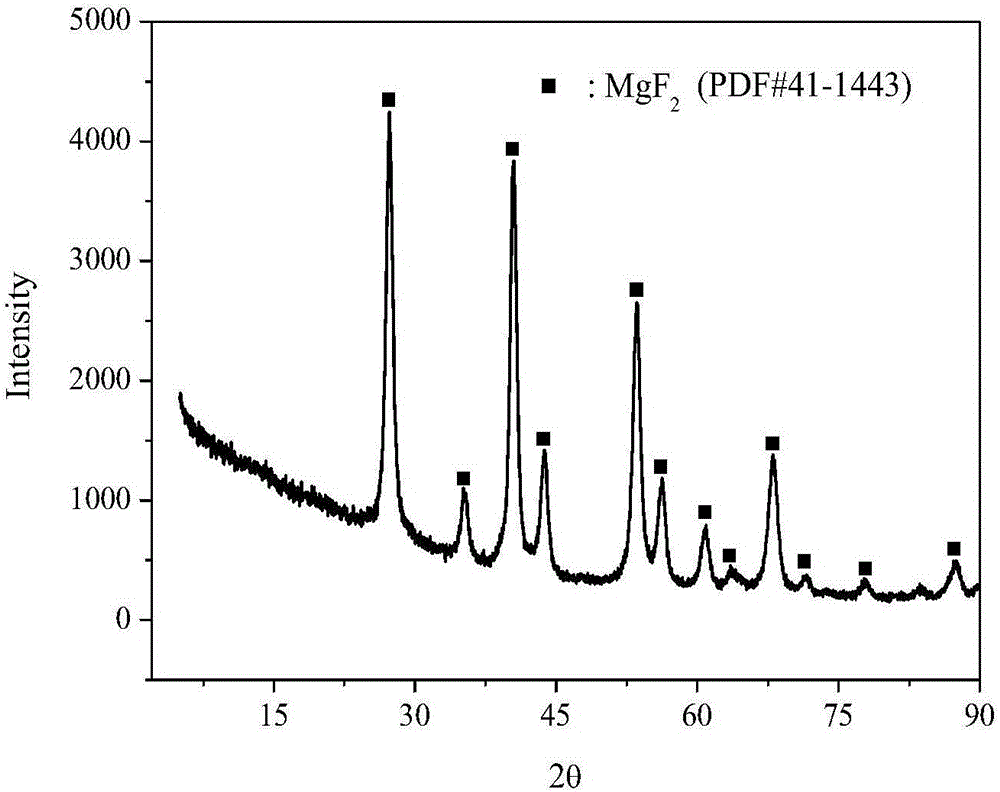
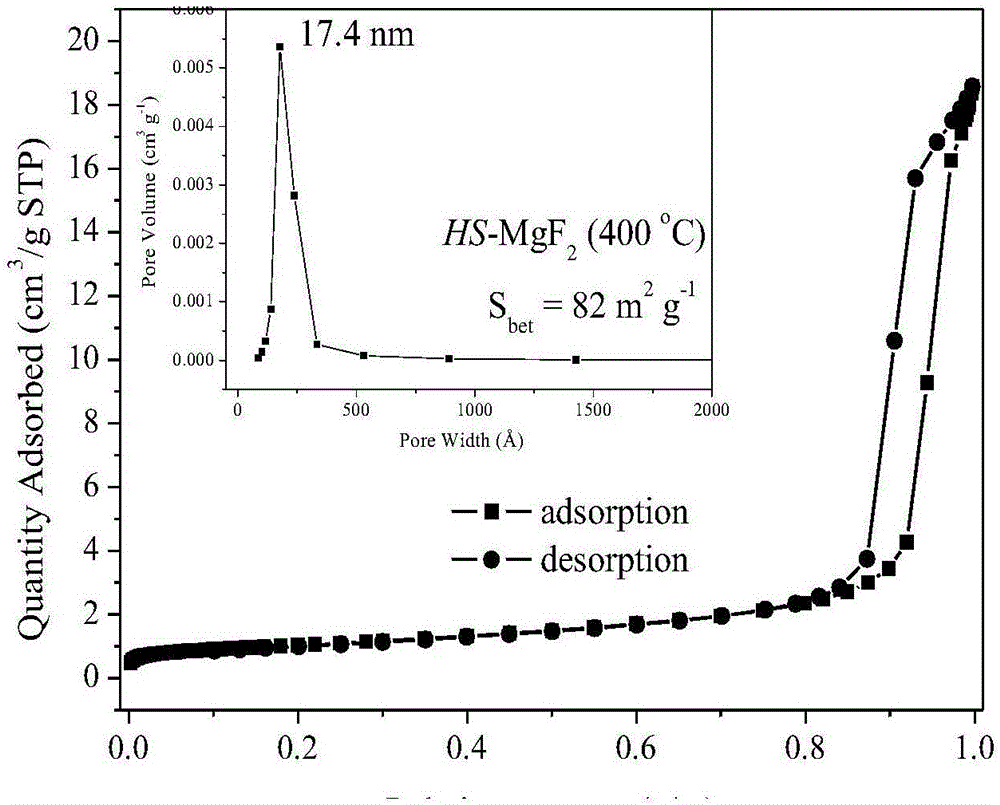
Method for preparing nano-crystal magnesium fluoride with high specific surface area
A high specific surface area, crystalline magnesium fluoride technology, applied in the direction of magnesium fluoride, nanotechnology for materials and surface science, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of high energy consumption, complicated process and high cost of reflux reaction , to achieve the effect of easy material surface coating, mild preparation conditions and low corrosion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Embodiment 1: Preparation of high specific surface area, nanocrystalline magnesium fluoride
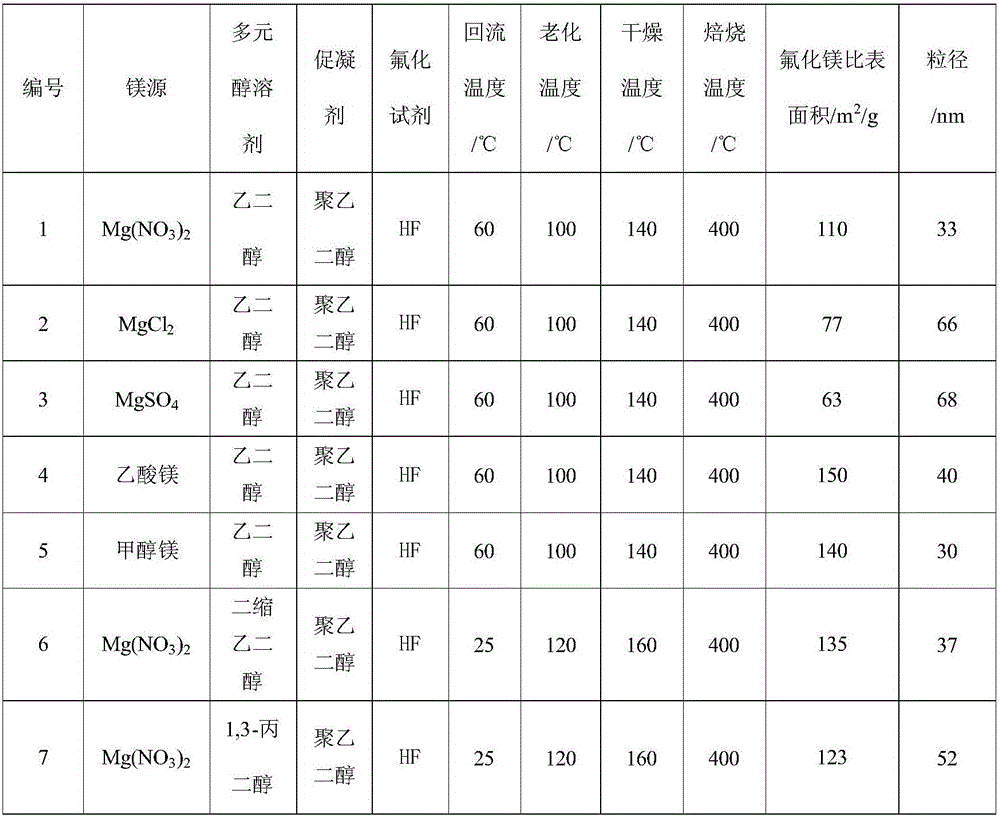
[0024] Dissolve 1.0M magnesium source in 50mL polyol solvent, reflux at 20-80°C for 6 hours, then add the fluorinated reagent dropwise to the above solution with stirring, the dropping time is 30min, after the dropping is completed, Stir for 6 hours to obtain a liquid sol; then statically age at 100-160°C for more than 24 hours to obtain a solid gel; then dry at 140-200°C for more than 24 hours, and finally roast at 350-450°C for more than 4 hours in an air atmosphere to obtain High specific surface area nanocrystalline magnesium fluoride at high temperature. The textural properties of magnesium fluoride prepared under different magnesium sources, polyol solvents, coagulants, fluorinating reagents, and calcination temperatures are shown in Table 1.
[0025] The magnesium fluoride physicochemical property result of table 1 embodiment 1
[0026]
[0027]
Embodiment 2
[0028] Embodiment 2: Preparation of high specific surface area nanocrystalline magnesium fluoride
[0029] Dissolve 1.0M magnesium nitrate and polyethylene glycol in 50mL of ethylene glycol, reflux at 30°C for 6h, then add HF aqueous solution (40wt.%) dropwise to the above solution while stirring, and the dropping time is After the dropwise addition, stir for 6 hours to obtain a liquid sol; then statically age at 100°C for more than 24 hours to obtain a solid gel; then dry at 140°C for more than 24 hours, and finally roast at 400°C for more than 4 hours to obtain a high-temperature High specific surface area nanocrystalline magnesium fluoride. The textures of magnesium fluoride obtained with different amounts of polyethylene glycol are shown in Table 2.
[0030] The magnesium fluoride physicochemical property result of table 2 embodiment 2
[0031]
Embodiment 3
[0032] Embodiment 3: Preparation of high specific surface area nanocrystalline magnesium fluoride
[0033] Dissolve 1.0M magnesium nitrate and polyethylene glycol (Mg / gelling agent mass ratio is 1:3) in 50mL of ethylene glycol, reflux at 30°C for 6h, then add HF solution dropwise to In the above solution, the dripping time is 30min, after the dripping is completed, stir for 6h to obtain a liquid sol; then statically age at 100°C for more than 24h to obtain a solid gel; then dry at 140°C for more than 24h, and finally dry at 400°C Calcining at lower temperature for more than 4 hours to prepare nanocrystalline magnesium fluoride with high specific surface area at high temperature. The textures of magnesium fluoride prepared with different HF concentrations are shown in Table 3.
[0034] The magnesium fluoride physicochemical property result of table 3 embodiment 3
[0035]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com