Nanocellulose and preparation method thereof
A technology of nano-cellulose and lignocellulose, applied in the field of cellulose, can solve the problems of long cycle time, chemical treatment of environmental pollution, fiber performance reduction, etc., and achieve excellent network structure, high economic benefits and utilization prospects, high long-diameter than the effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] The nanocellulose that this embodiment pours, its preparation method comprises the following steps:
[0044] (1) Steam explosion treatment
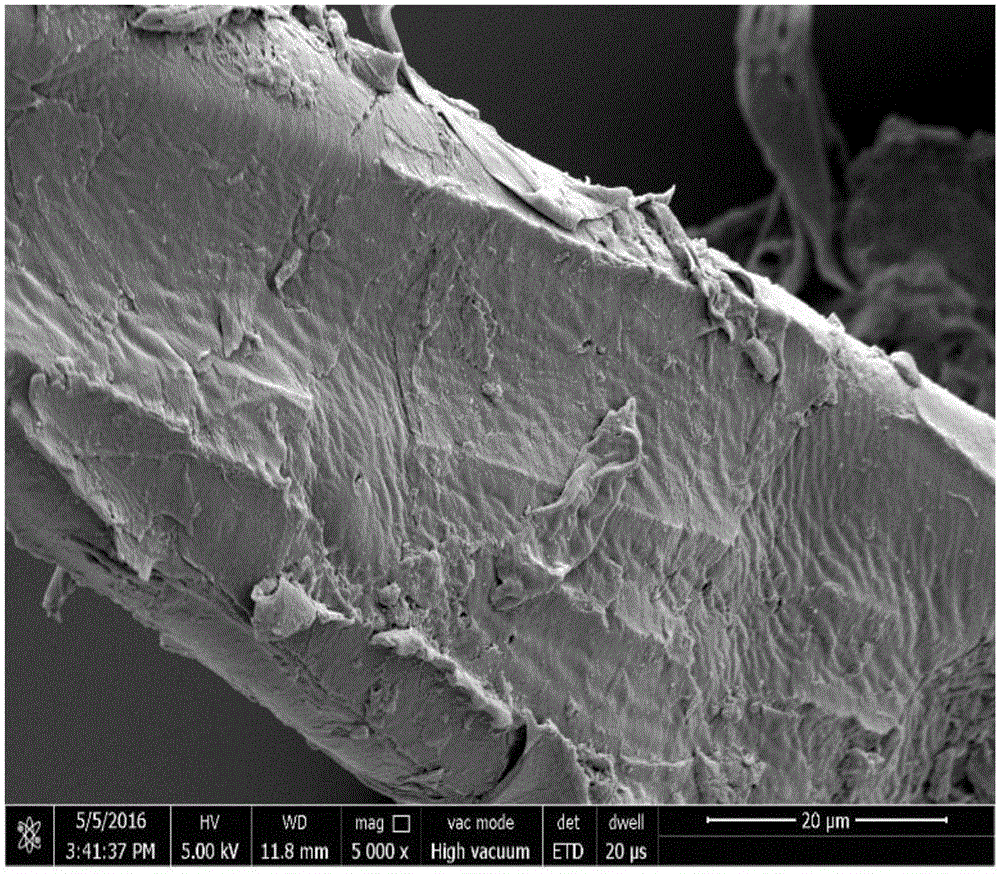
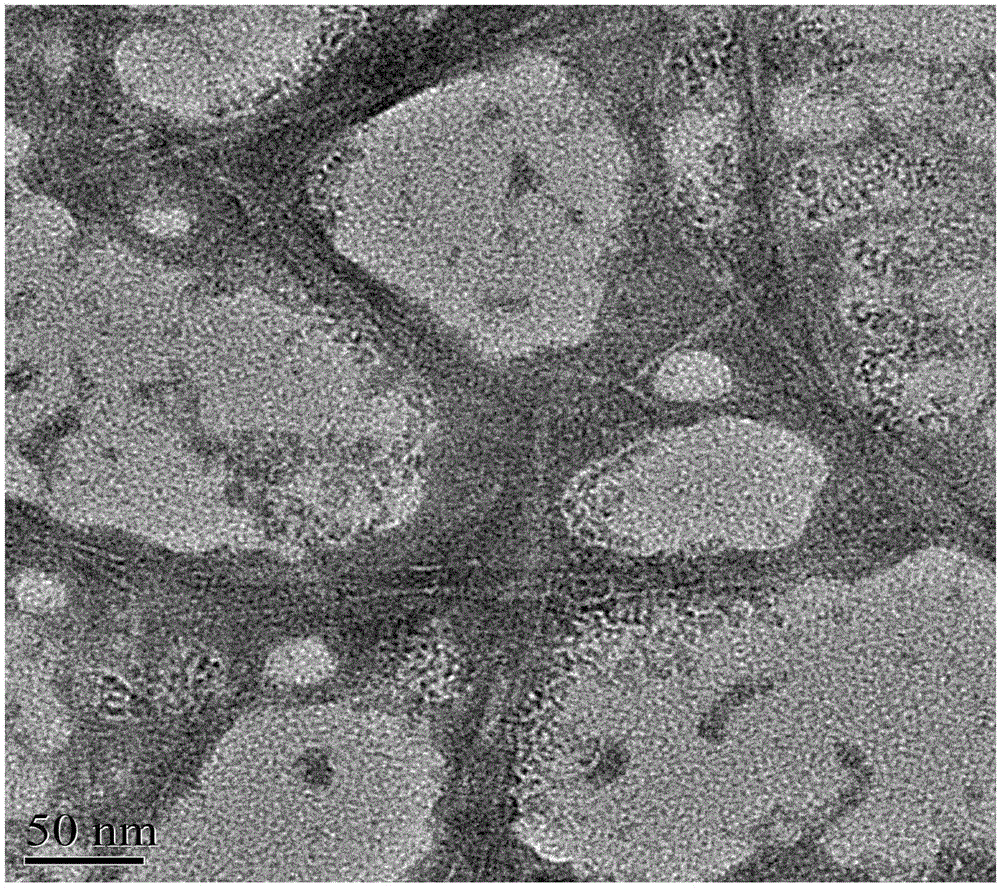
[0045] Select bagasse after sugar extraction with a size between 5-60 meshes, add appropriate amount of water, adjust its moisture content to 45% (mass fraction), seal and place for 12 hours, and then use a steam explosion device to carry out steam explosion treatment on the above-mentioned bagasse fibers ( Temperature 220 ℃, pressure 2.3MPa), the lignocellulosic fiber after steam explosion is placed in 70 ℃ blast drying box and dries 12h, obtains lignocellulose fiber A ( figure 1 ), sealed and stored for later use.
[0046] (2) High temperature water cooking
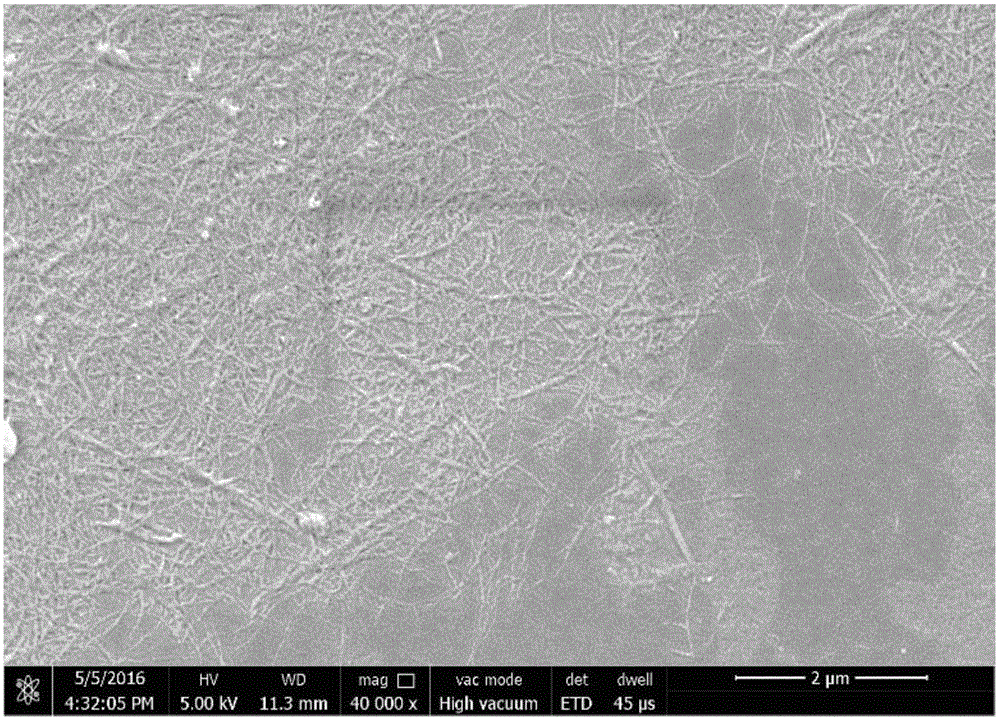
[0047] Weigh 20g of lignocellulose fiber A and put it into the reactor (500ml), then add 300ml of deionized water, 45ml of absolute ethanol, and 1g of NaOH, and seal the reactor after mixing evenly. Subsequently, the reactor was placed in an oil bath at 180° C. for 40 min...
Embodiment 2
[0057] The nanocellulose of the present embodiment, its preparation method comprises the following steps:
[0058] (1) Steam explosion treatment
[0059] The eucalyptus chips were crushed into coarse lignocellulose fibers of 2-60 meshes by using a claw crusher, an appropriate amount of water was added to adjust the moisture content of the fibers to 50% (mass fraction), and sealed for 12 hours. Subsequently, the above-mentioned lignocellulose fibers were subjected to steam explosion treatment (temperature 150° C., pressure 0.47 MPa). Dry the exploded lignocellulose fibers in a blast oven at 70°C for 12 hours to obtain lignocellulose fibers A, which are sealed and stored until use.
[0060] (2) High temperature water cooking
[0061] Weigh 15g of the lignocellulose fiber A and put it into a reactor (500ml), add 300ml of deionized water, 30ml of absolute ethanol, and 1.5g of NaOH, and seal the reactor after mixing evenly. Subsequently, the reactor was placed in an oil bath at ...
Embodiment 3
[0071] The nanocellulose of the present embodiment, its preparation method comprises the following steps:
[0072] (1) Steam explosion treatment
[0073] Take the sisal fiber and crush it into small pieces of about 10-30 mesh, add an appropriate amount of water, adjust the moisture content of the fiber to 55% (mass fraction), and place it sealed for 12 hours. Subsequently, steam explosion treatment (temperature 130° C., pressure 0.27 MPa) was carried out to the above-mentioned sisal fibers by using a steam explosion device. Dry the exploded lignocellulose fibers in a blast oven at 70°C for 12 hours to obtain lignocellulose fibers A, which are sealed and stored until use.
[0074] (2) High temperature water cooking
[0075] Weigh 20g of lignocellulose fiber A and put it into a reactor (500ml), add 300ml of deionized water, 30ml of absolute ethanol, and 3.5g of NaOH, mix well and seal the reactor. Subsequently, the reactor was placed in an oil bath at 210° C. for 15 minutes, ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com