Phytase mutants ykappa-l327v, yeappa-l327v and their coding genes and applications
A technology of phytase and mutant, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problem of reducing nutritional titer and so on
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Embodiment 1: Obtaining of mutant genes
[0035] Mutant enzymes YkAPPA-L327V and YeAPPA-L327V were produced by Overlap PCR method. The method uses recombinant plasmids pEASY-T3-YkAPPA and pEASY-T3-YeAPPA containing wild phytase gene as templates, and introduces mutations through two rounds of PCR reactions. The upstream and downstream primers for amplifying the complete coding sequence of the mutant gene have EcoR I and Not I recognition sequences, respectively YkAPPA Forward: 5'-cgcgaattcgcaccgcttgcagcacaatctac-3' and YkAPPA Reverse: 5'-gatgcggccgcttaaatatggcaggctggctcG-3'; YeAPPA Forward: 5' -cgcgaattcgcaccgcttgcagcacaatctac-3' and YeAPPA Reverse: 5'-gatgcggccgcttaaatggcaggctggctcg-3'. The upstream and downstream primers for introducing mutations at specific positions are L327V Forward: 5'-tcaccgcaaaccaaagtgctgttcctc-3' and L327V Reverse: 5'-gaggaacagcactttggtttgcggtga-3'. The desired mutated gene was ligated into pEASY-T3 vector and confirmed by sequencing.
Embodiment 2
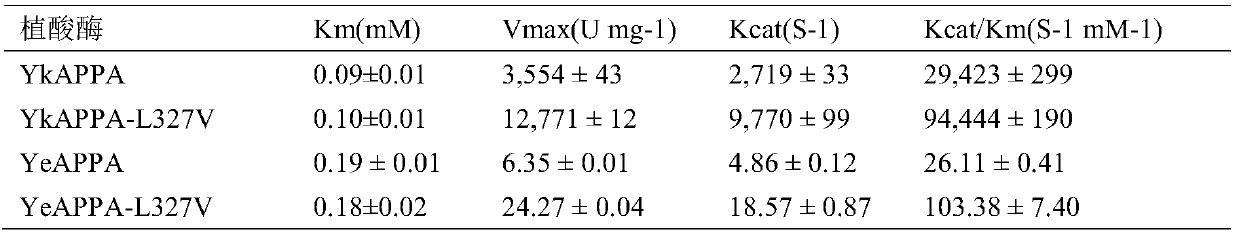
[0036] Example 2: Expression and purification of mutant phytase and wild enzyme in bacteria
[0037] After removing the signal peptide sequence, the wild enzyme and mutant enzyme were inserted into the expression vector pET-22b(+), and expressed in Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) cells induced by 2mM IPTG (isopropyl-β-D-galactoside) . The crude enzyme solution was purified by Ni-NTA (nickel-nitrilotriacetic acid) column and DEAE (diethylaminoethyl) column, and detected by 10% SDS-PAGE gel electrophoresis. The wild enzyme and the mutant enzyme encode 441 amino acids, and the N-terminal contains a signal peptide sequence of 23 amino acids. The theoretical molecular weight of the mature protein is 48.6kDa. Both the wild enzyme and the mutant enzyme after removing the signal peptide sequence showed a specific band of about 46 kDa in SDS-PAGE electrophoresis (data not shown).
Embodiment 3
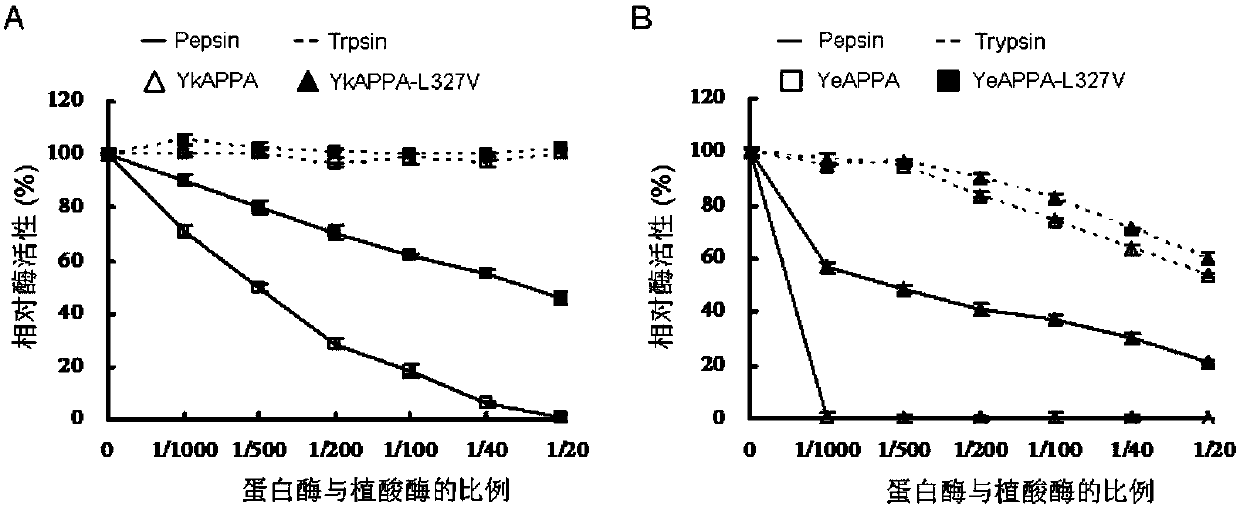
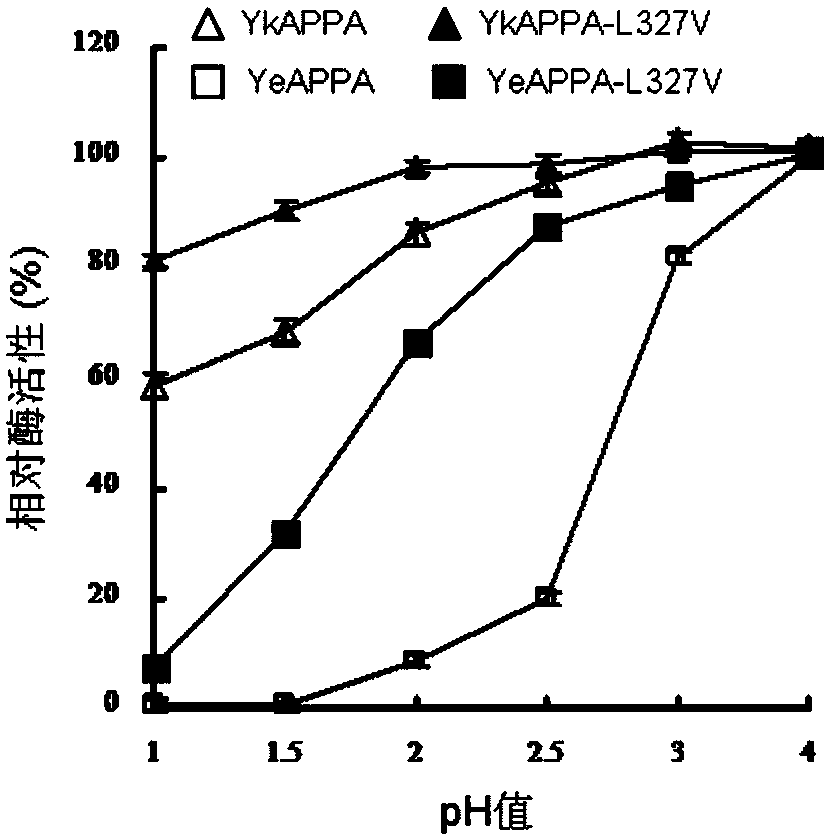
[0038] Embodiment 3: the protease resistance comparison of mutant phytase and wild enzyme
[0039] The wild enzyme and mutant enzyme were treated with pepsin (pH2) and trypsin (pH7) at 37°C for 2 hours, respectively, and the ratio of protease to phytase was between 1 / 1000 and 1 / 20. The samples treated with protease were diluted with optimum pH buffer, and the effect of protease on phytase activity was studied at 37°C and optimum pH conditions. Phytase activity was determined using the ferrous sulfate molybdenum blue method. Add 50 μL of the diluted enzyme solution to 950 μL of 1.5 mmol / L sodium phytate substrate (prepared with 0.25 mol / L pH 4.5 1.5 mmol / L sodium phytate buffer), react at 37°C for 30 min, and use 1 mL of 10% TCA was used to terminate the reaction, and then 2 mL of color developing solution (1% ammonium molybdate tetrahydrate, 3.2% concentrated sulfuric acid, 7.32% ferrous sulfate) was used for color development. The control is to add TCA and mix to denature t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com