A kind of diamond grinding wheel and its production method
A technology of diamond grinding wheel and production method, which is applied to bonded grinding wheels, metal processing equipment, abrasives, etc., can solve problems such as thermal damage, limited service life of grinding wheels, graphitization of diamond abrasive grains, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
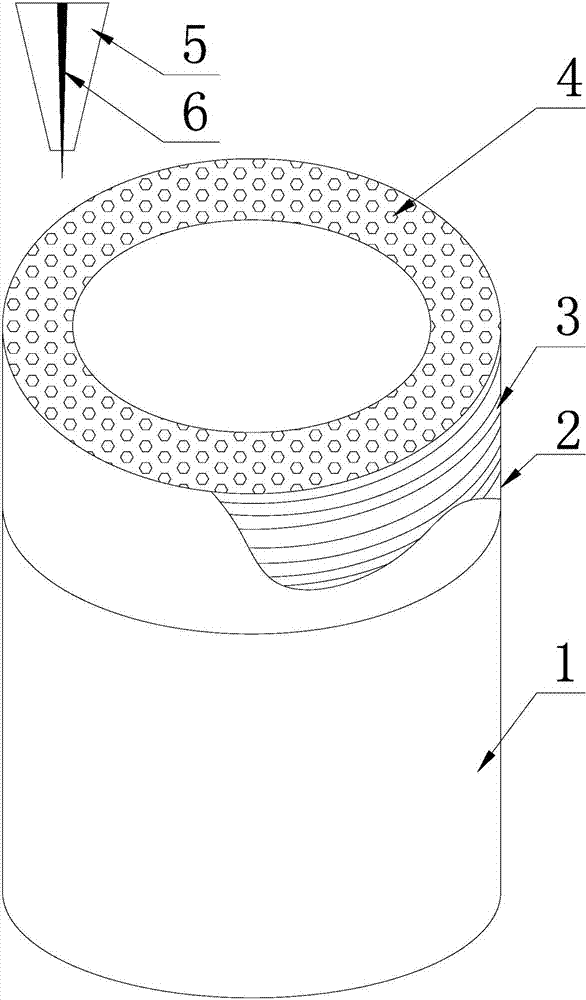
[0043] Depend on Figure 1 to Figure 6 As can be seen, a kind of production method of diamond grinding wheel, it comprises the following steps:
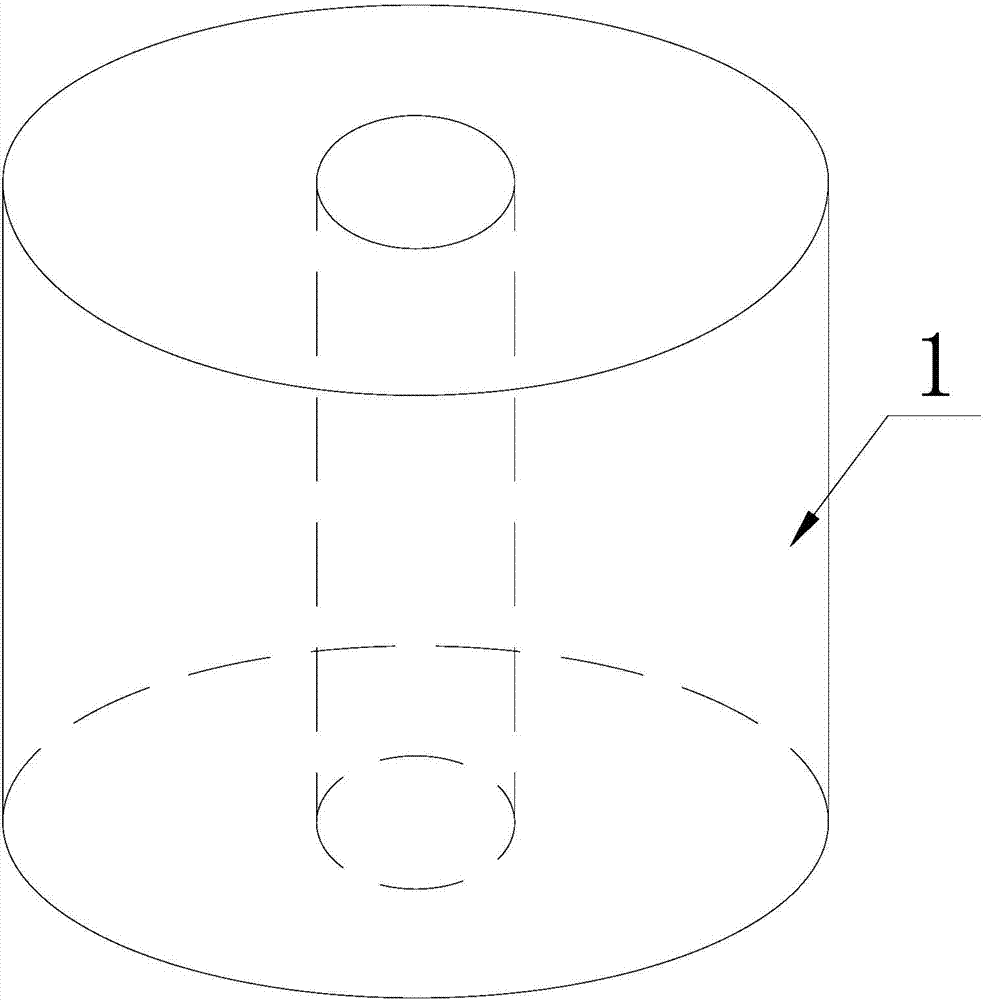
[0044] ⑴Processing the grinding wheel base 1: the cylindrical grinding wheel base 1 is made of steel;
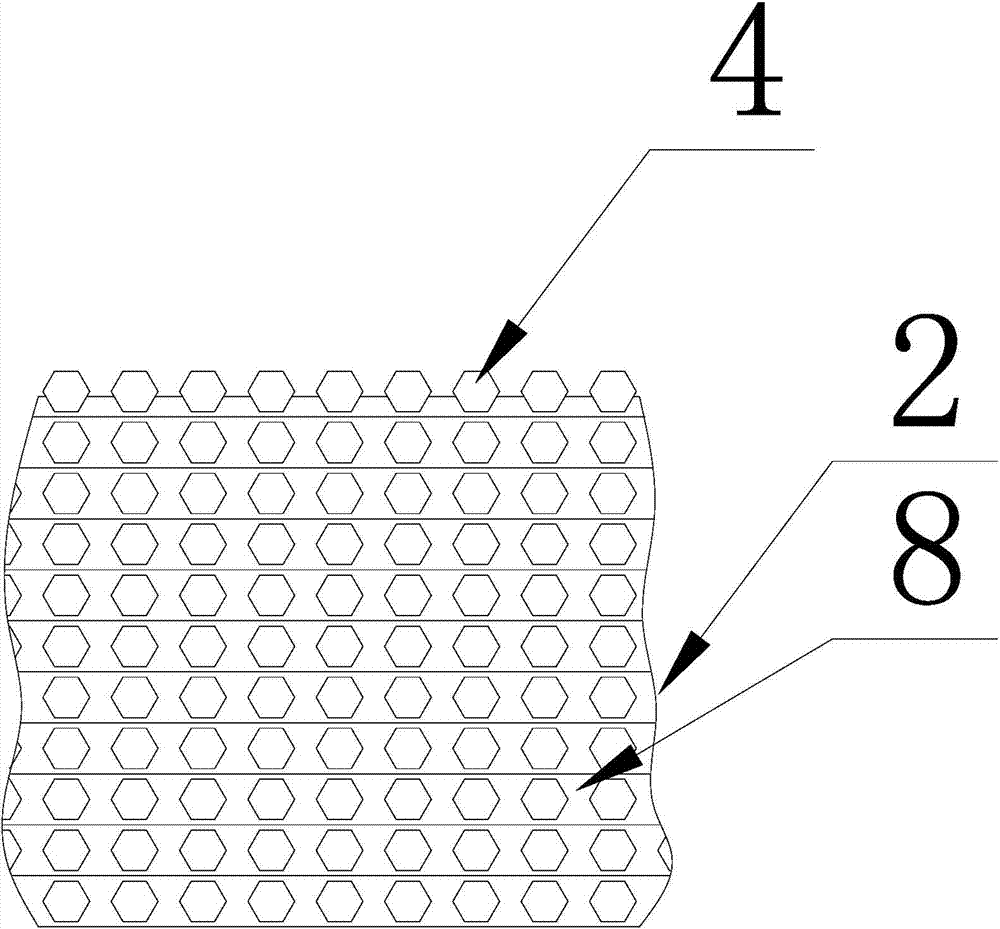
[0045] The steel material used in the grinding wheel base 1 of the present invention is No. 45 steel, and the diamond abrasive grains 4 are truncated octahedral single crystal diamonds with a particle size of 40 mesh (0.42mm-0.45mm) (diamond abrasive grains in this embodiment 4 with a particle size of 0.44 mm).
[0046] (2) Cleaning: Place the grinding wheel substrate 1 and diamond abrasive grains 4 in an organic solvent for ultrasonic cleaning to remove impurities such as oil stains and oxide layers on the surface;
[0047] (3) Hole layout: use a laser galvanometer scanning device (two-dimensional galvanometer short pulse laser scanning device), select appropriate laser parameters such as pulse width, average power, and pulse fr...
Embodiment 2
[0066] In this embodiment, the particle diameter of the diamond abrasive grains 4 is 0.44mm; the sintering temperature described in step (7) is 765°C; the thickness of the annular metal sheet 7 is 35% of the abrasive grain diameter; the diameter of the positioning hole 71 is the abrasive grain diameter 75%; the diameter of the powder hole 72 is three times the diameter of the positioning hole 71; the Cu content in the copper base is 55%, the Sn content is 30%, and the Ti content is 5%; the diamond abrasive grains on the working surface (the uppermost layer of the abrasive layer 22) 4 The cutting edge height is 55% of the abrasive grain height; the abrasive layer 22 includes a 10-layer "sandwich" structure.
[0067] The rest are the same as embodiment 1.
Embodiment 3
[0069] In this embodiment, the particle diameter of the diamond abrasive grains 4 is 0.45mm; the sintering temperature described in step (7) is 785°C; the thickness of the annular metal sheet 7 is 40% of the abrasive grain diameter; the diameter of the positioning hole 71 is the abrasive grain diameter 80%; the diameter of the powder hole 72 is 5 times the diameter of the positioning hole 71; the Cu content in the copper base is 60%, the Sn content is 27%, and the Ti content is 13%; the diamond abrasive grains on the working surface (the uppermost layer of the abrasive layer 22) 4 The cutting edge height is 60% of the abrasive grain height; the abrasive layer 22 includes a 15-layer "sandwich" structure.
[0070] The rest are the same as embodiment 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com