Method for preparing manganese ferrite-graphene composite materials
A technology of composite materials and graphene, applied in the direction of nanotechnology, iron compounds, chemical instruments and methods for materials and surface science, can solve the problems of poor absorbing performance and achieve good absorbing performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
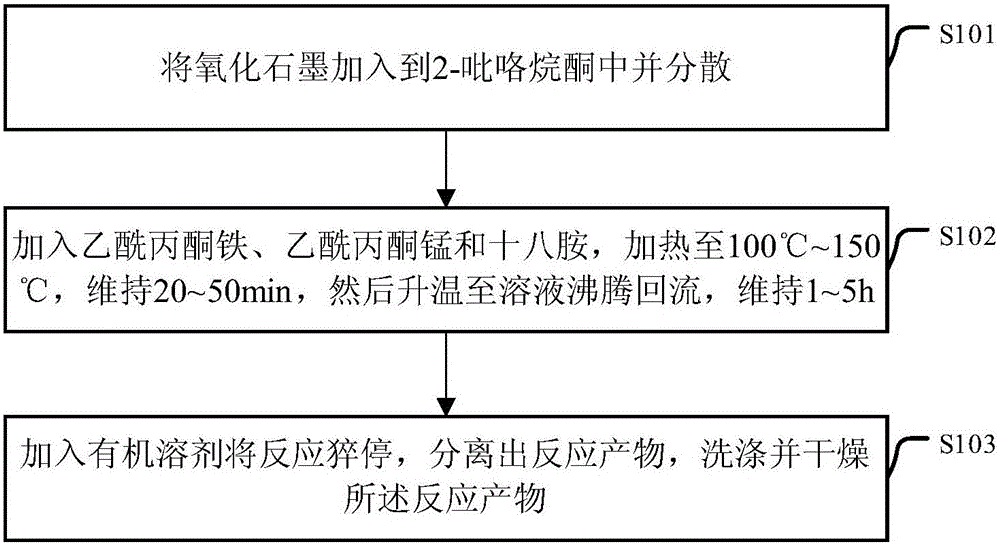
[0029] figure 1 A schematic flow diagram of a preparation method of a manganese ferrite-graphene composite material provided by an embodiment of the present invention, comprising the following steps:
[0030] S101: adding graphite oxide to 2-pyrrolidone and dispersing it;
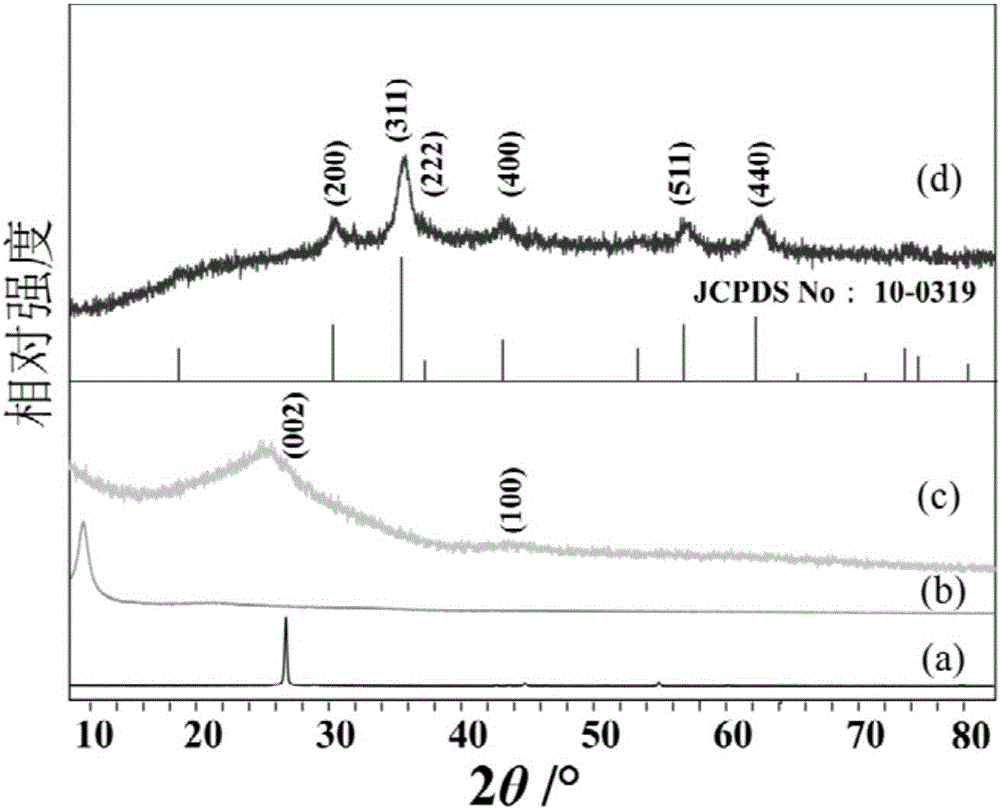
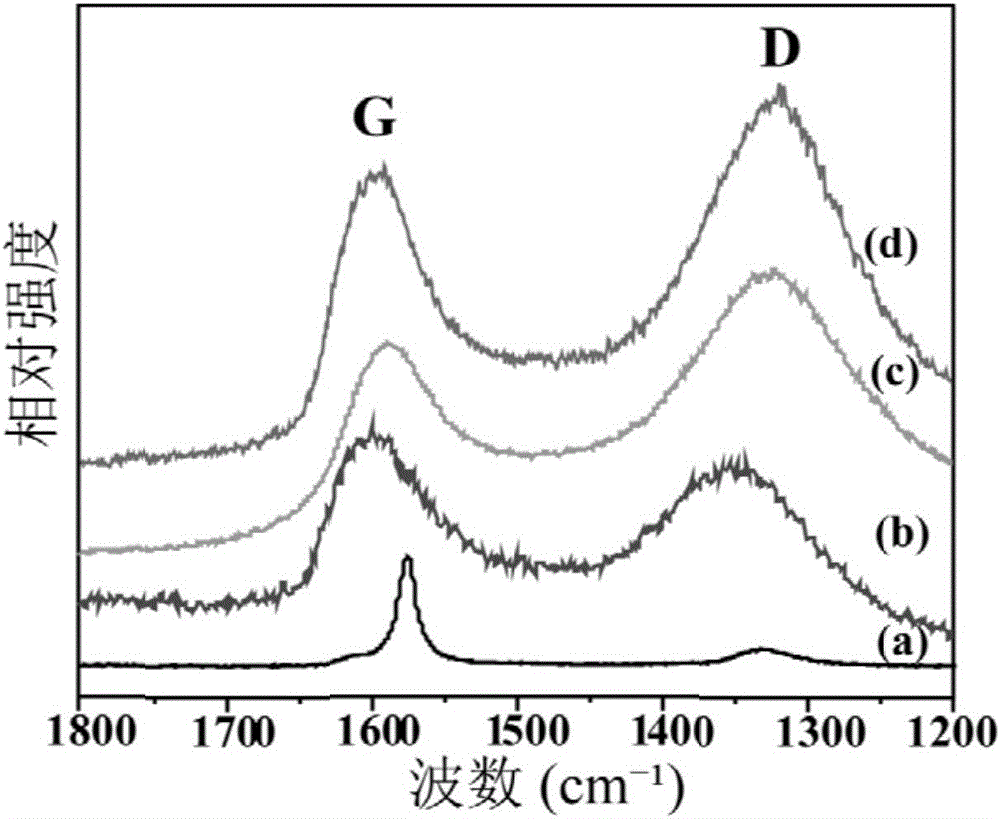
[0031] Wherein, the graphite oxide refers to a compound composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen elements with variable ratios of substances. Described graphite oxide can be obtained by preparing graphite oxide with a strong oxidant, specifically, it can be prepared by using the improved Hummers method (this method is recorded in the reference book "Graphene——structure, preparation, etc.) written by Zhu Hongwei, Xu Zhiping, Xie Dan, etc. Method and Performance Characterization" (Tsinghua University Press, first printing in November 2011), paragraph 2, page 32). The mass volume ratio of the graphite oxide to the 2-pyrrolidone is 0.8 mg / mL˜1.2 mg / mL, preferably, the mass volume ratio of the graphite oxide t...
Embodiment 1
[0042] Weigh 40mg of graphite oxide and 40mL of 2-pyrrolidone in a 50mL beaker, ultrasonically disperse for about 2h to obtain a brown mixed solution; Octamine was added to the above brown solution, the mixture was first heated to 120°C and maintained at this temperature for 30 minutes, then the temperature was raised to 245°C, maintained at this temperature for 2 hours, and magnetic stirring was maintained all the time. Then, 20 mL of ethanol was added to quench the reaction, and the temperature of the reaction system was rapidly lowered to room temperature. Finally, the reaction product was separated by centrifugation, washed alternately with n-hexane, acetone, and ethanol, and the product was vacuum-dried at 40°C.
Embodiment 2
[0044] Weigh 40mg of graphite oxide and 50mL of 2-pyrrolidone in a 50mL beaker, ultrasonically disperse for about 2h to obtain a brown mixed solution; Octadecylamine was added to the above brown solution, the mixture was first heated to 100°C and maintained at this temperature for 50 minutes, then raised to 245°C, maintained at this temperature for 5 hours, and kept magnetically stirred. Then, 20 mL of ethanol was added to quench the reaction, and the temperature of the reaction system was rapidly lowered to room temperature. Finally, the reaction product was separated by filtration, washed alternately with n-hexane, acetone, and ethanol, and the product was vacuum-dried at 40°C.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Maximum reflection loss | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Maximum reflection loss | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com