Rice brown planthopper resistance gene Bph6 and molecular markers closely linked with same
An anti-BPH and molecular marker technology, applied in the field of plant genetic engineering, can solve the problems of difficult operation, limited effect, increased production cost, etc., and achieve clear function and good effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
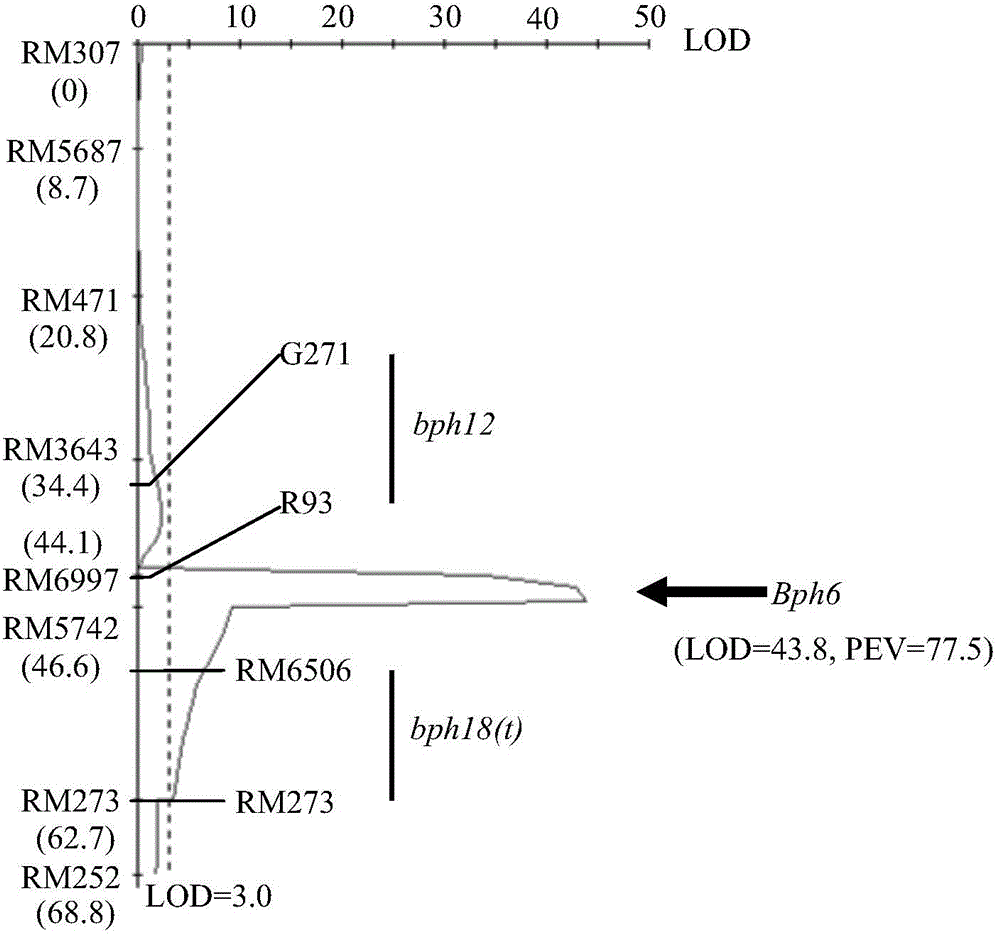
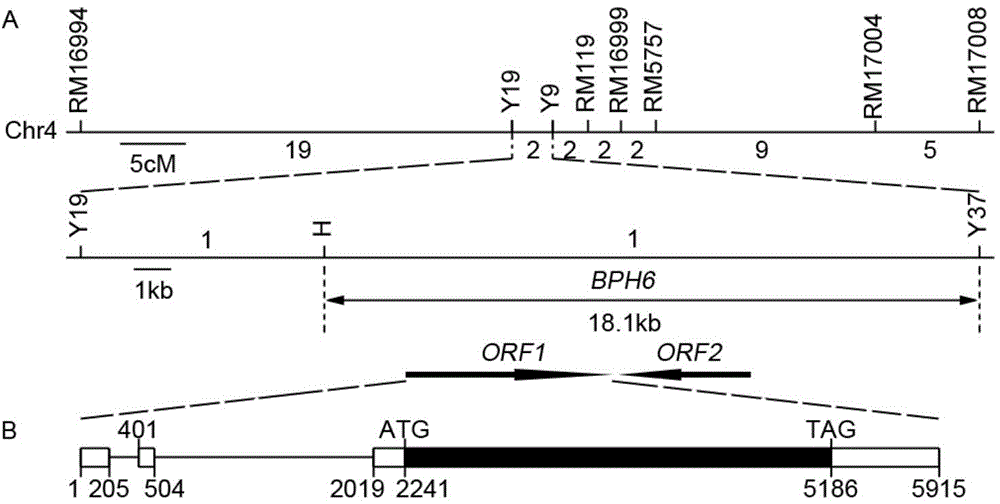
[0067] Example 1 Positional cloning of Bph6 gene and development of linked molecular markers
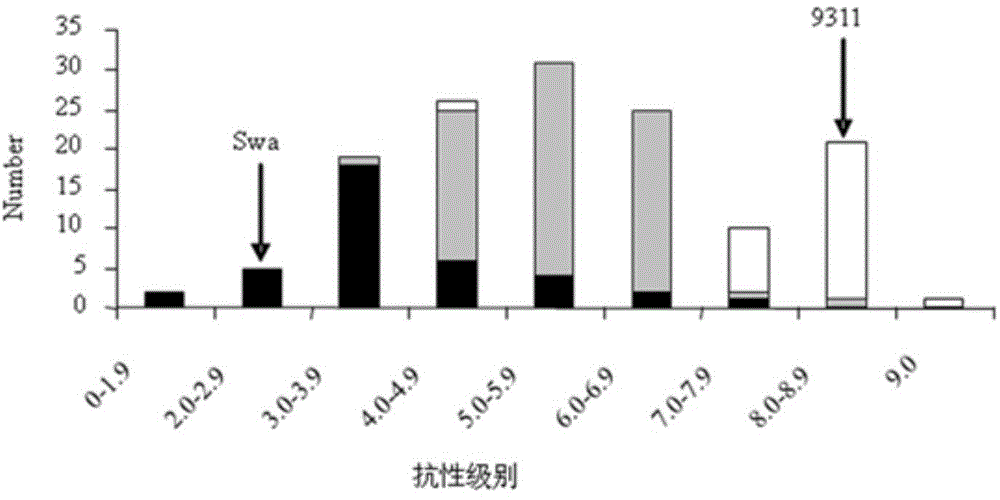
[0068] 1. Preliminary positioning results of Bph6
[0069] A Bph6-containing F 2 Populations, 93-11 and Swarnalata were all obtained from the National Crop Germplasm Conservation Center of the Institute of Crop Science, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, and used the CTAB method (Murray MG&Thompson, 1980 Rapidisolation of high-molecular-weight plant DNA.Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321-4325) Extract parent and F 2 Genomic DNA of each individual plant in the population. each F 2 A single plant obtains the corresponding F 2:3 family lineage. To identify F 2 The N. lugens resistance phenotype of each individual plant in the localization population was investigated by using the seedling stage group method to investigate the resistance performance of each individual plant of the F2:3 family. 2:3 Family resistance level represents F 2 BPH-resistant phenotype of individual plants. T...
Embodiment 2
[0092] Example 2 Functional Verification and Application of Bph6 Gene
[0093] 1. Construction of genetic transformation vector
[0094] (1) Construction of Bph6 gene overexpression vector. The vector used is pCXUN (provided by Professor Wang Guoliang of Ohio State University in the United States). The pCXUN vector is cut with XcmI, and the foreign fragment can be directly connected after adding A.
[0095] According to the results of RACE, PCR method was used to amplify the ORF directly, and after adding A, it was connected into the vector. After the sequence verification is correct, the obtained vector is the Bph6 gene overexpression vector, which is electrotransformed into Agrobacterium EHA105. Pick a single clone for expansion and culture, and after PCR verification, add an equal volume of 50% glycerol to mix, and store at -70°C for later use.
[0096] (2) Bph6 gene RNAi vector construction
[0097] The vector used is pCXUN (provided by Professor Wang Guoliang of Ohio ...
Embodiment 3
[0103] Example 3 Verification of molecular markers
[0104] 1. Materials and methods
[0105] 1.1 Materials: BPH-resistant parent Swarnalata (containing the brown planthopper-resistant gene Bph6), brown planthopper-susceptible rice variety Yangdao 6 (93-11) and F produced by crossing Swarnalata and Yangdao 6 23 family lineage.
[0106] Molecular marker primers: H and Y37, the nucleotide sequences of which are respectively shown in SEQ ID No.4-5.
[0107] 1.2 Method
[0108] Genomic DNA was extracted from rice samples by CTAB extraction. Sample DNA was amplified with primers H and Y37, respectively. 10 μl system. The 10 μl reaction system includes: 10×PCR buffer, 1.0 μl; 10 mM dNTPs, 0.1 μl; 10 μM primer, 0.4 μl; 5U / μl Taq DNA polymerase, 0.2 μl and 50ng DNA template. The amplification reaction was carried out on a Bioer PCR instrument: 94°C for 4min; 30 cycles of 94°C for 30s, 55°C for 30s, 72°C for 90s; 72°C for 5min. The amplified products of H were separated by 1% ag...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com