Kosakonia radicincitans and application thereof
A technology of nitrogen-fixing bacteria and nitrogen-free medium, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problem of not being able to widely act on other crops, and achieve the effects of good ammonium secretion performance and nitrogen-fixing activity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
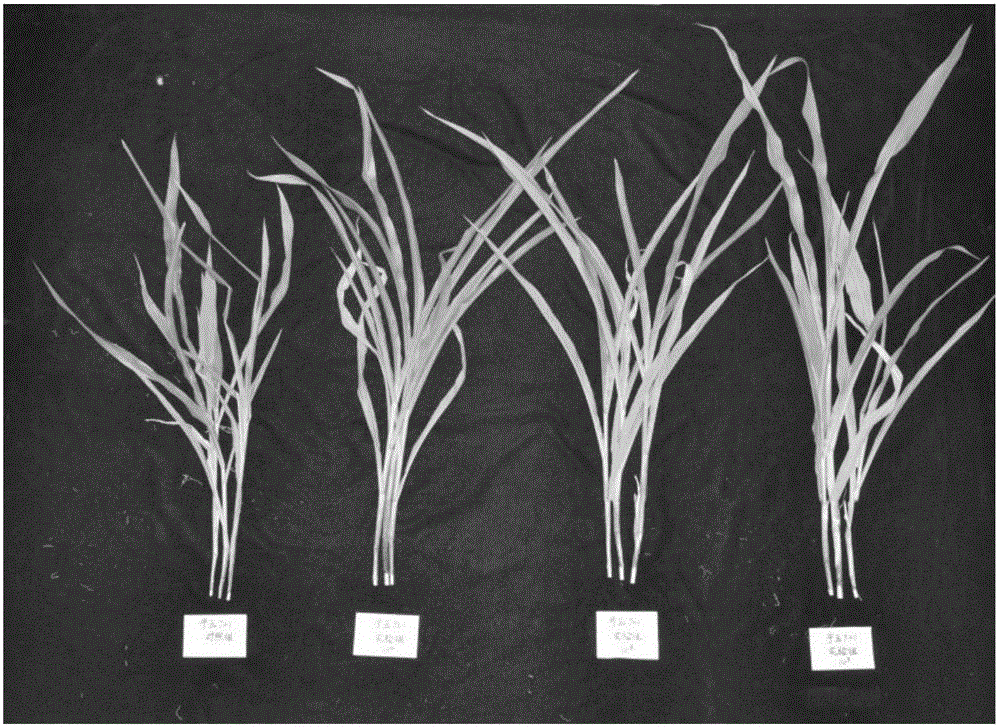
[0048] Embodiment 1: Screening and obtaining of bacterial strains
[0049] Take the root system, wash it with water and drain it. Soak it in 70% alcohol for 30 seconds, rinse it with sterile water for 3 times, and then soak it in 5%-20% NaClO solution with 1 drop of surfactant for 5-10 minutes. Then soak again in 70% alcohol for 30s, rinse with sterile water 5 times. Sterile water for the last rinse was applied to the LB solid plate. If there is no colony growth, it means that the disinfection is complete, otherwise, re-sampling and separation. Put the sterilized materials and 10 mL of phosphate buffer solution into a sterile mortar and grind them for 5 minutes, take 1 mL of the supernatant as the original solution, make a 10-fold serial dilution with sterile water, and then take 0.1 mL was spread on an Ashby nitrogen-free plate, cultured in an incubator at 28°C for 2 to 3 days, and single colonies with different colony shapes were selected, and the plate was streaked repea...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Embodiment 2: microscopic examination and electron microscope observation of bacterial strain
[0051] Pick Kosakonia radicincitans GXGL-4A from the inoculation loop under sterile conditions, smear it on a glass slide, make a slice and perform Gram staining, and observe the morphology of the bacteria under a microscope.
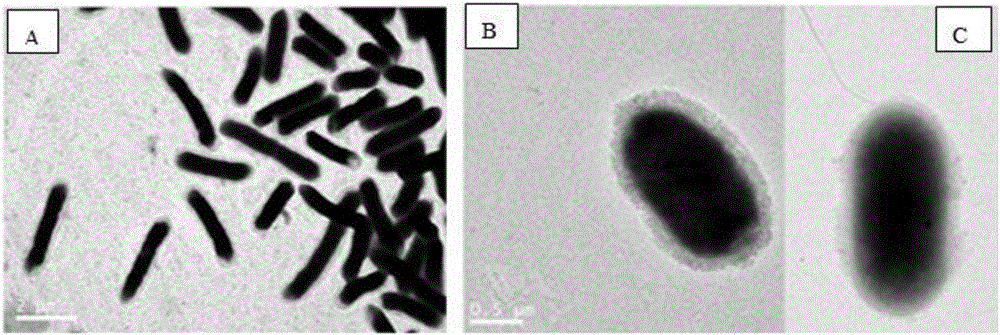
[0052] Cultivate the strain overnight with LB liquid medium, draw 1mL of the bacterial solution into a sterilized 1.5mL centrifuge tube, centrifuge at room temperature at 4000r / min for 2min, suck out the supernatant, add sterile water to resuspend the precipitate, and immediately absorb a small amount of bacterial solution Put it on a copper plate, place it in the air to dry, and use a scanning electron microscope (Tecnai G2spiritBiotwin, 120kV Bio-TEM) to observe the morphology of nitrogen-fixing bacteria after drying and fixing the sample.
[0053] Electron micrograph of the nitrogen-fixing bacterium Kosakonia radicincitans GXGL-4A figure 1 As shown...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Example 3: Identification of ammonium secretion characteristics of bacterial strains
[0055] Cultivate the GXGL-4A strain in LB medium at 37°C and 180r / min overnight, and the culture medium is 10 -5 After one-fold dilution, spread on Ashby nitrogen-free solid medium and grow for 4 days. Under nitrogen-free conditions, nitrogen-fixing bacteria GXGL-4A will use nitrogen in the air for nitrogen fixation, and finally secrete part of the fixed nitrogen out of the cell in the form of ammonia nitrogen. Therefore, use a pipette gun (under sterile conditions, cut off the Tip head with a monolithic knife) to absorb slightly viscous secretions, add 10 times the volume of sterile water to dilute, and pass the diluted solution through a 0.45 μm sterile filter. Membrane sterilized, collected into a sterile Eppendorf tube is the sample to be tested. The concentration of ammoniacal nitrogen in the samples was determined by indophenol blue-spectrophotometry.
[0056] (1) Preparation...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com