Method of Brazilian ginseng cutting seedling
A technology for raising seedlings by cuttings and Brazilian ginseng, which is applied in the fields of botanical equipment and methods, preservation of human or animal bodies, planting substrates, etc., and can solve the problems of growing seedling offspring, high cost of group-cultivating seedlings, complicated equipment and procedures, etc. , to achieve the effect of high nutrient content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
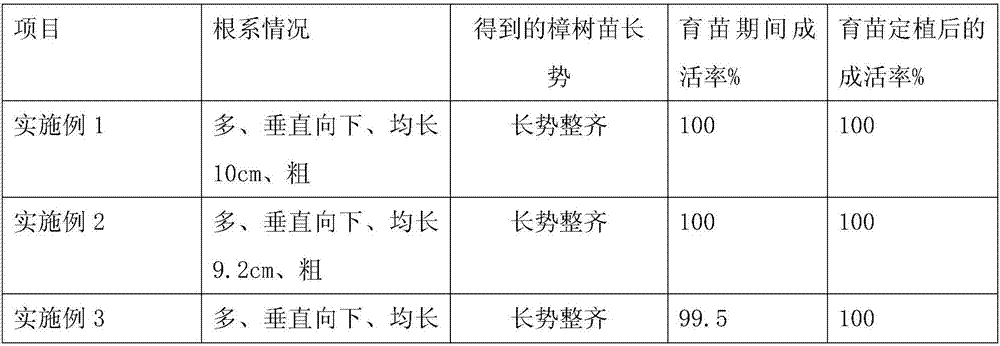
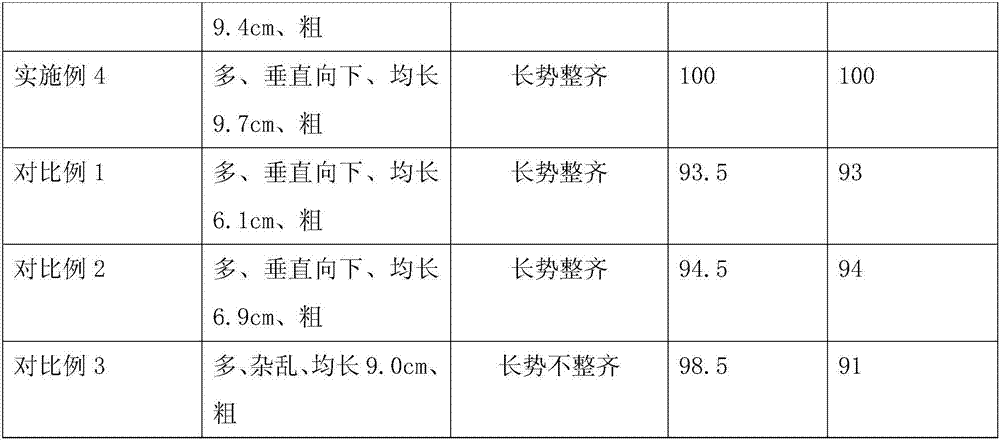
Embodiment 1
[0040] 1. Raw material preparation:
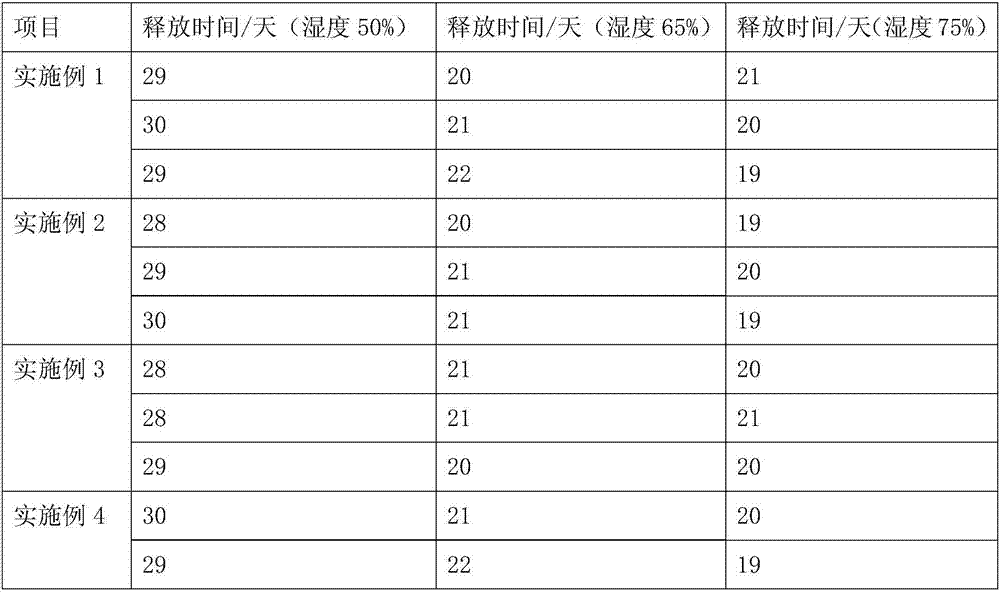
[0041] 1. Slow-release fertilizer granules are made of the following raw materials in parts by weight: 1 part of trace elements, 1 part of urea, 1 part of ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.5 parts of crab shells, 0.5 parts of pig testicles, 1.5 parts of molasses, 0.5 parts of coconut bark, 0.5 parts of dead branches of banyan tree, 0.5 parts of lotus stems, 0.5 parts of Cyperus cyperi, 0.5 parts of cow felt, 0.5 parts of firefly and 1.5 parts of cellulase
[0042] 2.5 parts of thiourea, 2.5 parts of phenylphosphoramide, 2 parts of propylene glycol alginate, 3 parts of cyanide;
[0043] Among them, trace elements include 1 part of boron fertilizer, 0.5 part of cobalt fertilizer, 1 part of zinc fertilizer, 1 part of copper fertilizer, 0.5 part of molybdenum fertilizer, 0.5 part of manganese fertilizer, and 0.5 part of iron fertilizer;
[0044] Apply the raw materials of the above ratio to the following method for preparing slow-release ferti...
Embodiment 2
[0065] 1. Raw material preparation:
[0066] 1. Slow-release fertilizer granules are made of the following raw materials in parts by weight: 5 parts of trace elements, 4 parts of urea, 3 parts of ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, 2 parts of crab shells, 2 parts of pig testicles, 0.5 parts of molasses, 1 part of coconut bark, 1 part of dead branch of banyan tree, 2 parts of lotus stem, 1 part of Cyperus cyperi, 1 part of cow felt, 1 part of firefly and 1.5 parts of cellulase
[0067] 5 parts of thiourea, 5 parts of phenylphosphoramide, 2 parts of propylene glycol alginate, 2 parts of cyanoacrylate-acetylated hydroxypropyl cellulose, 2 parts of furan resin and 2 parts of polyurethane;
[0068] Among them, trace elements include 2 parts of boron fertilizer, 3 parts of cobalt fertilizer, 3 parts of zinc fertilizer, 3 parts of copper fertilizer, 3 parts of molybdenum fertilizer, 3 parts of manganese fertilizer and 3 parts of iron fertilizer;
[0069] Apply the raw materials of the ab...
Embodiment 3
[0090] 1. Raw material preparation:
[0091] 1. Slow-release fertilizer granules are made of the following raw materials in parts by weight: 3 parts of trace elements, 2 parts of urea, 2 parts of ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, 1.5 parts of crab shells, 1.5 parts of pig testicles, 1 part of molasses, 1 part of coconut bark, 1.5 parts of dead branches of banyan tree, 1 part of lotus stem, 1.5 parts of Cyperus cyperi, 1 part of cow felt, 1 part of firefly and 1.5 parts of cellulase
[0092] 4 parts of thiourea, 5 parts of phenylphosphoramide, 2 parts of cyanoacrylate-acetylated hydroxypropyl cellulose, 2 parts of furan resin and 2 parts of polyurethane;
[0093] Among them, trace elements include 0.5 part of boron fertilizer, 1 part of cobalt fertilizer, 0.5 part of zinc fertilizer, 0.5 part of copper fertilizer, 0.5 part of molybdenum fertilizer, 1 part of manganese fertilizer and 1 part of iron fertilizer;
[0094] Apply the raw materials of the above ratio to the following me...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com