Determination method of chloride ion content of copper electrolyte
A technology of chloride ion content and copper electrolyte, applied in the direction of electrochemical variables of materials, etc., can solve the problems of absorbance interference deviation, large deviation between measurement results and actual values, long operation time, etc., to achieve high accuracy and precision, The potential sudden jump point is obvious, ensuring the effect of reliable recovery
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0017] Embodiment 1: the mensuration of chloride ion content in copper electrolytic solution
[0018] a. Add the silver nitrate standard solution with a concentration of 0.01mol / L to the reagent bottle of the potentiometer;
[0019] b. Add 10ml of copper electrolyte and 2ml of isopropanol to a beaker with a capacity of 100ml, add water to make the volume to 50ml, insert the silver composite electrode and titration head into the solution to be tested in the beaker, control the pipetting temperature and titration solution The temperature is 25°C-28°C, and the stirring speed is 625rpm;
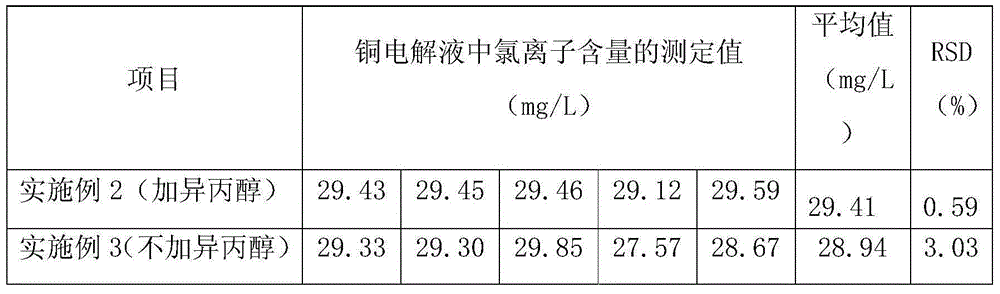
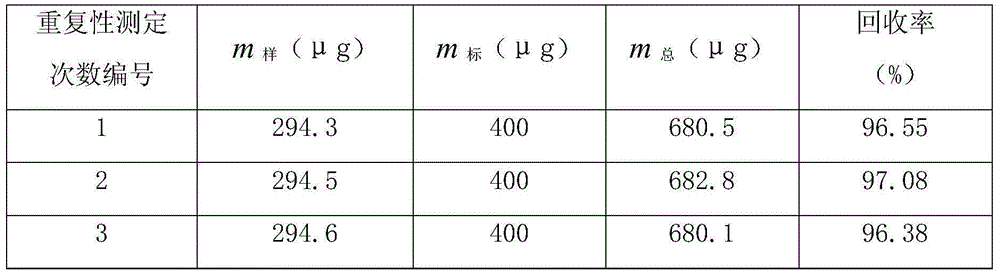
[0020] c. Titrate the silver nitrate standard solution in the reagent bottle into the beaker, and record the volume v of the silver nitrate standard solution corresponding to the titration consumption during the potential jump 0 According to the formula to calculate the content of chloride ions in the copper electrolyte, 5 groups were measured using the above method conditions, and the results s...
Embodiment 2
[0021] Embodiment 2: the mensuration of chloride ion content in copper electrolytic solution
[0022] a. Add the silver nitrate standard solution with a concentration of 0.01mol / L to the reagent bottle of the potentiometer;
[0023] b. Add 15ml of copper electrolyte and 3ml of isopropanol to a beaker with a capacity of 100ml, add water to make the volume to 50ml, insert the silver composite electrode and titration head into the solution to be tested in the beaker, control the temperature of the pipetting and the volume of the titration solution The temperature is 15°C-18°C, and the stirring speed is 625rpm;
[0024] c. Titrate the silver nitrate standard solution in the reagent bottle into the beaker, and record the volume v of the silver nitrate standard solution corresponding to the titration consumption during the potential jump 0 , according to the formula to calculate the content of chloride ions in the copper electrolyte, using the above method conditions to measure 5 g...
Embodiment 3
[0025] Embodiment 3: the mensuration of chloride ion content in copper electrolytic solution
[0026] a. Add the silver nitrate standard solution with a concentration of 0.01mol / L to the reagent bottle of the potentiometer;
[0027] b. Add 20ml of copper electrolyte and 4ml of isopropanol to a beaker with a capacity of 100ml, add water to make the volume to 50ml, insert the silver composite electrode and titration head into the solution to be tested in the beaker, control the temperature of the pipetting and the volume of the titration solution The temperature is 20°C-23°C, and the stirring speed is 625rpm;
[0028] c. Titrate the silver nitrate standard solution in the reagent bottle into the beaker, and record the volume v of the silver nitrate standard solution corresponding to the titration consumption during the potential jump 0 According to the formula to calculate the content of chloride ions in the copper electrolyte, 5 groups were measured using the above method cond...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com