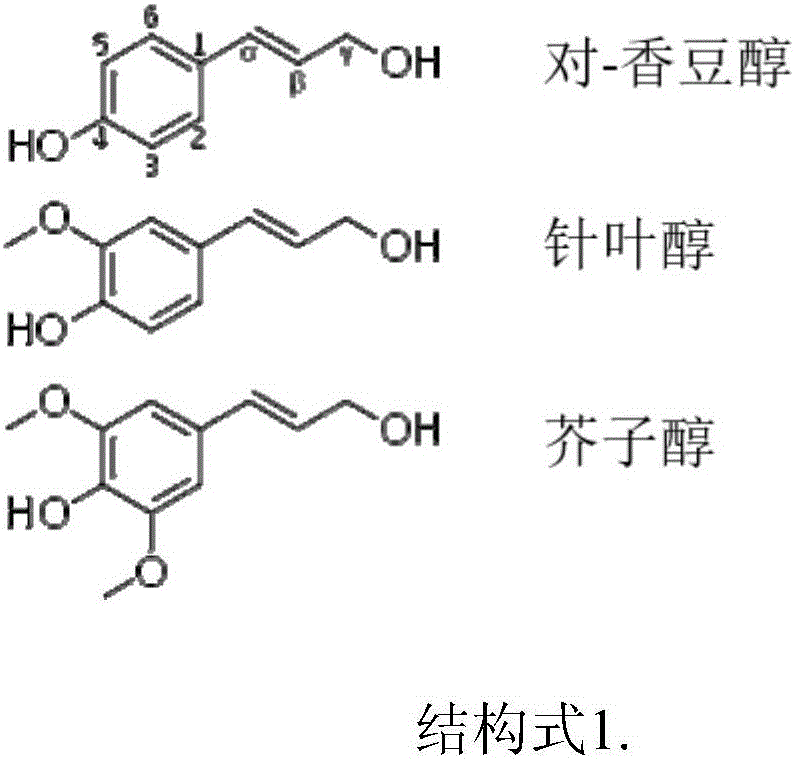
Adhesive
一种黏着剂、连接分子的技术,应用在胶粘剂、木素粘合剂、多糖粘合剂等方向
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
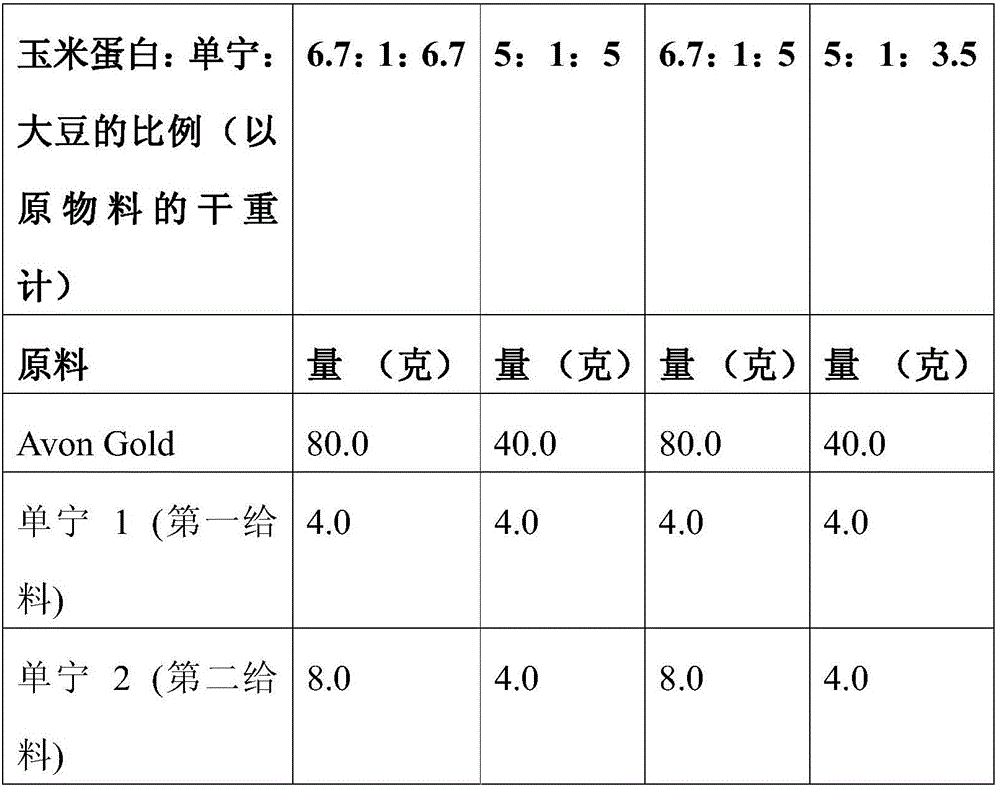
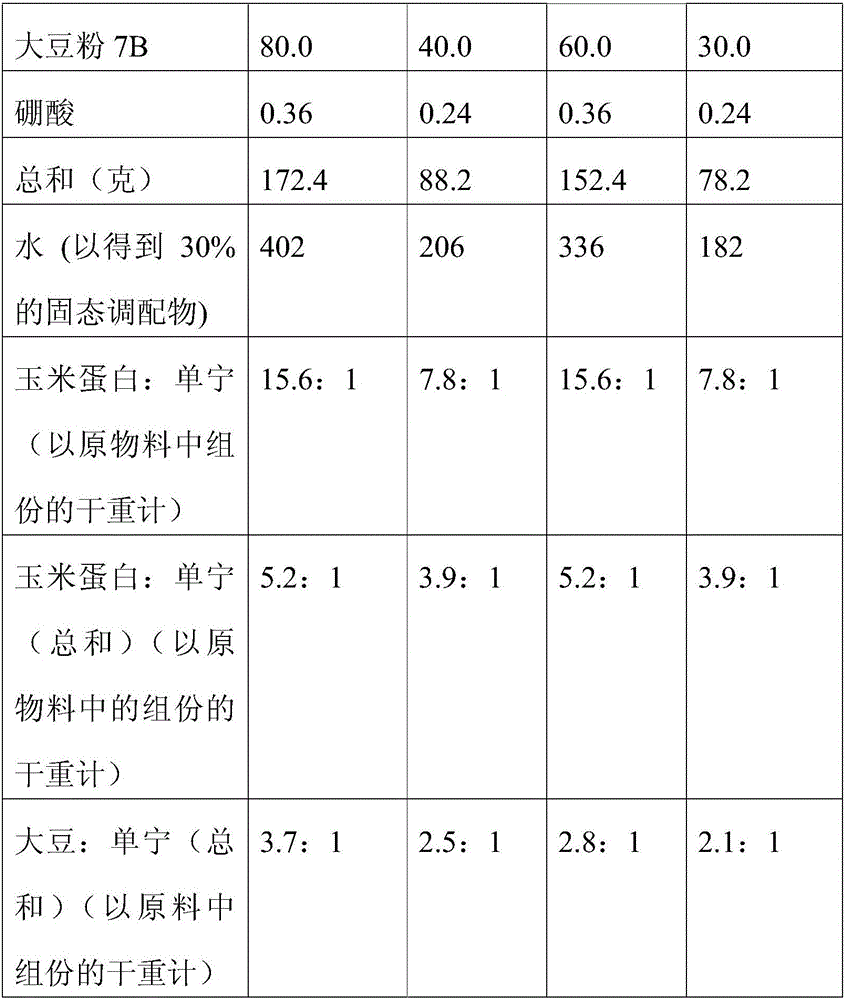
[0533] Example 1. Zein:Tannin:Soy MDF
[0534] Corn gluten meal (Avon Gold, about 70% zein) (100 g) was added to water (450 ml) followed by adjustment to pH 11 with 40% sodium hydroxide solution. The reaction mixture was heated to 90 °C for 50 minutes, ensuring that it maintained a pH of 11. After one hour, mimosa tannins (10 g) were added and the solution was stirred for 10 minutes while adjusting the pH to 9 with formic acid solution and reducing the temperature to 70°C. Additional tannin feed (10 grams) was added with continued stirring. Glycerin (130 mL) was added followed by soy flour 7B (100 g). Stirring was continued for 50 minutes, and then the solution was cooled to ambient temperature. During cooling, boric acid (0.55 g) was added. The final solution is then added in the form of a fine mist to the mechanically mixed wood fibers at a rate of 8 to 10% binder content in the fibers. Fibers were formed into mattresses and consolidated by hot pressing at 180°C to obta...
example 2
[0535] Example 2. Zein: Tannin: Medium Density Fiberboard of Soy
[0536] Avon Gold (80 g) was added to water (360 ml) followed by adjustment to pH 11 with 40% sodium hydroxide solution. The reaction mixture was heated to 90 °C for 50 minutes, ensuring that it maintained a pH of 11. After one hour, sulfited pine bark tannins (8 g) were added and the solution was stirred for 10 minutes while adjusting the pH to 9 with formic acid solution and reducing the temperature to 70°C. Additional tannin feed (8 grams) was added and stirring continued. Glycerin (130 mL) was added followed by soy flour 7B (about 50 to 52% soy protein) (80 g). Stirring was continued for 50 minutes, and then the solution was cooled to ambient temperature. During cooling, boric acid (0.48 g) was added. The final solution is then applied by mechanical mixing with the wood fibers at a binder content of 8 to 10% in the fibers. The fibers were formed into a mat and consolidated by hot pressing at 210° C. to ...
example 3
[0537] Example 3. Lignin:Tannin:Soybean MDF
[0538] Lignosulfonate (30 g) was added to water (310 ml) at 70° C. and adjusted to pH 11 with 40% sodium hydroxide solution. Lysine sulfate (30 g) was added and after its dissolution the pH was adjusted to 9 with formic acid solution. Pine bark tannin (10 grams) was added and stirring continued. After addition of glycerol (120 mL) followed by soy flour 7B (100 g) and stirring continued for 60 minutes, boric acid (0.50 g) was added and the solution was cooled. The brown solution is applied to wood fibers with a binder content of 8 to 10% in the fibers and mixed mechanically. The fiber was hot pressed at 180°C to obtain an 8 mm medium density fiberboard having an internal bond strength of 0.57 MPa and a 24-hour cold water penetration thickness expansion rate of 21%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com