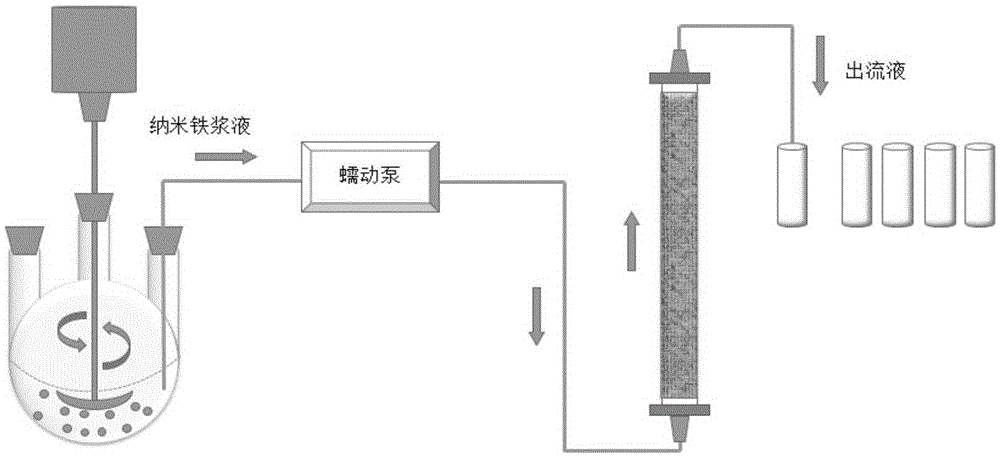
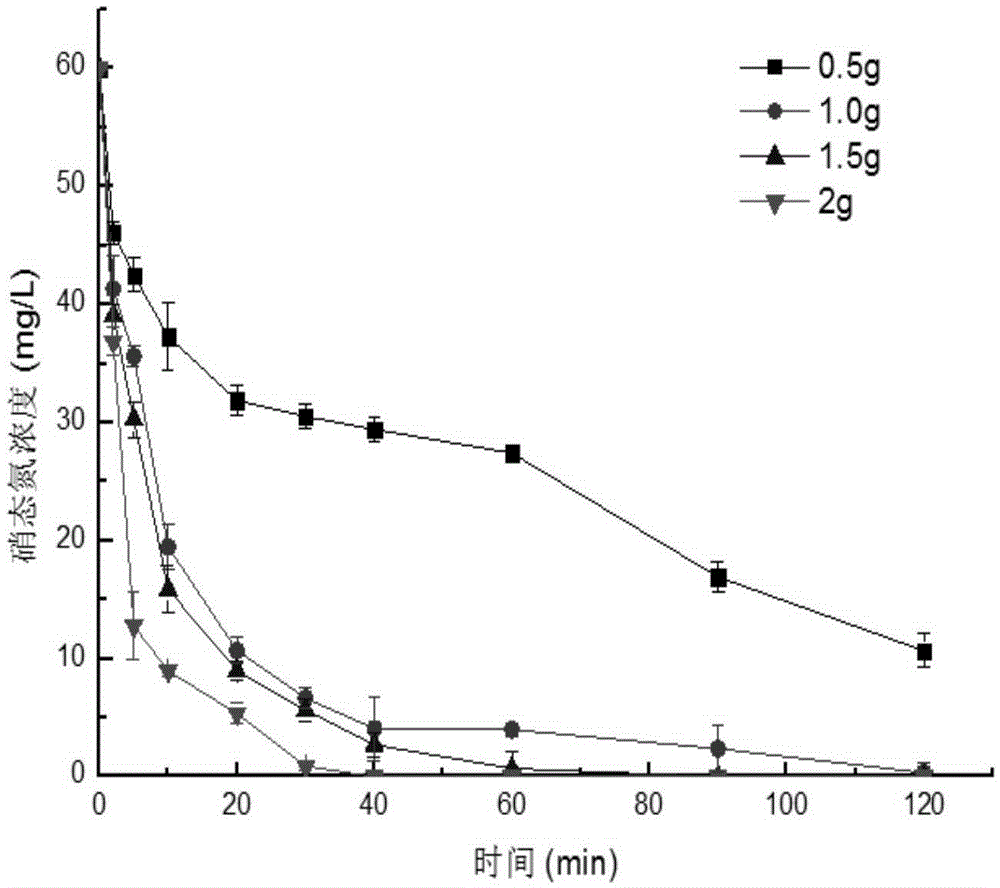
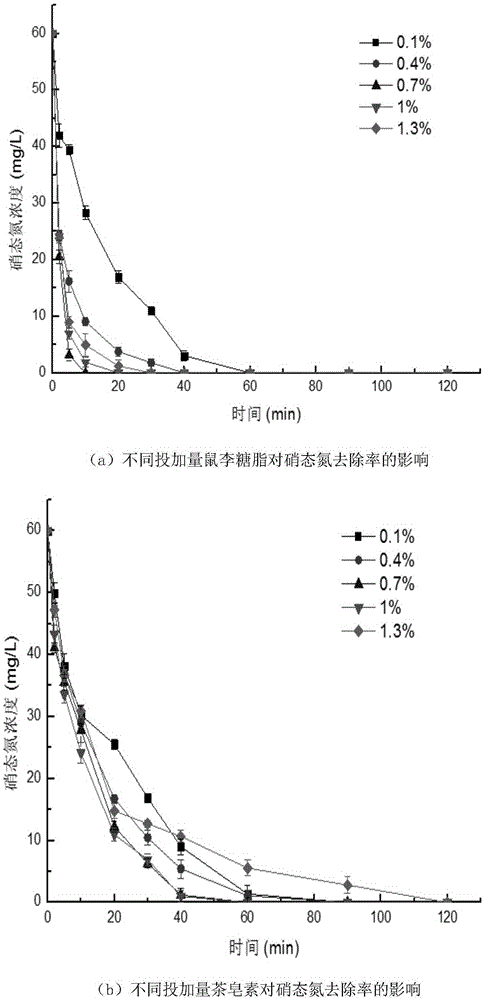
Preparation method of biosurfactants-modified nano-iron/carbon composite material and application in removing nitrate nitrogen in underground water
A technology of carbon composite material and biological surface, applied in the direction of contaminated groundwater/leachate treatment, chemical instruments and methods, oxidized water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve pollution, rare and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] The preparation of embodiment one nano-iron / carbon composite material
[0043] Nano-iron was prepared by liquid phase reduction method and loaded on activated carbon to form nano-iron / carbon composites. The reaction equation is as follows:
[0044] Fe 2+ (EQ) +2BH 4 - (EQ) +6H 2 o (I) → Fe 0 (S) ↓+B(OH) 3(EQ) +H 2(g) ↑
[0045] Preparation method: Measure 140mL of deoxygenated ultrapure water and 66mL of absolute ethanol, mix them to form an alcohol-water system and transfer them to a three-necked flask, fix the flask on an electric stirrer, start the stirrer and adjust the speed to 500rpm (rev / min ), to prepare the alcohol-water system. Weigh 1.8g of sodium borohydride solid, dissolve in 10ml of deoxygenated ultrapure water, and set aside. Take another 5 g of ferrous sulfate heptahydrate, dissolve ferrous sulfate heptahydrate in the alcoholic water system, and after it is completely dissolved, add the newly prepared sodium borohydride solution into the fl...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Preparation of Example 2 Modified Nano-iron / Carbon Composite Material
[0048] In addition to dissolving the biosurfactant rhamnoside aglycone and sapindus saponin in the alcohol-water system before dissolving ferrous sulfate heptahydrate, the preparation method of the modified nano-iron / carbon composite material, other materials, The reaction conditions and steps are the same as the preparation of nano-iron / carbon in Example 1. Among them, the feeding amount of rhamnolipid (Daqing Wotaisi Chemical Co., Ltd.), tea saponin (Xi'an Jiatian Biotechnology Co., Ltd.), and Sapindus saponin (Xi'an Jiatian Biotechnology Co., Ltd.) is shown in Table 1 :
[0049] Table 1: The feeding amount of rhamnolipid, tea saponin aglycon and sapindus saponin
[0050]
[0051] In this table, the calculation method of the amount of lyglycolipid and Sapindus sapindus saponin is: in terms of mass percentage, the ratio to the total amount of the reaction material (the sum of the amount of sod...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Embodiment 3 SEM characterization diagram
[0053] The nano-iron / carbon composite material prepared in Example 1 is characterized and analyzed by a scanning electron microscope. The SEM characterization diagram (scanning electron microscope characterization diagram) of the nano-iron / carbon composite material is shown in the appendix of the specification. Figure 5 (a). Among them, the sheet-like structure is activated carbon, and the particles adsorbed on the surface are nano-iron. Experiments show that the nano-iron particles in the unmodified nano-iron / carbon are not well attached to the activated carbon, and the agglomeration is obvious.
[0054] The modified nano-iron / carbon composite materials prepared in Example 2 of tea saponin modified group 4, rhamnolipid modified group 3, and Sapindus saponin modified group 3 were characterized and analyzed by scanning electron microscopy, and the nano-iron The SEM characterization diagram (scanning electron microscope chara...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com