Activated humic acid biological bacterial fertilizer and preparation method thereof
A technology of biological bacterial fertilizer and humic acid, which is applied in the direction of ammonium orthophosphate fertilizer, alkaline orthophosphate fertilizer, nitrogen fertilizer, etc., can solve the problems of little effect, and achieve the effects of reducing pollution, increasing yield, and improving nutritional status
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
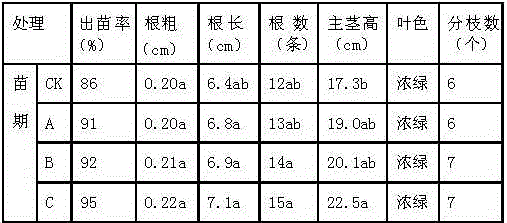
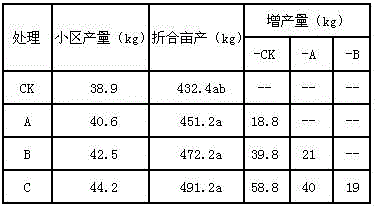
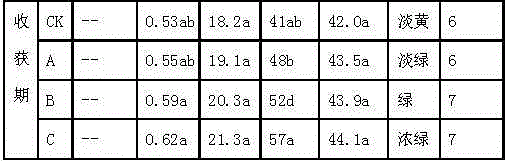
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] Sprayed humic urea solution: 180 parts of urea, 30 parts of ammonium sulfate, 90 parts of humic acid, 50 parts of water;
[0054] Solid granulation raw materials: 100 parts of peat, 100 parts of monoammonium phosphate, 100 parts of potassium sulfate, 380 parts of humic acid, 5 parts of anhydrous magnesium sulfate, 5 parts of boric acid, 4 parts of EDTA chelated zinc, 3 parts of EDTA chelated iron , 2 parts of EDTA chelated manganese, 1 part of ammonium heptamolybdate.
[0055] Its specific production process is as follows:
[0056] Step 1: Urea melting: Open the steam valve of the main pipe, start the urea melting tank to stir, first add 50 parts of water, add urea and ammonium sulfate to the urea tank at a ratio of 6:1, and control the temperature of the urea tank to 115-125°C. After stirring and melting completely, the urea solution reaches the overflow level, and liquid flows out from the overflow pipe, so stop dispensing urea.
[0057] Step 2: Prepare putrefaction...
Embodiment 2
[0064] Raw materials: 180 parts of urea, 30 parts of ammonium sulfate, 470 parts of humic acid, 100 parts of bacterial powder, 100 parts of monoammonium phosphate, 100 parts of potassium sulfate, 5 parts of anhydrous magnesium sulfate, 5 parts of boric acid, 4 parts of EDTA chelated zinc, 3 parts of EDTA chelated iron, 2 parts of EDTA chelated manganese, 1 part of ammonium heptamolybdate.
[0065] Its specific production process is as follows:
[0066] Step 1: Preparation of solid bacterial powder: Microbial bacteria used in the field of fertilizers (Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus large and Bacillus gelatinosa) are fermented and produced by fermentation equipment, and absorbed by the adsorption medium (peat) , the bacterial agent was crushed, and the total number of effective viable bacteria reached 3×10 8 piece / gram or more.
[0067] Step 2: Granulation: solid material bacterial powder, urea, ammonium sulfate, monoammonium phosphate, potassium sulfate, humic acid, anhydrous ma...
Embodiment 3
[0072] Sprayed humic urea solution: 180 parts of urea, 30 parts of ammonium sulfate, 90 parts of humic acid, and 50 parts of water.
[0073] Solid granulation raw materials: 100 parts of bacterial powder, 100 parts of monoammonium phosphate, 100 parts of potassium sulfate, 380 parts of humic acid, 5 parts of anhydrous magnesium sulfate, 5 parts of boric acid, 4 parts of EDTA chelated zinc, 3 parts of EDTA chelated iron 1 part, 2 parts of EDTA chelated manganese, 1 part of ammonium heptamolybdate.
[0074] Its specific production process is as follows:
[0075] Step 1: Preparation of solid bacterial powder: Microbial bacteria used in the field of fertilizers (Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus large and Bacillus gelatinosa) are fermented and produced by fermentation equipment, and absorbed by the adsorption medium (peat) , the bacterial agent was crushed, and the total number of effective viable bacteria reached 3×10 8 piece / gram or more.
[0076] Step 2: Urea melting: Open the ste...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com