Method of removing chromium (VI) and dye pollutants by using plant polyphenol substances for in-situ synthesizing iron-based material
A technology of plant polyphenols and iron-based materials, which is applied in the field of environmental pollution control and restoration, can solve the problems of failure to completely eliminate organic pollutants, poor dye treatment effect, and low wastewater adaptability, and achieve easy follow-up recycling process operations, Significant removal effect and reduction of recycling cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
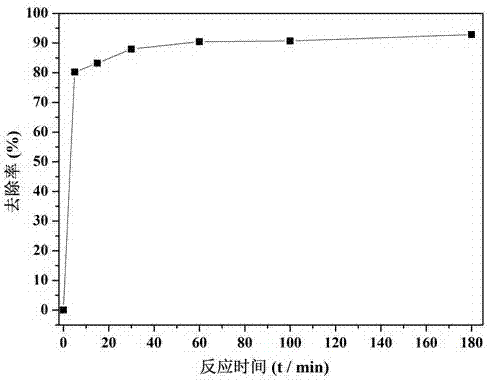
[0066] Example 1 Degradation of Cr(VI)-containing wastewater by in-situ synthesis of iron-based materials using green tea
[0067] 1. Using green tea to synthesize iron-based materials in situ to degrade Cr(VI)-containing wastewater includes the following steps:
[0068] Put 10 g of green tea in a blender and crush for 2 min, weigh 4 g of green tea powder in 200 mL of deionized water, boil at 80°C for 15 min, and filter out the tea dregs with filter paper after cooling to obtain the green tea extract;
[0069] Weigh 5g FeCl 3 •6H 2 O was dissolved in 500 mL deionized water to obtain an iron salt solution;
[0070] The Cr(VI)-containing wastewater used in this example is artificially prepared, that is, analytically pure potassium dichromate is dissolved in deionized water, and the Cr(VI) concentration is 50 mg / L.
[0071] Pipette 60 mL of the above wastewater into a 100 mL Erlenmeyer flask, add 2 mL of Fe(III) solution, shake it manually at 25°C, and let it stand for 5 min; ...
Embodiment 2
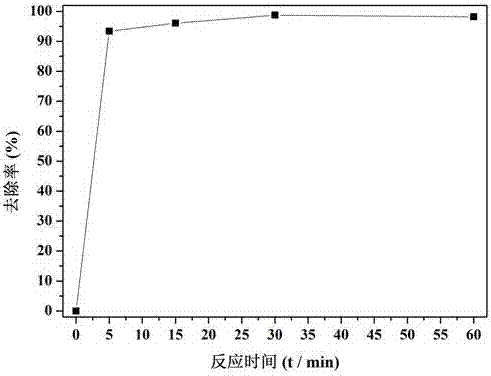
[0073] Example 2 Degradation of Cr(VI) in electroplating wastewater by in-situ synthesis of iron-based materials using green tea
[0074] 1. Using green tea to synthesize iron-based materials in situ to degrade Cr(VI) in electroplating wastewater, including the following steps:
[0075] Put 10 g of green tea in a blender and crush for 1 min, weigh 4 g of green tea powder in 200 mL of deionized water, boil at 80°C for 30 min, and filter out the tea dregs with filter paper after cooling to obtain the green tea extract;
[0076] Weigh 2g FeSO 4 •7H 2 O was dissolved in 150 mL deionized water to obtain an iron salt solution;
[0077] The electroplating wastewater used in this example comes from an electroplating company in Panyu District, Guangzhou, and the concentration of Cr(VI) is 56.8 mg / L.
[0078] Take 100 mL of the above wastewater into a 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask, add 3 mL of iron salt solution, shake it manually at 40 °C, and let it stand for 10 min; pipette 8 mL of gree...
Embodiment 3
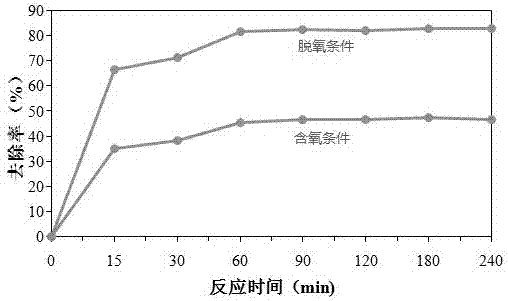
[0080] Example 3 Using green tea to synthesize iron-based materials in situ to degrade acid black 1 in water
[0081] 1. Using green tea to synthesize iron-based materials in situ to degrade acid black 1 in water, including the following steps:
[0082] Put 10g of green tea in a blender and crush for 1 min, weigh 4 g of green tea powder in 200 mL of deionized water, boil at 80°C for 1 h, filter out the tea dregs with filter paper after cooling, and collect the filtrate (green tea extract) in an anaerobic bottle In the middle, blow nitrogen for 30 min, and then seal it for later use.
[0083] Weigh 8g Fe 2 (SO 4 ) 3 Dissolve in 200mL deoxygenated water to obtain iron salt solution.
[0084] The dye used in this example is Acid Black 1, and the waste water is artificially prepared by dissolving analytically pure Acid Black 1 in deoxygenated water, wherein the concentration of Acid Black 1 is 50 mg / L.
[0085] Add 50 mL of Acid Black 1 wastewater into a 100 mL anaerobic bott...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com