Production process of efficient feed-grade monocalcium phosphate by using boiler waste residue for purification of phosphoric acid by wet process
A technology of calcium dihydrogen phosphate and wet-process phosphoric acid, which is applied in the field of phosphorus chemical industry, can solve the problems of low utilization rate of phosphorus resources, high production cost, negative product quality, etc., so as to be beneficial to filtration and separation, reduce direct emissions, and reduce production. cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
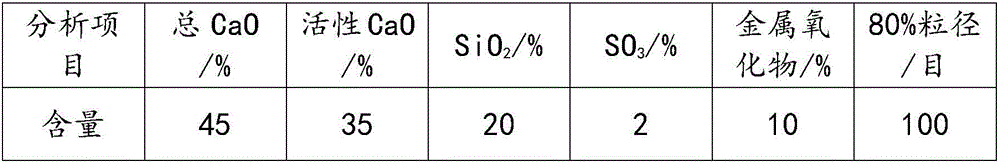
[0032] Boiler desulfurization slag indicators:
[0033]
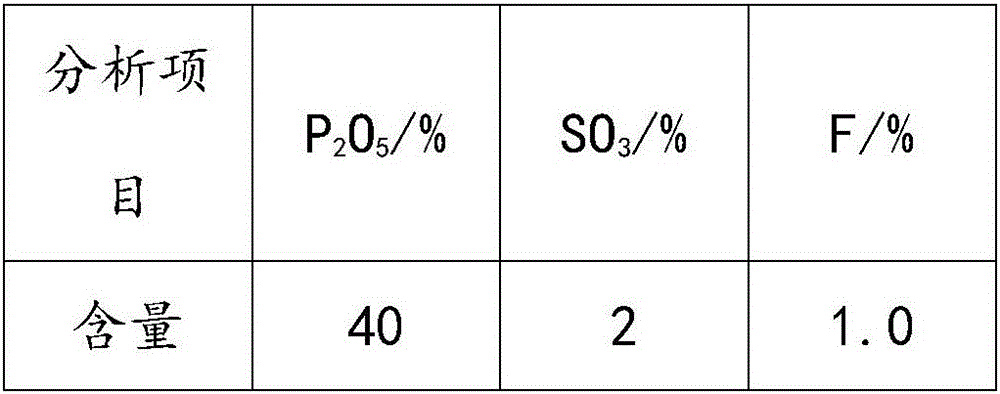
[0034] Phosphoric acid index:
[0035]
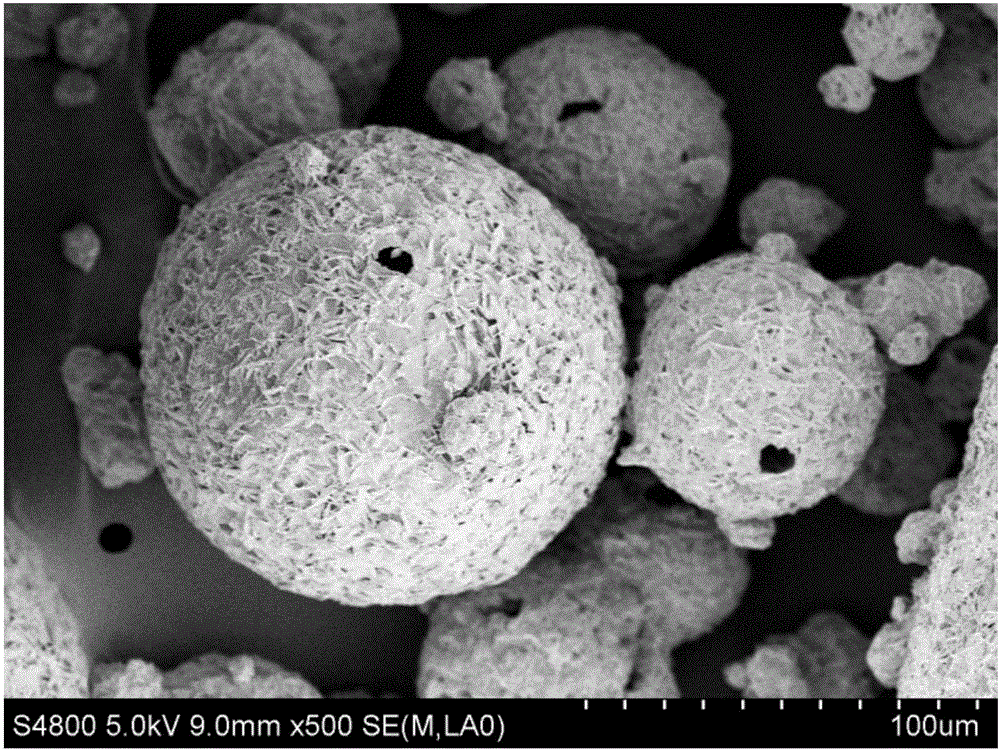
[0036] The reaction of boiler desulfurization waste slag with concentrated acid phosphoric acid for the above indicators is based on the active calcium in waste slag and SO in phosphoric acid 3 The molar ratio is 1:1, the reaction temperature is 60°C, the reaction time is 3.0h, and the stirring speed is 8m / s. After the reaction is completed, add an excess of 20% active silicon dioxide and sodium carbonate for defluorination treatment, the reaction temperature is 50°C, the reaction time is 1h, and the finished phosphoric acid is obtained by filtration. The reaction conditions of the finished phosphoric acid and calcium pulp are controlled as pulp moisture 40%, the reaction materials are mixed according to the calcium / phosphorus mass ratio of 0.55, the reaction temperature is 80°C, and the reaction time is 3.0h to obtain MCP slurry. The slurry is granulated and dried in a s...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Boiler desulfurization slag indicators:
[0039]
[0040] Phosphoric acid index:
[0041]
[0042] The reaction of boiler desulfurization waste slag with concentrated acid phosphoric acid for the above indicators is based on the active calcium in waste slag and SO in phosphoric acid 3 The molar ratio is 2:1, the reaction temperature is 70°C, the reaction time is 2h, and the stirring speed is 6m / s. After the reaction is completed, add an excess of 20% active silicon dioxide and sodium carbonate for defluorination treatment, the reaction temperature is 60° C., the reaction time is 2 hours, and the finished phosphoric acid is obtained by filtration. The reaction conditions of the finished phosphoric acid and calcium pulp are controlled as pulp moisture 50%, the reaction materials are mixed with a calcium / phosphorus mass ratio of 0.59, the reaction temperature is 70°C, and the reaction time is 2.0h to obtain MCP slurry. The slurry is granulated and dried in a spray ...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Boiler desulfurization slag indicators:
[0045]
[0046] Phosphoric acid index:
[0047]
[0048] The reaction of boiler desulfurization waste slag with concentrated acid phosphoric acid for the above indicators is based on the active calcium in waste slag and SO in phosphoric acid 3 The molar ratio is 1.5:1, the reaction temperature is 80°C, the reaction time is 0.5h, and the stirring speed is 3m / s. After the reaction is completed, an excess of 20% active silica and sodium carbonate is added for defluorination treatment, the reaction temperature is 70° C., the reaction time is 3 hours, and the finished phosphoric acid is obtained by filtration. The reaction conditions of the finished phosphoric acid and calcium pulp are controlled as pulp moisture 60%, the reaction materials are mixed with a calcium / phosphorus mass ratio of 0.65, the reaction temperature is 60°C, and the reaction time is 1.5h to obtain MCP slurry. The slurry is granulated and dried in a spray ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com