System and method for treating copper slag through ore grinding and magnetic separation
A technology for grinding, magnetic separation, and copper slag, which is applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, can solve the problems of high operating cost, low iron concentrate grade, and high environmental protection cost, and achieves good reduction effect, high grade, and reduced energy consumption. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
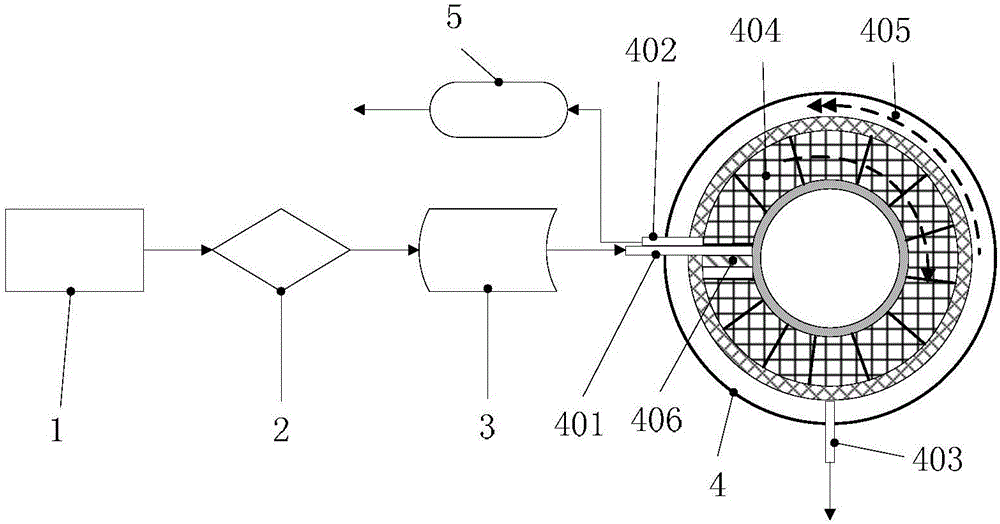
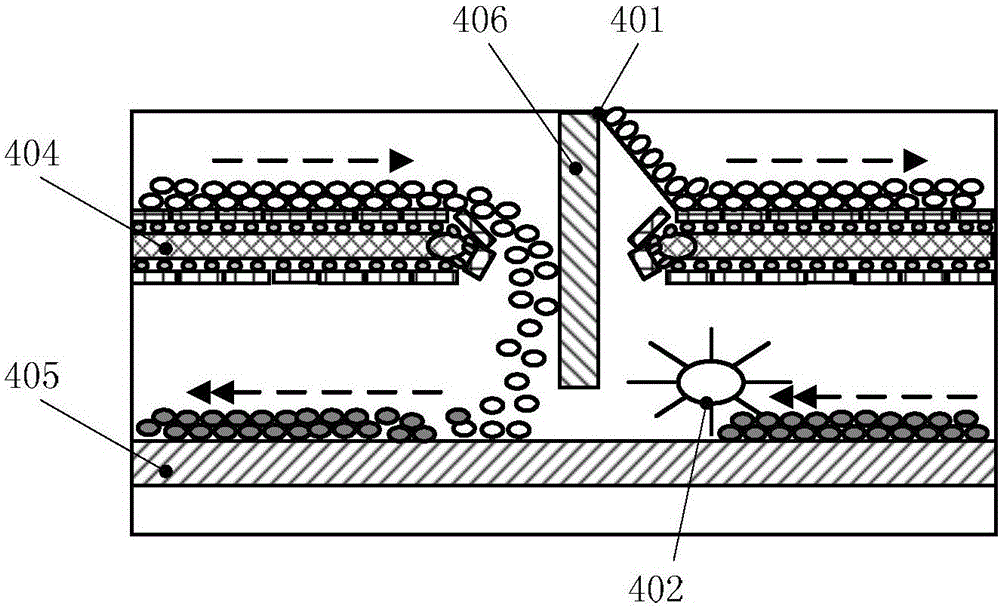
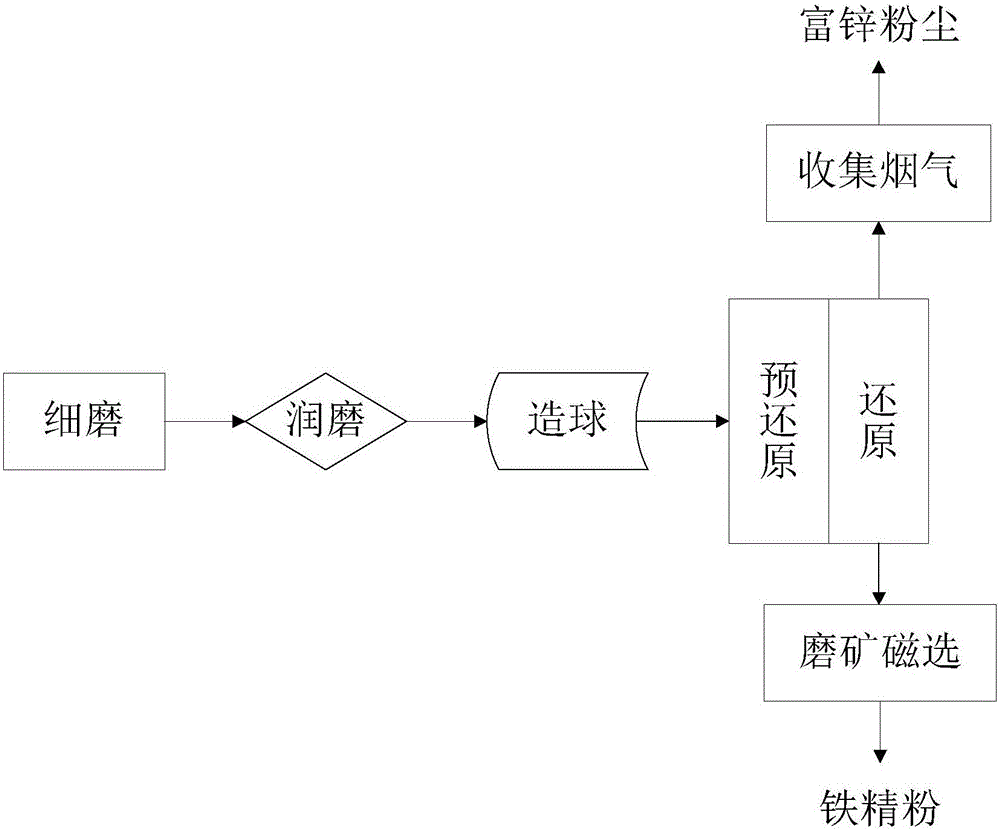
[0062] Finely grind 100 parts of copper slag, 20 parts of reduced coal (mass content of C: 82.06%), 8 parts of additives (limestone) until particle size ≤ 200 mesh accounts for 86.35%, and mix with 5 parts of binder to make pellets , enter from the feed port of the rotary hearth furnace, the reduction temperature of the rotary hearth furnace is 1280°C, the pre-reduction layer rotates for 35 minutes, and the reduction layer rotates for 45 minutes, and the pellets pass through the pre-reduction layer and the reduction layer respectively from the discharge port of the rotary hearth furnace Exhaust, collect the flue gas discharged from the rotary hearth furnace to obtain zinc-rich dust, water-quench and crush the metallized pellets discharged from the rotary hearth furnace, and grind them until the particle size is ≤ 200 mesh. The particle size accounts for 81.36% of the mass. Iron powder.
Embodiment 2
[0064] Finely grind 100 parts of copper slag, 30 parts of reduced coal (mass content of C: 81.58%), 5 parts of additives (limestone) until particle size ≤ 200 mesh accounts for 88.59%, and mix with 10 parts of binder to make pellets , enter from the feed port of the rotary hearth furnace, the reduction temperature of the rotary hearth furnace is 1200°C, the pre-reduction layer rotates for 20 minutes, and the reduction layer rotates for 60 minutes, and the pellets pass through the pre-reduction layer and the reduction layer respectively from the discharge port of the rotary hearth furnace Exhaust, collect the flue gas discharged from the rotary hearth furnace to obtain zinc-rich dust, water-quench and crush the metallized pellets discharged from the rotary hearth furnace, and grind them until the particle size is ≤ 200 mesh. The particle size accounts for 82.38% of the mass. Iron powder.
Embodiment 3
[0066] Finely grind 100 parts of copper slag, 25 parts of reduced coal (mass content of C: 83.58%), 10 parts of additive (limestone) until particle size ≤ 200 mesh accounts for 87.49%, and mix with 8 parts of binder to make pellets , enter from the feed port of the rotary hearth furnace, the reduction temperature of the rotary hearth furnace is 1350°C, the pre-reduction layer rotates for 50 minutes, and the reduction layer rotates for 30 minutes, and the pellets pass through the pre-reduction layer and the reduction layer respectively from the discharge port of the rotary hearth furnace Exhaust, collect the flue gas discharged from the rotary hearth furnace to obtain zinc-rich dust, water-quench and crush the metallized pellets discharged from the rotary hearth furnace, and grind them until the particle size is ≤ 200 mesh. The particle size accounts for 82.35% of the mass. Iron powder.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com