Preparation method of opening agent for high resilience polyurethane foam
A polyurethane foam and cell-opening agent technology, which is applied in the field of polyether polyol synthesis, can solve the problem of loss of material properties, achieve no loss of material properties, improve foam structure, and increase the effect of opening cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] (1) At room temperature, add 32 g of propylene glycol, 29 g of sucrose, and 9 g of potassium hydroxide to the autoclave. Replace with nitrogen. After the oxygen content in the autoclave is measured to be less than 50 ppm, the temperature is increased to 115° C., and vacuum (-0.09 MPa) is used for dehydration. hour.
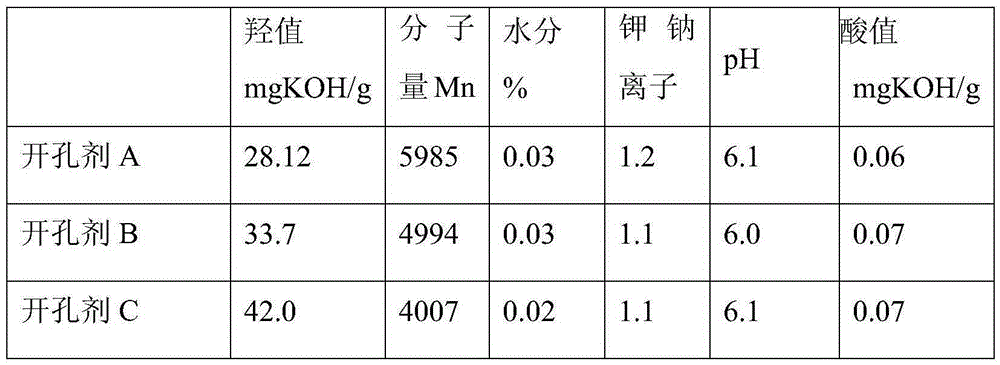
[0025] (2) Control the temperature in the kettle at 115°C, add 490g of propylene oxide and 2450g of ethylene oxide dropwise to carry out the polymerization reaction. After the dropwise addition is completed, after the pressure in the kettle does not change, the residual monomers are removed under a vacuum of -0.09MPa for 1 hour . Cool down to 80℃, add 18g phosphoric acid and 90g distilled water, stir and react for 40min, then add 4.5g magnesium silicate, stir for 40min, vacuum dehydration at 115℃, -0.09MPa for 2 hours, filter to obtain pore opener A, specific test data See Table 1.
Embodiment 2
[0027] (1) At room temperature, add 57g of propylene glycol, 46g of sorbitol, and 10g of potassium hydroxide into the autoclave, and replace with nitrogen. After measuring the oxygen content in the autoclave to be less than 50ppm, the temperature is increased to 115°C, and nitrogen is blown to vacuum (-0.09MPa) for dehydration. 2 hours.
[0028] (2) Control the temperature in the kettle to 115°C, drop 980g of propylene oxide and 3918g of ethylene oxide to carry out polymerization reaction. After the dropwise addition is completed and the pressure in the kettle does not change, the residual monomers are removed under vacuum at -0.09MPa for 1 hour. Cool down to 80℃, add 20g phosphoric acid and 150g distilled water, stir and react for 40min, then add 7.5g magnesium silicate, stir for 40min, vacuum dehydration at 115℃, -0.09MPa for 1 hour, filter to obtain pore opener B, specific test data See Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0030] (1) At room temperature, add 45.5g of sorbitol, 79.5g of diethylene glycol, 100g of glycerol, and 4g of potassium hydroxide to the autoclave at room temperature. Replace with nitrogen. After measuring the oxygen content in the kettle to be less than 50ppm, increase the temperature to 115°C and blow nitrogen. Vacuum (-0.09MPa) dehydration for 2 hours.
[0031] (2) Control the temperature in the kettle at 115°C, drop 944 g of propylene oxide and 2831 g of ethylene oxide to carry out the polymerization reaction. After the dropwise addition is completed and the pressure in the kettle remains unchanged, the residual monomers are removed under vacuum at -0.09MPa for 1 hour. Cool down to 80℃, add 8g phosphoric acid and 120g distilled water, stir and react for 40min, then add 6g magnesium silicate, stir for 40min, vacuum dehydration at 115℃, -0.09MPa for 3 hours, filter to get pore opener C, see specific test data Table 1.
[0032] Table 1 Specific test data of the pore openers pre...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com