Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degradation gene engineering strain, and construction method and application thereof
A technology of genetically engineered strains and genetically engineered bacteria, applied in the field of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons degrading genetically engineered strains, can solve problems such as inability to guarantee lethality, and achieve the effects of reducing biosafety risks and improving controllability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Example 1: Fusion of lac promoter with nuclease gene nuc
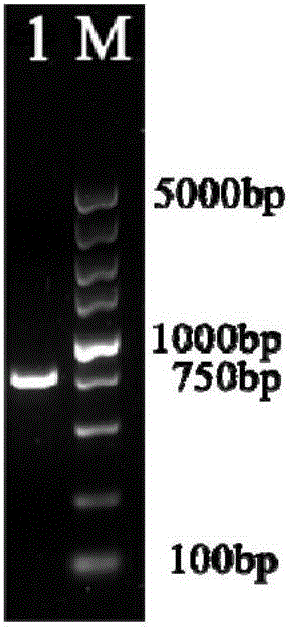
[0045] Amplify the nuc fragment with primers nuc-f and nuc-r; PCR reaction system (50 μl): template DNA 1.0 μl; HS Premix (Bao Sheng Gong, Dalian) 25.0 μl; 50 μM primer 0.5 μl; ddH 2 O 23.0 μl; PCR reaction program: pre-denaturation at 94°C for 3 min; (pre-denaturation at 94°C for 30 s—annealing at 57°C for 5 s—extension at 72°C for 90 s)×30 cycles; extension at 72°C for 10 min. Amplification results see figure 1 ( figure 1 : PCR amplification of nuc gene, wherein M: 5000bp DNA Marker, 1: nuc gene fragment). Gel electrophoresis imaging showed specific amplification bands, and the fragment length was expected (801bp). Use Nde I and HindIII to digest the vector pUC-18 and the amplified product of the nuc fragment. After ligation, the plasmid pUC-nuc is transformed into E.coli DH5α to amplify and extract the plasmid, and then use it as a template to amplify the nuc fragment. Digest the visible pUC-18 vector a...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Example 2: Construction of recombinant transposon vector pUT-lacnuc
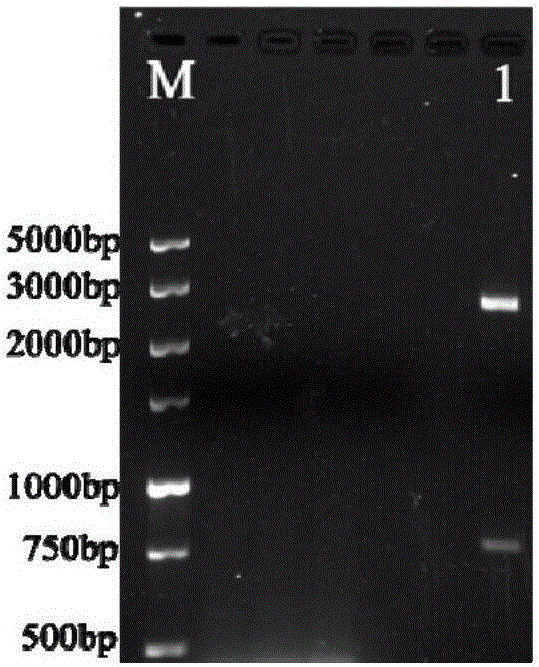
[0047] The lacnuc gene and the vector pUT / mini-Tn5Km were digested with Not I restriction endonuclease, and the lacnuc fragment was recovered after purification and ligated with pUT / mini-Tn5Km, and the ligated product was transformed into E.coli DH5αλpir. The positive clones on the pick plate were verified by colony PCR using primers lacnuc-f and lacnuc-r, and the verification results were positive (see Figure 4 : PCR verification of pUT-lacnuc vector, where M: 10000bp DNA Marker, 1: lacnuc gene fragment); at the same time, the extracted plasmid was digested with Not I, and the results of gel electrophoresis showed that there were two lines near 7.1kb and 1kb. strip (see Figure 5 : Enzyme digestion identification of pUT-lacnuc vector, where M: 5000bp DNA Marker, 1: Not I digestion product), corresponding to pUT / mini-Tn5Km plasmid and lacnuc gene respectively, proving that the pUT-lacnuc recombinant...
Embodiment 3
[0048] Embodiment 3: the construction of genetic engineering bacterial strain Pseudomonas putida GLEB3
[0049] The fusion gene lacnuc was recombined into the chromosome of Pseudomonas putida GLB3 by means of triparental combination. The strains required for the operation were as follows: recipient bacteria (Pseudomonas putida GLB3), auxiliary bacteria (E.coli DH5α(pRK2073)), donor bacteria (E. .coli DH5α(pUT-lacnuc)). The mixing ratio of each strain is 1:2:1, and the mixed system uses 10mM MgSO 4 Solution, the plate medium used should be the LB plate medium containing kanamycin (25mg / L) and chloramphenicol (25mg / L). After culturing until the colonies were visible, the colonies were picked, and the colony PCR verification of the lacnuc gene was performed using primers lacnuc-f and lacnuc-r. Image 6 It shows that the lacnuc gene has been successfully transformed into the recipient bacterium Pseudomonas putida GLB3, and the recombinant bacterium is named Pseudomonas putida GL...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com