Preparation method of sustained-release microparticles
A technology of slow-release microparticles and microparticles, which is applied to medical preparations with non-active ingredients, medical preparations containing active ingredients, and pharmaceutical formulas, and can solve problems such as unfavorable, unstable release, and aggregation and precipitation of active substances.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
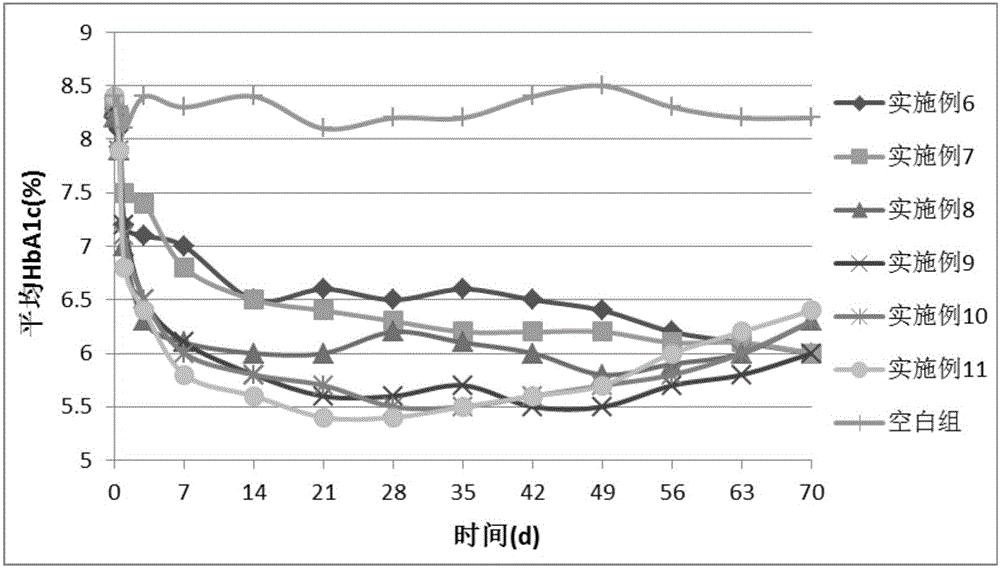
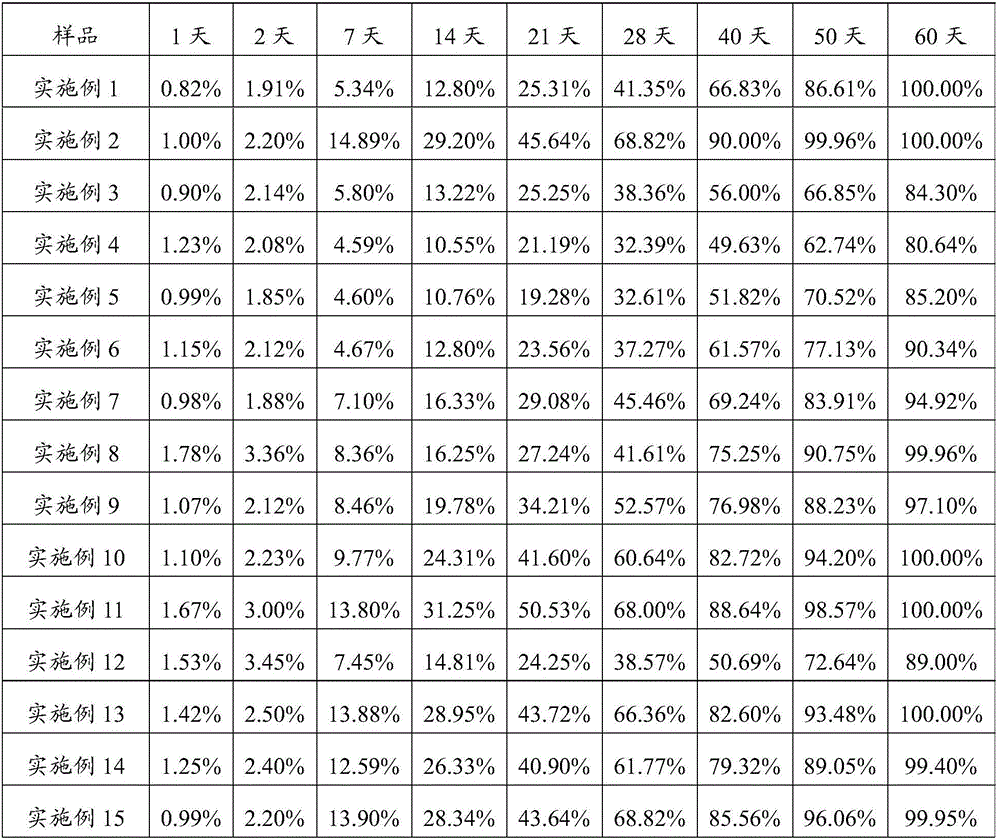
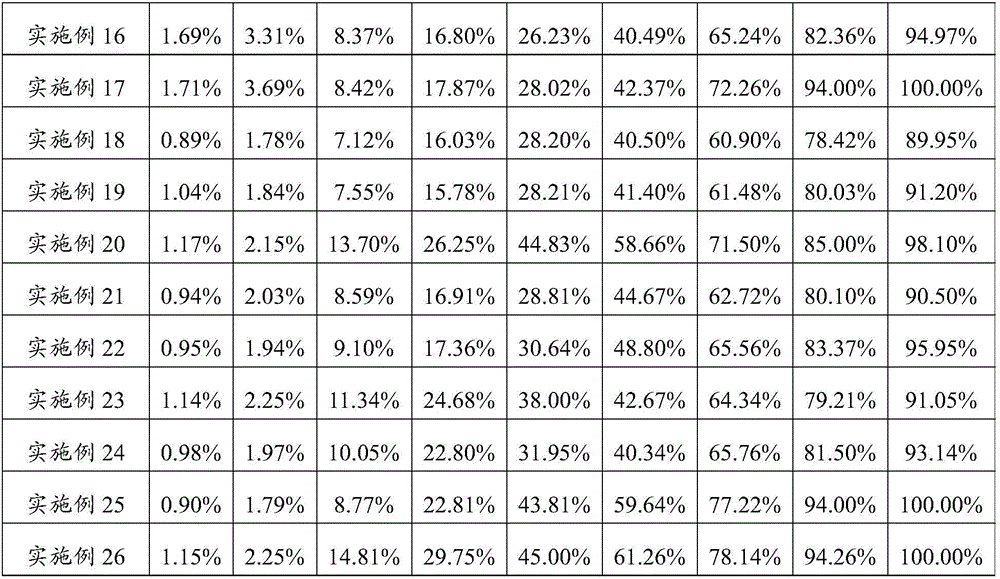
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0096] Embodiment 1: Preparation of albiglutide / PLGA microparticles
[0097] (1) Preparation of solid dispersion
[0098] Dissolve 0.90g PLGA (molecular weight 25kDa, monomer ratio 65 / 35, carboxyl-terminated) in about 6.00mL glacial acetic acid, then add 0.10g albiglutide acetate, dissolve under vortex, and then slowly pour into a stirring In water ether (6°C), a white precipitate was produced, collected the white precipitate and extracted about 5 times with anhydrous ether, dried in a vacuum oven for 24 hours (10°C) after collecting the precipitate, to obtain a solid dispersion.
[0099] (II) Preparation of microparticles
[0100] The solid dispersion obtained in step I was uniformly dispersed in about 6.00 g of dichloromethane to obtain an internal oil phase, and then the internal oil phase was injected into 230 mL of 1% (w / w) polyvinyl alcohol aqueous solution that had been pre-heated to about 4°C , and use a high-speed homogenizer to prepare S / O / W emulsion (rotor speed a...
Embodiment 2
[0101] Example 2: Preparation of dulaglutide / PLGA microparticles
[0102] (1) Preparation of solid dispersion
[0103]Dissolve 0.95g PLGA (molecular weight 30kDa, monomer ratio 50 / 50, carboxyl-terminated) in about 7.92mL glacial acetic acid, then add 0.05g dulaglutide acetate, dissolve under vortex, and then slowly pour into a stirring In water ether (6°C), a white precipitate was produced, collected the white precipitate and extracted about 5 times with anhydrous ether, dried in a vacuum oven for 24 hours (10°C) after collecting the precipitate, to obtain a solid dispersion.
[0104] (II) Preparation of microparticles
[0105] The solid dispersion obtained in step I was uniformly dispersed in about 7.92 g of dichloromethane to obtain an internal oil phase, and then the internal oil phase was injected into 420 mL of 1.5% (w / w) polyvinyl alcohol aqueous solution that had been pre-heated to about 4°C , and use a high-speed homogenizer to prepare S / O / W emulsion (rotor speed abo...
Embodiment 3
[0106] Example 3: Preparation of follicle stimulating hormone / PLA microparticles
[0107] (1) Preparation of solid dispersion
[0108] Dissolve 0.97g of PLA (molecular weight 20kDa, terminal ester group) in about 5.39mL of glacial acetic acid / acetonitrile mixture, then add 0.03g of follicle-stimulating hormone acetate, 0.05g of xylitol and 0.03g of zinc chloride, and dissolve under vortex , and then slowly inject cyclohexane (8°C) under stirring to produce a white precipitate, collect the white precipitate and take it about 5 times with cyclohexane, dry the precipitate in a vacuum oven for 24 hours (10°C), to obtain a solid dispersion.
[0109] (II) Preparation of microparticles
[0110] The solid dispersion obtained in step I was uniformly dispersed in about 5.39 g of chloroform to obtain an internal oil phase, and then the internal oil phase was injected into 400 mL of a 0.5% (w / w) hypromellose aqueous solution that had been pre-heated to about 6°C and emulsifying with a ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com