Synthesized breast milk fat substitute product from mixed fatty acid under enzymatic condition in microwave and method for preparing breast milk fat substitute product
A technology of mixing fatty acids and breast milk fat, applied in the direction of fermentation, can solve problems such as unfavorable digestion and absorption of infants and young children, and achieve the effect of improving resource utilization and extending the industrial chain
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] This example illustrates the fatty acid composition analysis of substrates used for transesterification.
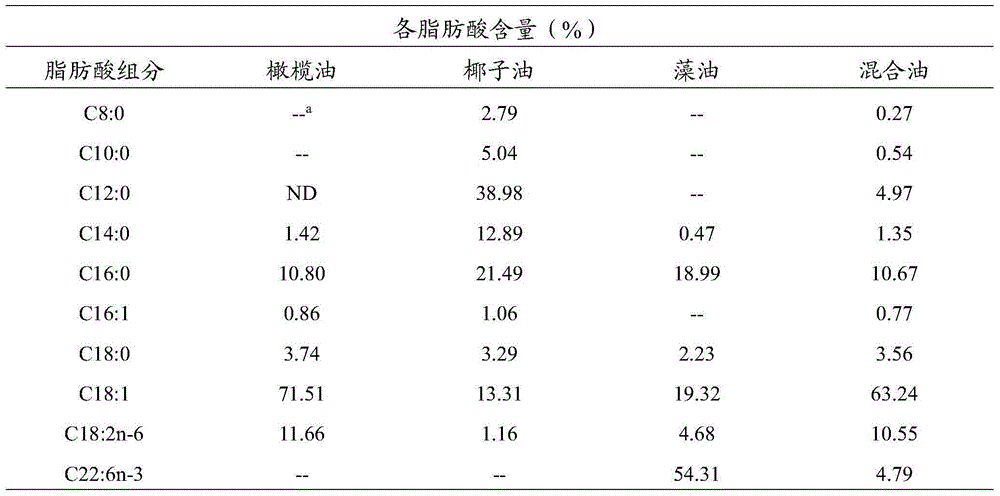
[0019] Olive oil, coconut oil, and algae oil were purified by urea inclusion method to obtain free fatty acids respectively, and the free fatty acids of the three oils were 70:15:15~98:1:1 according to the mass ratio (olive oil:coconut oil:algae oil ) after mixing through gas chromatography, obtain olive oil, coconut oil and algae oil and mixed free fatty acid (with mass ratio olive oil: coconut oil: algae oil=90:5:5 is example) the content of each fatty acid is shown in the table below 1. The mixed free fatty acids used in subsequent examples are all based on this example.
[0020] Content of each fatty acid in table 1 olive oil, coconut oil and algae oil and mixed oil (olive oil: coconut oil: algae oil=90:5:5)
[0021]
[0022] a: not detected
[0023] The following examples illustrate the process of using lipase as a catalyst to catalyze the esterification...
Embodiment 2
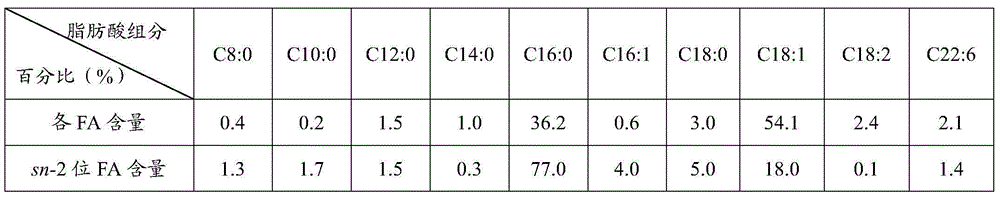
[0025]After mixing PPP (0.62g) and mixed free fatty acids (1.88g) at a molar ratio of 1:9, add sn-1, 3-position-specific lipase LipozymeRMIM10% (0.25g), and put it in a water bath shaker at 60°C for 3h .
[0026] After the reaction, take out 500 μL, add 60 mg of porcine pancreatic lipase to hydrolyze for 3 min, extract with ether, take the organic layer for thin-layer chromatography, and scrape the sn-2 monoglyceride band. Add 2 mL of n-hexane and 2 mL of 0.5 mol KOH-methanol solution and react in a water-bath shaker at 65°C for 60 minutes for methyl esterification, and then perform gas chromatography detection. The content of each fatty acid in the product oil is measured as shown in Table 2.
[0027]
Embodiment 3
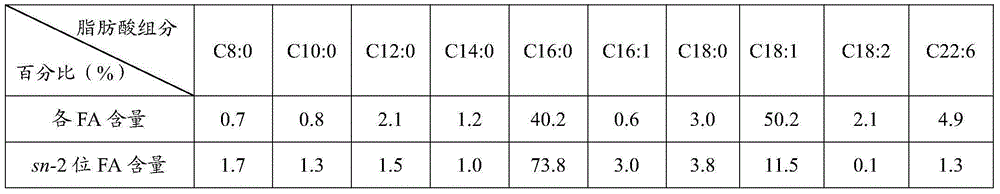
[0029] After mixing PPP (0.74g) and mixed free fatty acid (1.76g) at a molar ratio of 1:7, add sn-1, 3-position specific lipase LipozymeRMIM6% (0.15g), and put it in a water bath shaker at 60°C for reaction 3h.
[0030] After the reaction, take out 500 μL, add 60 mg of porcine pancreatic lipase to hydrolyze for 3 min, extract with ether, take the organic layer for thin-layer chromatography, and scrape the sn-2 monoglyceride band. Add 2 mL of n-hexane and 2 mL of 0.5 mol KOH-methanol solution and react in a water-bath shaker at 65°C for 60 minutes for methyl esterification, and then perform gas chromatography detection. The content of each fatty acid in the product oil is measured as shown in Table 3.
[0031]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com