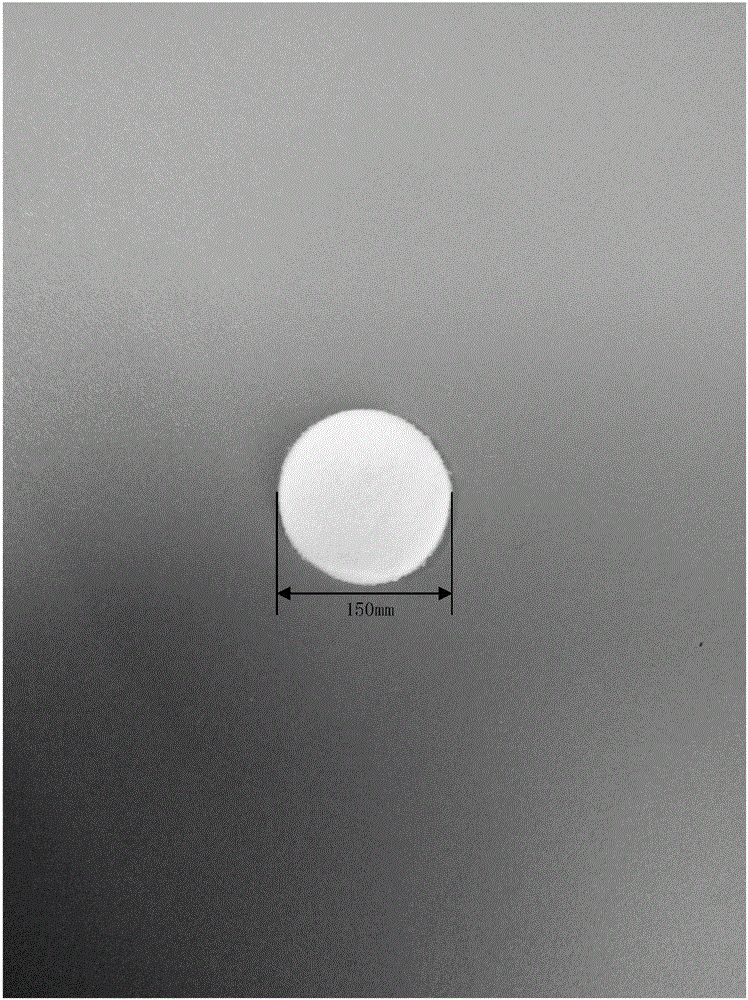
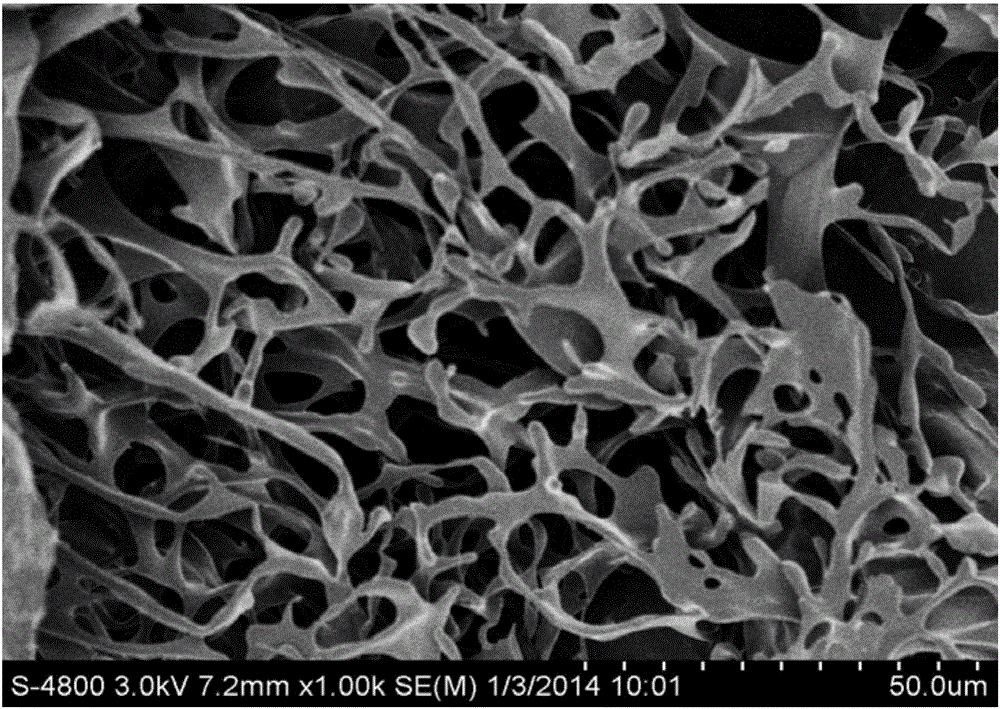
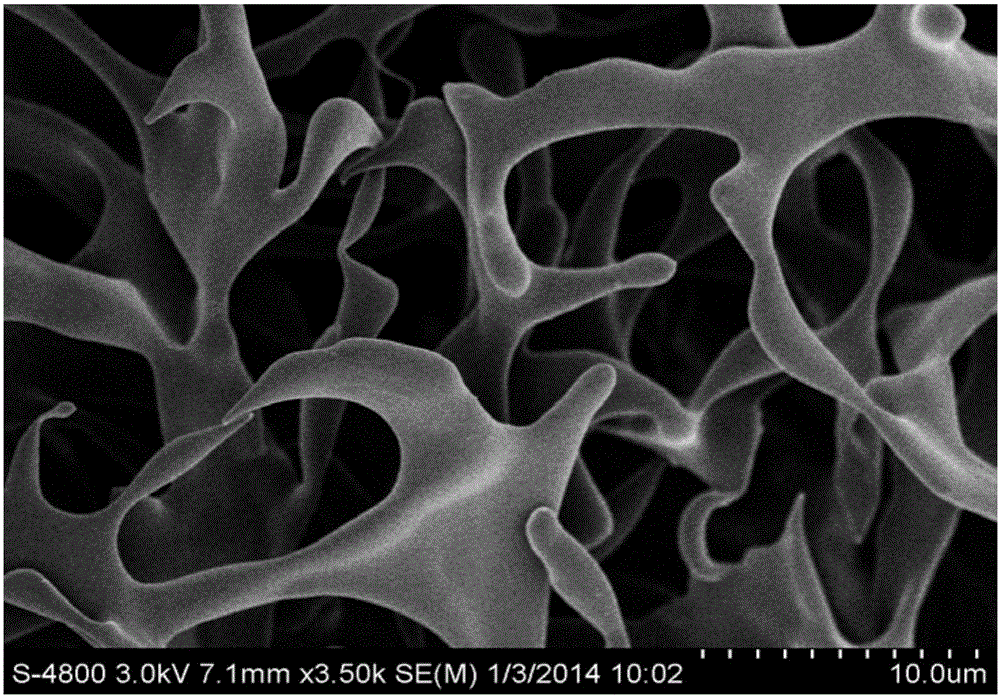
Tissue engineering cartilage stent and method for preparing same
A technology of tissue engineering and cartilage, which is applied in the field of tissue engineering cartilage scaffolds and its preparation, can solve the problems of unsatisfactory treatment effects, and achieve the effect of convenient application, good biocompatibility, and compact appearance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] The preparation method of tissue engineered cartilage scaffold of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0034] Step 1: Extraction of type II collagen.
[0035] First, select fresh bovine cartilage, remove the periosteum with chloroform and methanol, and pulverize the fresh bovine cartilage. Next, the pulverized cartilage tissue was stirred with 0.05 mol / L Tris-HCl solution containing 4 mol / L guanidine hydrochloride, centrifuged at 4° C., and the supernatant was removed. Repeat several times to remove proteoglycan. Then, thoroughly wash the precipitate obtained by centrifugation with 0.1-0.5mol / L acetic acid, dissolve it in acetic acid of the same concentration, add pepsin to digest the precipitate for 10-18 hours, store it at 4°C and centrifuge, and centrifuge the obtained The supernatant was then digested for 5-8 hours, and the supernatant obtained above was combined to prepare a type II collagen solution. Finally, the above supernatant was salted o...
Embodiment 2
[0047] The difference between this example and Example 1 is that in Step 3, the CII-HA-CS-HAP three-dimensional cartilage primary scaffold was soaked in a mixed solution of ethanol and MES for 30 minutes at room temperature. Then, soak the primary three-dimensional cartilage scaffold in a mixed solution containing ethanol, MES, NHS, and EDC, and place it in an incubator at 25° C. for 36 hours for cross-linking. The various conditions of other experimental steps are kept unchanged, and the tissue engineering three-dimensional cartilage scaffold of the present invention is obtained.
Embodiment 3
[0049] The difference between this example and Example 1 is that in Step 3, the CII-HA-CS-HAP three-dimensional cartilage primary scaffold was soaked in a mixed solution of ethanol and MES for 30 minutes at room temperature. Then, soak the primary three-dimensional cartilage scaffold in a mixed solution containing ethanol, MES, NHS, and EDC, and put it in an incubator at 22° C. for 30 hours for cross-linking. With other conditions unchanged, the tissue engineered cartilage scaffold of the present invention is finally obtained.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com