A kind of coordination polymer porous material maf-49 and its preparation method and application
A coordination polymer, MAF-49 technology, applied in waste fuels, separation methods, zinc organic compounds, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient separation efficiency and high energy consumption, and achieve good thermal and chemical stability, Good thermal stability and improved purification efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1 Porous material MAF-49 single crystal preparation
[0035] Ligand H 2 Batz is synthesized according to the prior art method;
[0036] Ligand H 2 batz (0.180 g, 1.0 mmol), Zn(OH) 2 (0.100 g, 1.0 mmol), ammonia water (25%, 4 mL), and water (4 mL) were added into a hydrothermal reaction kettle, heated to 160 °C for 3 days to obtain a colorless MAF-49 single crystal, producing The rate is 86%.
Embodiment 2
[0037] Example 2 Structural characterization of MAF-49 with and without guest molecules
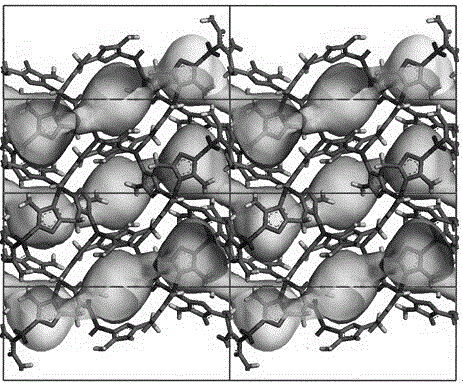
[0038] The single crystal X-ray diffraction data were collected on a Bruker Smart APEX CCD diffractometer with a graphite monochromator, using Mo-K rays to collect data in an ω-scan manner, and the absorption correction was performed using the REQAB program. The direct method is used for analysis, and then the coordinates of all non-hydrogen atoms are obtained by the difference Fourier function method and the least square method, and finally the structure is corrected by the least square method. The hydrogen atoms of the compounds are obtained by theoretical hydrogenation. The calculation work is done on the PC using SHELXTL program. The detailed crystal determination data are shown in Table 1. structure see figure 1 .
[0039] Table 1
[0040] complex MAF-49 MAF-49·H 2 o
[0041] R 1 =∑|| F o | - | F c || / ∑| F o |. wxya 2 =[∑ w ( F o 2 - F c 2 ) 2 / ...
Embodiment 3 Embodiment 1
[0042] Example 3 The thermal stability characterization of the porous coordination polymer MAF-49 obtained in Example 1
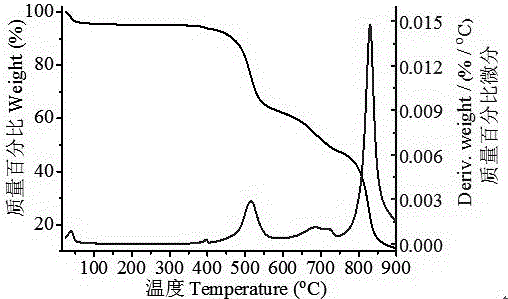
[0043] The thermal stability of the porous material was obtained by thermogravimetric analysis. The MAF-49 provided by the present invention has excellent thermal stability and can be stable to 723 K. For thermogravimetric curves, see image 3 .
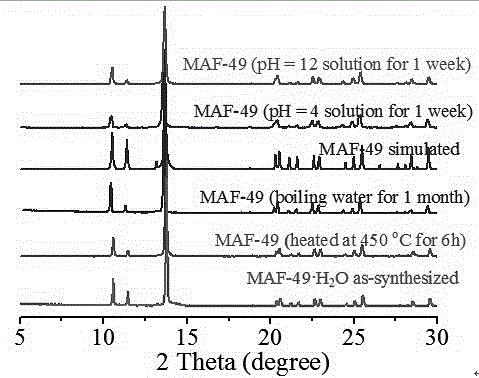
[0044] At the same time, in the present invention, the synthesized MAF-49 is directly immersed in an aqueous solution of 4 ≤ pH ≤ 12, and its framework structure will not be destroyed after structural determination and characterization, showing its good acid-base stability, and the corresponding powder diffraction characterization See figure 2 .
[0045] Example 4 Characterization of gas adsorption properties of the porous coordination polymer MAF-49 obtained in Example 1
[0046] The porous material to remove the guest was put into a quartz sample tube, and then its methane (CH 4 ), carbon dioxide (CO 2 )...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com