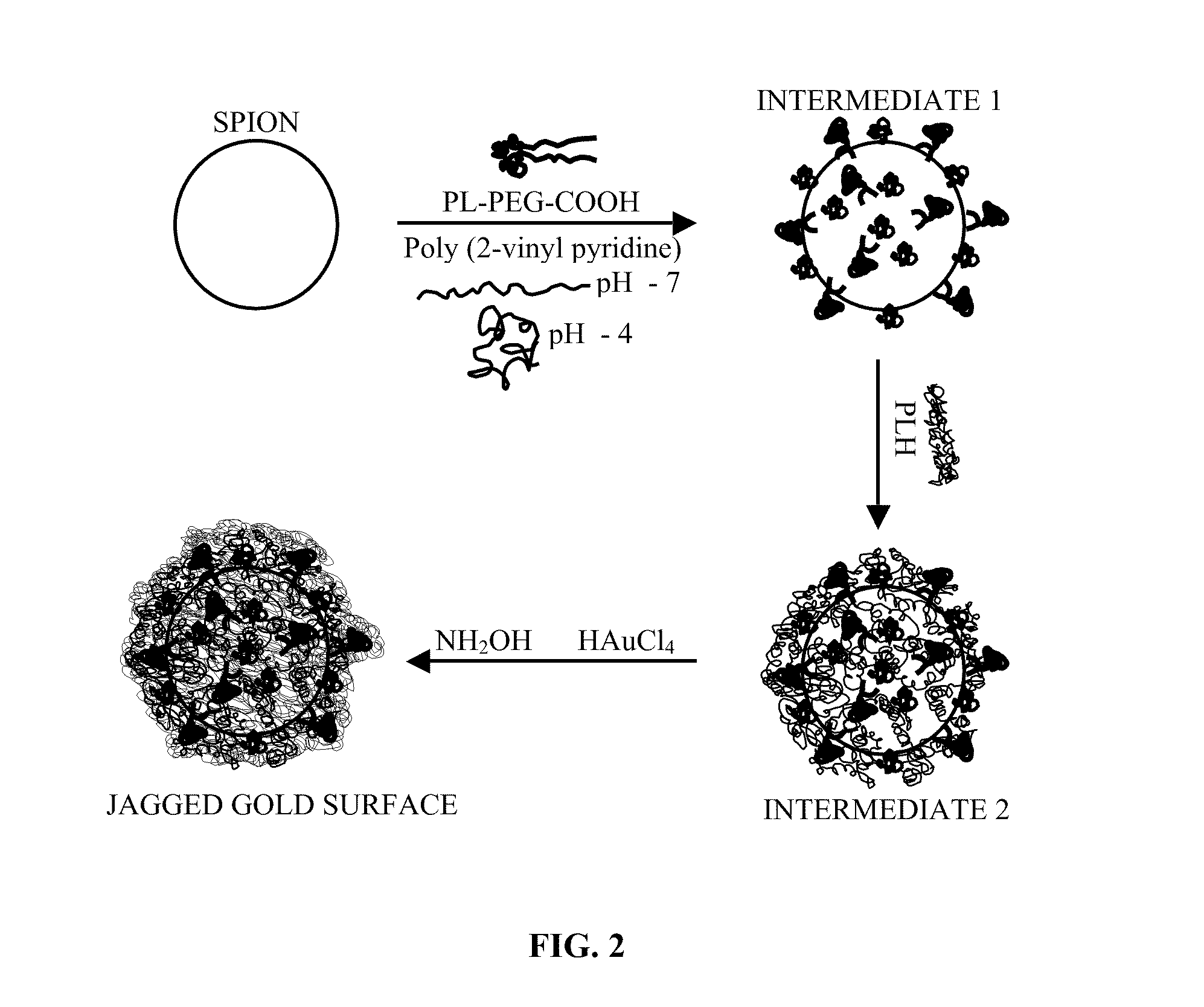
Gold coated super paramagnetic iron oxide nano-particles (spions) and a method of synthesizing the same
InactiveUS20110206619A1Non-uniform gapImprove abilitiesPowder deliveryMaterial nanotechnologySynthesis methodsPH-sensitive polymers
The various embodiments herein provide a gold coated SPIONs with jagged surface. The gold coated SPIONs have a core and a shell. The core is a SPION molecule and the shell is a jagged gold layer. A non-uniform polymeric gap exists between the core and the shell. The embodiments also provide a method of producing the jagged gold coated SPIONs by mixing a colloidal dispersion of SPIONs with pH sensitive polymers. Adding a gold salt to the above mixture and reducing the gold salt to form jagged gold coated SPIONs.
Owner:MAHMOUDI MORTEZA +1
Coating compositions for bitterness inhibition
InactiveUS20050281874A1Improve protectionMask bitternessPowder deliveryInksPH-sensitive polymersBitter taste
The present invention discloses coating compositions with taste masking property, comprising a blend of pH sensitive polymers and optionally a pH independent polymer or a blend of the pH sensitive polymer and pH independent polymer used for taste masking of highly bitter drugs. The pH sensitive polymers used comprise the acid soluble polymers and the enteric polymers. The process for the preparation of taste masked pharmaceutical compositions of the bitter drugs comprising the said coating compositions is disclosed. The concomitant use of the polymers inhibits the release of the bitter drug at the pH of saliva. The said coating compositions deliver substantial amount of the bitter drug immediately with improved palatability.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Pharmaceutical formulation with enhanced solubility for the delivery of corticosteroids
InactiveUS20080081070A1Improve solubilityPrecision releaseOrganic active ingredientsBiocidePorositySolubility
Formulations have been developed to improve the solubility of corticosteroids such as fluticasone proprionate in a composition designed to achieve localized release of the drug in the small intestine and / or colon. In one embodiment, solid dispersions of fluticasone are prepared wherein the drug is blended with or coated onto a highly water soluble substrate such as nonpareil (sugar beads) then coated with a layer of polymer soluble in small intestinal fluid, then coated with an enteric coating. The inner polymer layer controls release of the drug, and the enteric coating, a pH sensitive polymer that is broken down in the ileum and colon, controls localized release of drug at various sites within the gastrointestinal tract. The multilayer pharmaceutical composition can be in the form of pellets, tablets compressed from pellets or pellets packed into capsules. The release profile of the drug can be manipulated by (1) altering size or shape (i.e., surface area) and solubility of the inert substrate; (2) the ratio of drug to polymer, the polymer composition and solubility, the porosity of the polymer; (3) the drug form (i.e., free base or salt, or which salt); and the thickness and / or surface area of the drug / polymer and / or enteric coating. In a preferred embodiment, the composition is administered orally. This may also be packaged to provide for an escalating or tapering dosage.
Owner:AURIGA LAB +1
Ph-sensitive polymeric micelles for drug delivery
Mixed micelles containing poly(L-histidine-co-phenylalanine)-poly(ethylene glycol) block copolymer and poly(L-lactic acid)-poly(ethylene glycol) block copolymer are a pH-sensitive drug carrier that release the drug in an acidic microenvironment, but not in the blood. Since the microenvironment of solid tumors is acidic, these mixed micelles are useful for treating cancer, including those cancers exhibiting multidrug resistance. Targeting ligands, such as folate, can also be attached to the mixed micelles for enhancing drug delivery into cells. Methods of treating a warm-blooded animal with such a drug are disclosed.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Pharmaceutical Compositions For Poorly Water-Soluble Compounds
InactiveUS20150182457A1Reduced food effectMinimizing pH sensitivityPowder deliveryBiocideSolubilityPH-sensitive polymers
This present invention is concerned with novel solid dispersion pharmaceutical compositions for preparation of composition which is comprised of a compound with poor water solubility (a weakly basic, neutral and / or non-ionizable, or a weakly acidic compound), water-soluble polymer(s), pH-sensitive polymer(s) (either enteric polymer or gastric-soluble polymer that is soluble at gastric fluid and insoluble at intestine pH range such as Eudragit E), and / or pharmaceutical acceptable surfactant(s) that would improve the solubility / dissolution of the compound in aqueous media of both low and neutral pHs and provide a relative pH-independent dissolution profile.
Owner:ASCENDIA PHARMA
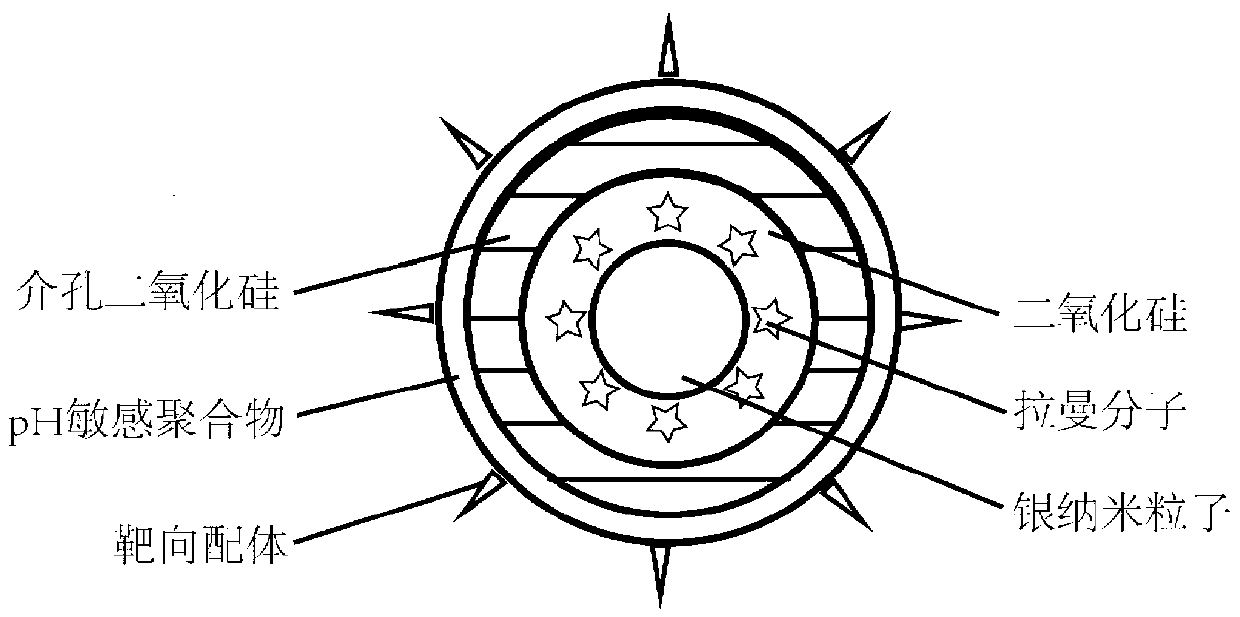
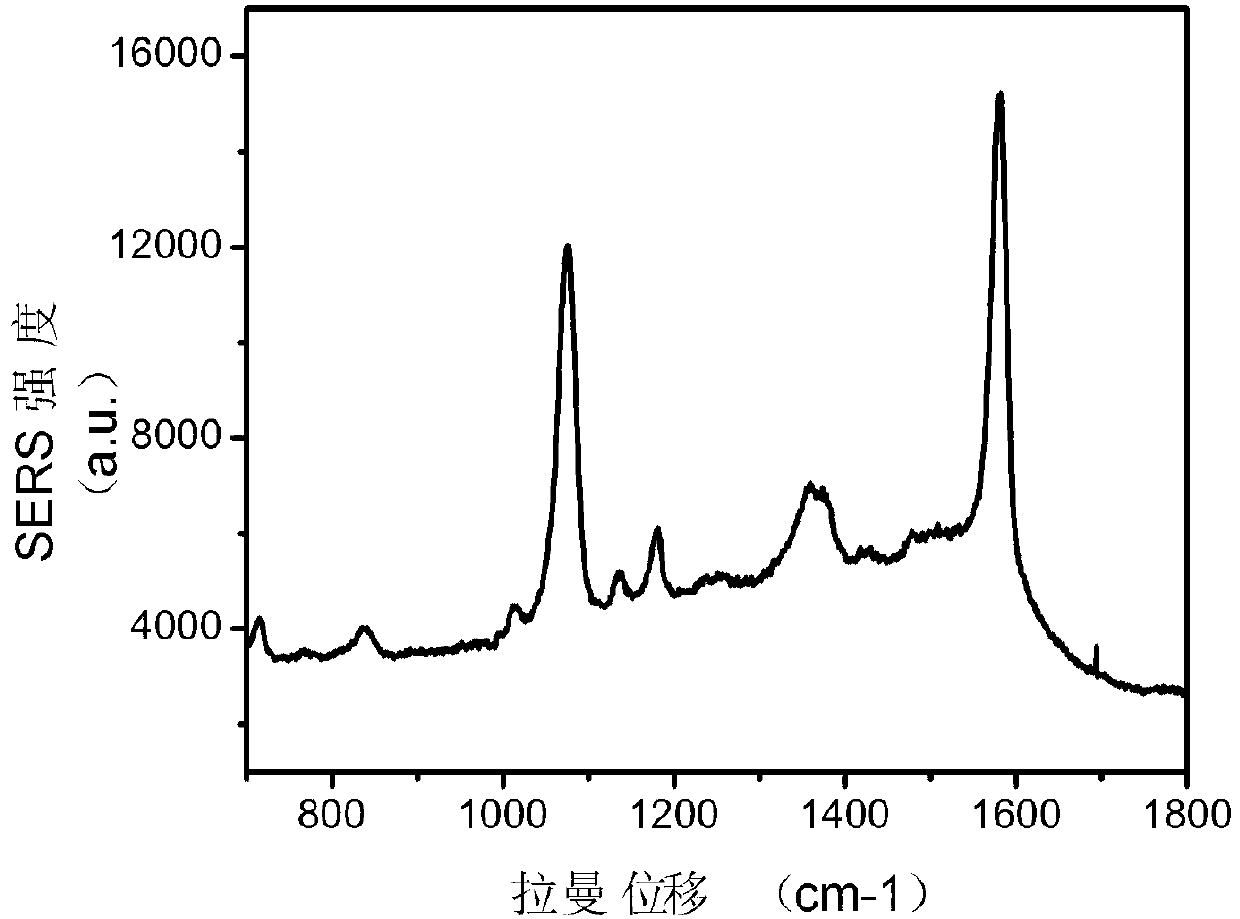
Target SERS (Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering) probe with pH-sensitive drug release characteristic, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103272241AIncrease savingsEasy to transportOrganic active ingredientsInorganic non-active ingredientsPH-sensitive polymersMesoporous silica
The invention discloses a target SERS (Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering) probe with pH-sensitive drug release characteristic. The probe comprises a Raman molecule-labeled gold nanoparticle core, a silicon dioxide intermediate layer, a mesoporous silica layer, a pH-sensitive polymer layer, a shell layer and a target ligand on the surface of the shell layer sequentially from inside to outside, the pH-sensitive polymer layer is a chitosan / polymethylacrylic acid layer, and the target ligand is transferrin. The invention further discloses a preparation method for the SERS probe. The probe and the preparation method thereof have the advantages that a pH-sensitive drug release system is combined with SERS, and the target ligand is connected with target tumor cells; the diffusion and release speed of drug in nano-particles can be regulated and controlled according to the pH value of the environment; the tracking on the nano-drug carrier particles can be more accurate through SERS signals in nano-drug carriers; and the target ligand is used for increasing the accumulation of drug in tumor parts, and increasing the transfer of drug in tumor cells.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
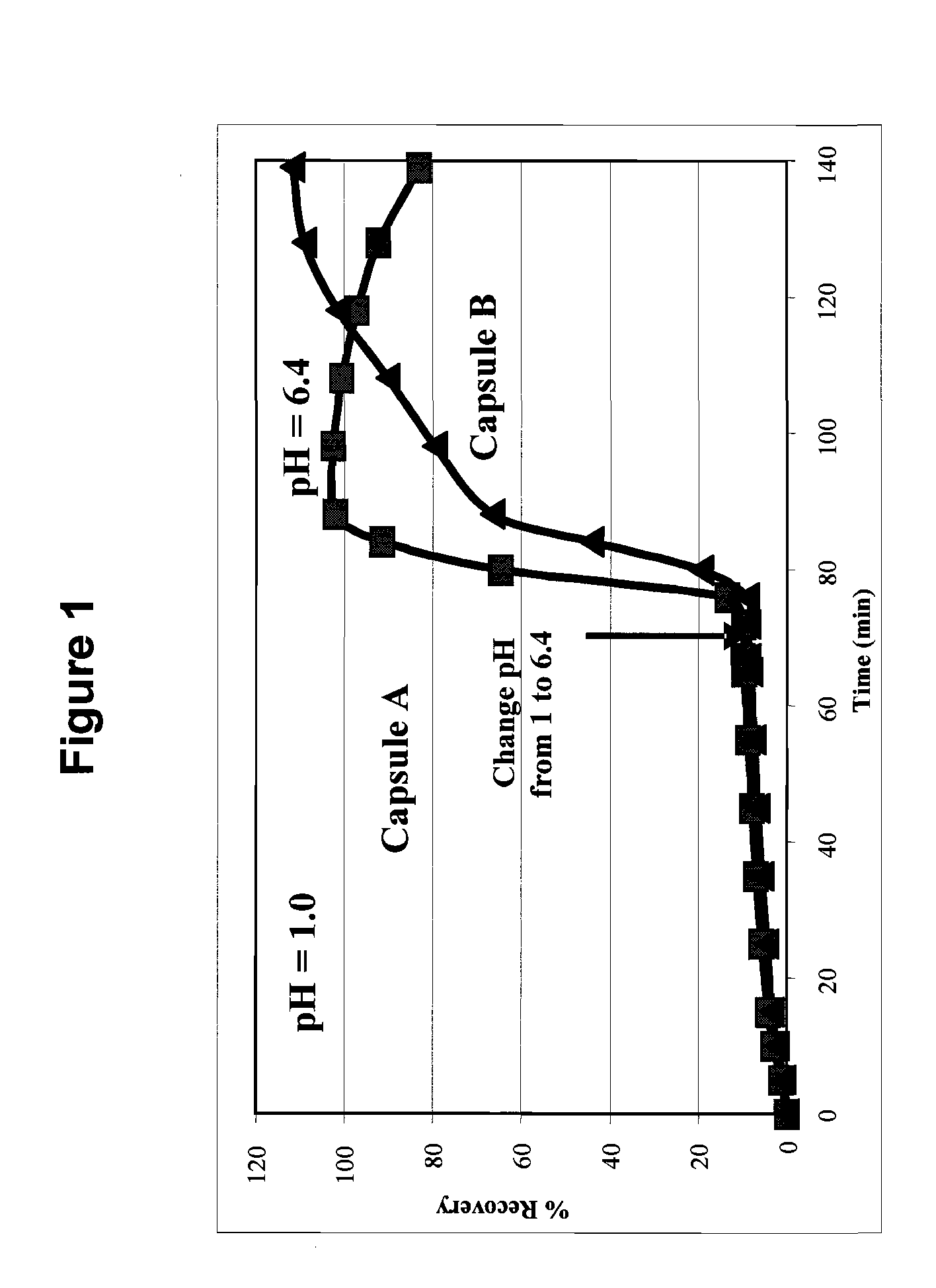
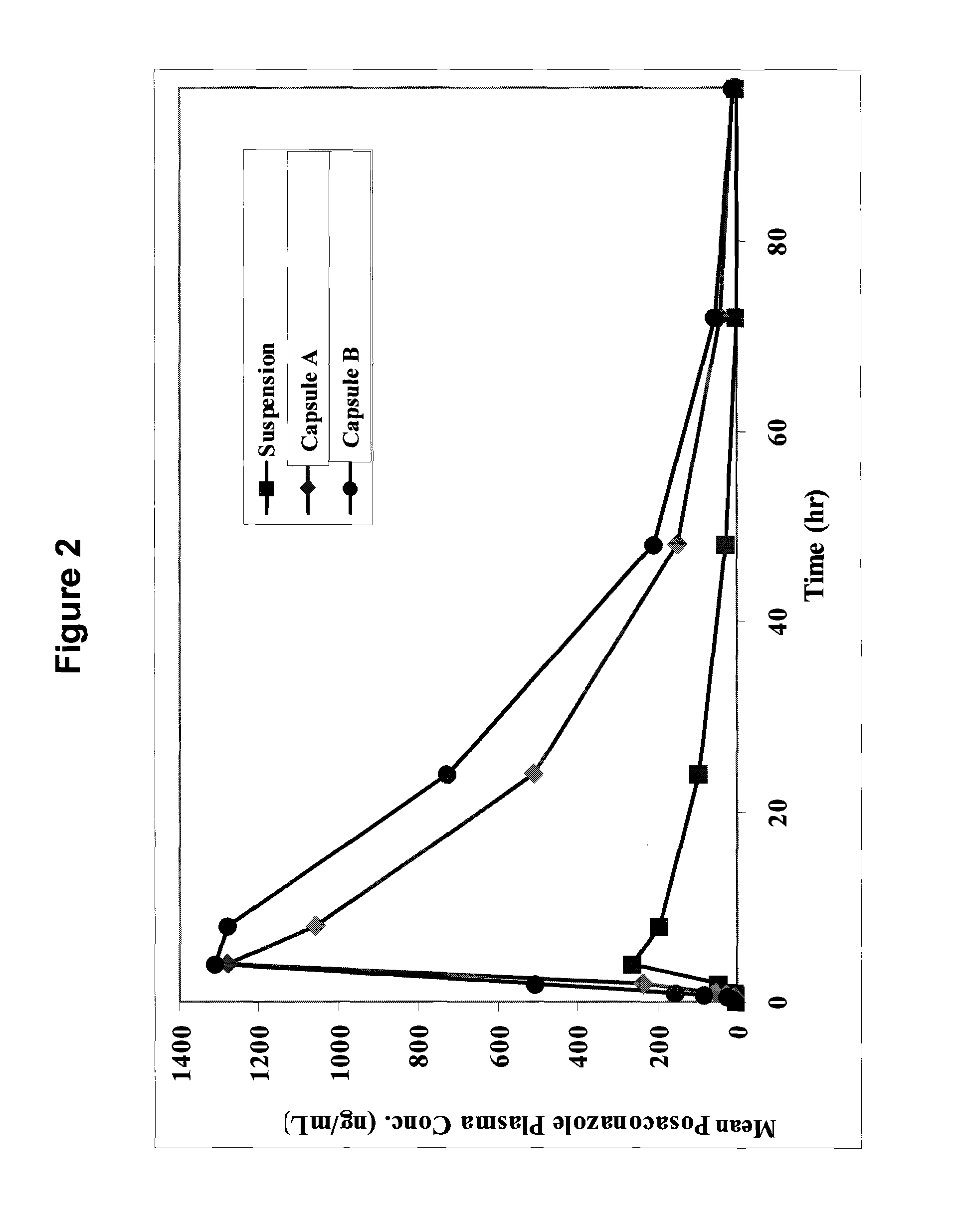
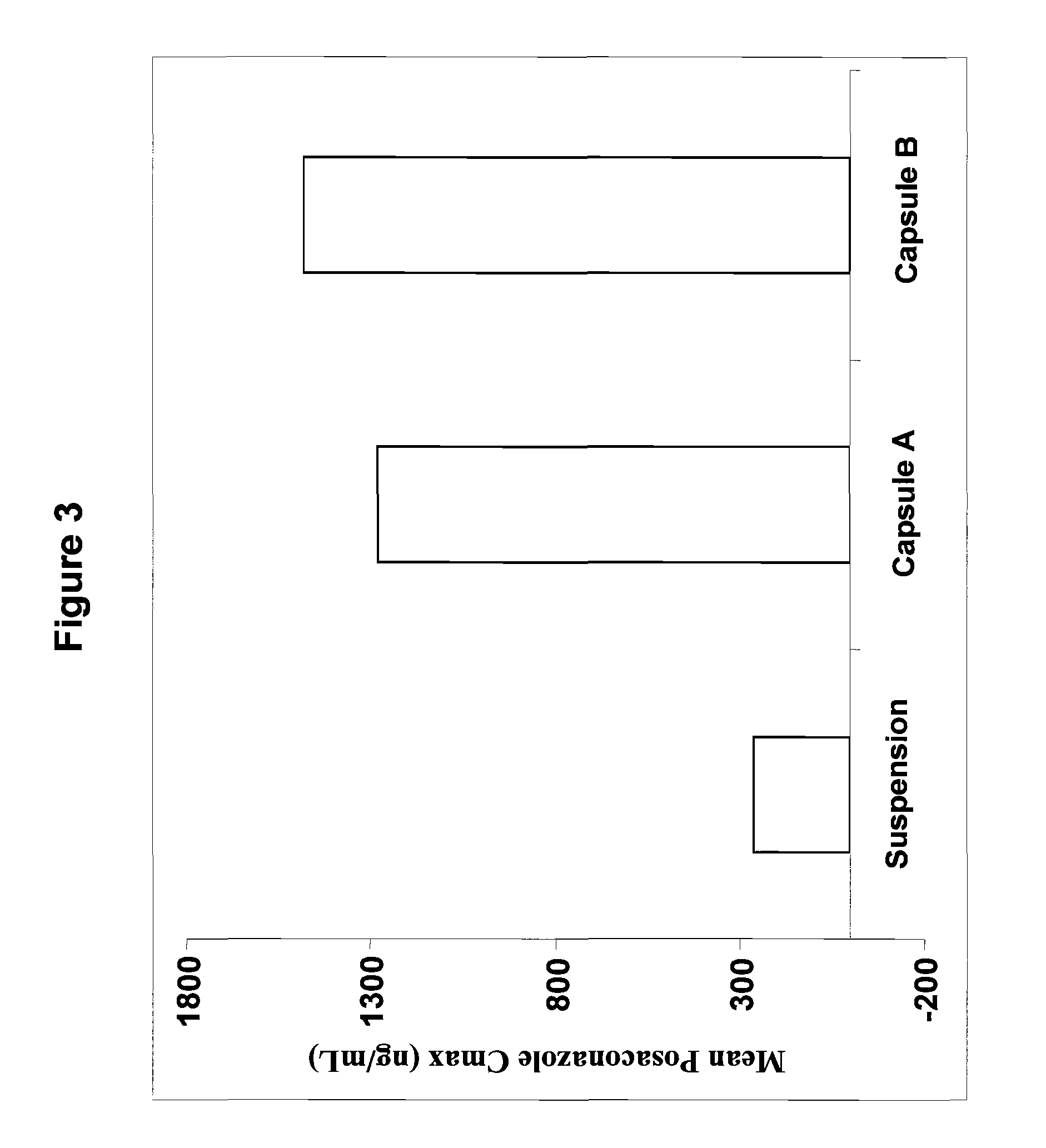
Oral Pharmaceutical Compositions in a Solid Dispersion Comprising Preferably Posaconazole and HPMCAs
InactiveUS20110034478A1Low variabilityReduce the impactOrganic active ingredientsAntimycoticsPH-sensitive polymersWater soluble
The present invention provides a solid molecularly dispersed composition comprising a poorly water soluble and weakly basic azole antifungal compound and a pH sensitive polymer, pharmaceutical compositions, comprising the solid molecularly dispersed composition of the invention and methods of treating and / or preventing a fungal infection in a patient in need thereof comprising orally administering a pharmaceutical composition comprising a composition of the invention to a patient in need thereof. Preferably the antifungal, compound is posaconazole, and the pH sensitive polymer is HPMCAS.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
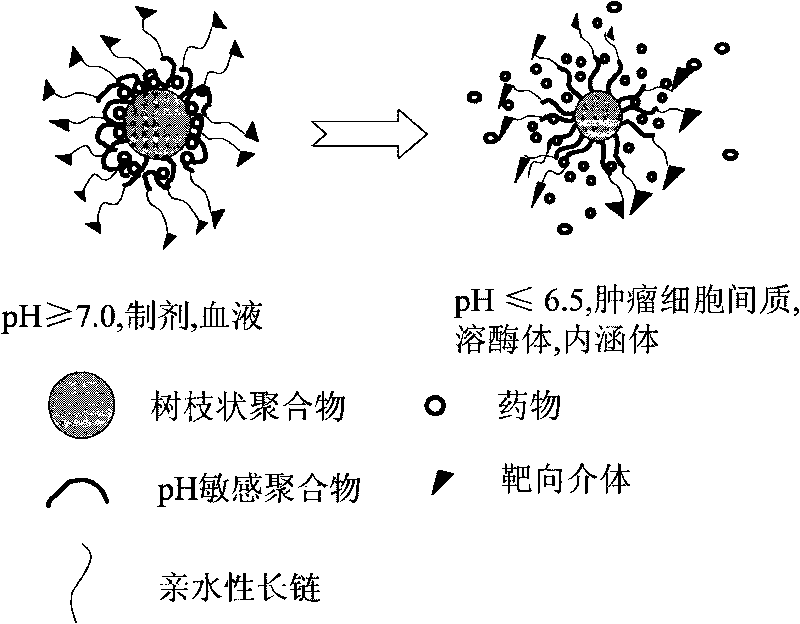
PH-sensitive dentritic polymer drug carrier
InactiveCN101708335AHigh drug loadingStrong tumor targetingPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsTumor targetPH-sensitive polymers
The invention discloses a pH-sensitive dentritic polymer drug carrier. The structure of the drug carrier is one of the following: (1) A-B-C, (2), (3) A-B-C-D and (4), wherein A is dentritic polymer core comprising repeated groups, B is pH-sensitive polymer, C is hydrophilic polymer and D is targeting molecule. The pH-sensitive dentritic polymer has a nano-grade grain diameter, and can be used for coating antitumor drug. Besides, the pH-sensitive dentritic polymer has strong tumor targeting effect in vivo, thereby releasing drug quickly after reaching the tumor position.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE PLA
Tumor-targeting pH-sensitive polymeric micelle composition
InactiveCN104116710AGood pH sensitivitySignificant targetingPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsEmulsion deliveryHigh concentrationTumor target
The invention belongs to the field of medicinal preparations, and relates to a tumor-targeting pH-sensitive polymeric micelle composition, and especially relates to a pH-sensitive polymeric micelle composition encapsulating a poorly-soluble anti-tumor medicine. The tumor-targeting pH-sensitive polymeric micelle composition is constructed by employing biologically-compatible pH-sensitive amphiphilic block polymer and an amphiphilic polymer connected with a targeting ligand or an antibody in a certain ratio, and the composition encapsulates a poorly-soluble anti-tumor medicine. Experiments prove that the polymeric micelle composition has pH-dependent release characteristic, is accumulated in tumor tissue in a high concentration, has specifically targeting inhibiting effect on growth of tumor cells, and provides a novel carrier and preparation strategy for poorly-soluble anti-tumor medicines.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
pH sensitive polymer for inhibiting transformation in drugs
InactiveUS7282218B2Bioavailability is maintainedHigh molecular weightPowder deliveryDispersion deliverySolvent evaporationPH-sensitive polymers
The present invention discloses a substantially amorphous pharmaceutical composition comprising a drug that can exist in a variety of polymorphic forms and a pH sensitive polymer, which inhibits the crystallization of the drug during formulation and reconstitution. Polymers of higher molecular weight are more effective at lower loading, especially when the drug polymer matrix is prepared by the solvent evaporation or solvent extraction technique. The compositions used as dry syrups maintain bioavailability of the drug and effectively mask the taste of the drug when the composition is reconstituted.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
pH-SENSITIVE NANOPARTICLES FOR ORAL INSULIN DELIVERY
ActiveUS20130034589A1Novel and effective pH-sensitiveImprove oral bioavailabilityPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsPh sensitive nanoparticlesOral medication
The present invention discloses the pH-sensitive nanoparticles composed of pH-sensitive polymer, hydrophobic material, internal stabilizer, external stabilizer content and insulin drug. The present invention also includes a method for preparation of pH-sensitive nanoparticles, in particular, a multiple emulsions solvent evaporation method. The pH-sensitive nanoparticles of the present invention show good pH-sensitive property with 100-300 nanometer particle size. Significant decrease in blood glucose level is observed in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats and the bioavailability of insulin is more than 10% after oral administration of the insulin-loaded pH-sensitive nanoparticles.
Owner:NANO & ADVANCED MATERIALS INST
Tumor-targeting pH-sensitive polymeric micelle composition resisting tumor drug resistance
InactiveCN104116709APharmaceutical non-active ingredientsEmulsion deliveryHigh concentrationTumor target
The invention belongs to the field of medicinal preparations, relates to a tumor-targeting pH-sensitive polymeric micelle composition resisting tumor drug resistance, and especially relates to a tumor-targeting pH-sensitive polymeric micelle composition resisting tumor drug resistance and encapsulating a poorly-soluble anti-tumor medicine. The tumor-targeting pH-sensitive polymeric micelle composition resisting tumor drug resistance is constructed by employing a biologically-compatible pH-sensitive amphiphilic, an amphiphilic polymer connected with a targeting ligand or an antibody and D-alpha-tocopherol polyethyleneglycol succinate (TPGS) in a certain ratio, and encapsulates a poorly-soluble anti-tumor medicine. Experiments prove that the polymeric micelle composition has pH-dependent release characteristic, is accumulated in tumor tissue in a high concentration, has specifically targeting inhibiting effect on growth of tumor cells generating drug resistance because of over expression of P-glycoprotein, and provides a novel carrier and preparation strategy for poorly-soluble anti-tumor medicines and reversing of drug resistance of tumor cells.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
ph-sensitive polymeric micelle composition resisting tumor drug resistance
InactiveCN104116711AGood pH sensitivityObvious passive targetingPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsEmulsion deliveryHigh concentrationPH-sensitive polymers
The invention belongs to the field of medicinal preparations, relates to a pH-sensitive polymeric micelle composition resisting tumor drug resistance, and especially relates to a pH-sensitive polymeric micelle composition resisting tumor drug resistance and encapsulating a poorly-soluble anti-tumor medicine. The pH-sensitive polymeric micelle composition resisting tumor drug resistance is constructed by employing two kinds of biologically-compactable pH-sensitive amphiphilic block polymer and an amphiphilic polymer D-alpha-tocopherol polyethyleneglycol succinate (TPGS) as a P-gp inhibitor in a certain ratio, and encapsulates a poorly-soluble anti-tumor medicine. Experiments prove that the polymeric micelle composition has pH-dependent release characteristic, is accumulated in tumor tissue in a high concentration, has specifically targeting inhibiting effect on growth of tumor cells generating drug resistance because of over expression of P-glycoprotein, and provides a novel carrier and preparation strategy for poorly-soluble anti-tumor medicines and reversing of drug resistance of tumor cells.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
pH-sensitive polymer
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
pH-sensitive nanoparticles for oral insulin delivery
ActiveUS8859004B2Improve bioavailabilityImprove oral bioavailabilityBiocideNanotechPh sensitive nanoparticlesPH-sensitive polymers
Owner:NANO & ADVANCED MATERIALS INST
Taste masked pharmaceutical compositions comprising bitter drug and pH sensitive polymer
The present invention discloses pharmaceutical compositions comprising of pH sensitive polymers used for taste masking highly bitter drugs. The pH sensitive polymer acts as a reverse enteric coating, which is soluble in the acidic pH range 1.0 to 3.0 normally found in the stomach but is insoluble in the pH range 3.5 to 7 thus inhibiting the release of the bitter drug at the pH of saliva and also at the pH of reconstitution medium in case of liquid orals.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
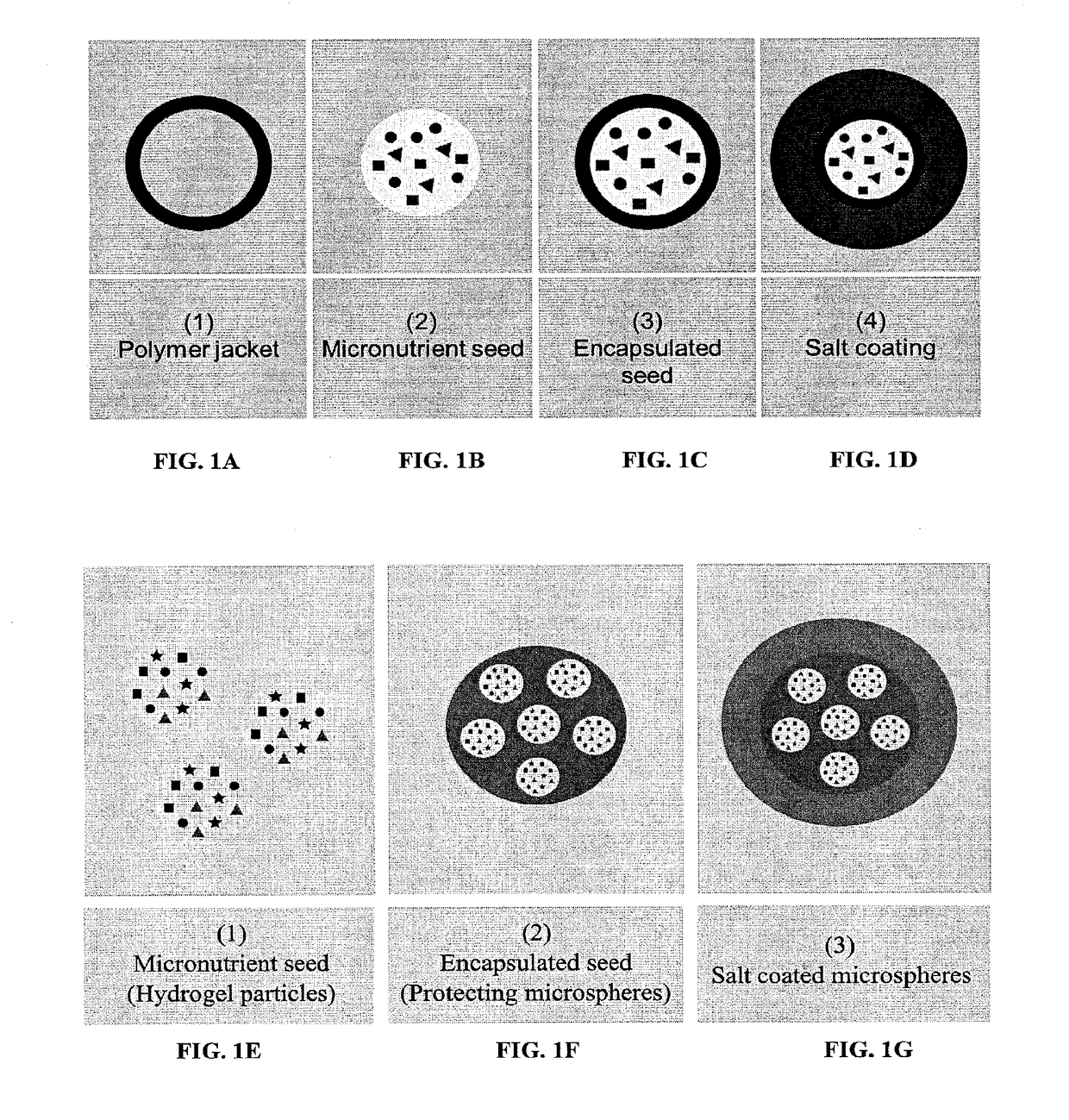
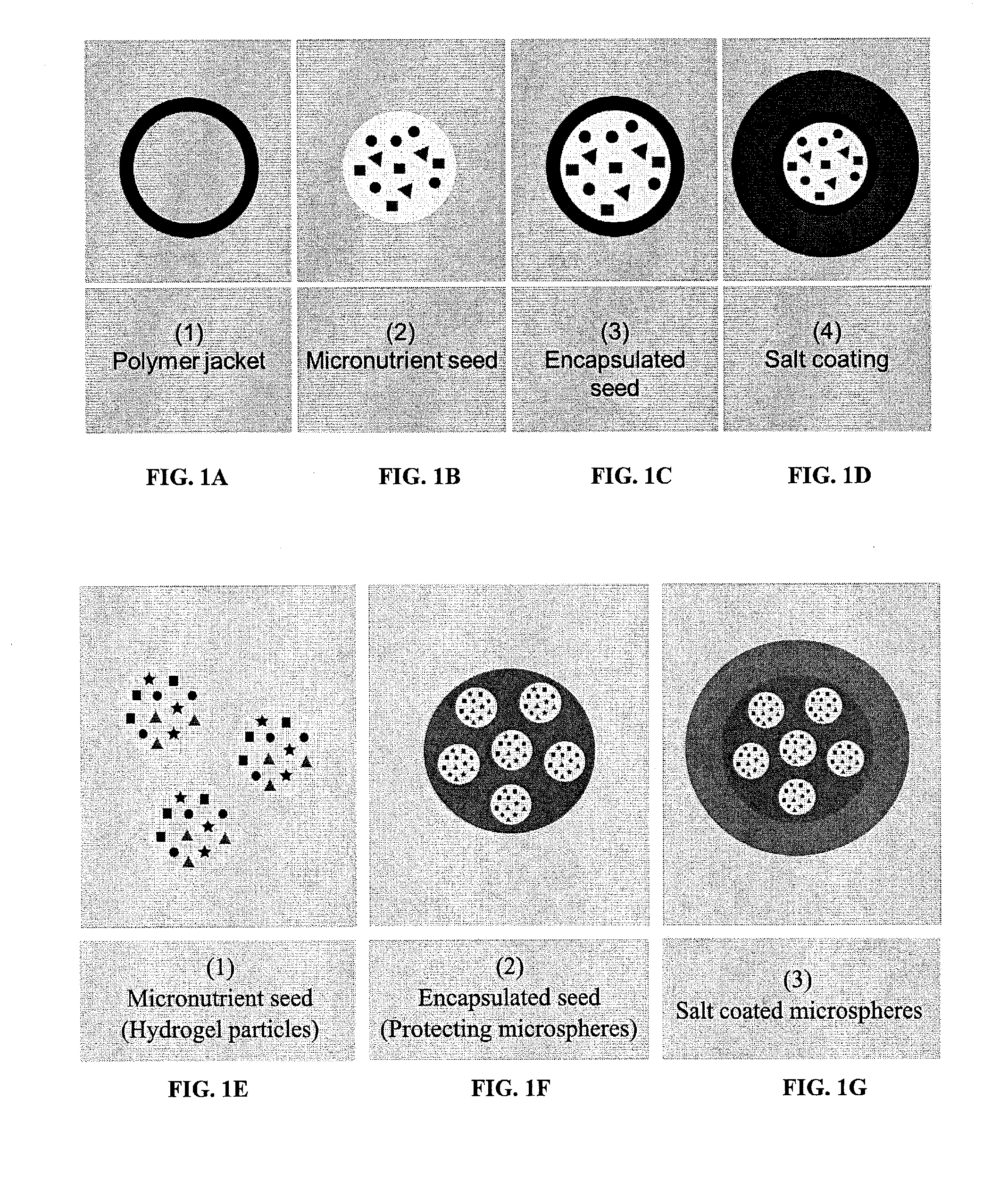
Fortified micronutrient salt formulations
ActiveUS20170216216A1Uniform colorHeat stableHeavy metal active ingredientsHydroxy compound active ingredientsWater insolubleSevere malnutrition
Owner:TOKITAE LLC +1
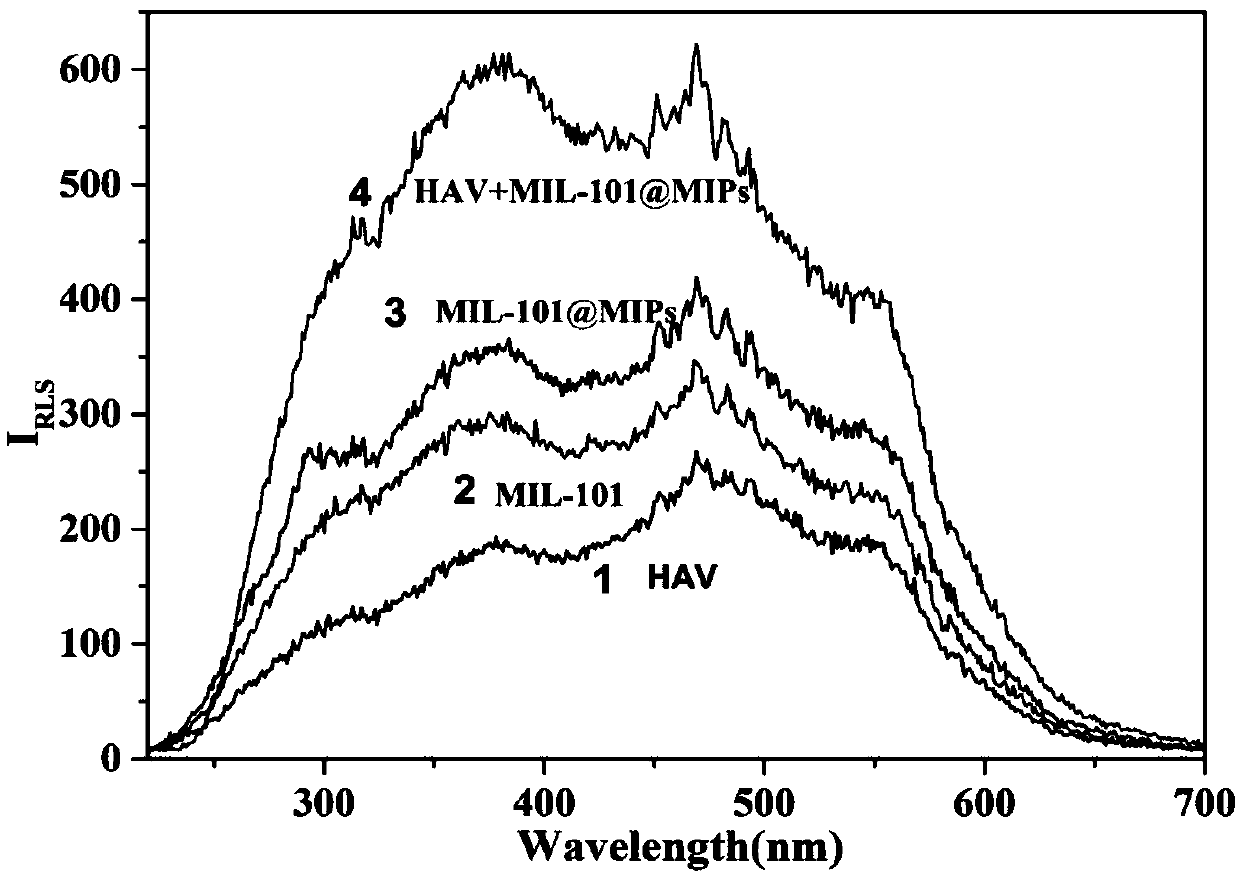
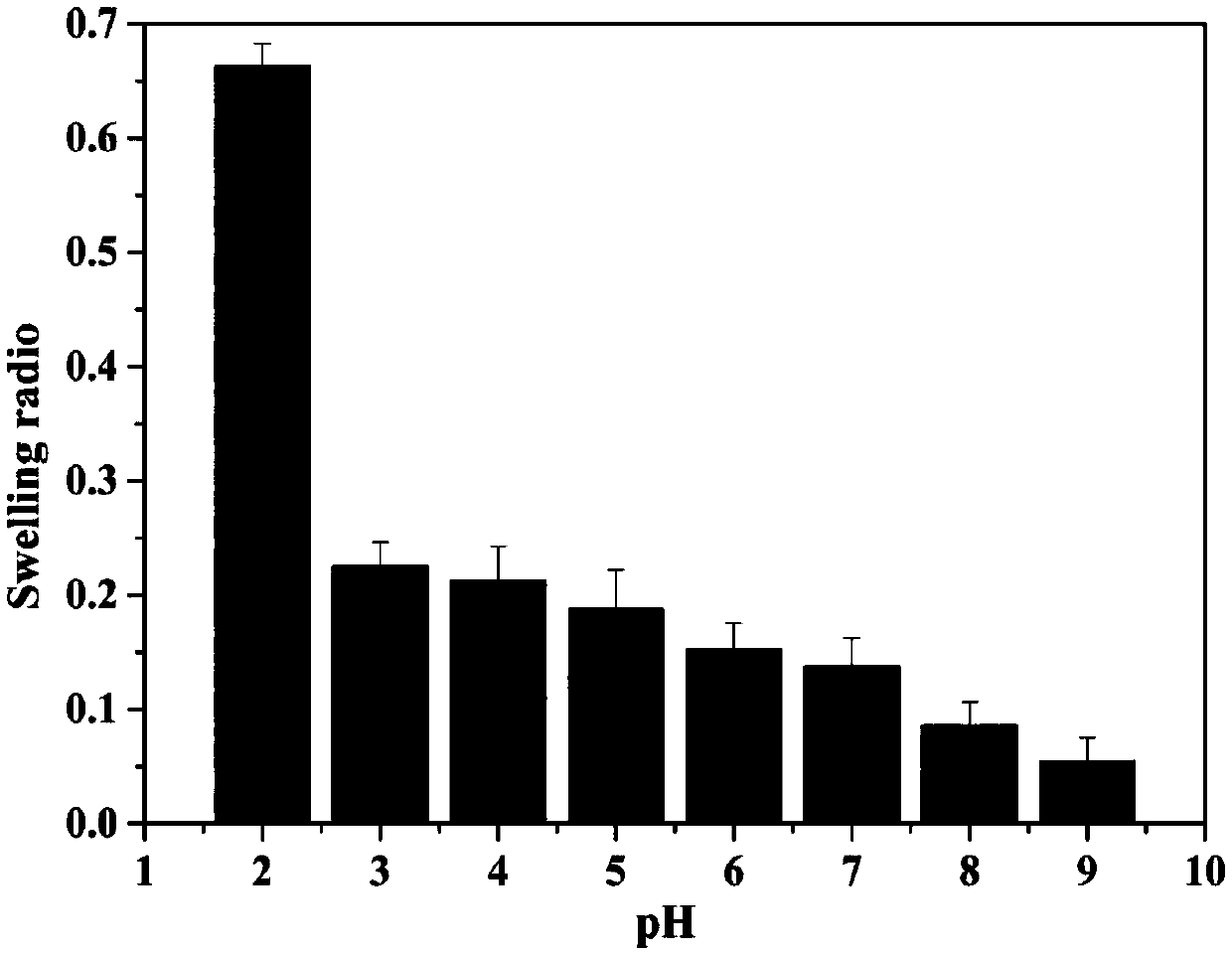
Preparation and application of intelligent virus molecular imprinting resonance light sensor based on metal organic framework
ActiveCN109632730ALarge specific surface areaMany binding sitesScattering properties measurementsFluorescence/phosphorescenceBinding siteResonance
The invention discloses a preparation and application of an intelligent virus molecular imprinting resonance light sensor based on a metal organic framework. According to the preparation method, a metal organic framework material is used as a supporting body for the first time, and a pH sensitive polymer is an imprinting layer material, so that the molecular imprinting resonance light sensor for detecting viruses is prepared. Due to the fact that the specific surface area of the metal organic framework material is large, more binding sites can be provided; and meanwhile, the pH sensitive polymer has the property of intelligently responding to a pH value so that adsorption and elution of virus macromolecules can be realized more conveniently and more efficiently. Experimental results show that the sensor has good selectivity to template molecules and has a wide linear range, and the detection limit reaches 0.1 pM; the imprinted polymer can be recycled; and finally, the sensor is simpleto prepare, the detection process is simple and convenient to operate, powerful means for detection and diagnosis of the viruses are provided, and an important application prospect is achieved.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Fortified micronutrient salt formulations
ActiveUS20150164816A1Uniform colorHeat stableHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideSevere malnutritionWater insoluble
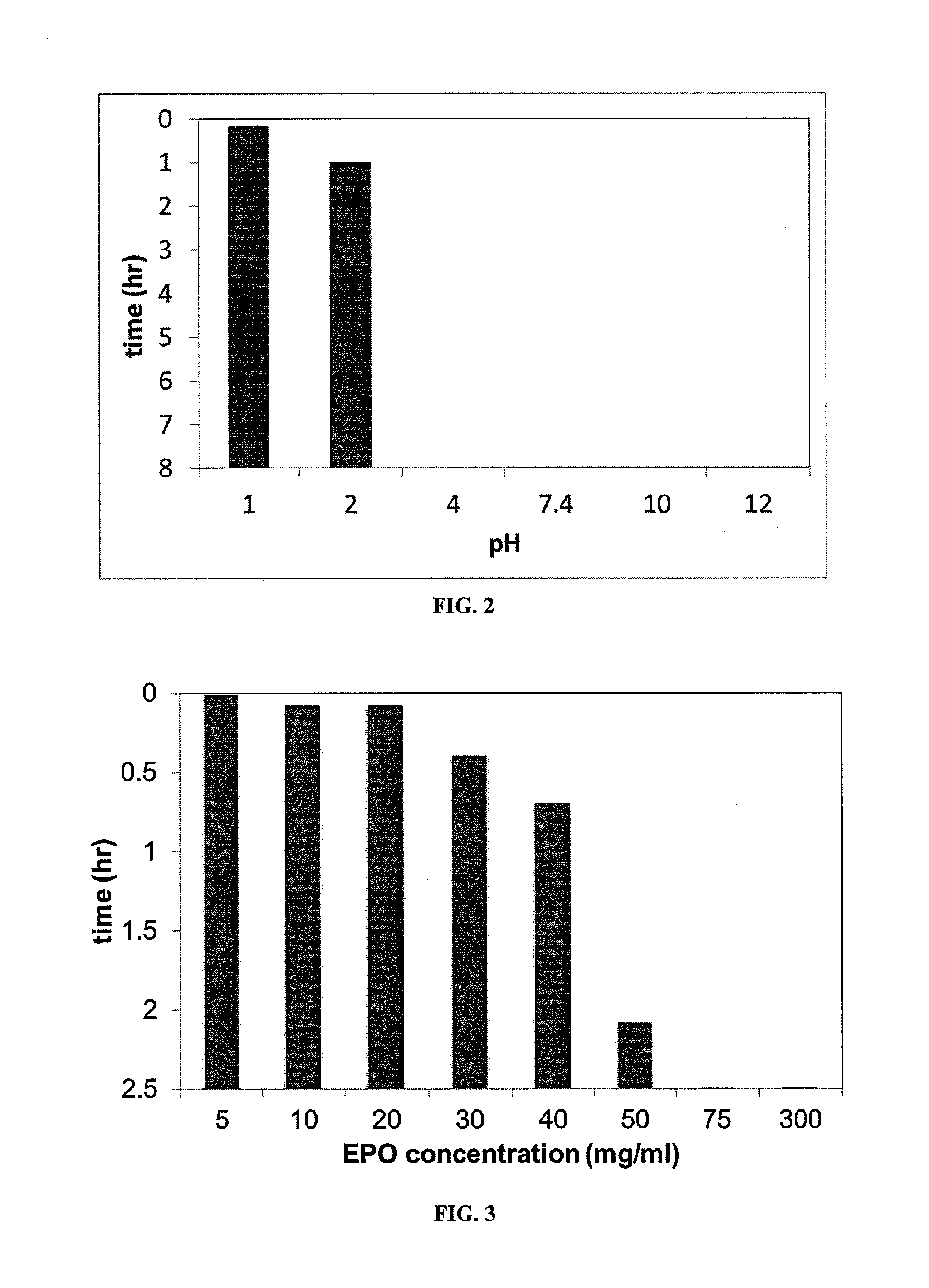
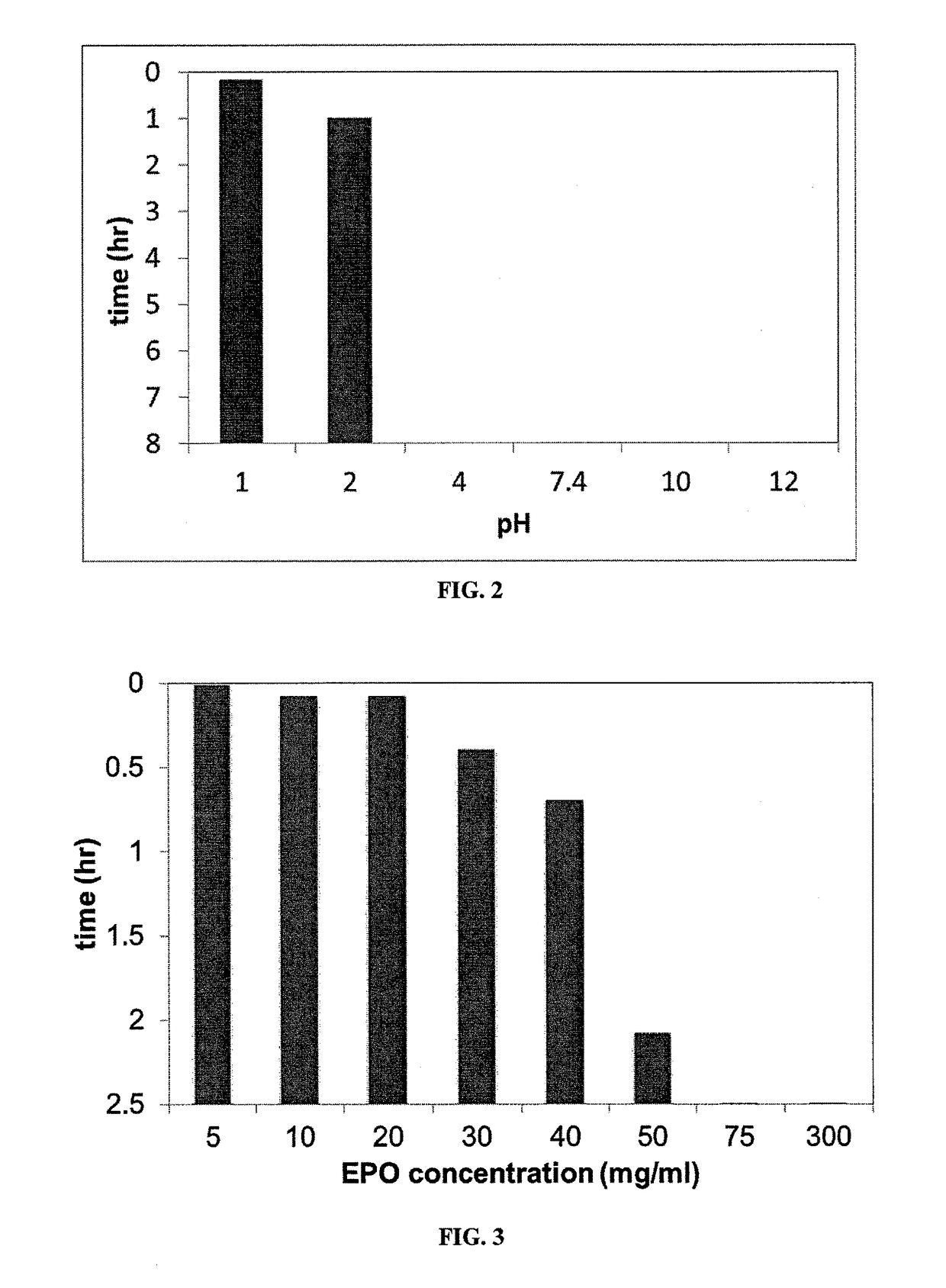
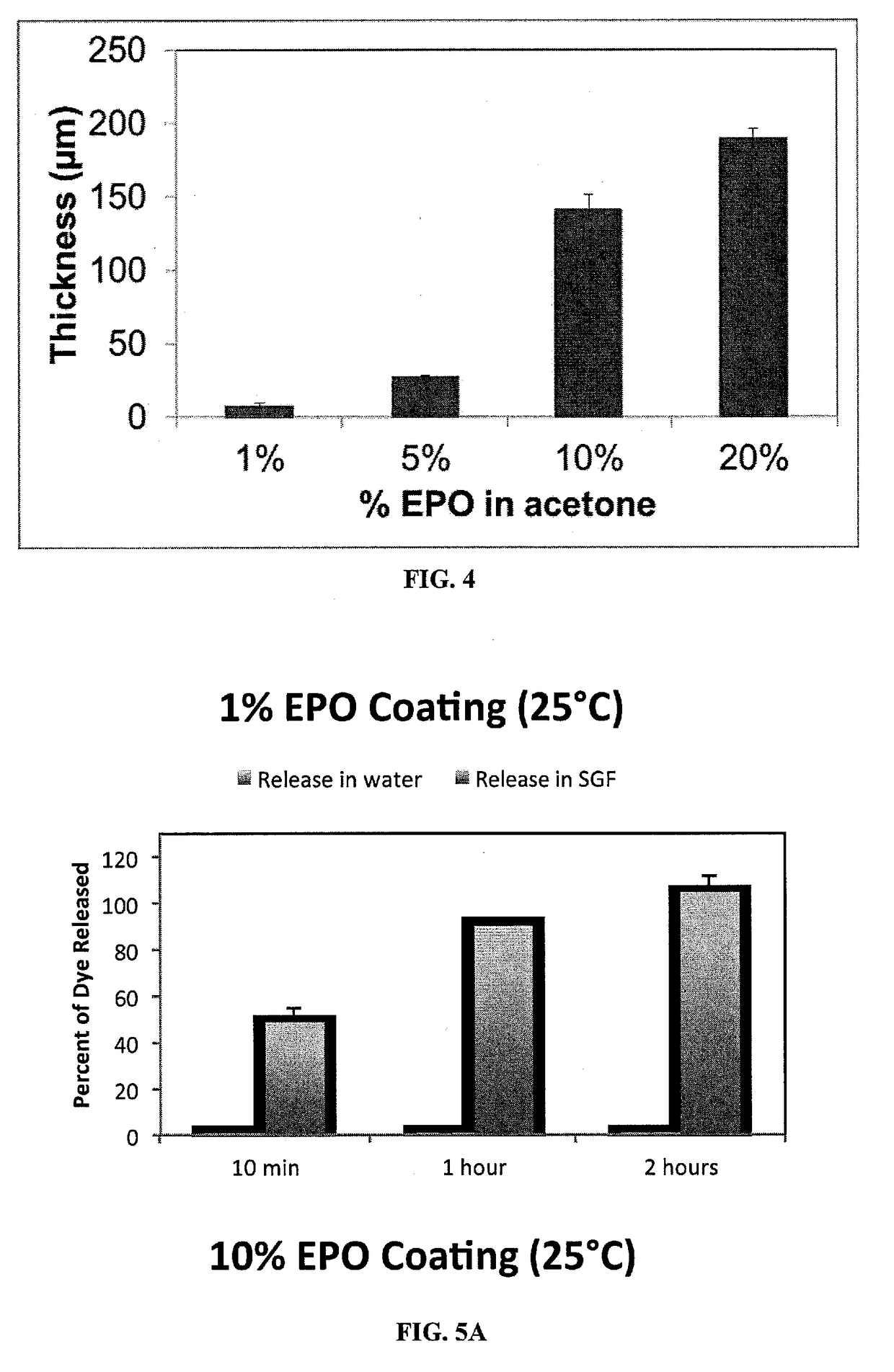
Salt formulations, which are resistant to moisture and cooking conditions, are described herein. The formulations provide particles of micronutrients and vitamins encapsulated within heat resistant pH-sensitive water-insoluble polymers, which are packaged within a salt shell. The pH-sensitive, water-insoluble, thermally stable materials stabilize the micronutrients, particularly at high temperatures, such as during food preparation and cooking, and release the micronutrients at the desired locations such as the stomach, small intestine, etc. Preferred pH-sensitive polymers release at a low pH, less than the pH present in the stomach. The particles can be used to deliver daily-recommended doses of micronutrients simultaneously with salt, eliminating the need for vitamin pills. This is particularly important in populations suffering from severe malnutrition.
Owner:TOKITAE LLC +1
Delayed release dosage form
The present invention is directed to a delayed release pharmaceutical composition in solid dosage form comprising a core comprised of a therapeutically effective amount of drug, e.g., mesalamine, and a pH sensitive coating comprising a mixture of two different pH sensitive polymers, the first pH sensitive polymer dissolves in an aqueous solution at a pH of about 7 or greater and the second pH sensitive polymer dissolves in an aqueous solution at a pH of about 6 or greater, wherein the weight ratio of the first pH sensitive polymer to the second pH sensitive polymer ranges from about 2:1 to about 4:1 and the percent weight gain resulting from the addition of the pH sensitive coating ranges from about 8% up to and including 15% by weight of the core, including any subcoating.
Owner:EMET PHARMA
Fortified micronutrient salt formulations
ActiveUS9649279B2Uniform colorHeat stableHeavy metal active ingredientsHydroxy compound active ingredientsWater insolubleSevere malnutrition
Owner:TOKITAE LLC +1
Degradable polymer with pH sensitivity of tumor tissues and preparation method for degradable polymer and application of degradable polymer
InactiveCN105017510AReduced release rateFacilitated releaseOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsHigh concentrationSide effect
A degradable polymer with pH sensitivity of tumor tissues is a compound in the structure in the formula, wherein the formula is shown in the description, n is greater than or equal to 150 but less than or equal to 420, and n is an integer. The pH sensitive polymer provided by the invention as a drug-loading micelle has the characteristics that (1) the polymer is truly nanoscale (less than 200 nm) and is very uniform and stable; (2) multi-target technology (which overcomes the deficiencies of single targeting) comprises natural targeting of a long-circulating nanoparticle and pH sensitive physical and chemical targeting, so that tumor targeting is sufficiently obtained; (3) the polymer is large drug loading capacity and good in stability, and the treatment cost is lowered and the side effects generated by free drug release; (4) the drug is quickly released in a tumor tissue to obtain a local high concentration so as to quickly kill the cancer cells, and drug resistance is not easily generated; and (5) the polymer is less in distribution in normal tissues and few in side effects as a result of high tumor targeting; even if a small amount of polymer reaches the non-tumor parts, the drug is nearly not released or the release rate is less as a result of pH sensitivity, so that the polymer is few in side effects.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
Hydrazide pH sensitive polymer as well as preparation method and application thereof
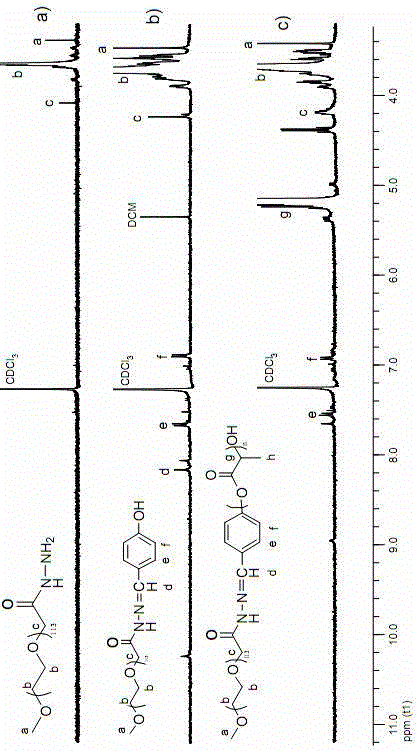
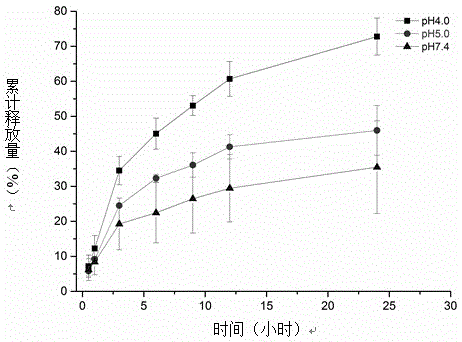
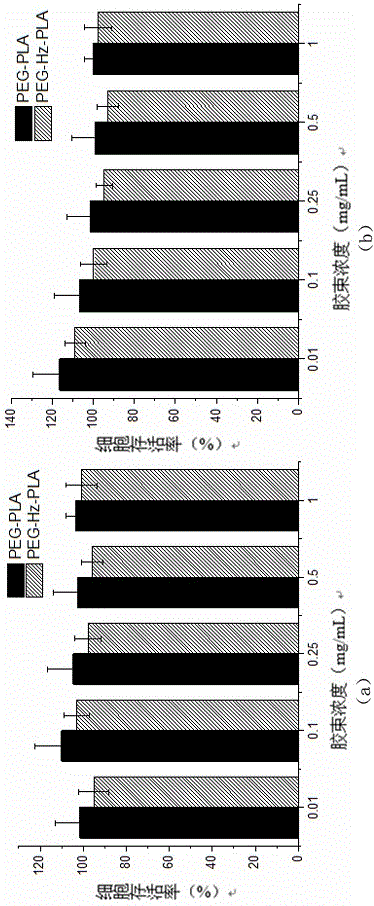
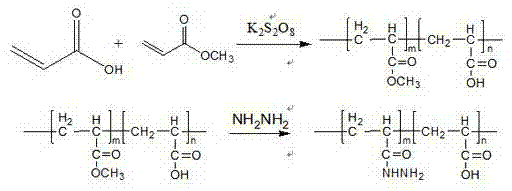
ActiveCN104761674AIncrease contentHigh enrichment efficiencyPeptide preparation methodsPH-sensitive polymersGlycopeptide
The invention discloses a hydrazide pH sensitive polymer. The hydrazide pH sensitive polymer comprises the following raw materials: acrylic acid, methyl acrylate, an initiator, hydrazine hydrate, an organic phase and water, wherein the molar ratio of acrylic acid to methyl acrylate is 1: 10 to 10: 1, the molar ratio of hydrazine hydrate to methyl acrylate is 1: 10 to 10: 1, the addition amount of the initiator is 0.02-2%w / v, and the volume ratio of the organic phase to a water phase is 1: 10 to 10: 1. The hydrazide pH sensitive polymer disclosed by the invention is prepared by steps of copolymerizing acrylic acid and methyl acrylate and then carrying out a hydrazine reaction through hydrazine hydrate, wherein the content of hydrazide is obviously higher than the content of hydrazide in a commercialized hydrazide material; the reaction between a hydrazide functional group in the hydrazide pH sensitive polymer and an aldehyde group in oxidized glycopeptide is covalent binding, and the enrichment specificity of glycopeptide can be provided; the hydrazide pH sensitive polymer is in a dissolved state in a system with a pH value of higher than 4, and the phase homogeneity of the reaction of the functional group hydrazide and the aldehyde group of the glycopeptide can be realized, thus increasing the reaction speed and the glycopeptide enrichment efficiency.
Owner:ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI
PH sensitive polyvinylidene fluoride gel film and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102068921BAdjustable sizeAdjust filter characteristicsSemi-permeable membranesCross-linkPolymer science
The invention relates to a pH sensitive polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) gel film and a preparation method thereof. The pH sensitive PVDF gel film comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 0.5 to 2.5 percent of pH sensitive macromolecular polymer gel and 97.5 to 99.5 percent of PVDF polymer. The preparation method comprises the following processes of: a) preparing the pH sensitivemacromolecular polymer gel, namely, dissolving pH sensitive polymer monomers and a cross linking agent into absolute ethanol, and performing free radical polymerization under nitrogen protection condition to obtain the pH sensitive polymer gel; b) preparing casting solution, namely, dispersing the pH sensitive polymer gel obtained by the step (a) into an organic solvent, gradually adding a certain amount of PVDF powder, and performing dissolution and degassing to obtain the casting solution; and c) preparing the gel film, namely, scraping the casting solution obtained by the step (b) to form a liquid film on a clean and flat glass plate, and curing the liquid film in a coagulating bath to form the film. The PVDF gel film prepared by the method has the aperture size of 100 to 300 nm; and the inner surfaces of holes consist of the pH sensitive polymer gel which can give a response according to the environmental pH change to change the sizes of the film holes, so the PVDF gel film can beused for the intelligent selective separation of separated substances.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Ph-sensitive degradable polymer, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104961887AHigh drug loadingFacilitated releasePharmaceutical non-active ingredientsEmulsion deliverySide effectCancer cell
The invention discloses a pH-sensitive degradable polymer, and a preparation method and application thereof. The polymer is the compound with the following structure as shown in figure, n is not larger than 410 and not smaller than 140, and n is an integer. The pH-sensitive polymer as a medicine carrying micelle has the characteristics that (1), nanoscale is truly realized (smaller than 200nm), and uniformity and stability are high; (2) a multi-targeting technology is realized (defects of mono-targeting are overcome), and comprises natural targeting of long circulation nano particles and pH-sensitive physical chemistry targeting, and tumor targeting is fully obtained; (3) medicine carrying amount is larger, stability is good, treatment cost is reduced and side effects generated by release of free medicine are reduced; (5) the polymer has little distribution in normal tissues due to high tumor targeting, and has very small side effects; even a small amount of polymer arrive at a non-tumor position, the medicine is barely released or very small in release rate due to pH sensitivity and the side effects are very small.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com