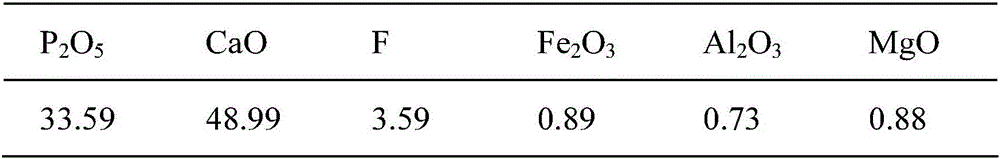Method for producing feed-grade wet-process purified phosphoric acid and high-purity high-whiteness semi-hydrated gypsum
A technology of wet purification and hemihydrate gypsum, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, inorganic chemistry, organic fertilizers, etc., can solve the problems of high impurity content of ordinary hemihydrate gypsum and reduction of common Problems such as the scope of phosphogypsum utilization, to achieve the effects of low phosphorus content, reduced storage and treatment costs, and reduced energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
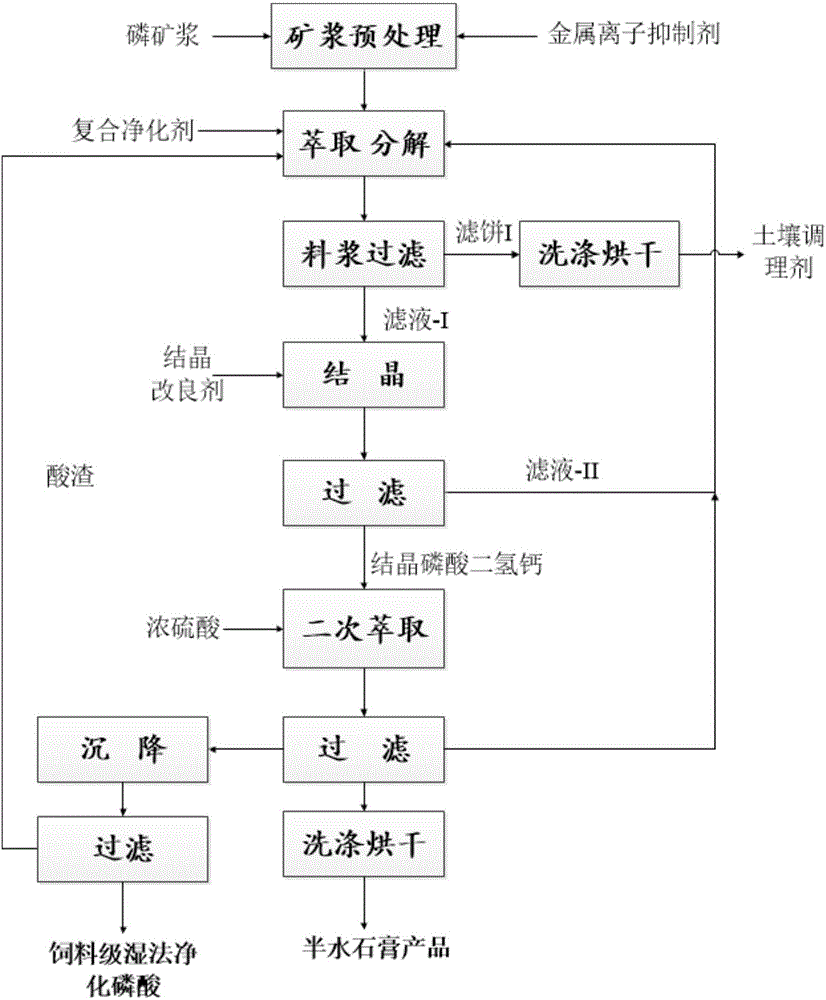
[0039] Step 1 Phosphate ore pretreatment: The phosphate ore raw ore is crushed and ground into a fineness of more than 85% through a 200-mesh Taylor sieve, and the raw ore is subjected to single reverse flotation to obtain a concentrate pulp with a solid content of 75%; according to the weight of the concentrate pulp, 2.0% Nitric acid and 0.5% sodium sulfate are slowly added to the concentrate slurry, the reaction temperature is 40° C., and the reaction time is 2 hours. After the reaction, the obtained slurry is filtered and separated to obtain the pretreated concentrate slurry.
[0040] Step 2 Phosphoric acid extraction and decomposition of phosphate rock: Phosphoric acid (P 2 o 5 content of 30%-45%) and the pretreated concentrate pulp are added to the extraction reaction tank according to the mass ratio of 10:1, and at the same time, 0.5% of active diatomite (according to the weight of the pretreated concentrate pulp) is added , sodium carbonate 1.0% (according to the weigh...
Embodiment example 2
[0054] Step 1 Phosphate ore pretreatment: The raw phosphate ore is crushed and ground into a fineness of more than 85% through a 200-mesh Taylor sieve, and the raw ore is subjected to single reverse flotation to obtain a concentrate slurry with a solid content of 65%; mix 0.5% sodium nitrate with 4.5% Sulfuric acid is slowly added to the concentrate slurry, the reaction temperature is 20°C, and the reaction time is 6h. After the reaction, the obtained slurry is filtered and separated to obtain the concentrate slurry.
[0055] Step 2 Phosphoric acid extraction and decomposition of phosphate rock: Phosphoric acid (P 2 o 5 content of 30%-45%) and concentrate pulp are added to the extraction reaction tank according to the mass ratio of 20:1, and at the same time, 1.0% of active diatomite, 2.0% of sodium sulfate, and 0.001% of potassium sulfide are added to extract The reaction temperature was 60°C and the reaction time was 6 hours. The extracted slurry obtained from the reaction ...
Embodiment 2
[0058] The main chemical composition table (Wt%) of concentrated ore slurry (dry basis) in step 1 in embodiment 2
[0059]
[0060] The main chemical composition list (Wt%) of crystalline calcium dihydrogen phosphate in step 3 in embodiment 2
[0061]
[0062] The main chemical composition list (Wt%) of wet-process phosphoric acid product in step 4 in embodiment 2
[0063]
[0064] P in wet process phosphoric acid 2 o 5 / F(P 2 o 5 Ratio to the quality of F: 407 (feed grade phosphate national standard P 2 o 5 / F>280).
[0065] The main chemical composition table (wt%) of the high-purity and high-whiteness hemihydrate gypsum product (dry basis) in step 4 of embodiment 2.
[0066]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com